Nevada Food Handlers Card
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
FOODBORNE ILNESS RISK FACTORS
1.Poor Personal Hygiene
•Improper hand washing
• Bare hand contact with ready-to-eat (RTE) foods
• Food handlers working while ill with the following
symptoms: vomiting, diarrhea, sore throat with a fever, infected cuts on the hands, and jaundice
FOODBORNE ILNESS RISK FACTORS
2.Food from unsafe sources
• Food from an unapproved source and/or prepared in unpermitted locations
• Receiving adulterated food
FOODBORNE ILNESS RISK FACTORS
3.Improper Cooking Temperatures/Methods
• Cooking
• Reheating
• Freezing (kill step to eliminate parasites in fish)
FOODBORNE ILNESS RISK FACTORS
4. Improper Holding, Time and Temperature
• Improper hot and cold holding of TCS foods • Improper use of time as a control
• Improper cooling of TCS foods
FOODBORNE ILNESS RISK FACTORS
5. Food Contamination
• Use of contaminated/improperly constructed equipment
• Poor employee practices
• Improper food storage/preparation
• Exposure to chemicals
FOOD HAZARDS
1.Biological
• Microorganisms that can cause foodborne illness
• Bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi
FOOD HAZARDS
2. Chemical
• Chemicals not meant to be consumed
• Sanitizers, cleaning agents, or pest control
products must be separated from food
FOOD HAZARDS
3. Physical
• Foreign objects that can cause injury
• Glass, metal, or bone
PROPER HANDWASHING TECHNIQUE
Wash your hands in a DESIGNATED HAND WASHING SINK
PROPER HANDWASHING TECHNIQUE
1. WET HANDS (with warm water) MIN 100 ° F
2. SOAP
3. RUB VIGOROUSLY (for 15 seconds)
4. RINSE
5. DRY
6. TURN OFF WATER (with paper towel)
WASH YOUR HANDS...
•when entering the kitchen
WASH YOUR HANDS...
After touching your face, hair, or skin
WASH YOUR HANDS...
After using the restroom
WASH YOUR HANDS...
After handling raw animal products
WASH YOUR HANDS...
After taking out trash or cleaning
WASH YOUR HANDS...
After handling ANYTHING dirty
If you have a cut on your hand...
•Wash your hands
•Put on clean bandage
•Wear gloves
If you cannot wash your hands because of a splint, wound, bandage, or brace...
YOU CANNOT WORK WITH FOOD
Personal Hygiene: READY TO EAT FOODS
NO BARE HAND CONTACT WITH READY TO EAT FOODS
Personal Hygiene: READY TO EAT FOODS
Use a physical barrier to prevent contamination from germs that have the potential to cause foodborne illness.
Personal Hygiene: READY TO EAT FOODS
Ready-to-eat foods include cooked food, raw fruits and vegetables, baked goods, snack foods, and ice.
Personal Hygiene: READY TO EAT FOODS
Physical barriers include deli/wax paper, gloves, and utensils such as tongs, scoops, and spatulas.
Personal Hygiene: UNIFORMS
Proper Hair Restraint ✔️
Hair coming outside the cap🚫
Personal Hygiene: UNIFORMS
Neat and Clean Clothes✔️
Dirty clothes🚫
Personal Hygiene: UNIFORMS
All wounds covered✔️
Open and bleeding wounds🚫
Personal Hygiene: UNIFORMS
No wrist jewelry✔️
Wrist jewelry🚫
Personal Hygiene: UNIFORMS
Plain band ring✔️
Omate or jeweled ring🚫
Personal Hygiene: UNIFORMS
Short and clean nails✔️
Long, painted, and/or artificial nails🚫
Personal Hygiene: EMPLOYEE HEALTH POLICY
All of us carry disease causing germs that can cause illness
Personal Hygiene: EMPLOYEE HEALTH POLICY
As a food handler, YOU ARE RESPONSIBLE for caring for your own health to prevent foodborne illness.
Personal Hygiene: EMPLOYEE HEALTH POLICY
Tell your employer if you have been diagnosed with Salmonella, Shigella, E. coli O157:H7, Hepatitis A, or Norovirus.
Personal Hygiene: EMPLOYEE HEALTH POLICY
Tell your employer if you have any of the following symptoms:
•Diarrhea
•Vomiting
•Sore throat with a fever
• Infected cuts or wounds
• Jaundice
An easy way to remember the 5 foodborne illnesses:
Send•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••Salmonela
Sick•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••Shigella
Employees••••••••••••••••••••••••E. Coli
Home••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••Hepatitis A
Now••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••Norovirus
Personal Hygiene: EMPLOYEE HEALTH POLICY
YOU CANNOT WORK AGAIN UNTIL SYMPTOM-FREE FOR 24 HOURS WITHOUT THE USE OF MEDICINE
Approved Sources: FOOD FROM AN UNAPPROVED AND/OR UNPERMITTED SOURCE
You cannot make unsafe food safe once again
TCS
Time and Temperature Control for Safety
PHF
TCS foods also known as, POTENTIALLY HAZARDOUS FOODS.
Approved Sources: FOOD FROM AN UNAPPROVED AND/OR UNPERMITTED SOURCE
TCS foods, also known as potentially hazardous foods (PHF), require time and temperature control to limit pathogenic microorganism growth or toxin formation.
An approved source is...
A reputable supplier that has been inspected and follows regulations
You should always...
Check food before you except it from the supplier.
REJECT FOOD IF...
IT DOES NOT MEET STANDARDS RATHER THAN ACCEPTING IT FROM THE SUPPLIER.
During receiving you should always check foods for...
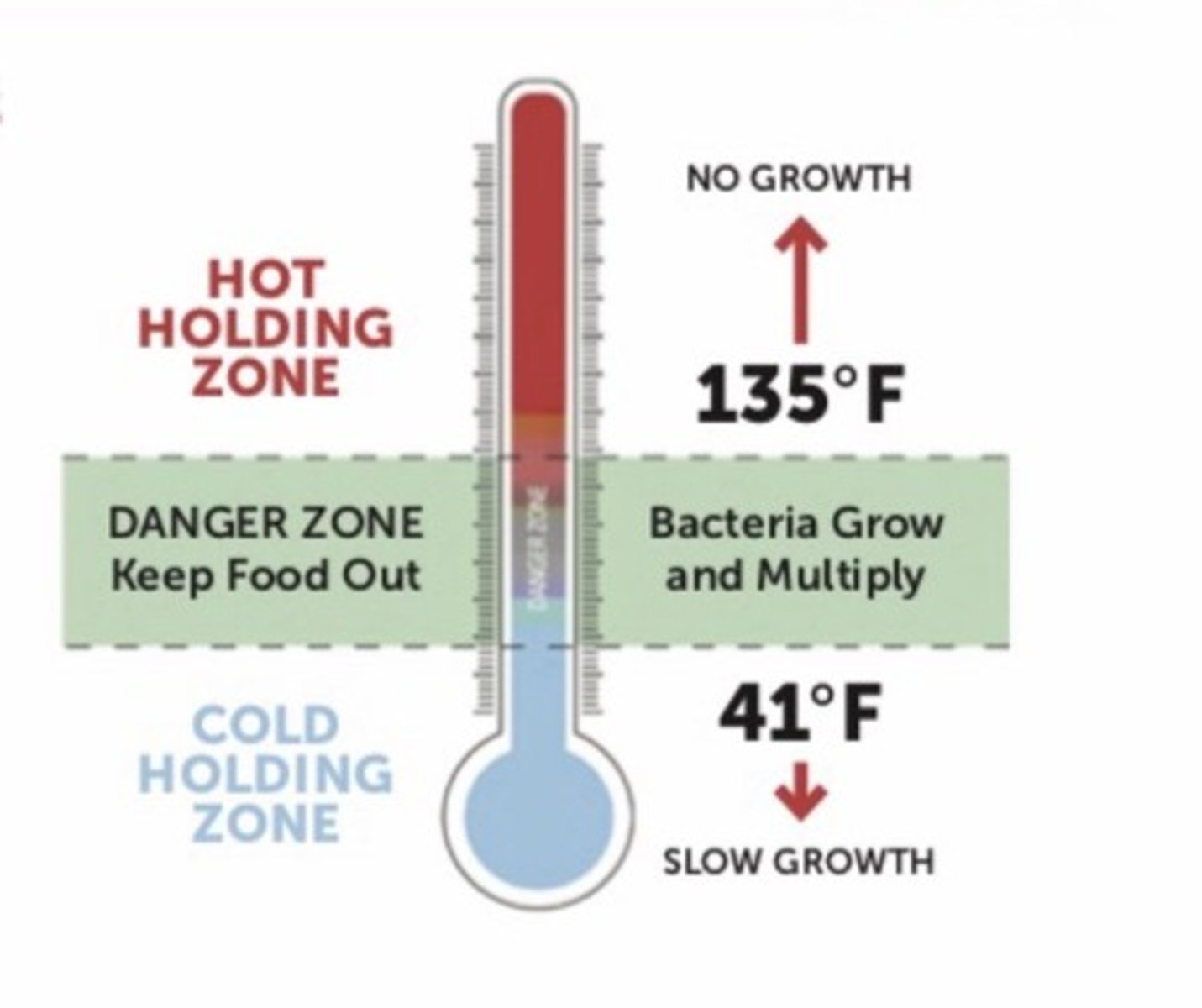
Temperatures for receiving TCS food:
•Hot foods hot (above 135°F)
•DANGER ZONE:Between 41°F and 135°F
•It is acceptable to receive eggs, milk, and live shellstock at 45°F
•41°F OR BELOW:Cold foods cold (below 41°F) Frozen foods should be frozen solid
HOT FOODS
Hot foods hot (above 135°F)
DANGER ZONE
41°F to 135°F
EGGS, MILK, LIVE SHELLSTOCK
Acceptable to receive at 45°F
COLD FOODS
41°F or below
Frozen foods should be FROZEN SOLID
During receiving you should always check foods for...
Overall wholesomeness:
Reject cans that are dented, swollen, or leaking.
During receiving you should always check foods for...
Frozen Foods:
Reject frozen foods that have ice crystals or liquid in the package.
During receiving you should always check foods for...
Spoilage:
Foods should NOT be slimy, sticky, off-color, or have a bad odor.
During receiving you should always check foods for...
Expiration dates:
Foods should be within the use-by date marked from the manufacture.
During receiving you should always check foods for...
Signs of contamination by pests or spills:
Packages should be clean, dry, and intact.
During receiving you should always check foods for...
Proper labeling and invoices:
Food must be identified as to what it is and where it came from.
During receiving you should always check foods for...
Shellstock tags:
Shellfish tags must be kept on file for 90 days.
During receiving you should always check foods for...
Parasite destruction for some fish:
Fish served under cooked or raw must have documents from the supplier explaining how the fish is frozen or raised.
Holding Temperatures
You must store TCS foods at correct temperatures for safety
Holding Temperatures
Proper Thawing
It is important to maintain foods 41°F or below when thawing
Approved thawing method: Under Refrigeration
Plan ahead — large items may take several days to thaw. Maintain refrigeration at 41°F or less.
Approved thawing method: As part of Cooking
Take directly from frozen to cooking. This is great for foods that are small.
Approved thawing method: In Microwave
Transfer immediately to a conventional cooking process or cook completely in the microwave.
Approved thawing method: Fully Submerged Under Cold Running Water
Ensure running water flows fast enough to remove and float off loose particles. Ensure all portions of food are fully submerged under water. Running water should be cold; food should not rise above 41°F.
Cooking
Cooking TCS foods to their required temperatures is the only way to reduce the amount of germs to safe levels.
To check food temperatures...
Use a calibrated and sanitized stem thermometer to check food temperatures.
Insert thermometer:
into the thickest part of the food away from bones to be sure all parts of the food are cooked thoroughly.