bacte lec - non-fermentative Gram-negative bacilli (new)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Nonfermenters
Group of Gram negative bacilli that do not ferment glucose and other sugars
(+) positive
Oxidase test result of nonfermenters (except Acinetobacter spp.)
Pseudomonas
→ strictly aerobic
→ catalase-positive, oxidase-positive (except P. luteolus and P. oryzihabitans)
→ motile, some have polar flagella
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
→ most common pseudomonas
→ ound in moist environments, pools, hot tubs, catheters, and humidifiers in hospitals (ubiquitous)
→ opportunistic pathogen, and causes nosocomial infection
slime polysaccharide, endotoxin, proteases, anti-complementary, exotoxin A, pili, alginate
Pathogenesis/ Virulence of P. aeruginosa
exotoxin a
promotes cellular damage and tissue invasion and is toxic for macrophages, blocks protein synthesis
Pili
(P. aeruginosa) found on bacterial surface, mediate attachment to host cells
alginate
a polysaccharide, polymer that inhibits phagocytosis and contributes to the infection potential in patients with cystic fibrosis
Pyocyanin, Pyoverdin, Pyorubin, Pyomelanin
pigments of P. aeruginosa
Pyocyanin
water-soluble, bright bluish phenazine pigment, damages cells by producing reactive oxygen species
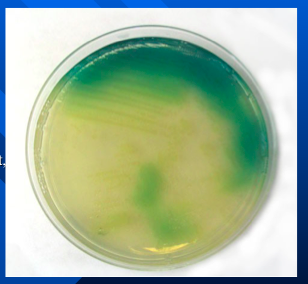
Pyoverdin
green, water-soluble and fluoresces under short- wavelength ultraviolet light
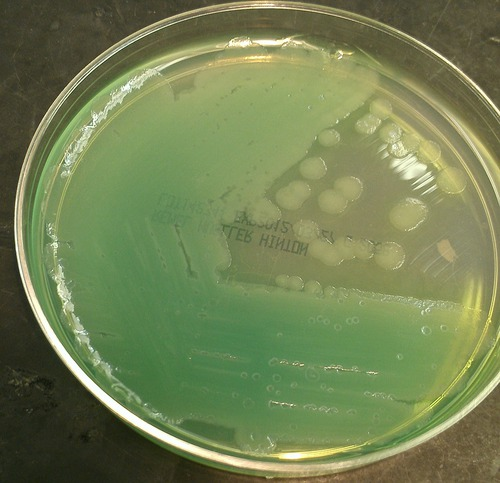
Pyorubin
red pigment of P. aeruginosa
Pyomelanin
brown pigment of P. aeruginosa
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Common cause of lung infection in people with Cystic fibrosis
Jacuzzi or hot tub syndrome
What syndrome is caused by P. aeruginosa which manifests as necrotizing rash in divers and swimmers?
Ecthyma gangrenosum
A disease caused by P. aeruginosa
Gram negative, medium-size, straight rods
Gram staining, size, and shape of P. aeruginosa
5% Sheep blood agar, MacConkey agar, thioglycolate broth, brain-heart infusion broth
Culture Media of choice for cultivation of P. aeruginosa
Cetrimide agar
a selective and differential medium for the identification of P. aeruginosa
Cetrimide
acts as a detergent and
inhibits most bacteria; enhances production of pigments
green
colornies of P. aruginosa on Cetrimide agar
B-hemolytic, rough or ground glass appearance
colonies of P. aeruginosa on sheep blood agar
Pseudomonas aerugionosa
formation of sheen and/or pigment on the slants of TSIA and Pseudomonas P agar, Mueller-Hinton agar, Trypticase soy agar
oxidase +, ADH +, citrate +
results of P. aeruginosa in oxidase test, Arginine dihydrolase (ADH) test, citrate test
alkaline slant/neutral butt
P. aeruginosa reaction in TSIA
42C
The temperature in which P. aeruginosa grows
musty grape-like (or corn tortilla), 2-aminoacetophenone
What is the odor of P. aeruginosa? What causes this odor?
aminoglycosides, the carboxypenicillins and ureidopenicillins, ceftazidime (or cefepime), carbapenems, the
quinolones
Antimicrobial susceptibility of P. aeruginosa: Susceptible
sulfamethoxazole- trimethoprim (SXT) and tetracyclines, tigecycline,
ertapenem, nitrofurantoin
Antimicrobial susceptibility of P. aeruginosa: Resistant
colistin, polymyxin B
Antimicrobial susceptibility of P. aeruginosa: Multiple resistant strains
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas putida, Pseudomonas veronii, Pseudomonas monteilii, Pseudomonas mosselii
Fluorescent pseudomonads
Pseudomonas stutzeri, Pseudomonas mendocina, Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes, Pseudomonas alcaligenes, Pseudomonas luteola, Pseudomonas oryzihabitans
Nonfluorescent pseudomonads
Pseudomonas putida
→ A psudomonas specie associated with catheter-related sepsis in cancer patients
→ A pseudomonas specie that has low virulence, rarely causes clinical disease
→ A pseudomonas specie that is gelatin hydrolysis negative
Pseudomonas fluorescens
→ Pseudobacteremia related to contaminated catheters and catheter-related devices
→ A pseudomonas specie that is gelatin hydrolysis positive
Pseudomonas stutzeri
→ A pseudomonas specie that is rarely isolated, rarely causes infection. It is wrinkled, leathery, adherent colonies that may produce a light-yellow or brown pigment.
→ A pseudomonas specie that is ADH (-) and starch hydrolysis (+)
Acinetobacter
→ short, rod shaped to spherical Gram negative bacilli
→ non motile and strictly aerobic
→ difficult to decolorize in Gram stain, more that 25 species are known but differentiation biochemically is difficult
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus - Acinetobacter baumanii complex
Acinobabcter is often collectively known as
oxidase -, catalase +
Acinetobacter oxidase test, and catalase test results
purplish
color of Acinetobacter colonies in MacConkey's agar
Acinetobacter baumanii
glucose-oxidizing (saccharolytic), nonhemolytic Acinetobacter
Acinetobacter Iwoffi
non-glucose oxidizer (nonsaccharolytic), nonhemolytic Acinetobacter
Acinetobacter haemolyticus
nonsaccharolytic, hemolytic acinobacter
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, quinolones, ureidopenicillins, imipenem, ampicillin-sulbactam, ceftazidime, carbapenems (except ertapenem)
Acinetobacter baumanii complex is susceptible to
β-lactam, aminoglycoside antibiotics
Acinetobacter baumanii complex is resistant to
plasmid-mediated acetyl-, adenylyl-, phosphotransferases
Resistance of Acinetobacter baumanii complex to the
aminoglycosides is caused by __________
CRAB (carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumanii)
resistant to all classes of antibiotics, except colistin and tigecycline
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
→ third most common nonfermentative, Gram negative bacilli isolated in the clinical laboratory
→ nonmotile, nosocomial pathogen
mechanical ventilation, use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, catheterization, neutropenia
Risk factors for colonization or infection (S. maltophilia)
oxidase -, DNAse +, catalase +, esculin and gelatin hydrolysis +, Lysine decarboxylase +
S. maltophilia results on oxidase test, DNAse test, catalase test, esculin and gelatin hydrolysis, Lysine decarboxylase
blood agar plate, MacConkey agar
culture media for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
lavender green colonies
color of S. maltophilia colonies on Blood agar plate
bluish
color of S. maltophilia colonies on MacConkey agar
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
antibiotic of choice for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Burkholderia
Aerobic, non-spore-forming, all are motile polar flagella except for 1 specie, nosocomial
Burkholderia mallei
Burkholderia specie that is nonmotile _____________
Burkholderia pseudomallei
Burkholderia that is acquired via inhalation or contact through cut or abraded skin
Melioidosis
Burkholderia pseudomallei causes what illness
Burkholderia pseudomallei
nonfermentative, wrinkled colonies, bipolar staining in gram stain
earthy
odor of Burkholderia pseudomallei
Ashdown's medium
selective culture medium for the isolation and characterization of Burkholderia pseudomallei
colistin
inhibitor in Ashdown's medium
neutral red
indicator in Ashdown's medium responsible for deep pink Burkholderia pseudomallei colonies
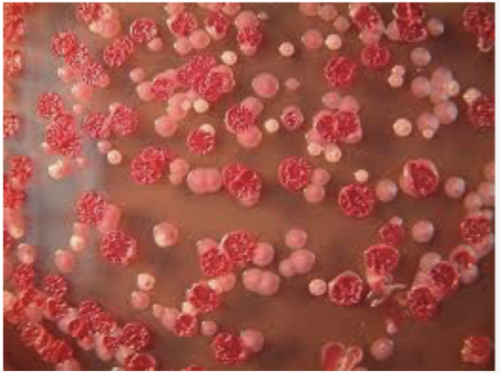
Burkholderia cepacia complex
→ Nosocomial pathogen associated with contaminated equipment, medications, disinfectants
→ Can cause bacteremia, UTI, septic arthritis, respiratory tract infection
→ Opportunistic pathogens in patients with cystic fibrosis and Chronic granulomatous disease
Burkholderia mallei
nonmotile, growth on MAC, Variable glucose oxidation, (+) ADH, Reduce nitrates to nitrites
Glanders
Burkholderia mallei causes what disease
livestock (horse, mule, donkey)
Burkholderia mallei primarily affects
Burkholderia mallei
parasite that causes an infection in humans, May cause severe local suppurative or acute pulmonary infections
Aeromonas
Facultative anaerobes, widely distributed in freshwater, estuarine, and marine environments
Septicemia, wound infections
(Aeromonas) Extraintestinal infections:
Mesophilic Group
Optimal growth at 37 degrees celsius, A. hydrophilia complex, A. veronii complex, A. caviae complex
Psychrophilic group
Optimal growth at 22 degrees celsius, A. Salmonicida
Aeromonas
pink-centered colonies from the fermentation of mannitol
Aeromonas hydrophlia
An infection in fish which manifests as iridial hemorrhage, external/internal hemorrhage, reddened fins, adipose fin clipped
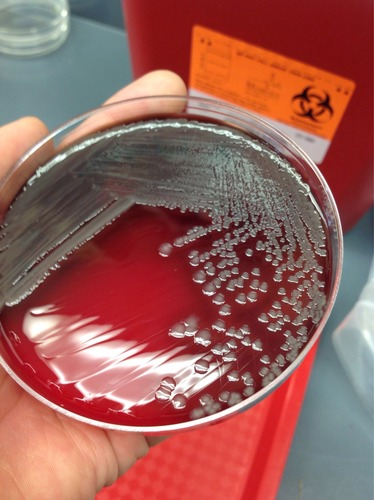
Moraxella
→ nonmotile, strongly oxidase (+), strictly aerobic, asaccharolytic
→ opportunists that reside on the mucous membranes of humans and lower animals
penicillin
An example of antibiotic that moraxella is susceptible to
Moraxella catarrhalis
→ Most frequent isolate, COMMENSAL of the upper respiratory tract of humans; respiratory and ear specimens
→ resembles neisseria due to Gram-negative coccal morphology
→ previously called Neiserria catarrhalis and also Branhamella catarrhalis
Moraxella
Smooth, opaque, gray-to-white colonies,
hockey puck
description of Moraxella colonies because the colony remains intact when pushed across the plate with a loop
SBA, CHOC agar
culture media for moraxella
Moraxella nonliquefaciens
Second most frequently isolated, normal flora of the respiratory tract of humans, does not grow on MAC
Moraxella ostoensis
part of the normal flora in the genitourinary tract, and similar morphologically and biochemically to M. nonliquefaciens
Moraxella lacunata
common conjunctival isolate
Oligella
Small, paired, Gram negative bacilli or coccoid, do not grow on MAC, and non-oxidative
Oligella ureolytica
motile by petrichous flagella
Alcaligenes
→ Found in water, and is resistant to disinfectants such as chlorhexidine and quaternary ammonium compounds
→ Obligate aerobe, and is Grown on MAC
→ Motile with 1-12 peritrichous flagella
eye infections, pancreatic abscesses
Alcaligenes faecalis is linked to what illnesses?
Achromobacter xylosoxidans
Most commonly isolated from this genus, Achromobacter
Chromobacterium violaceum
Reservoirs are soil and water
Skin lesion
Common portal of entry of C. violaceum
Violecein
Pigment produced by C. violaceum
Flavobacteriaceae
Which bacteria hydrolyzes esculin and is indole positive?
Elizabethkingia meningoseptica
What spp. causes meningitis and septicemia in newborns?
Ralstonia
This nonfermentative bacteria is a slow grower requiring 72 hours to grow on primary cultures
Sphingomonas
This bacteria does NOT grow on MAC and needs more than 48 hours for colonies to grow on SBA
Haemophilus
- Carbohydrate fermenter
- Requires X and V factors to grow
Aggregatibacter
- Major contributor to periodontitis
- Star shaped colonies at 48 hours
- Glucose fermenter
- Does not grow on MAC
Eikenella corrodens
- Acquired from human bites/fights
- High susceptibility to people with poor dental hygiene
- Bacilli pits on the surface of the agar
Kingella kingae
- Causes indolent, slowly progressive endocarditis
- Most common cause of osteoarthritis in children under 4 years old
- Grows on Neisseria Selective Agar
Cardiobacterium hominis
- Does not grow on MAC
- Grows in the absence of X and V factors
- Microaerophilic, facultative, anaerobe
- Characteristic rosette formation
✨PASAR BACTERIOLOGY✨
✨MANIFESTING✨