physics aqa specific latent heat
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what does changing the internal energy do
Changing the internal energy of a material will cause it to change temperature or change state:
what is specific heat capcaity
he energy required for a particular change in temperature
specific latent heat
the energy required for a particular change in state
As there are two boundaries, solid/liquid and liquid/gas, each material has two specific latent heats:
latent heat of fusion - the amount of energy needed to melt orfreeze the material at its melting point
latent heat of vaporisation - the amount of energy needed to boil or condense the material at its boiling point
what is specific latent heat
Specific latent heat is the amount of energy required to change the state of 1 kilogram (kg) of a material without changing its temperature.
The amount of thermal energy stored or released as the temperature of a system changes can be calculated using the equation:
change in thermal energy = mass × specific latent heat
ΔEt =m x l
mass (m) is measured in kilograms (kg)
specific latent heat (l) is measured in joules per kilogram (J/kg)
change in thermal energy (ΔEt) is measured in joules (J)
Measuring latent heat
Latent heat can be measured from a heating or cooling curve line graph. If a heater of known power is used, such as a 60 W immersion heater that provides 60 J/s, the temperature of a known mass of ice can be monitored each second. This will generate a graph that looks like this.
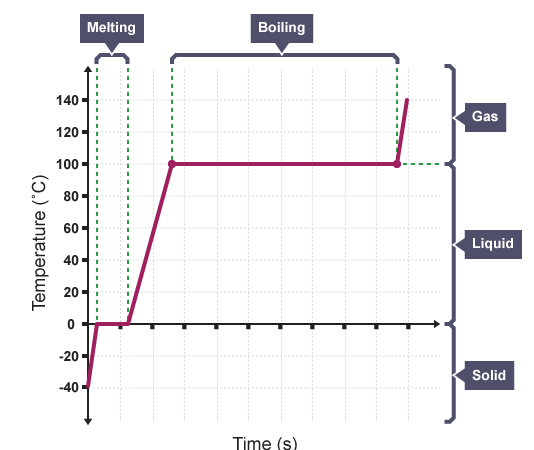
the horizontal line meaning
The graph is horizontal at two places. These are the places where the energy is not being used to increase the speed of the particles, increasing temperature, but is being used to break the bonds between the particles to change the state.The longer the horizontal line, the more energy has been used to cause the change of state. The amount of energy represented by these horizontal lines is equal to the latent heat.