Anatomy of the Brain and Spinal Cord
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Meninges
3 layers of tissue provide protection to the brain and spinal cord
Dura Mater (Meninges)
outermost layer, it’s tough and leathery (Meninges)
Arachnoid (Meninges)
middle layer, it is fairly delicate and impermeable (Meninges)
Subdural Space
separates the arachnoid mater from the dura
Subarachnoid Space
separates the arachnoid mater from the pia mater
filled with cerebrospinal fluid
Pia Mater (Meninges)
the innermost layer, it adheres to the surface of the brain
covers the gyri and descending into the sulci
it appears glossy, it is so thin it’s almost invisible to the naked eye
Meningitis
infection/inflammation of the meninges (viral) (bacterial: more serious)
Ventricular System
a series of interconnected, fluid-filled spaces within the core of the CNS (brain and spinal cord)
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
fluid in the ventricle
derived from the choroid plexus
can be collected for testing (i.e meningitis)
drugs can be delivered into (epidural)
Choroid Plexus
a specialized vascular tissue within walls of ventricles
filters capillary blood and secretes the CSF product into the ventricles
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Neutral Buoyancy
the brain can be dense without being damaged by its own weight
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Protection
protects the brain tissue from injury by providing a fluid buffer that acts as a shock absorber
Blood-Brain-Barrier(BBB)
protects the brain from substances in the blood
formed by the tight junctions between capillary endothelial cells within the brain and spinal cord
helps keep blood cells, proteins, toxins, hormones, bacteria, etc. out of brain tissue
preserves “optimal balance of extracellular chemical composition within the brain
Astrocytes
maintain tight junctions via their “end feet”, which contact vascular endothelial cells
Brain capillaries
NON-FENESTRATED ( have tights junctions that form a barrier)
Capillaries in the rest of the body
FENESTRATED (no tight junction/no barriers)
What gets through the Blood Brain Barrier?
anything that is both small and lipid-soluble, or for which specific transporters exist
Oxygen, CO2, and other blood gases
Glucose, insuline, amino acids
Alcohol, nicotine, cocaine, other psychoactive drugs
Circumventricular Organs
NOT protected by the Blood Brain Barrier
on brain midline, adjacent to ventricles
detect osmolarity of extracellular fluid
lets us know when we are thirsty
its receptors help us detect the presence of toxins in the blood
Axes and Directional Terminology
Rostral
Caudal
Coronal
Sagittal
Horizontal
Axes and Directional Terminology: Anterior
in front of
Axes and Directional Terminology: Posterior
behind
Axes and Directional Terminology: Superior
above
Axes and Directional Terminology: Inferior
below
Axes and Directional Terminology: Rostral (BRAIN)
front of the brain
Axes and Directional Terminology: Caudal (BRAIN)
back of the brain
Axes and Directional Terminology: Dorsal (BRAIN)
top of the brain
Axes and Directional Terminology: Ventral (BRAIN)
bottom of the brain
Axes and Directional Terminology: Dorsal (Spinal Cord/Brain Stem)
back of the brain stem/spinal cord
Axes and Directional Terminology: Ventral (Spinal Cord/Brain Stem)
front of the brain stem/spinal cord
Axes and Directional Terminology: Caudal (Spinal Cord/Brain Stem)
bottom of the brain stem/spinal cord
Axes and Directional Terminology: Rostral (Spinal Cord/Brain Stem)
top of the brain stem/spinal cord
Axes and Directional Terminology: Coronal
slicing to have a front and back
Axes and Directional Terminology: Horizontal
slicing to have a top and bottom
Axes and Directional Terminology: Sagittal
slicing in half; having a left/right side
White Matter
myelinated (white) axons
Gray Matter
consists mostly of cell bodies and dendrites
Which of the following cells are found in the white matter of the spinal cord?
Oligodendrocytes
Spinal Cord
located within the vertebral column
transfer information between the CNS and PNS
Pairs of spinal nerves are attached to the cord at 31 different levels
Sensory information enters the dorsal (back) portion and motor commands exit on the ventral (stomach) side.
Ganglion
Root - axons entering and exiting the spinal cord
Ganglion
collection of somas
Ventral Root
conveys motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles
Cranial Nerves
12 pairs of nerves
emerge from the brain, rather than from segments of the spinal cord
send motor commands to and receive sensory information from the head and neck
Some nerves are only sensory or motor, and some are both
Cranial Nerves can be identified by:
Rostro-caudal position
Information type (sensory v. motor)
function
Divisions of the Brainstem: Medulla
closest to the spinal cord
includes neurons that maintain normal rhythmic breathing
Divisions of the Brainstem: Pons
above the Medulla
includes axons that allow the cerebellum to communicate with the brainstem and the cerebral cortex
fourth ventricle is on the dorsal side of this region
Divisions of the Brainstem: Midbrain
above the pons
has a superior and inferior colliculi
has a nucleus called the Ventral Tegmental Area and another called the Substantia Nigra
Superior and Inferior Colliculi
involved in localization of visual and auditory stimuli
Brainstem
all levels contain sensory and motor axons
Cerebellum
motor planning
motor learning
Motor planning
aids the motor cortices in planning complex movement
Motor learning
error correction when learning movement: compares intended movement with actual movement and correct errors that might occur
synapses change with experience
Diencephalon
include the Thalamus and Hypothalamus
Thalamus
located rostral to the midbrain
“Relay” for information going to and coming from the neocortex
Hypothalamus
located below the thalamus
regulates the autonomic nervous system
regulates hormone release
Cerebral Cortex (neocortex)
Sulci (sulcus): grooves
Fissures: deep sulci
Gyri (gyrus): rounded regions between sulci
Cerebral Cortex (neocortex) Function
processing of sensory input
Initiation/planning of movements
“Higher-order” functions including memory, cognition, language
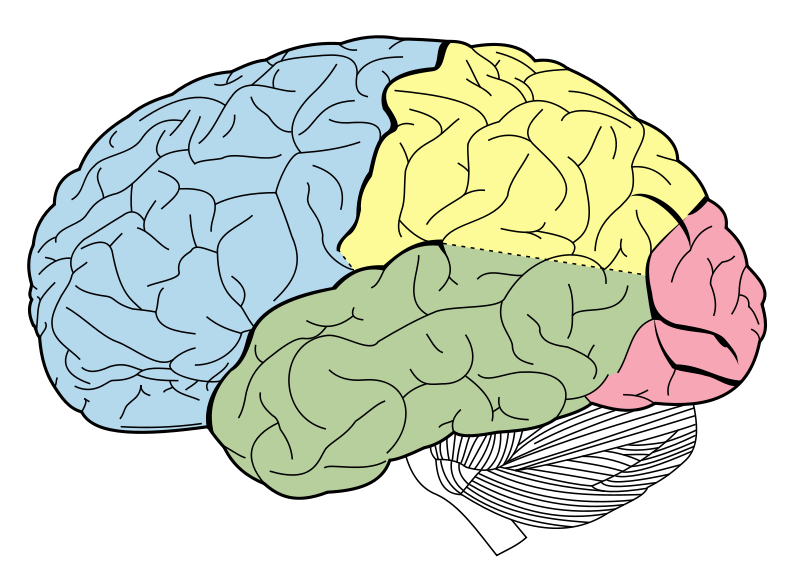
Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex
Occipital
Parietal
Temporal
Frontal
Central sulcus (Cerebral Cortex)
separates parietal and frontal lobes
Lateral fissure (Cerebral Cortex)
separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and the parietal lobe
Longitudinal fissure (Cerebral Cortex)
separates the two hemispheres of the brain
Postcentral gyrus
directly caudal to the central sulcus
contains the primary somatosensory cortex, which process touch and pain information
Precentral gyrus
directly rostral to the central sulcus
contains the primary motor cortex, which helps plan movement and sends motor (movement) signal to the spinal cord
Occipital Lobe
early-stage vision
first place in the cortex (NOT THE BRAIN) where your visual information is processed after coming though the eye
Parietal Lobe
somatosensory (touch and pain)
late stage vision
Temporal Lobe
memory
hearing
language comprehension
has a region called Hornica’s Area
Lateralization of function
functions are either located on one side of the brain or the other (left/right hemisphere)
Hornica’s Area
located on the left side of the temporal lobe in most people
Frontal Lobe
planning and signaling movements
working memory
inhibition of inappropriate behaviors
planning
Where is the occipital lobe located with respect to the parietal? (The occipital lobe is ____ to the parietal lobe?)
Caudal
A 41-year old male presents to the ER with paralysis involving the left arm and hand. Imaging shows a small lesion in his cerebral cortex. The lesion is located in which lobe of the brain?
Frontal Lobe
Neocortex
6 layer cortex
layer 1 is a molecular layer and consist mainly of Dendrites
layers 2/3 are processing layers
layer 4 is the main input layer; receives input from the thalamus
layer 5 is the maini output layer; sends projections to other parts of neocortex and to other brain region
layer 6 is a multiform layer; sends input to the thalamus
white matter: were all axons are leaving the cortex
Thickness of the cortical layers
dependent of where you are in the cortex
layers can be different in thickness (thicker it is the more signal you get for it)
Why do cortical layers vary in size across different regions of the cortex?
Different cortical regions are specialized for distinct functions, requiring varying amounts of input, output, and processing capacity.
Limbic System
a group of interconnected structures that are related to emotional behavior and emotional interpretation
sexual behavior
involved in the formation of memory, contains primary reward and punishment centers
site of action of drugs which produce euphoria (direct and indirect)
Hypothalamus
in the limbic system
regulates many motivated functions (e.g eating and drinking), sleep/wake cycle
controls activity of the pituitary gland
Pituitary gland
master gland that interacts with the hypothalamus to regulate many functions via the release of hormones
Hippocampus
involved in memory consolidation and provide the organism’s spacial awareness
in limbic system
Amygdala
coordinates autonomic responses in with emotional states
in the limbic system
Cerebral Cortex
interacts with subcortical structures to guide behavior (e.g sweat when scared)
in the limbic system
Basal Ganglia
A group of interconnected structures that control voluntary, smooth movement
The action of stimulants (drugs) increases motor activity
Basal Ganglia structure includes
striatum (caudate/putamen)
globus pallidus
Substantia nigra: sends dopamine to other regions on the basal ganglia to help control movement
Corpus Callosum
Long-range neurons that connect the two halves of the brain
axons going from one hemisphere of the brain to the other