Genetics & Biotech. CH. 3- Meiosis and Reproduction
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
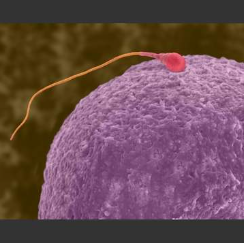
Male Gamete
Sperm
2
New cards
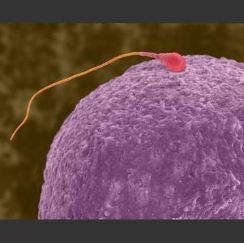
How much larger is an Oocyte than a Sperm?
x90,000 the volume of a sperm
3
New cards
How many chromosomes do gametes have? Why does it have this number?
Gametes have 23 chromosomes; this is half the normal amount in any other human cell (46).
4
New cards
Where do Gametes form from?
Germline Cells
5
New cards
Maturation sculps the _____________.
distinctive characteristics of egg and sperm.
6
New cards
What is a Homologous Pair?
Chromosomes that have genes in the same order, but may carry different alleles.
7
New cards
Polyploidy
having extra chromosomes
8
New cards
What happens in Interphase, Prior to to Meiosis?
DNA is replicated
9
New cards
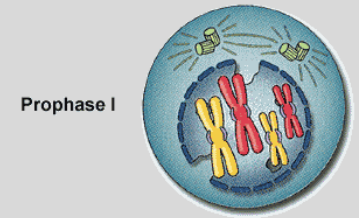
Prophase 1
-Replicated chromosomes condense
-Spindles form
-Synapsis: Homologs line up next to one another
-Crossing Over may occur
-Synapsed chromosomes start to pull apart. Stay slightly connected.
-Spindles form
-Synapsis: Homologs line up next to one another
-Crossing Over may occur
-Synapsed chromosomes start to pull apart. Stay slightly connected.
10
New cards
Chromatid
Singular part of a chromosome.
11
New cards
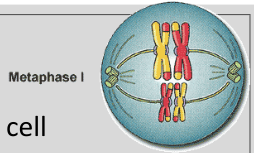
Metaphase 1
-Homologues align at the center of the cell.
-Spindle fibers connect to the chromosomes.
-Independent Assortment: Random arrangement of the chromosomes.
-Spindle fibers connect to the chromosomes.
-Independent Assortment: Random arrangement of the chromosomes.
12
New cards
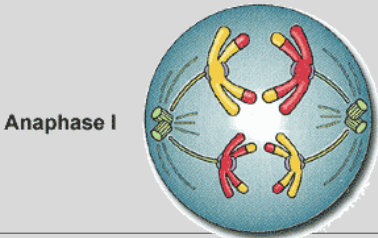
Anaphase 1
-Homologues separate, pulled to pole(sides) by spindle fibers.
13
New cards
Gonads
ovaries and testes, organs that produce sex cells
14
New cards
Oocyte
a cell in an ovary that may undergo meiotic division to form an ovum.
15
New cards
Testes
male gonads
16
New cards
Ovaries
female gonads
17
New cards
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
18
New cards
Haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
19
New cards
Independent assortment
the random distribution of the pairs of genes on different chromosomes to the gametes
20
New cards
Crossing over
the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics in offspring.
21
New cards
Reductive division
where meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes in each cell from 2n to 1n
22
New cards
Equational division
Another name for meiosis II because cells in meiosis II have the same number of chromosomes at the beginning and at the end of the process.
23
New cards
Homologous pairs
A pair of chromosomes of the same type, one from each parent.
24
New cards
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm cells
25
New cards
Spermatogonia
The diploid cells in a testis that can give rise to primary spermatocytes.
26
New cards
Oogenesis
the production, growth, and maturation of an egg, or ovum
27
New cards
Oogonia
an immature female reproductive cell that gives rise to primary oocytes by mitosis
28
New cards
Polar body
haploid cell produced during meiosis in the female of many species; these cells have little more than DNA and eventually disintegrate
29
New cards
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
30
New cards
Embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month
31
New cards
Fetus
In humans, the term for the developing organism between the embryonic stage and birth.
32
New cards
Primary germ layers
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm; layers of cells that develop into the body's systems and tissues
33
New cards
Neural tube
an embryonic structure that gives rise to the central nervous system
34
New cards
Teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm