Psychological Assessment
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Differential Validity (2)
A test or other predictor has this when it's substantially different validity coefficients for members of diffferent groups (e.g. Men and women).
This is one cause of adverse impact.
AAMD Adaptive Behavior Scale
The AAMD Adaptive Behavior Scale is designed to measure children's personal independence and social skills. Adaptive behavior is a critical component in the diagnostic classification of the mentally retarded and is defined as "the effectiveness or degree with which the individual meets the standards of personal independence and social responsibility expected for his or her age and cultural group." Recommended as part of a classification/diagnostic battery in screening and placement decisions regarded the mentally handicapped.
Adult Neuropsychological Questionnaire
he Adult Neuropsychological Questionnaire consists of 54 items designed to be administered as a semi-structured interview. It can also be self-administered. The purpose of the questionnaire is to "inquire about complaints, symptoms, and signs that may suggest underlying brain dysfunction or other organic conditions" (manual, p.1). It was developed initially as an aid for students who were not well versed in signs and symptoms associated with neurologic conditions. Although designed to help students and non-neuropsychologist inquire about symptoms, history, or other complaints that may be associated with neuropsychological disorders, reviewers discourage its use claiming poor organization and over-interpretations about the significance and possible attribution of specific symptoms.
Alcohol Use Inventory
Designed to assess the nature of and problems associated with alcohol use pattern. A useful assessment tool when working with individuals with alcohol problems. The scales can be interpreted based on the benefits, styles, consequences and concerns associated with alcohol use, and is helpful in treatment. Combinations of scores have been developed into typologies which indicate ways to relate to the client, and can help with treatment planning.
Balthazar Scales of Adaptive Behavior I: Scales of Functional Independence
Designed to measure self-care differences in mentally retarded children and adults. Recommended uses include assessment of the developmentally disabled in clinical and research settings.
Kaufman Assessment Battery For Children (KABC-II)
Based on Luria's neuropsychological model and the Catell-Horn-Carroll theory of cognitive abilities.
Because of its emphasis on nonverbal instructions and items, this is considered "culture-fair"
Beery-Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual-Motor Integration, Fifth Edition
2004 The Beery-Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual-Motor Integration (VMI), Fifth Edition, is a developmental sequence of geometric forms to be copied on paper with pencil. The purposes of the VMI are to help identify, through early screening, children who may need special assistance, to obtain needed services, to test the effectiveness of educational and other interventions, and to advance research. The short form has 21 items and is for children 2-7 years of age. The full form has 30-items and can be either group or individually administered in 10-15 minutes for ages 2-18. The 2004 edition has two supplemental tests, VMI Visual Perception and VMI Motor Coordination. Reliability and validity are discussed and norms are provided. Also included in this edition are norms for two-year old children; 600 developmental stepping stones norms for birth through age six and visual-motor teaching methods from birth through early elementary school. (JW)
Bender-Gestalt II (3)
Used as a measure of visual-motor integration and can be used as a screning tool for neuropsychological impairment. The test includes 16 stimulus cards consisting of geometric figures.
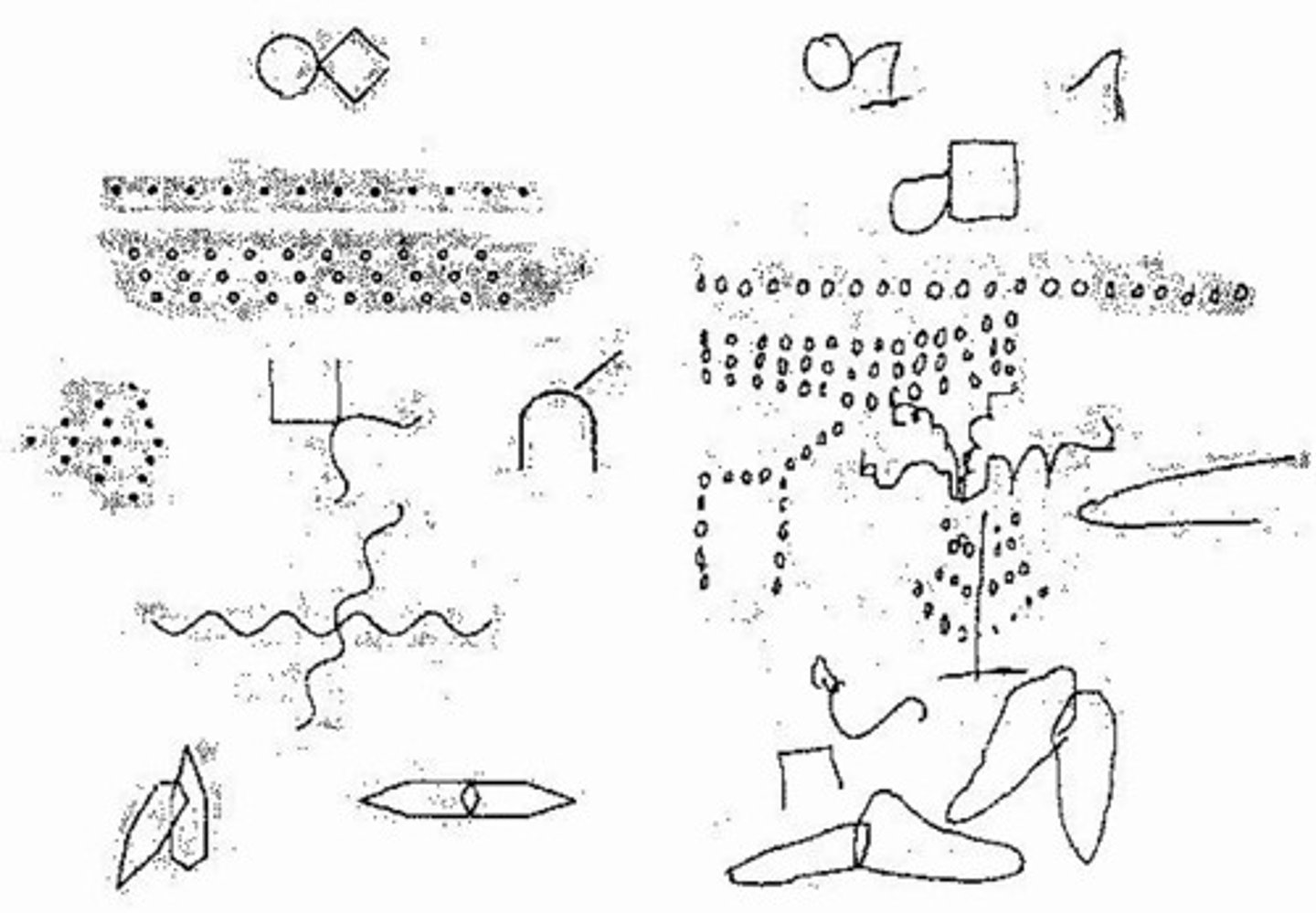
Bender Visual-Motor Gestalt Test - Second Edition
2003 The Bender Visual-Motor Gestalt Test, Second Edition (Bender-Gestalt II) was designed to measure visual-motor integration skills in children and adults from 4 to 85 + years of age. It may be used as an aid in diagnosing the difficulties of emotionally disturbed and brain damage. it requires the copying of designs. The second edition has seven new designs to increase the ability range. A recall phase and two supplementary tests (the Motor Test and the Perception Test) have been added. New Norms are provided. There is no time limit. Reliability and validity are discussed.
Stanford Binet Intelligence Scale - Fifth Edition
2003 The SBS may be used to diagnose development disabilities, to research clinical and neuropsychological assessment, abilities, early childhood, special education placements, adult social security and worker's compensation evaluations. It provides information for interventions such as individual family plans, individual educational plans, career assessment, work transition, career change, employee selection and adult neuropsychological treatment. It may be useful in a variety of forensic contexts. It has been used to diagnose mental retardation, learning disabilities, developmental cognitive delays in young children, as well as placement of students in school programs for the intellectually gifted. The examiner must be professionally trained and certified. Reliability and validity are discussed.
The Stanford Binet, Fifth Edition (SB5) is an individually administered assessment of intelligence and cognitive abilities. It is appropriate for examinees ages 2 through 85+ years. The complete scale consists of 10 subtests: 5 verbal and 5 nonverbal. It takes 15 -75 minutes to administer depending on the scale administered. Differences in this edition include: five factors rather than four (fluid reasoning, knowledge, quantitative reasoning, visual-spatial processing and working memory). Half of the subtests use a nonverbal mode of testing. New Items include very low and very high discriminating items.
Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales II (2)
2005 The Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales, Second Edition is a measure of personal and social skills of people ranging in age from birth to age 90. It is used with special needs populations, such as individuals with mental retardation, autism spectrum disorder, ADHD, Asperger Syndrome, and developmental delays. The test is organized in a three domain structure: communication (receptive, expressive, written); daily living skills (personal, domestic, community); and socialization (interpersonal relationships, play and leisure time, coping skills). There is also a motor skills domain and an optional maladaptive behavior index. The test is available in four formats: survey interview form, parent/caregiver rating form, expanded interview form, and teacher rating form.
Flynn Effect (2)
Research by author (1987) and others has shown that IQ test scores have consistenly increased over the last 70 years in the United Stages and other industrialized countries.
This increase- (referred to as the term)- involves a rate of at least three IQ points per decade and is apparently due primarily to increases in fluid intelligence.
Actuarial v. Clinical Predicitons (3)
1 are based on empirically-validated relationships between test results and target criteria and make use of a regression equation, multiple regression equation, or similar technique,
2 are based on the decision maker's intuition, experience, and knowledge.
Studies comparing the two methods have genrally found that the actuarial method alone is more accurate than clinical judgment alone, and about equally accurate as a combination of actuarial and clinical methods.
Domain-referenced testing (2)
Involves scoring an examinee's test performance in terms of how much he/she has mastered the domain being assessed. It is also known as conten and criterion ___________ ___________.
Kuder Occupatoinal Interest Inventory (3)
Term was designed for high school juniors and seniors, college students, and adults. It was developed on the basis of empirical criterion keying but, unlike the Strong test, did not include a general reference group.
Instead, items elected for inclusion in the test were those that distinguished between different occupational groups.
Rorschach Inblot Test
(Scoring and Interpretation) (4+)
This is a projective personality tes that presens the examinee with 10 inkblots.
Administration usually entaliis two phases-free association and inquiry.
Responses to the inkblots presumably reflect the examinee's underlying personality, conflicts, etc. Most scoring systems involve looking at the following dimensions:
- Location
-Determinants
- Form Quality
-Content
-Frequency of Occurence
WAIS-III Factor Scores
(ADHD, Alzheimer's Disease) (6+)
This provides scores on two verbal factors (Verbal Comprehension and Working Memory)
and two performance factors (Perceptual Organization and Processing Speed).
Discrepancies in these correlate with several conditions. For example, the test manuals report a similar pattern for individuals with ADHD or learning disabilites (i.e., a Verbal Comprehension score higher than a Working Memory score couple with a Perceptual Organization score higher than a Processing Speed score).
It also reports the folowing pattern of mean scores for aging patients with Alzheimer's Disease:
- 79.6 on Processing Speed;
-84.8 on Perceptual Organization;
87.2 on Working Memory, and
-93.0 on Verbal Comprehension.
Big Five Personality Traits
Identification of these
-extraversion
-agreeableness
-conscientiousness
-neuroticism
-openness to experience
Gender-related differences in Cognitive Ability (3)
on measures of specific cogntive abliities, most studies have found that:
-femlaes do better on some tests of verbal abilty
-Males do better on certain measures of spatial and qualtitiative skills
-spatial skills show the largest gender gap.
Performance-Based Measurement (2)
Involves "observing and judging a pupil's skill in actually carryhing out a physical activity (givng a speech) or producing a product (building a birdhouse) (Airasian 1994, p. 426)
Strong Interest Inventory (3)
There are two versions of this:
The 1994 (1)
The Newly Revised (1)
In the 1994 (1) , the General Occupatoinal Theme and Basic Intersest scales were developed based on the logical content method, whereas the Occupational scales was devloped based on a criterion keying strategy method.
The Newly Revised (1) draws from a general representative sample.
Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (3)
Is for individuals ages 6-1/2 to 80 years and is used to assess the ability to form abstract concepts and shift cognitive strategies in respons to feedack.
is sensitive to frontal lobe damage. Impaired performance onthe test has been linked to alcoholism, autism, schizophrenia, depression and malingering.
Americans with Disabilities Act (2)
(1990) Requires that any test administered to a job applicant or employee with a disablity must accurately measure the skills and abilites the test was designed to measure rather than reflect the examinee's disabliity.
It also mandates that employers make reasonable accommodations when testing disabled examinees.
Dynamic Assessment (and) Testing the Limit 2/2
Derived from Vygotsky's method for evaluating a child's mental development and involves deliberate deviation from standardized testing procedures to determine if an examinee has the abliity to profit from assistance or instruction.
(2) a type of dynamic assessment, involves providing an examinee with additional cues or prompts. It is ordinarily done after standard administration of the test to preserve the applicablity of the test's norms.
Larry P. v. Riles (3)
A legal case brough by plaintiffs on behalf of AA children who were disproportionately enrolled in EMR classes in the SF school system.
Based primarliy on the testimony of experts, the judge handed down the opinon that "IQ tests are racially and culturally biased, (and) have a dscriminatory impact on Black children" and enjoined the SF public schools from using them to place Black children in EMR classes.
Seattle Longitudinal Study (2)
Found that a cross-sectional design is more likely to find early age-related declines in IQ because it is more vulnerable to the confounding effects of educational and other differences between different age groups (cohort effects).
It aslo found that, of the six primary mental abilities, only perceptual speed declines substantialy prior to age 60.
WAIS III Profile Analysis (2)
involves comparing each subtest score to the mean full-scale, verbal, or performance subtest score to derive information about the examinee's strengths and weaknesses.
It is important to keep in mind that significant variabliity in subtest scores can be expected for an examiee as the result of chance, and consequently that the analysis of subtest fluctuations may result in some false positives.
Crystallized Intelligence
Fluid Intelligence (2)
Horn and Cattell proposed that general intellgence can be desribed in terms of two types- a crystallized intelligence (Gc). refers to acquired knowledge and skills and is affeced by educational and cultural experiences, whereas
fluid intelligence (Gf). enables an individual to solve novel problems and to perceive relations and simiarlites and does not depend on specfic instruction.
Heredity and Intelligence
Correlations betwen the IQ scores of people with varying degrees of genetic smiliarity are used to deomstrate the impact of genetics on intelligence.
The studies have found that, the closer the genetic simliarity, the higher the correlation (e.g., identical twins reared together, r = .85; identical twins reared apart, r = .67)
PL 94-142
the Individuals with Disabilities Act (IDEA) requires that:
1) All disabled people from infancy to 21 years of age must be evaluated by a team of specialsits to determine their specific needs
2) An individualized Education Program (IEP) must be developed for each disabled child enrolled in the public education system that provides education for the student in the "least restrictive environment" and that has been approved by the child's parents and
3) while reliable, valid, and nondiscrininatory psychological tests can be used, assignment to special education classes cannot be made on the basis of IQ tests alone.
Stroop Color-Word Association Test
Assesses the degree to which the examinee can suppress a habitual response in favor of an unusual one and is considered to be a measure of cogntive flexibility and seletive attention.
It presents the examinee with a list of color names that are printed in ink colors that differ from the name (the name red might be printed in blue innk), and the examee is asked to go through the list and say the ink color rather than read the color name, which is the prepotent response.
Beck Depression Inventory-II
Contains 21 items that address the mood, cognitive, behavioral, and physical aspeccts of depression.
The examinee rates eachitem in terms of severity on a 4-point scale that ranges from 0 to 3.
The following score guidelines are usually used for individuals who have been diagnosed with major depression
0-13 = minimal depression
14-19 = mild depression
20-28 = moderate depression
29 - 63 = severe depression.
Embedded Figures Test
A measure of field dependece/independence. Children with autism tend to find the embedded figures included in this test faster than their non-autistic peers.
MMPI-2
TScores and Profile Analysis
These have a mean of 50 and standard deviation of 10. A (1) of 65 or higher on the MMPI-2 is considered clinically significant. Scores are commonly interpreted through profile analysis, which involves considering the highest two or three scale scores.
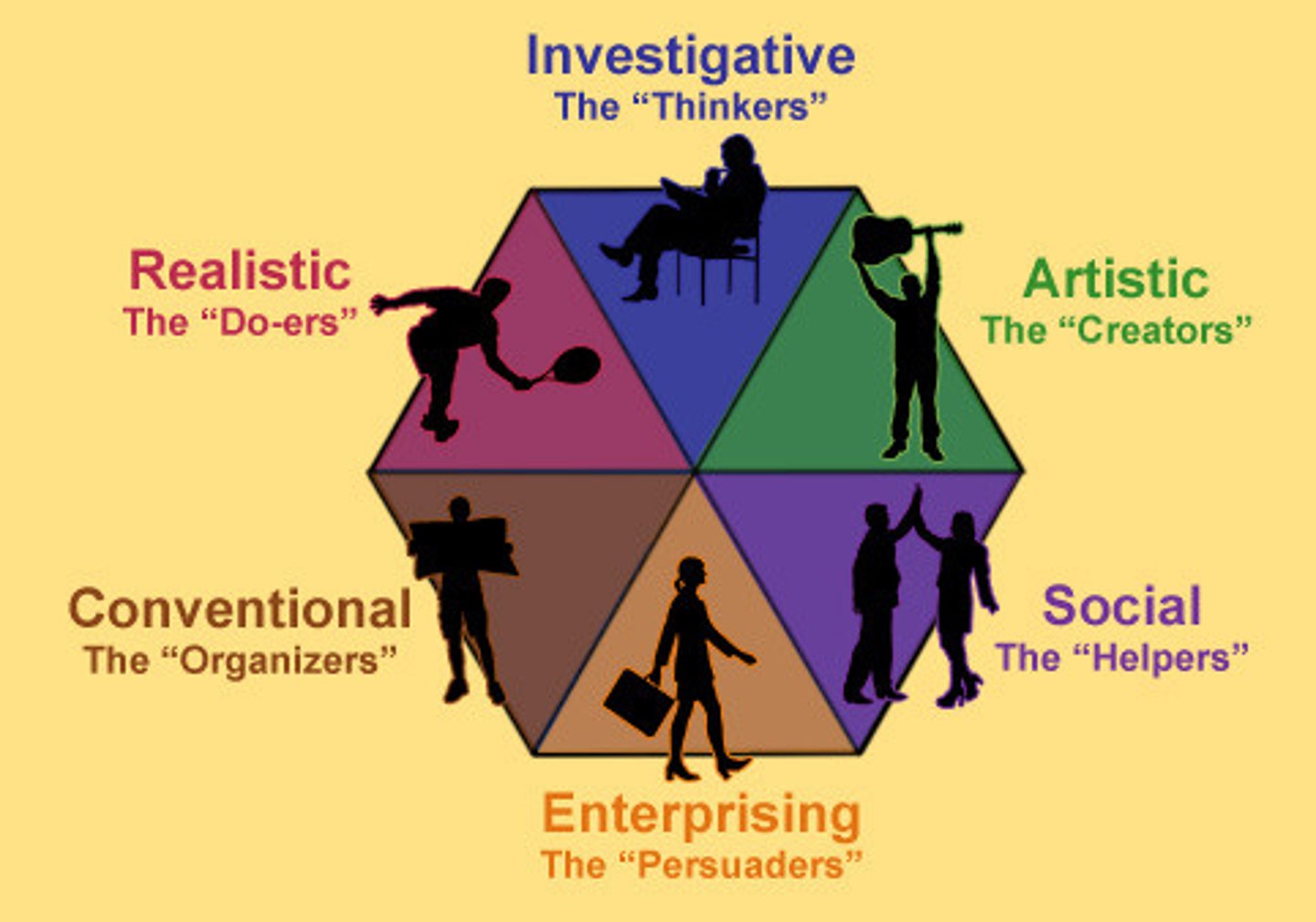
Self-Directed Search
Holland classified occupations and occupational interest into six thematic areas, which he believed reflect basic personality characteristics.
The relationshp between these themes in conceptualized in terms of a hexagon with themes located closer to one another being more similar.
Starting in the upper right of the hexagon, the themes are:
Realistic
Investigative
Artistic
Social
Enterprising
Conventional
These themes are measured by his (1)
WAIS-III Verbal Performance Discrepancy (3)
One method for interpreting Wechsler test scores is to consider the discrepancy betwen Verbal IQ and Performance IQ.
A discrepancy of 12 points or more is statistically significant. A higher Verbal IQ suggests right hemisphere damage, neurosis, or psychosis.
A higher Performance IQ may indicate left hemishpere damage, educational deficits, or sociopathy.
Infant and Preschool Tests
These are generally considered valid as screening devices for developmental delays and disabilties; But when administered to children aged two or younger, they have little predictive validity.
Examples include:
-the Denver Develolpment Screen Test
-the Bayley Scales
-the Fagan Test of Inteligence
PPVT-III
Measures receptive vocabulary for standard American English and provides a nonverbal estimate of intelligence.
It was designed for people with orthopedic disabilities aged 2.5 to 85 years, and can be administed to any examinee who is able to hear the stimulus word, see the drawings, and in some way communicate a response.
Types of Test Bias
(Slope and Intercept)
(1) occurs when there is differential validity (when the validity coefficients for a predictor (e.g. cognitive ability test) differ for different gropus.
Consequently, the predictor is more accurate for one group than another.
(2) also called "unfairness" occurs when the validity coefficients and criterion preformance for different groups are the same, but their mean scores on the predictor differ. As a result, the predictor consistently over- or underpredicts performance on the criterion for members of one of the groups.
Stanford-Binet Fifth Edition
(SB5)
An individually-administered intelligence test that is based on a hierarchical model of intelligence that begins with "g" and incorporates five cognitive factors-
Fluid Reasoning
Knowledge
Quantitative Reasonoing
Visual-Spatial Processing
Working Memory.
Administration of the (1) is tailored to the examinee's level of cognitive functioning.
Differential Validity
A test or other predictor has (1) when it has substantially different validity coefficients for memers od different groups (e.g. men and women).
This is one cause of adverse impact, which is I think good.
MMPI 3 Validity Scales
Designed to assess test-taking attidues and to determine if the results of a test for a particular examinee are valid.
High score on L scale: attempt to present oneself in a favorable light
High score on the F scale: Response carelessness
High score on the K scale: clinical defensiveness (faKing good). K scale scores are used to Korrect socres on several clinical scales.
WAIS III
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
Third Edition
1997 The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, Third Edition is an individually administered clinical instrument designed to assess the intellectual ability of adults ages 16 through 89. WAIS-III consists of various subtests, each measuring a different facet of intelligence. The test yields the three traditional composite IQ scores - verbal, performance, and full scale - and four index scores - verbal comprehension, perceptual organization, working memory, and processing speed. WAIS-III contains 14 subtests: picture completion, vocabulary, digit symbol-coding, similarities, block design, arithmetic, matrix reasoning, digit-span, information, picture arrangement, comprehension, symbol search, letter-number sequencing, and object assembly. The WAIS-III can be used as a psychoeducational test for secondary and postsecondary school planning and placement and also for differential diagnosis of neurological and psychiatric disorders that affect mental functioning. (MH)
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, Third Edition
2003 The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children--Fourth Edition (WISC-IV) is an individually administered, comprehensive clinical instrument for assessing the intelligence of children from 6-16. It provides composite socres that represent intellectual functioning in verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory and processing speed as well as a composite score that represents a child's general intellectual ability. Subtests include: block design, similarities, digit span, picture concepts, coding, vocabulary, letter-number sequencing, matrix reasoning, comprehension and symbol search. Supplemental subtests include: picture completion, cancellation, information, arithmetic, and word reasoning. It differs from WISC-III in that three subtests were dropped: picture arrangement, object assembly and mazes. Item content, administration and scoring procedures of all subtests were revised. Five new subtests were added: picture concepts, letter-number sequencing, matrix reasoning, and word reasoning.
Wide Range Achievement Test - 4
2006 The Wide Range Achievement Test 4 (WRAT4) is a norm-referenced test that measures the basic academic skills using four subtests: word reading, sentence comprehension, spelling, and math computation. Word reading measures letter and word decoding through letter identification and word recognition. Sentence comprehension measures an individual's ability to gain meaning from words and to comprehend ideas and information contained in sentences through the use of a modified cloze technique. Spelling measures an individual's ability to encode sounds into written form through the use of a dictated spelling format containing both letters and words. Math computation measures an individual's ability to perform basic mathematics computations through counting, identifying numbers, solving oral problems, and calculating written mathematics problems. The test can be administered to individuals ranging in age from 5 through 94 years old. The WRAT4 is most often administered individually but some of the subtests or section
Woodcock-Johnson III, Tests of Achievement
2001 Woodcock-Johnson III (WJ III) consists of two co-normed batteries: Tests of Achievement and Tests of Cognitive Abilities. The two batteries assess general intellectual ability, specific cognitive abilities, oral language and academic achievement. The tests can be used with a population ranging in age from 2 years to 80+ years. The achievement battery is available as a standard battery comprising 12 tests or an extended battery that has 10 tests that provide more in-depth diagnostic information on specific academic strengths and weaknesses. The achievement tests are primarily organized into five broad curricular areas: reading, oral language, mathematics, writing and academic knowledge. The test is also available in two forms, form A and form B, that have parallel content. (MH)
Aging and Intelligence
(Processing speed)
This is associated with a decrease in speed of information processing as well as declines in fluid (vs. crystallized) intelligence.
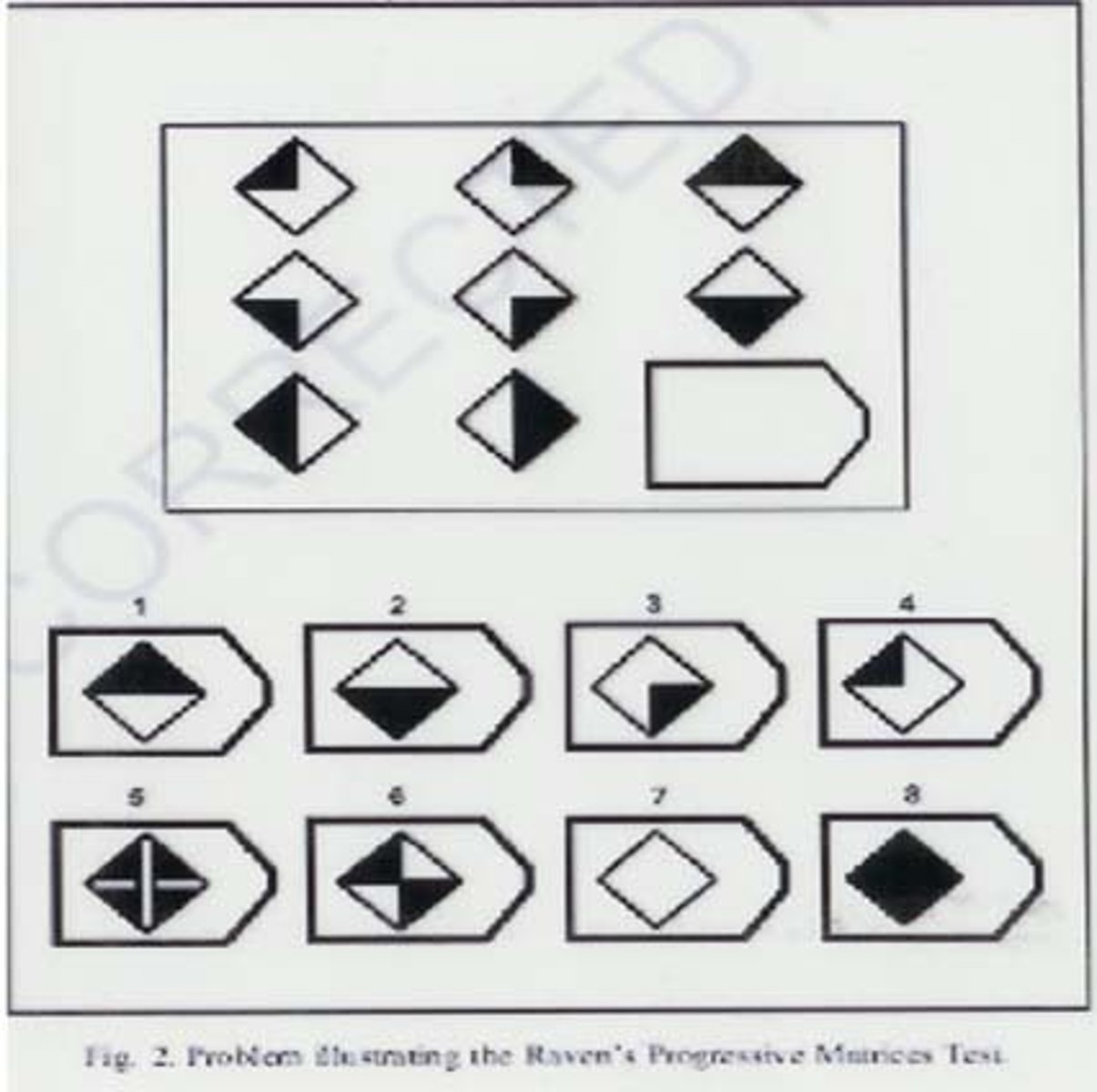
Raven's Progressive Matrices
A nonverbal measure of general intelligence (g). and is considered useful as a multicultural test
It is relatively independent of the effects of specific educational and cultural learning.
There are several versions including the Standard Progressive Matrices and
The Colored Progressive Matrices
Rorschach Inkblot Test
1951-1970 Scoring techniques for Rorschach Test including Davis Rorschach Miniature Location Charts in Color: Bruno Klopfer Scoring Areas; Beck's scoring method; Frequency Tables for Scoring Rorschach Responses by Marguerite Hertz; and Leonard Small's Rorschach Location and Scoring Manual. These techniques are individually available from the publisher.
MSE: EMOTIONS-Affect
Affect= behavioral/observable manifestations of clients mood via examiner
Affect observations
Appropriateness, Congruency, Intensity, Stability, Reactivity, Range
When a client's affect range is sustained euphoria
Expansive Affect
When affect is constrained to depressed range
Limited Range Affect
When no change in affect, commonly seen in negative symptoms of psychosis
Flat Affect
MSE- MOOD
reported in clients own words
Euthymic (pleasant), Angry, Euphoric, Dysphoric (down), Apathetic (dull), Apprehensive
MSE: General Appearance & Behavior parts
Physical Characteristics
Attire & Hygiene
Alertness
Motor Activity
Facial Expressions
Speech/Voice (RAVRS)
Attitude Toward Examiner
MSE: General Appearance & Behavior: ALERTNESS- awake but not fully alert, confusion, momentary sleepiness/somnolence, often present in intoxication
"Drowsy, Sedated, Clouding of Consciousness"
MSE: General Appearance & Behavior: ALERTNESS- responsive to painful stimuli or vigorous touching only, often present in drug overdose
Stuporous (alertness)
MSE General Appearance & Behavior Alertness (consciousness) Descriptors
Alert & Responsive
Drowsy, sedated, Clouding of consciousness
Stuporous
Comatose
HyperalertHypervigilant
MSE traditionally follows conventions of
Medical Model/psychiatric assessment
Major categories of MSE (MET SIGI)
Memory, Attention, Concentration
Emotion (mood/affect)
Thought (content/process)
Sensorium
Intellectual Functioning
General Appearance & Behavior
Insight, Judgment, Impulse Control
Akathisias
Restlessness (motor activity in GA&B)
MASE GA&B: Speech/Voice descriptors
RAVRS
Rate
Articulation
Volume
Rhythm
Spontaneity
Parts of Affect observed (ARRIS)
Appropriateness
Range
Reactivity
Intensity
Stability