MCAT Biochemistry
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Macromolecules
Are polymers made from monomers - enzymes that make polymers are polymerases via reactions called polymerization.
Proteins
made up of amino acids(20 kinds)
Have an N-C-C backbone, amine group, carboxylic group, and variable group
Bond together by a peptide bond(formed by dehydration synthesis - loss of H2O)
Protein Structures(4)
Primary = amino acids joined
Secondary = alpha-helix or beta-sheets
Tertiary: formation of a polypeptide and side chain interactions - inner core becomes hydrophobic and outer becomes hydrophilic
Non-covalent interactions: non-polar/non-polar, polar neutral/polar neutral, acid/base(charged)
Covalent: disulphide bridges(harder to break)
Quaternary structure: side chain interactions between different polypeptides - subunits come to form larger units
Carbohydrates
Made from monosaccharides to disaccharides to polysaccharides
Monosaccharide
CnH2On - 3 common are glucose, fructose, galactose - ribose and deoxyribose
Disaccharide
2 monosaccharides - 3 common = maltose, sucrose, lactose - C12H22O11 formula
Polysaccharides
Made of many monosaccharides - 3 common are glycogen, starch, and cellulose - function as an energy source
Lipids
The fats - made of a hydrocarbon structure(many C and H)
Unsaturated
Have space for more H to bind - liquid at room temp
saturated fatty acids
No more space for H to bind - are solid at room temperature
Triglyceride
3 fatty acids combined
Phospholipids
2 lipid structures and one phosphate - form the lipid bilayer due to having polar and non-polar sides
Terpenes
built from isoprene structures and need at least 2 of them - terpenes form waxes and lipid rings like vitamin A
Cholesterol and steroid hormones
3 six-carbon rings and 1 five-carbon ring)
Thermodynamics
the study of the relations between heat, work, temperature, and energy

ΔG
When G<0 = negative G, spontaneous - gives E
When G>0 = positive, non-spontaneous - needs E
When G = 0, equilibrium
Reaction Coupling
Using ATP as a source of energy - a very favourable reaction is used to drive an unfavourable one
ATP = ADP + Pi → very exergonic
Exergonic = giving off E
Endergonic = using up E
Chemical Kinetics
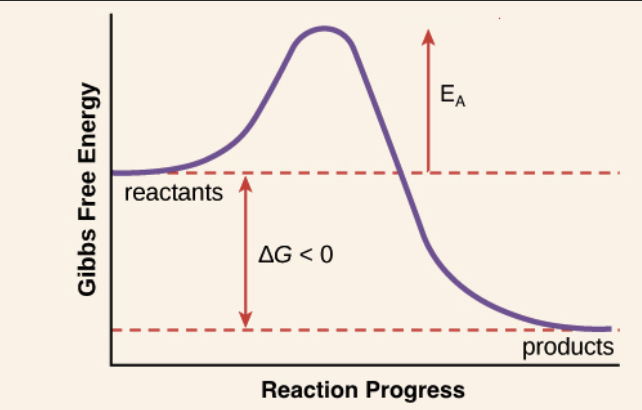
The study of reaction rates - all reaction rates proceed through a transition state which tends to be unstable
Activation Energy
Is the required E to produce the TS
if Ea is High = slow rate
if Ea is low = faster rate
Reaction Coordinate Graph
shows the energy vs reaction coordinates over time - the smaller the Ea, the better
We can make the Ea smaller using catalysts - speeding the reaction up by stabilizing TS and reducing Ea
Enzymes
a physiological catalyst - works to speed up a reaction by increasing the rate of reaction, not used up in a reaction, a must be specific
Enzyme Structure
an enzyme has an allosteric site and an active site - the active site is where the substrate binds(where the reaction occurs) and the allosteric site is another place for enzyme regulation)inhibition or activation)
Two models - active site and induced fit; active is lock and key while the induced fit is when the enzyme needs to change shape to fit a substrate
Can perform both positive and negative feedback
Enzyme Function and regulation
Function: to speed up a reaction
Regulation: by many inhibitions ways, allosteric site, feedback inhibitionV vs. [S] Graph
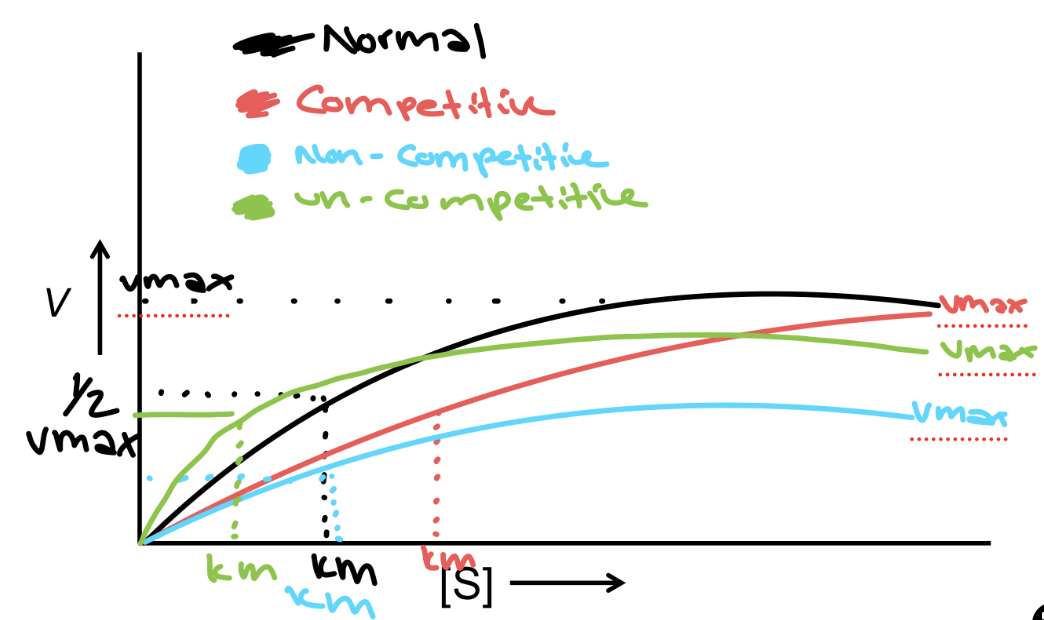
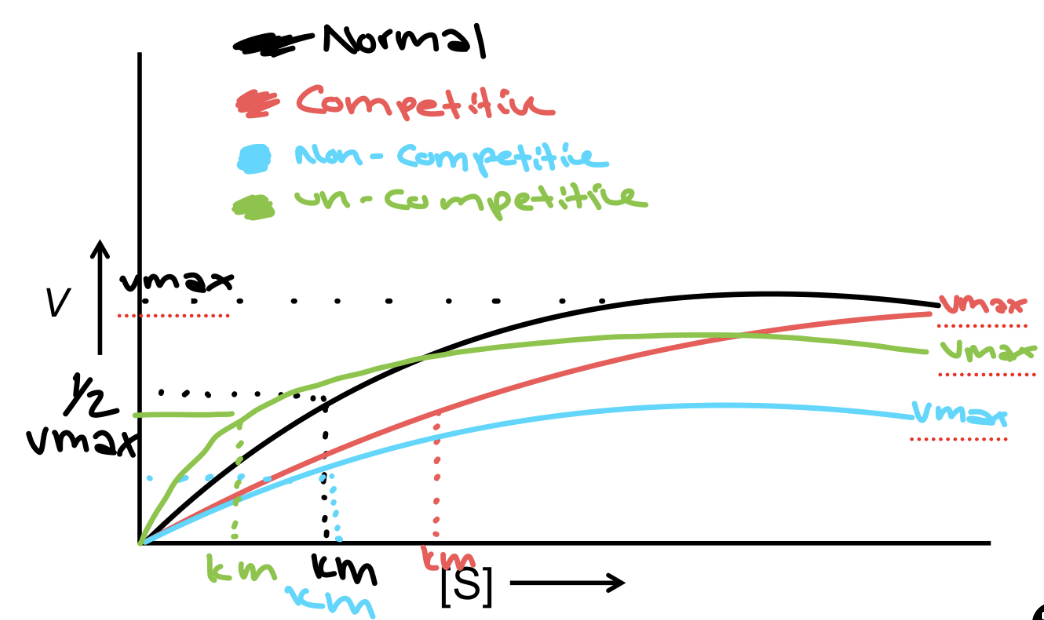
V vs. [S] Graph
the reaction rate in Velocity vs the substrate concentration [S] → vmax is when the enzyme is saturated and depends on enzyme [C], and the [S] becomes constant - Vmax/2 is when the linear part of the graph is equal to [S]. Km is the substrate [S] required to reach ½ Vmax
![<p>the reaction rate in Velocity vs the substrate concentration [S] → vmax is when the enzyme is saturated and depends on enzyme [C], and the [S] becomes constant - Vmax/2 is when the linear part of the graph is equal to [S]. Km is the substrate [S] required to reach ½ Vmax</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/13266abc-73f8-4bac-a1ee-793b57d8933d.png)
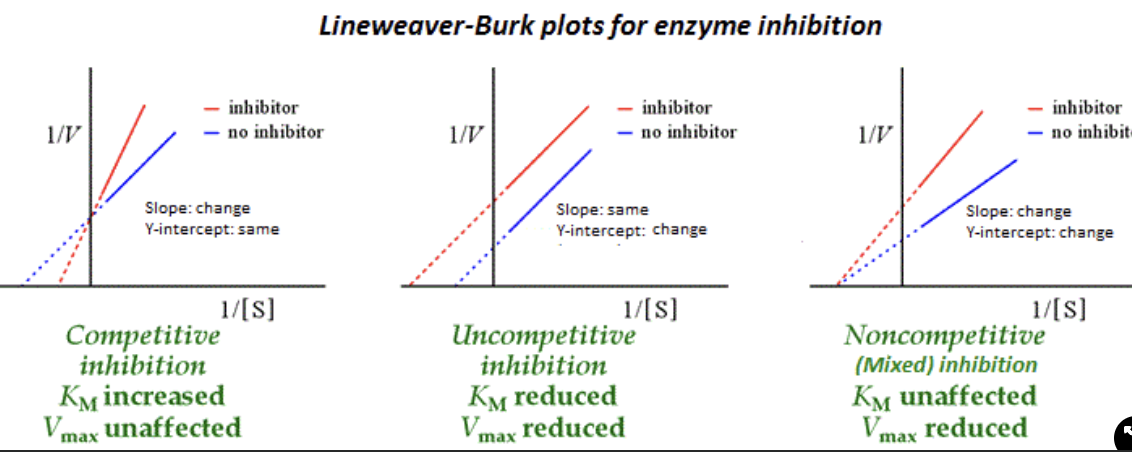
Competitive Inhibition
Compete for enzyme binding - same Vmax but the effect on Km is more since you need more substrate - a longer time to reach the same Km - binds at the active site
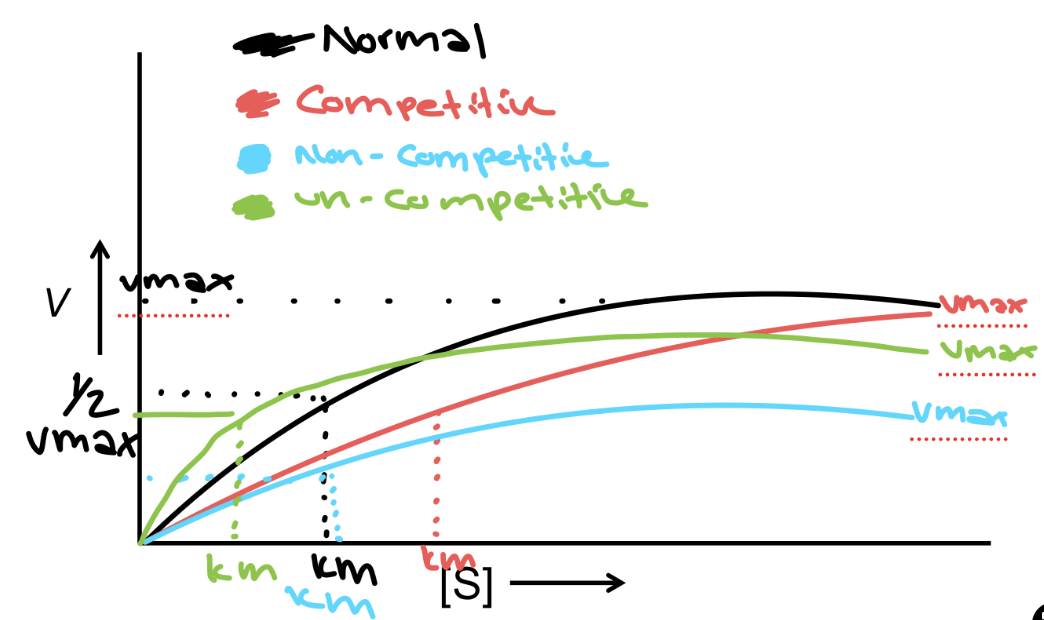
Non-competitive Inhibition
it affects the Vmax since we need more enzymes to deal with the substrate, but Km is unchanged since the active site is the same but prevents the activity of the enzyme- binds to the allosteric site
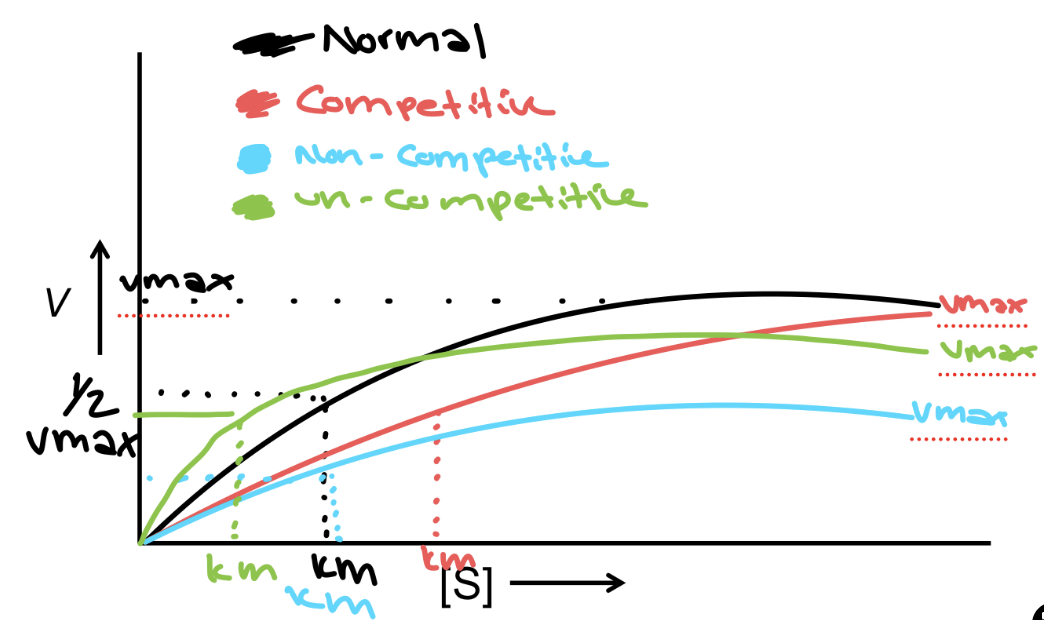
Un-competitive Inhibition
it affects both the Vmax and Km since it binds to the allosteric site after the substrate is bound, which affects both enzyme performance and the amount of product being produced - binds to an allosteric site
Mixed-Type Inhibition
binds at the allosteric site either when the enzyme is bound to the substrate or empty the active site. Vmax will become lowered, but Km can vary whether enzyme bound or empty Active site
when bound to the substrate, Km decreases(like un-comp)
When an empty active site, Km increases(like comp
Lineweaver Burk Plots