Biology DNA/RNA, Protein Synthesis, & Genetic Engineering
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Monomers of DNA
nucleotides
3 main parts of a nucleotide
a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base
Double helix
term used to describe the physical structure of DNA
4 nitrogenous bases of DNA
adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine
Difference between DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases
RNA contains uracil instead of thymine
Base pairs in DNA
AT GC — Adenine paired with thymine and cytosine paired with guanine.
Difference between DNA and RNA base pair
DNA pairs adenine with thymine instead of uracil.
Purines
Have 2 carbon/nitrogen rings and are made of Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines
have 1 carbon/nitrogen ring and are made of Thymine and Cytosine
Holds DNA together
Hydrogen Bonds
Transcription
DNA → RNA — copying of genetic information from code of DNA to code of mRNA
Translation
RNA → protein — process in which instructions in mRNA are used to assemble polypeptides to make a protein
Genetic Code
the sequence of nitrogen bases
Codon
series of 3 mRNA nucleotides which code for a specific amino acid
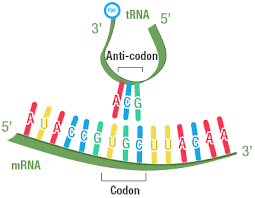
Anti-codon
a loop on clover leaf shaped tRNA which pairs with its complementary mRNA codon
Polypeptide Chain
a chain of amino acids made from the pairing of the codon and the anti-codon (Translation)
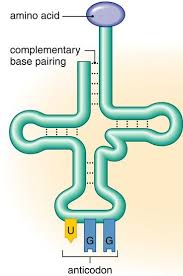
tRNA
Transfer RNA — serves as a link between the mRNA and the chain of amino acids
Complimentary base pairing
the way nitrogen bases pair together
Helicase
Unzips DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs to start replication
Primase
Creates small RNA primers on the unzipped DNA to mark the starting point of new DNA
Polymerase
Creates DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides on the unzipped DNA
Exonuclease
Removes RNA primers
Ligase
Seals DNA fragments into a single strand
Semi-conservative replication
When each new strand of DNA has one original (conserved) parent strand
Prokaryotic DNA
Has no nucleus and instead has a single DNA strand in the cytoplasm
Eurkaryotic DNA
Enclosed in a nucleus and has 8-46 chromosomes
Chromosomes are made of
A protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Substitution Mutation
A type of point mutation where a nucleotide is replaced by another
Deletion Mutatiton
A type of frame shift mutation where a base is deleted and the rest are shifted down
Insertion Mutation
A type of frame shift mutation where a base is inserted and the rest are shifted away
Point mutation
a mutation where only one base pair is affected