AVIATION 2100 Final OSU
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
between the wing chord line and the relative wind.
The term "angle of attack" is defined as the angle
Stalled
In what flight condition must an aircraft be placed in order to spin?
developing lift.
Wingtip vortices are created only when an aircraft is
less than the length of the wingspan above the surface.
Floating caused by the phenomenon of ground effect will be most realized during an approach to land when at
attack.
(Refer to Figure 1.) The acute angle A is the angle of
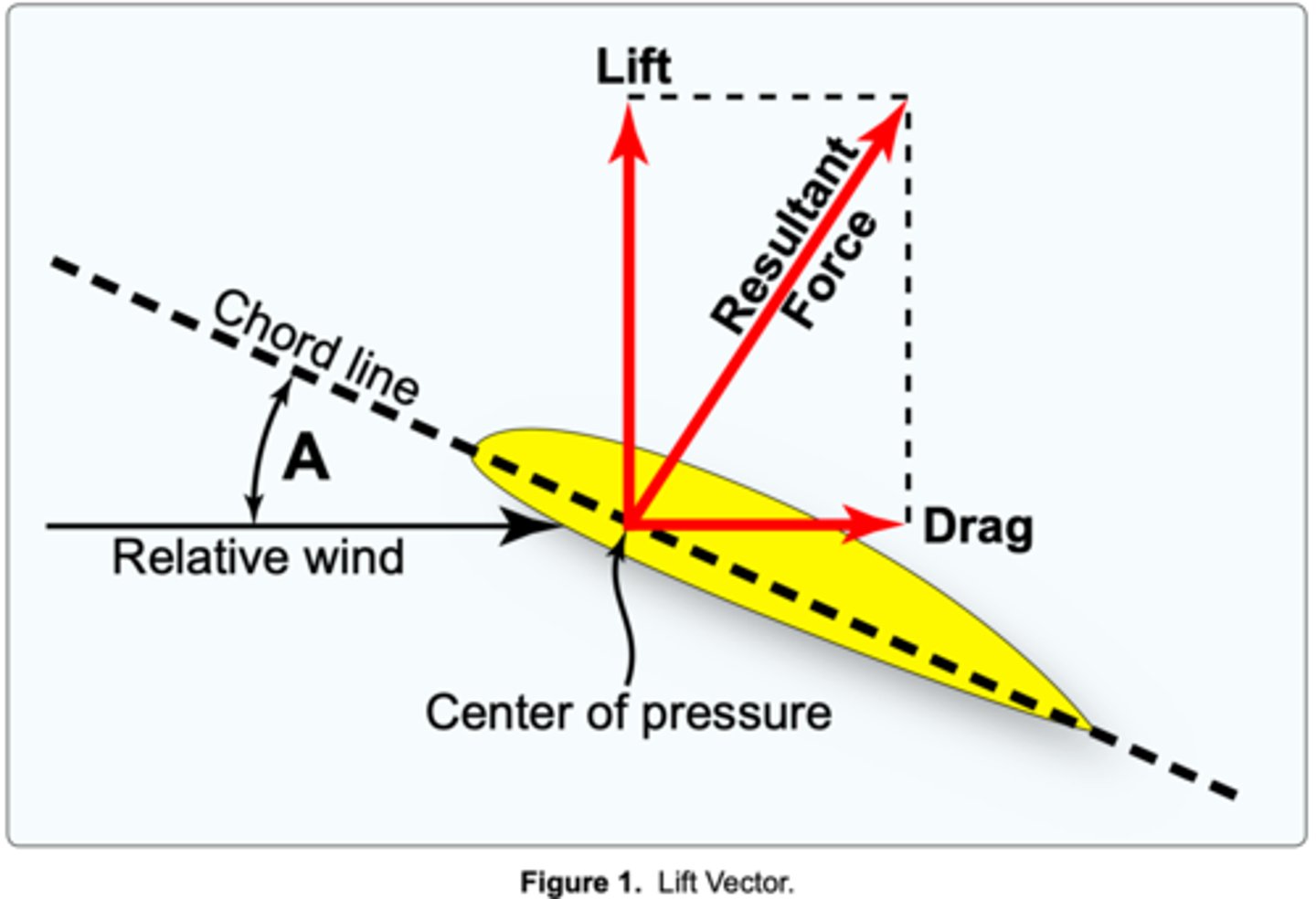
During unaccelerated flight.
When are the four forces that act on an airplane in equilibrium?
The downwash on the elevators from the propeller slipstream is reduced and elevator effectiveness is reduced.
What causes an airplane (except a T-tail) to pitch nose down when power is reduced and controls are not adjusted?
aerodynamic balance and controllability.
Changes in the center of pressure of a wing affect the aircraft's
heavy, clean, and slow.
The greatest vortex strength occurs when the generating aircraft is
light quartering tailwind.
The wind condition that requires maximum caution when avoiding wake turbulence on landing is a
The horizontal component of lift.
What force makes an aircraft turn?
less stable at all speeds.
Loading an airplane to the most aft CG will cause the airplane to be
chord line of the wing and the relative wind.
The term angle of attack is defined as the angle between the
heavy, clean, and slow.
The greatest vortex strength occurs when the generating aircraft is
Lift equals weight and thrust equals drag.
What is the relationship of lift, drag, thrust, and weight when the airplane is in straight-and-level flight?
Both wings are stalled.
During a spin to the left, which wing(s) is/are stalled?
To enable the pilot to make steeper approaches to a landing without increasing the airspeed.
What is one purpose of wing flaps?
Induced drag decreases; therefore, any excess speed at the point of flare may cause considerable floating.
What must a pilot be aware of as a result of ground effect?
Turns
Which basic flight maneuver increases the load factor on an airplane as compared to straight and level flight?
difficulty recovering from a stalled condition.
An airplane has been loaded in such a manner that the CG is located aft of the aft CG limit. One undesirable flight characteristic a pilot might experience with this airplane would be
magnetic variation.
The angular difference between true north and magnetic north is
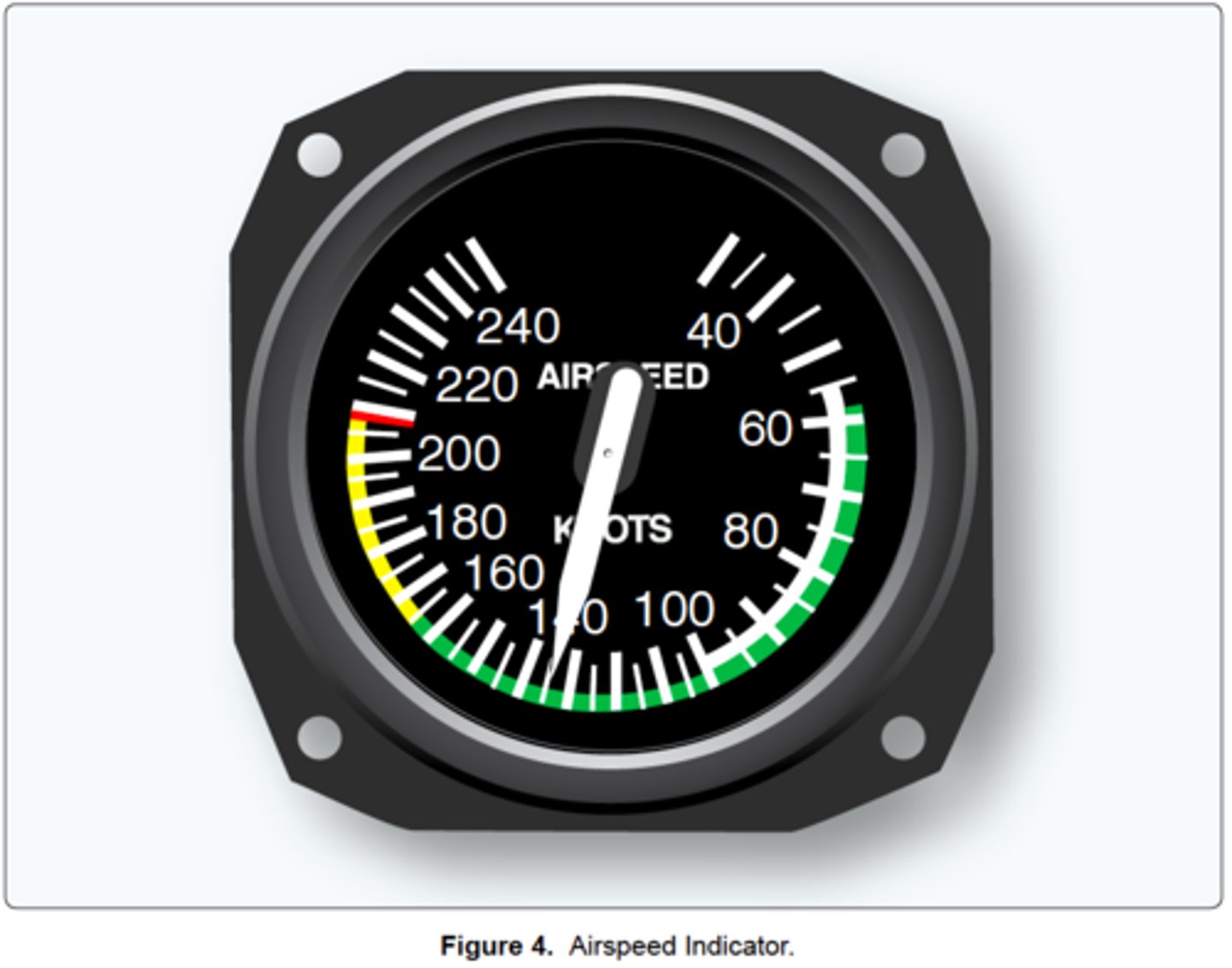
Never-exceed speed.
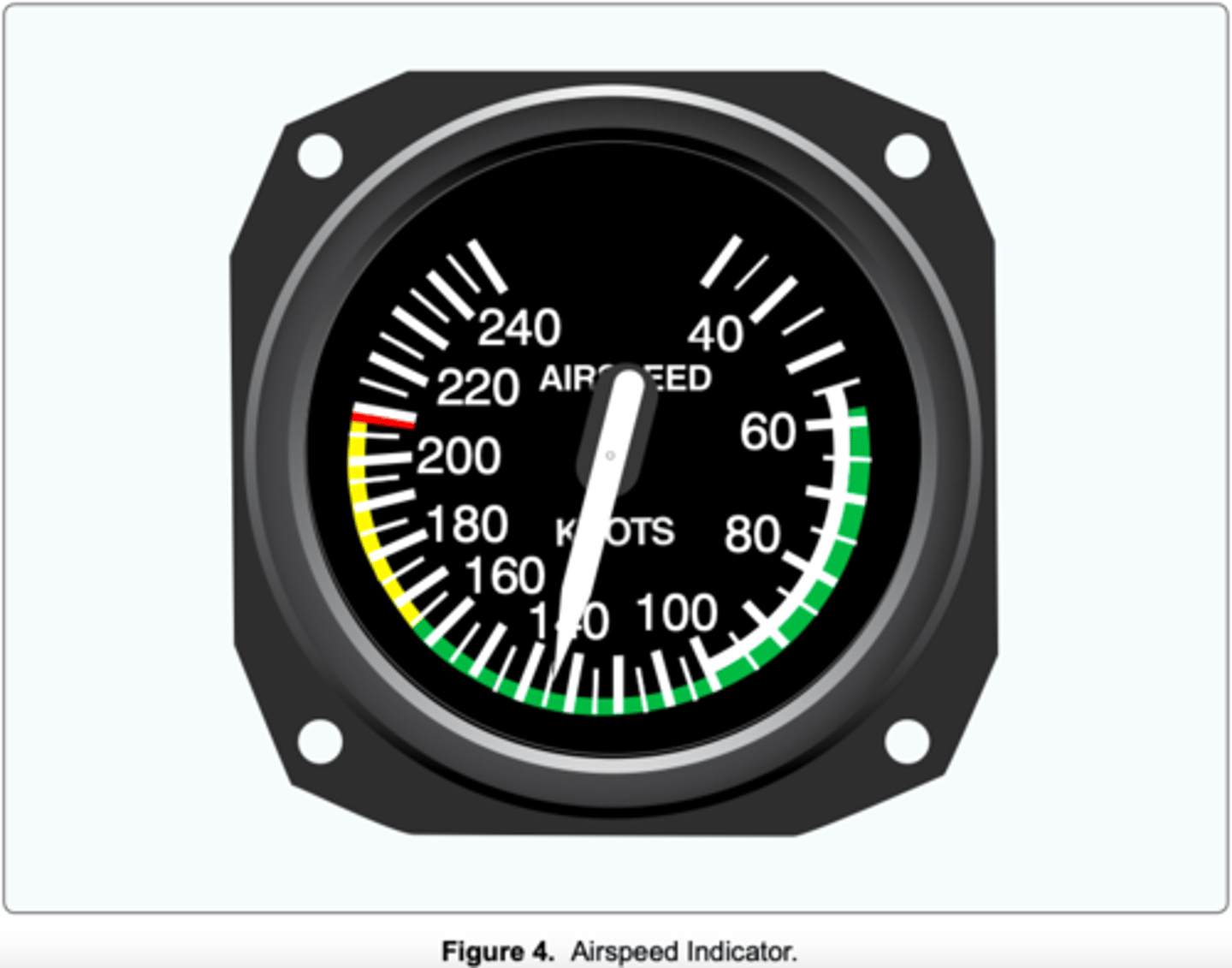
What does the red line on the airspeed indicator represent?
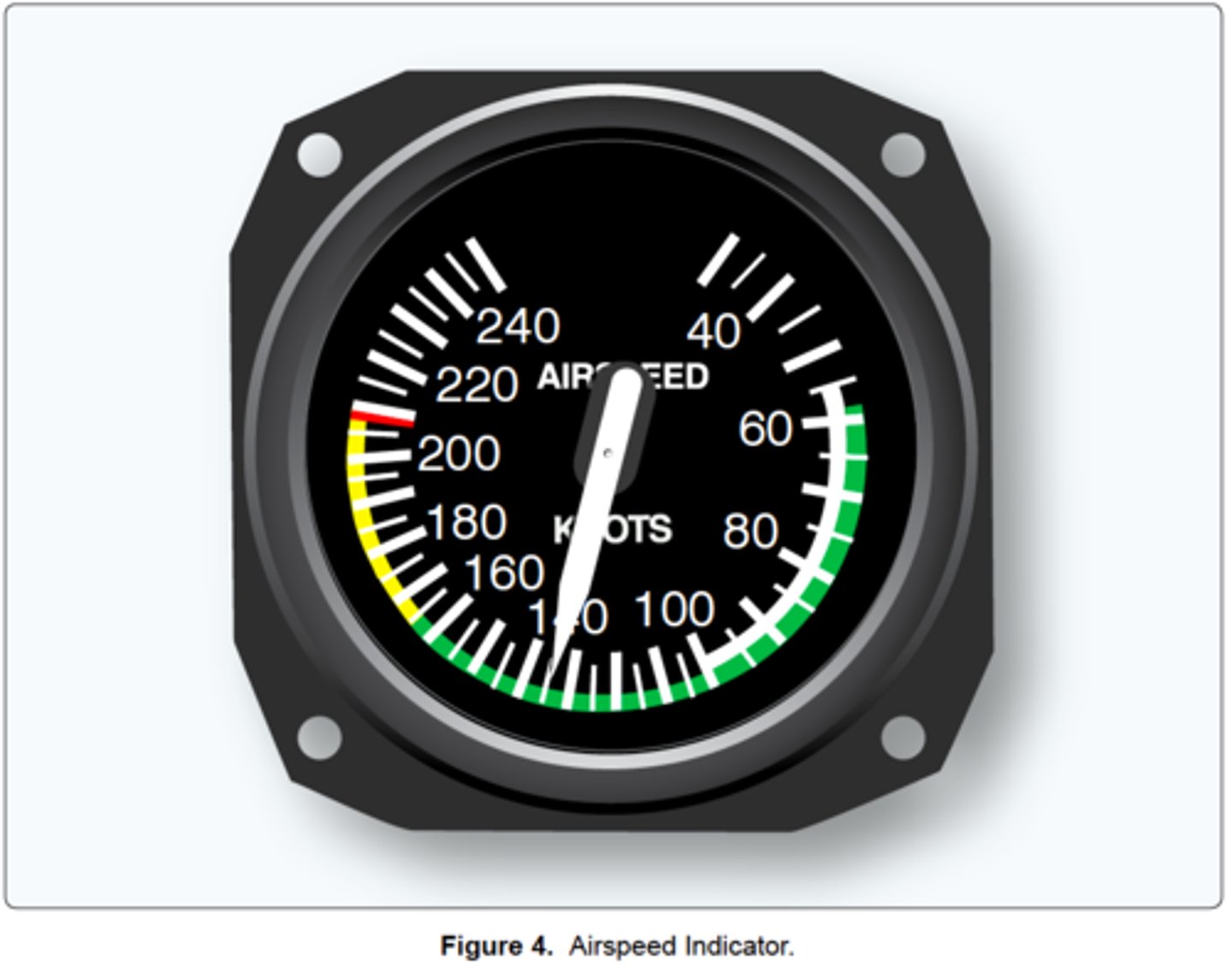
The white arc.
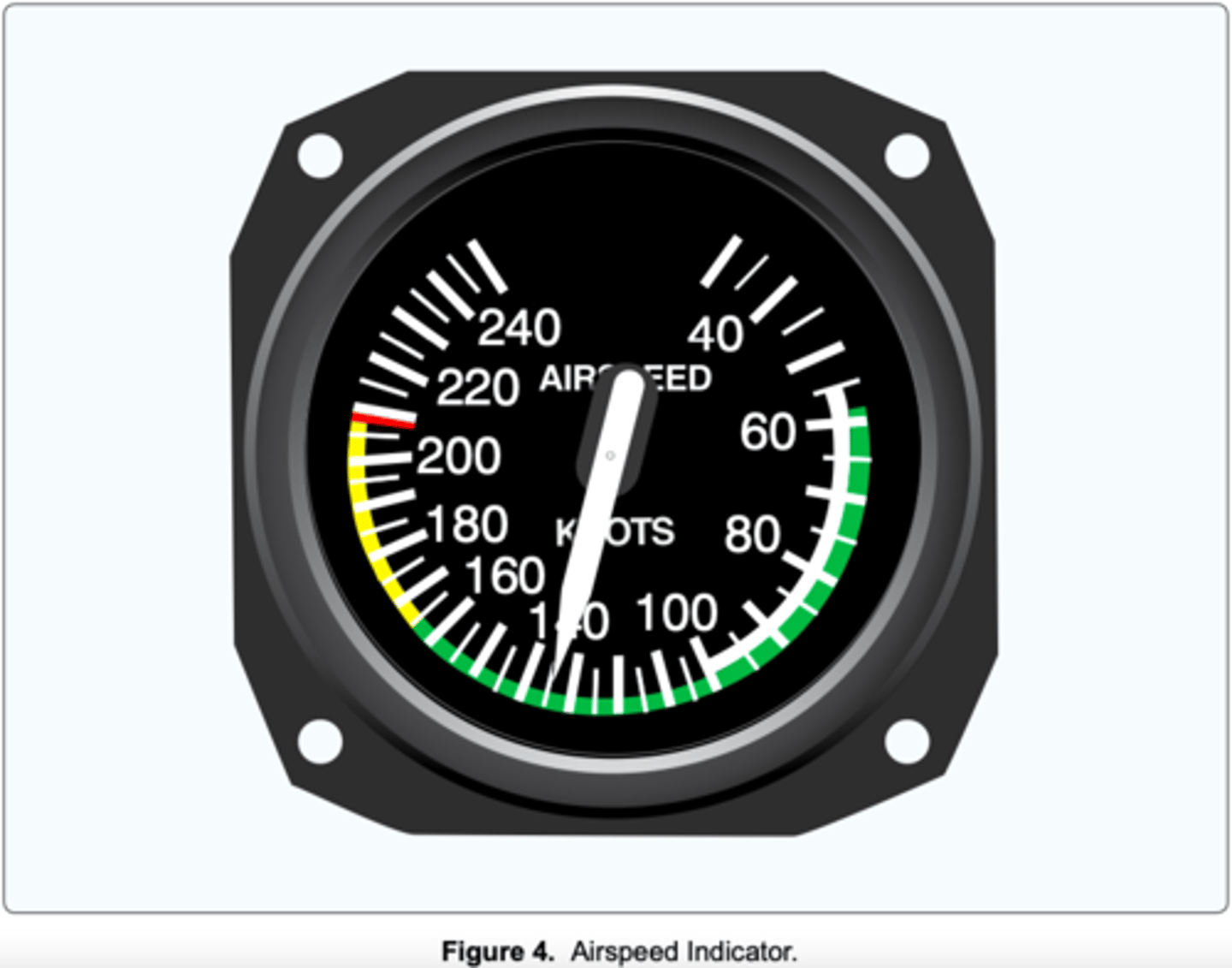
(Refer to figure 4) Which color identifies the normal flap operating range?
The Pilot-in-Command
During the preflight inspection who is responsible for determining the aircraft is safe for flight?
decrease engine performance.
Generally speaking, the use of carburetor heat tends to
detonation
If the grade of fuel used in an aircraft engine is lower octane than specified for the engine, it will most likely cause
the circulation of lubricating oil.
For internal cooling, reciprocating aircraft engines are especially dependent on
9,500 feet.
(Refer to figure 3) Altimeter 3 indicates

The altimeter, airspeed indicator, and vertical speed indicator.
If the pitot tube and outside static vents become clogged, which instruments would be affected?
An aircraft is accelerated while on an east or west heading.
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic compass will normally indicate a turn towards the north if
Unusable fuel and undrainable oil.
Which items are included in the empty weight of an aircraft?
18.4 gallons.
An aircraft is loaded 110 pounds over maximum certified gross weight. If fuel (gasoline) is drained to bring the aircraft weight within limits, how much fuel should be drained?
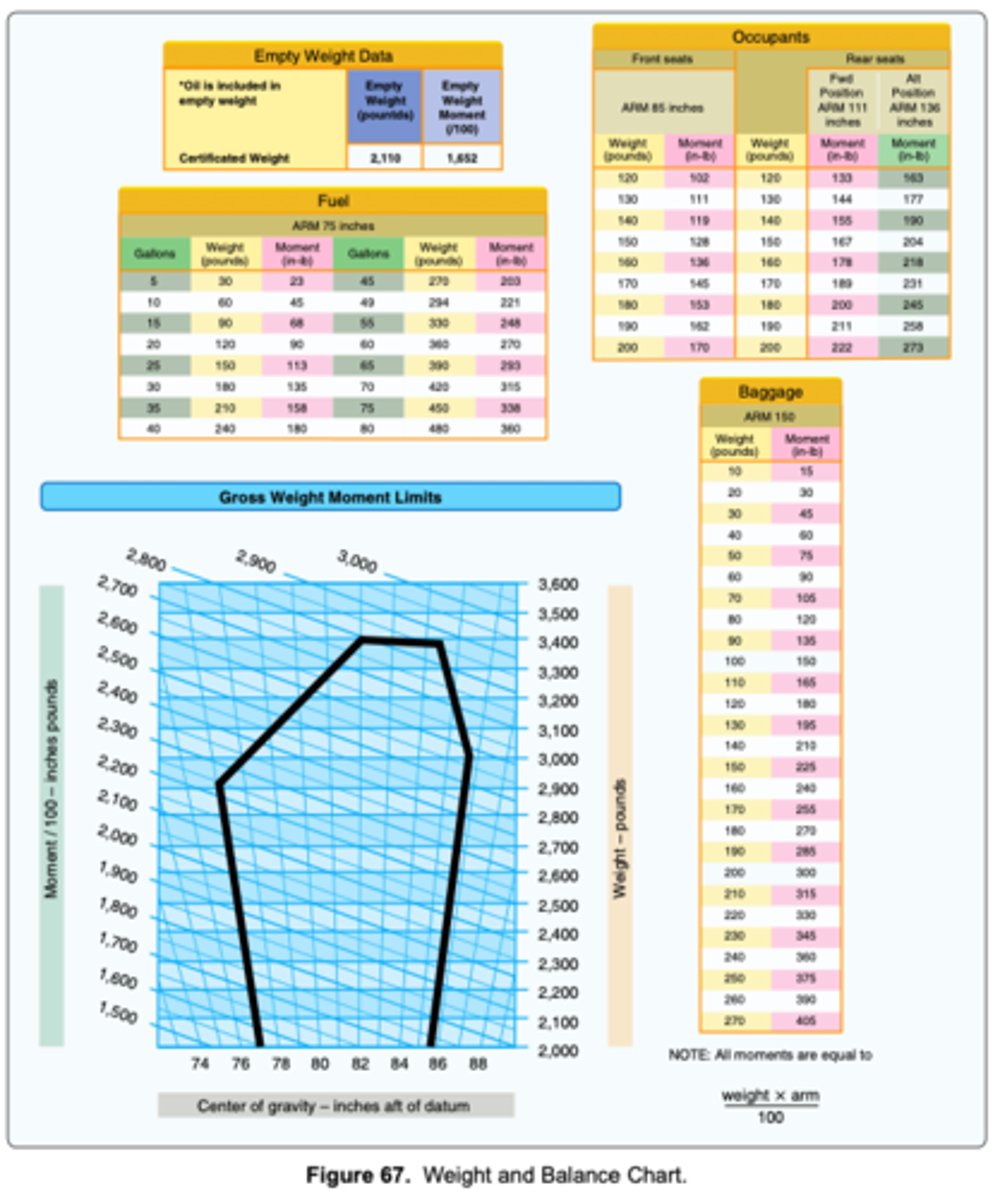
Moment will decrease to 2,087 in-lb.
(Refer to Figure 67.) What effect does a 30-gallon fuel burn have on the weight and balance if the airplane weighed 2,784 pounds and the MOM/100 was 2,222 at takeoff?
300 pounds.
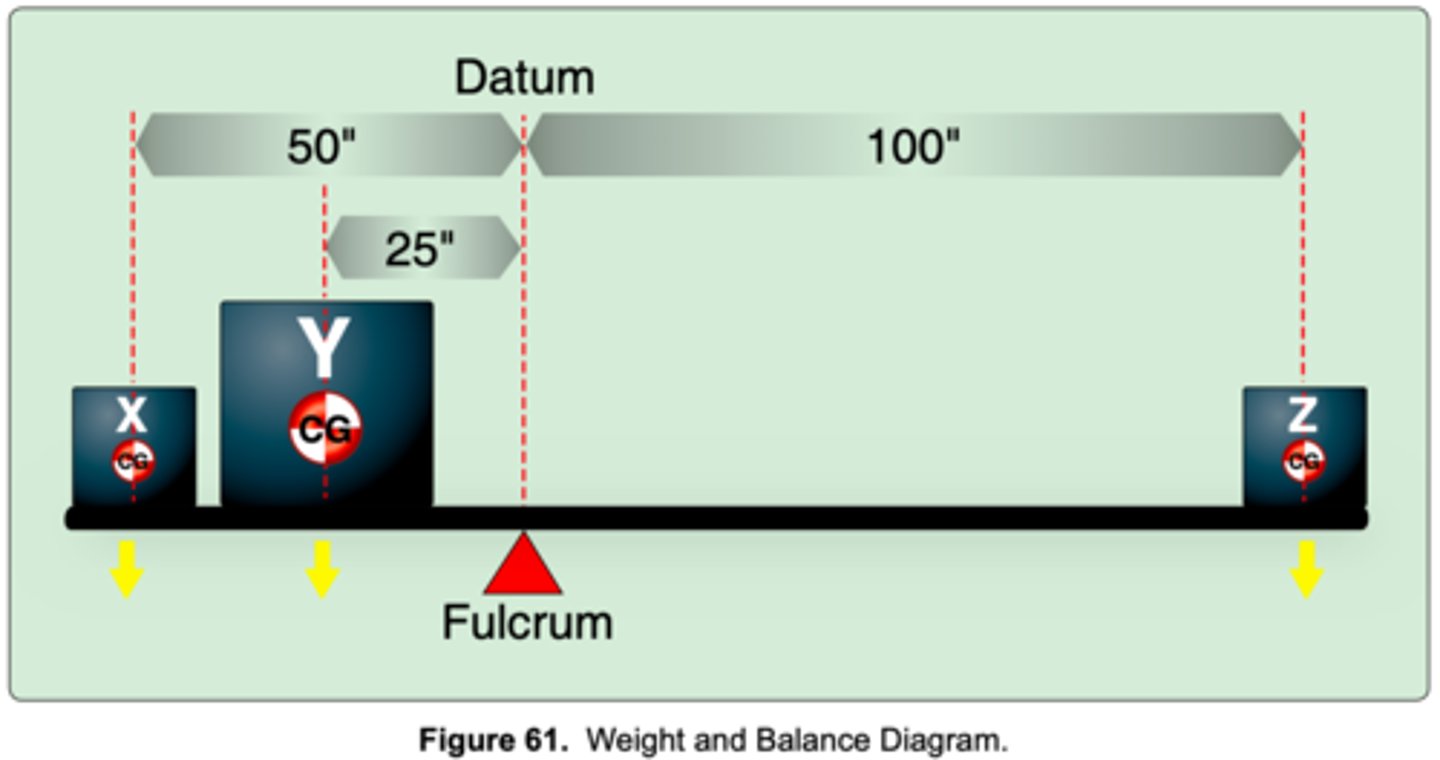
(Refer to Figure 61.) If 50 pounds of weight is located at point X and 100 pounds at point Z, how much weight must be located at point Y to balance the plank?
1 inch to the left.
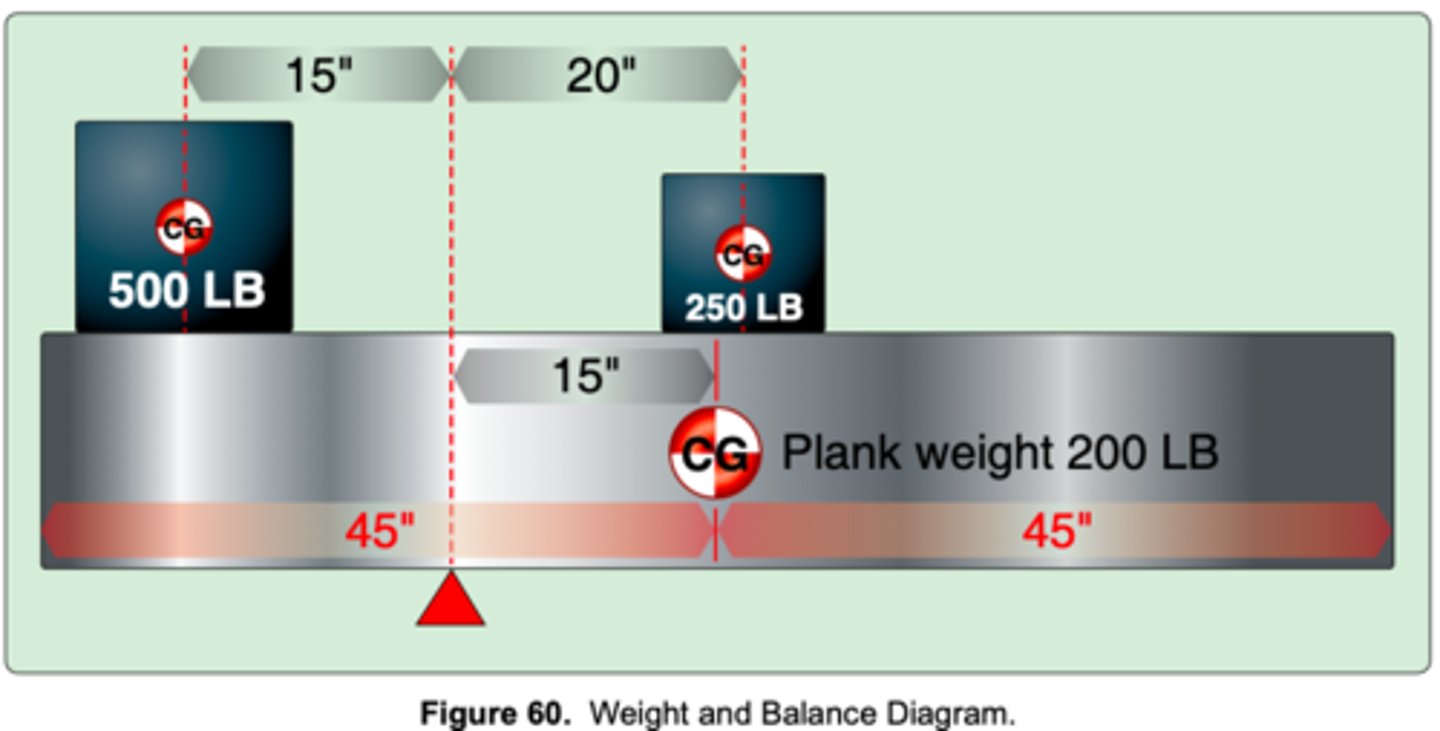
(Refer to Figure 60.) How should the 500-pound weight be shifted to balance the plank on the fulcrum?

attack.
The angle between the chord line of an airfoil and the relative wind is known as the angle of
Air traveling faster over the curved upper surface of an airfoil causes lower pressure on the top surface.
Which statement relates to Bernoulli's principle?
lift, weight, thrust, and drag.
The four forces acting on an airplane in flight are
The location of the CG with respect to the center of lift.
What determines the longitudinal stability of an airplane?
4,600 pounds.
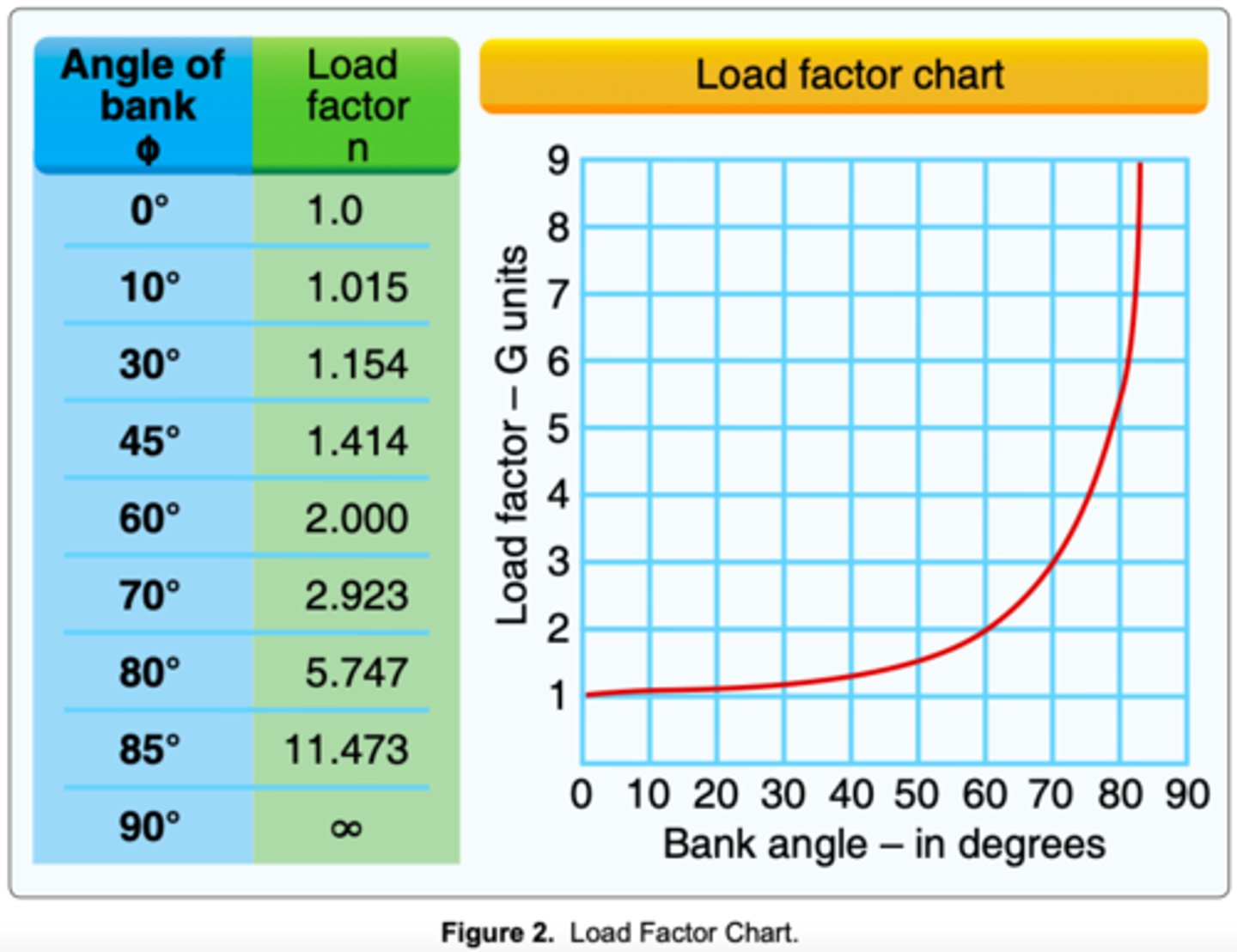
(Refer to Figure 2.) If an airplane weighs 2,300 pounds, what approximate weight would the airplane structure be required to support during a 60° banked turn while maintaining altitude?
The horizontal component of lift.
What force makes an airplane turn?
remain the same regardless of gross weight.
The angle of attack at which an airplane wing stalls will
To enable the pilot to make steeper approach to landing without increasing the airspeed.
What is one purpose of wing flaps?
Becoming airborne before reaching recommended takeoff speed.
Ground effect is most likely to result in which problem?
Stay above its final approach flightpath all the way to touchdown.
When landing behind a large aircraft, which procedure should be followed for vortex avoidance?
The pilot-in-command.
During the preflight inspection who is responsible for determining the aircraft is safe for flight?
improved engine performance.
One purpose of the dual ignition system on an aircraft engine is to provide for
decrease the fuel flow in order to compensate for decreased air density.
The basic purpose of adjusting the fuel/air mixture at altitude is to
loss of RPM.
If an aircraft is equipped with a fixed-pitch propeller and a float-type carburetor, the first indication of carburetor ice would most likely be
detonation.
If the grade of fuel used in an aircraft engine is lower than specified for the engine, it will most likely cause
the oil level being too low.
An abnormally high engine oil temperature indication my be caused by
propeller blade descending on the right, producing more thrust than the ascending blade on the left.
The left turning tendency of an airplane caused by P-factor is the result of the
Airspeed.
Which instruments will become inoperative if the pitot tube becomes clogged?
The red radial line.
(Refer to Figure 4.) Which color identifies the never-exceed speed?
The vertical distance of the aircraft above sea level.
What is true altitude?
periodically realigned with the magnetic compass as the gyro precesses.
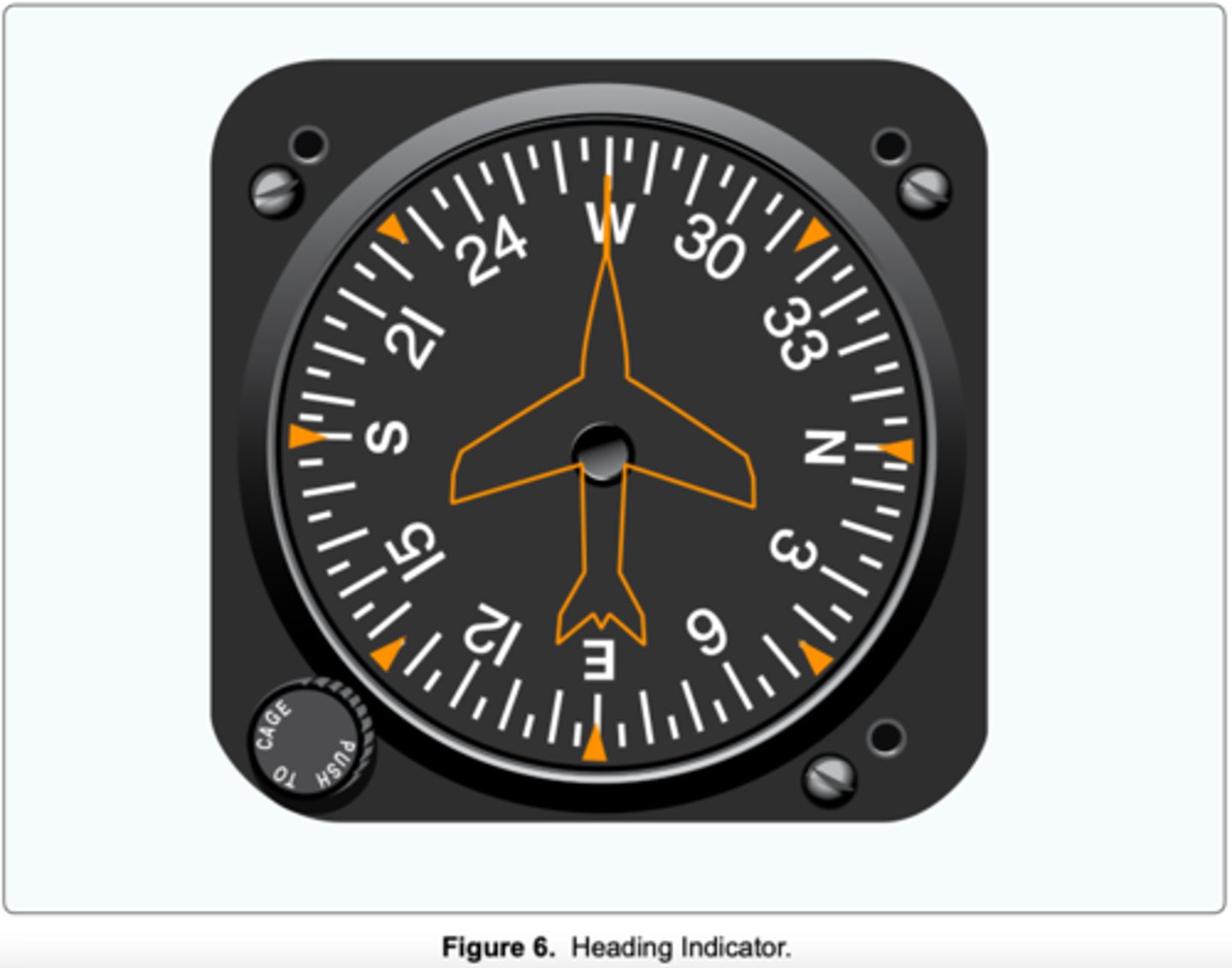
(Refer to Figure 6.) To receive accurate indications during flight from a heading indicator, the instrument must be
magnetic fields within the aircraft distorting the lines of magnetic force.
Deviation in a magnetic compass is caused by the
Only in straight-and-level unaccelerated flight.
During flight, when are the indications of a magnetic compass accurate?
1 inch to the left.
(Refer to Figure 60.) How should the 500-pound weight be shifted to balance the plank on the fulcrum?
100 knots.
(Refer to Figure 4.) What is the maximum flap extended speed?
The pressure altitude corrected for nonstandard temperature.
What is density altitude?
heavy, clean, and slow.
The greatest vortex strength occurs when the generating aircraft is
15 gallons.
If an aircraft is loaded 90 pounds over maximum certified gross weight and fuel (gasoline) is drained to bring the aircraft weight within limits, how much fuel should be drained?
Airspeed, altimeter, and vertical speed.
Which instrument(s) will become inoperative if the static vents become clogged?
The temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated.
What is meant by the term dew point?
Continuous updraft.
What feature is normally associated with the cumulus stage of a thunderstorm?
All aircraft.
SIGMETs are issued as a warning of weather conditions hazardous to which aircraft?
lowest broken or overcast layer or vertical visibility into an obscuration.
For aviation purposes, ceiling is defined as the height above the Earth's surface of the
180° true at 4 knots.
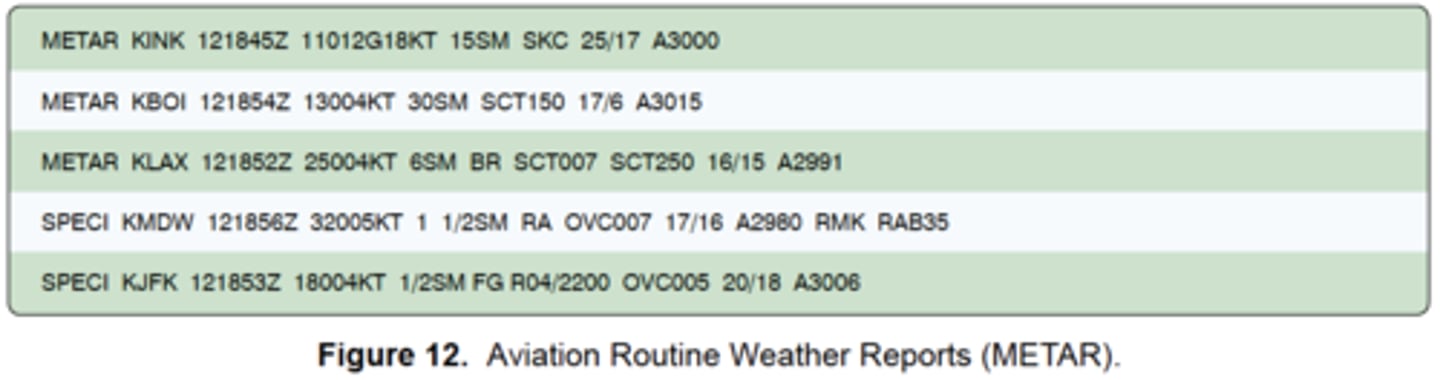
(Refer to Figure 12) The wind direction at KJFK is from

Variable in direction at 6 knots.
(Refer to Figure 15) What is the forecast wind for KMEM from the 13th at 1600Z until the end of the forecast?

Stratiform clouds.
What is a characteristic of stable air?
12th 1800Z to 13th 2400Z
(Refer to Figure 15) What is the valid period for the TAF for KMEM?

230° true at 39 knots.
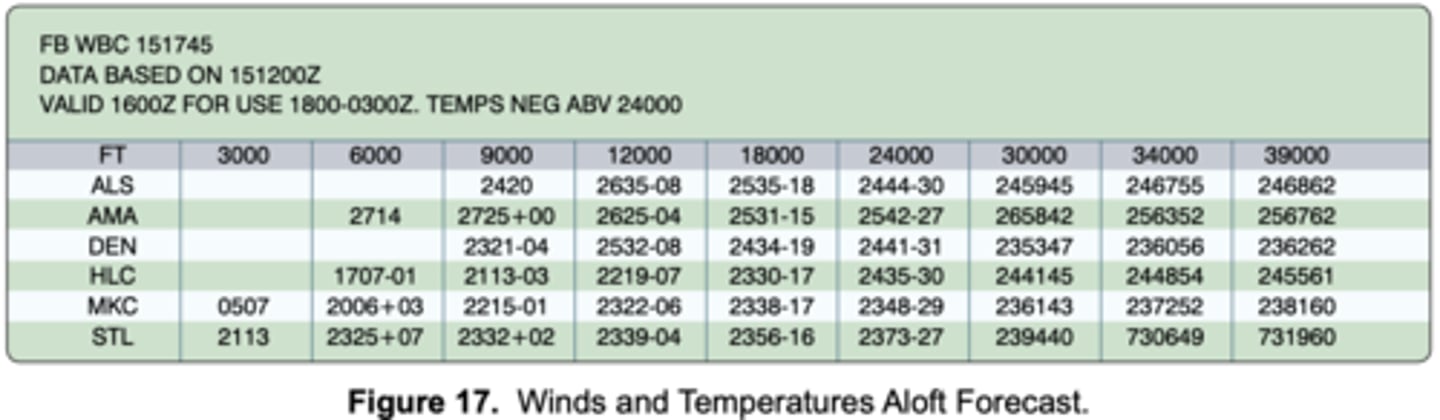
(Refer to Figure 17.) What wind is forecast for STL at 12,000 feet?
Frost will disrupt the smooth flow of air over the wings, adversely affecting its lift capability.
How will frost on the wings of an airplane affect takeoff performance?
19 knots.
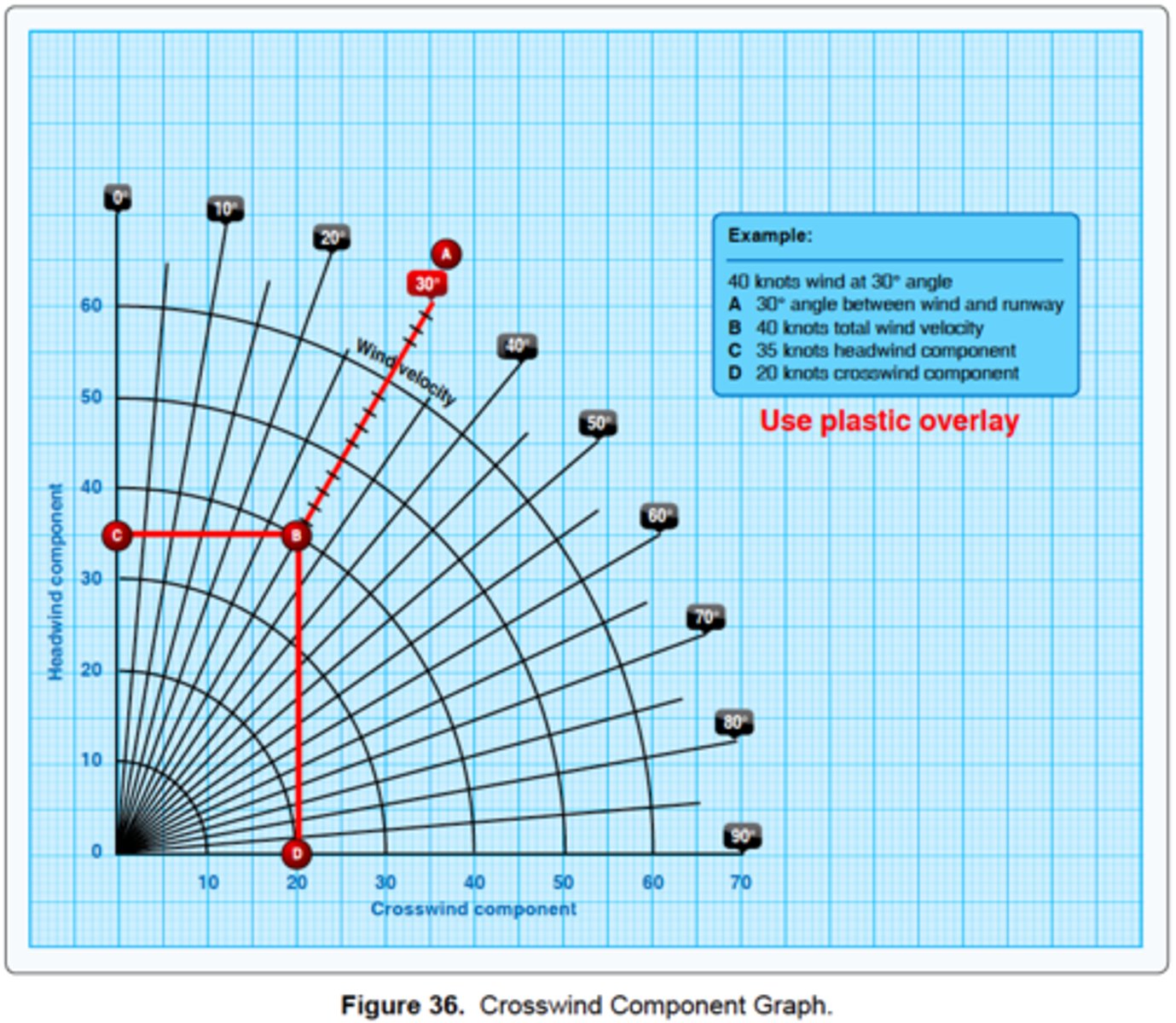
(Refer to figure 36.) What is the crosswind component for a landing on Runway 18 if the tower reports the wind as 220° at 30 knots?
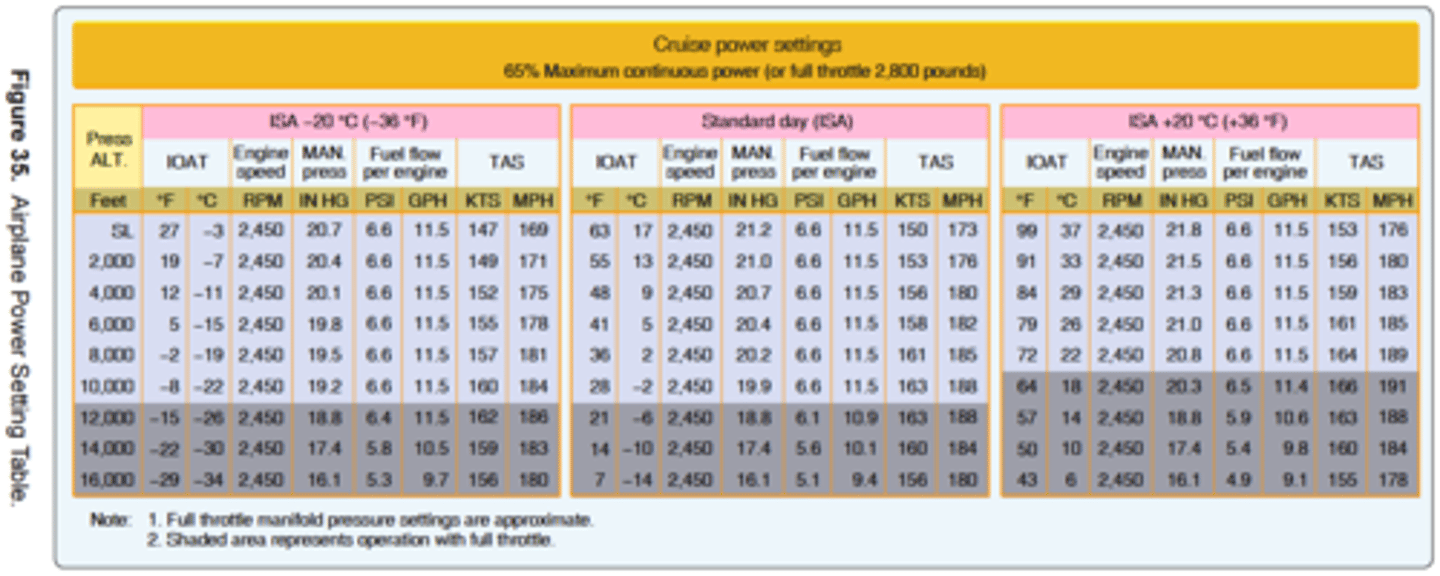
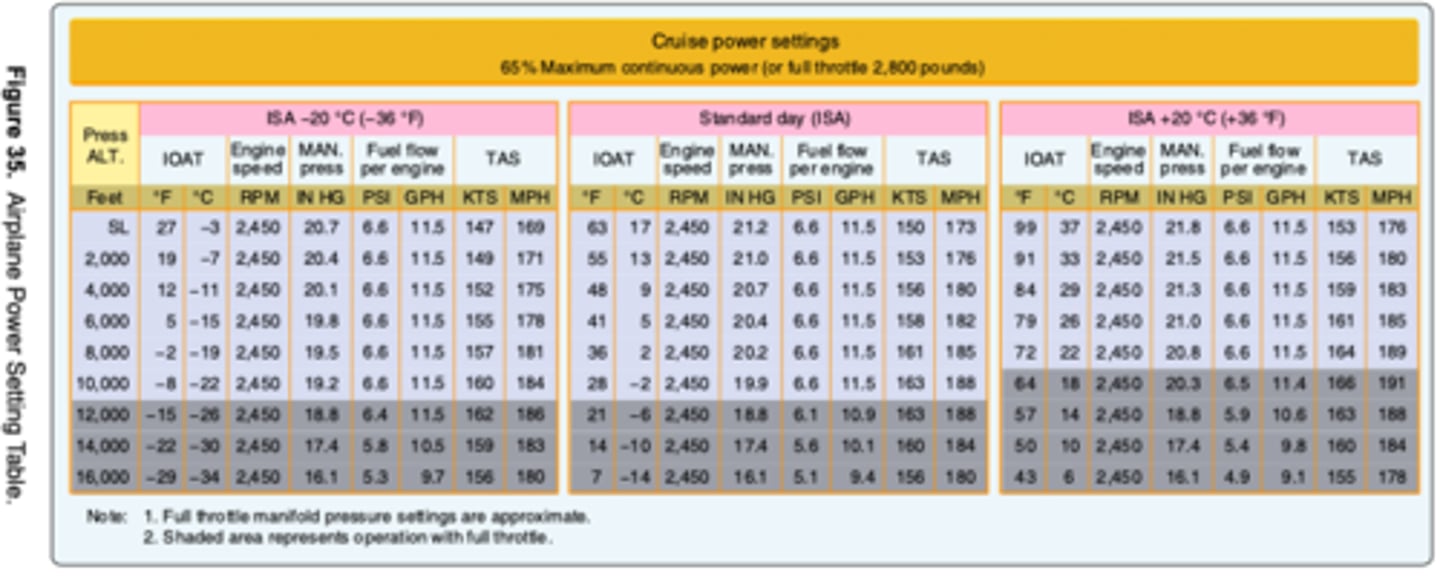
165 kts.
(Refer to figure 35.) Approximately what true airspeed should a pilot expect with full throttle at 10,500 feet with a temperature of 36°F above standard?
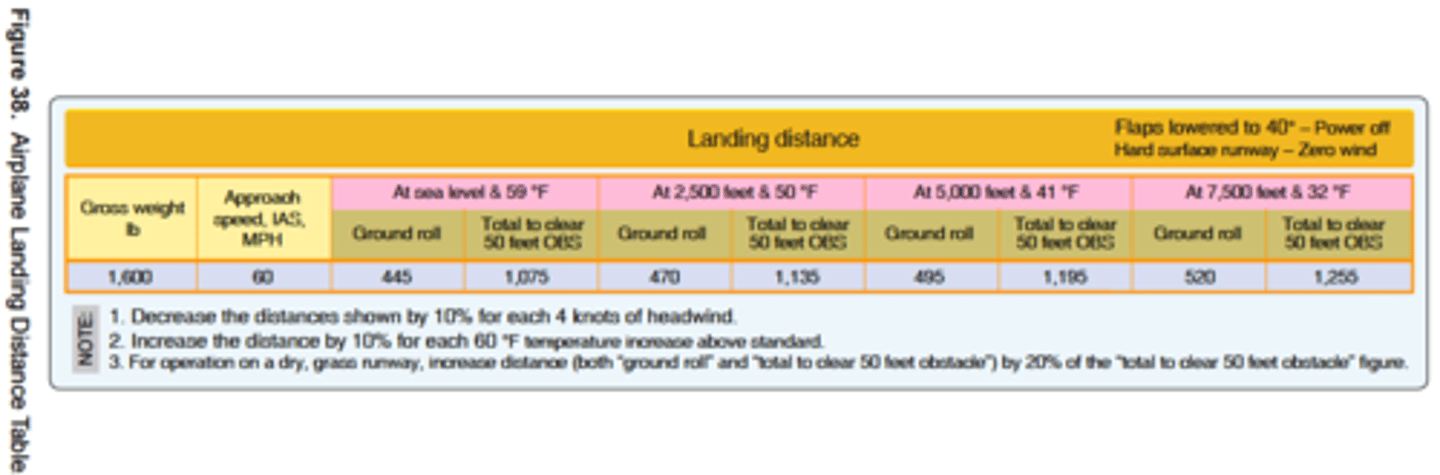
1,004 feet.
(Refer to Figure 38.) Determine the total distance required to land over a 50-foot obstacle.
Pressure altitude....... 7,500
Headwind................... 8 kts
Temperature............... 32°F
Runway....................... Hard surface
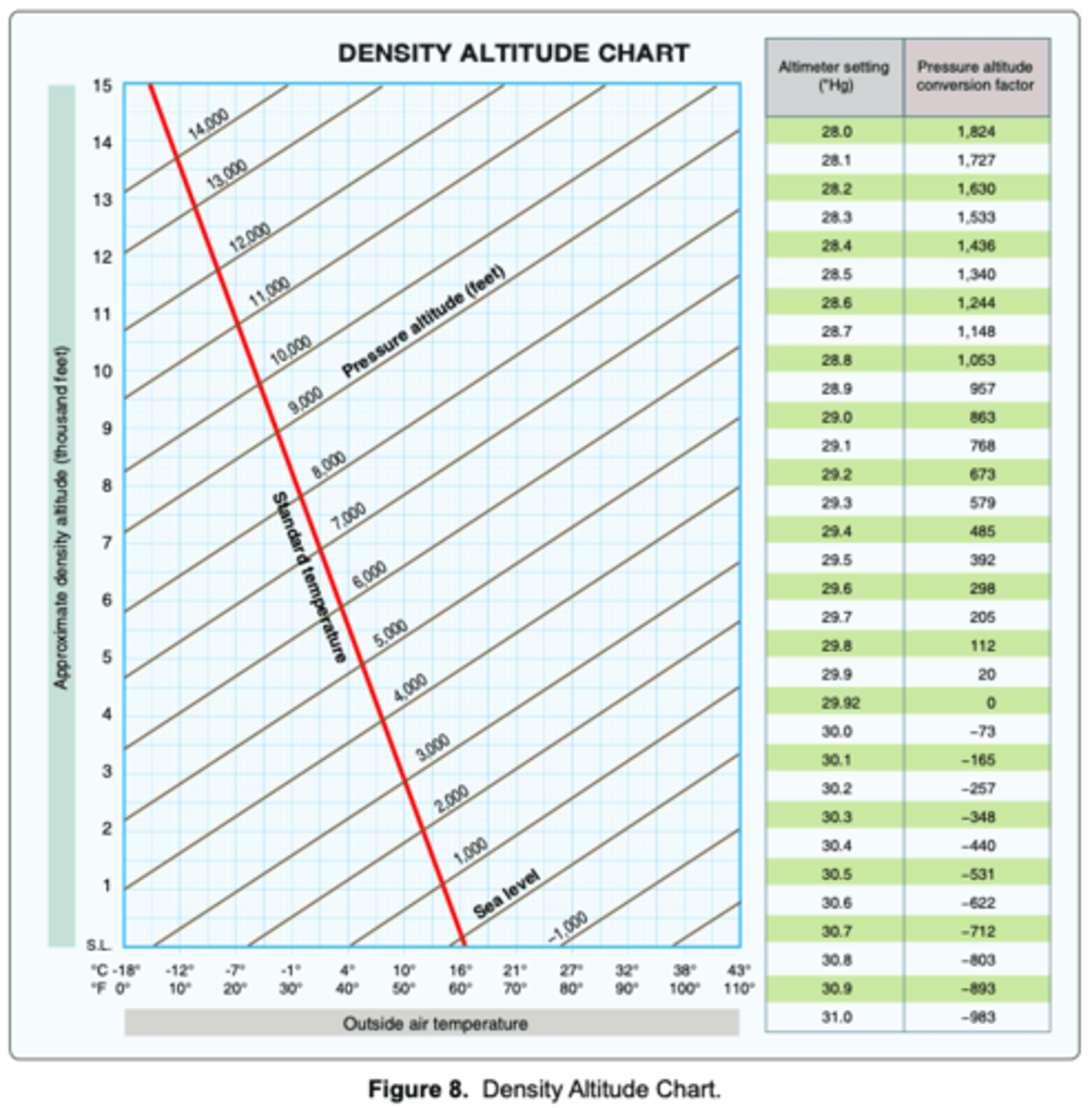
15°C and 29.92 "Hg
What are the standard temperature and pressure values for sea level?
higher that pressure altitude.
If the outside air temperature (OAT) at a given altitude is warmer than standard, the density altitude is
3,527 feet MSL
(Refer to Figure 8.) Determine the pressure altitude at an airport that is 3,563 feet MSL with an altimeter setting of 29.96.
High temperatures, high relative humidity, and high density altitude.
Which combination of atmospheric conditions will reduce aircraft takeoff and climb performance?
It reduces climb performance.
What effect does high density altitude have on aircraft performance?
It decreases performance.
What effect, if any does high humidity have on aircraft performance?
36.1 gallons.
(Refer to Figure 35) What is the expected fuel consumption for a 500-nautical mile flight under the following conditions?
Pressure altitude......................4,000 ft
Temperature............................. +29°C
Manifold Pressure.................. 21.3 "Hg
Wind......................................... Calm
Unequal heating of the Earth's surface.
What causes variations in altimeter settings between weather reporting points?
air temperature.
The amount of water vapor which air can hold depends on the
a change in temperature.
One of the most easily recognized discontinuities across a front is
Warming from below.
What would decrease the stability of an air mass?
unstable, moist air.
The conditions necessary for the formation of cumulonimbus clouds are a lifting action and
standing lenticular clouds.
Crests of standing mountain waves may be marked by stationary, lens-shaped clouds known as
Precipitation beginning to fall.
Which weather phenomenon signals the beginning of the mature stage of a thunderstorm?
Warm, moist air over low, flatlands on clear, calm, nights.
What situation is most conductive to the formation of radiation fog?
Dissipating
During the life cycle of a thunderstorm, which stage is characterized predominantly by downdrafts?
110° at 12 knots, gusts 18 knots.
(Refer to Figure 12.) What are the wind conditions at Wink, Texas (KINK)?
An increase in ambient temperature.
Which factor would tend to increase the density altitude at a given airport?
When it compromises safety.
When should pilots decline a land and hold short (LAHSO) clearance?
blue omnidirectional lights.
Airport taxiway edge lights are identified at night by
on the glide slope.
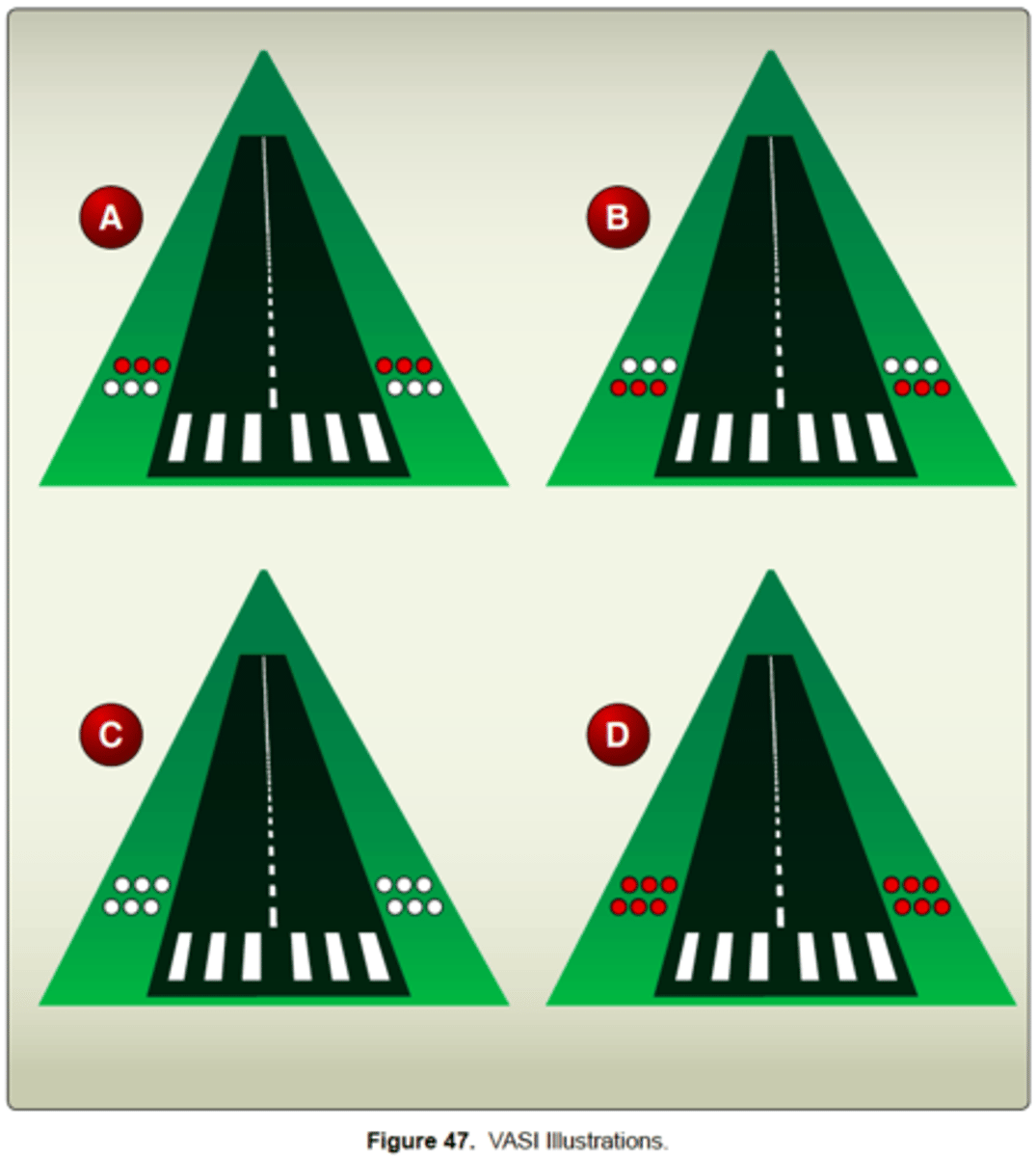
(Refer to Figure 47.) Illustration A indicates that the aircraft is
not pay less than the pro rata share of the operating expenses of a flight with passengers providing the operating expenses involve only fuel, oil, airport expenditures, or rental fees.
According to regulations pertaining to privileges and limitations, a private pilot may
Airplane, rotorcraft, glider, lighter-than-air.
With respect to the certification of airmen, which are categories of aircraft.