AQA Physics Paper 1
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
sound energy
Energy caused by an object's vibrations
thermal energy
The total energy of motion in the particles of a substance
chemical energy
A form of potential energy that is stored in chemical bonds between atoms.
nuclear energy
the potential energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
electrical energy
Energy caused by the movement of electrons.
light energy
Energy in the form of moving waves of light
kinetic energy
energy of motion
gravitional potential energy
potential energy that depends on the height of an object
elastic potential energy
the energy of stretched or compressed objects
conservation of energy
law that says energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can change forms
uses of friction
- rubbing hands for warmth
- break pads on bikes
Efficiency =
Useful Energy Output / Total Energy Input
Increase efficiency
- add lubricant
- reduce friction
internal energy
the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all particles in the system
Conduction
The direct transfer of heat from one substance to another substance that it is touching.
Convection
The transfer of thermal energy by the circulation or movement of a liquid or gas
convection current
a current caused by the rising of heated fluid and sinking of cooled fluid
Insulator
A material that does not allow heat or electrons to move through it easily.
Infra red radiation
Electromagnetic waves of heat energy.
Radiation
Energy that is radiated or transmitted in the form of rays or waves or particles.
greenhouse effect
CO2 and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb long wavelength radiation radiated from the Earth's surface and prevent it escaping.
black
good absorber of radiation
white
poor absorber of radiation
specific heat capacity
the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius
Reduce heat loss from homes
- loft insulation (fibre glass is a good insulator)
- cavity wall insulation (foam prevents convection currents)
- aluminum foil behind radiator (reflects radiation)
- double glazing (vacuum slows conduction and radiation)
energy transfer
power x time
non-renewable energy
A natural resource such as coal, gas, or oil that, once consumed, cannot be replaced.
renewable energy
A resource that has a theoretically unlimited supply and is not depleted when used by humans.
solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, tidal, wave, nuclear, biofuel
dis: unreliable (except hydroelectric and geothermal)
nuclear power
energy from splitting Uranium atoms.
dis: nuclear waste, expensive
carbon neutral
an activity that does not change atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations
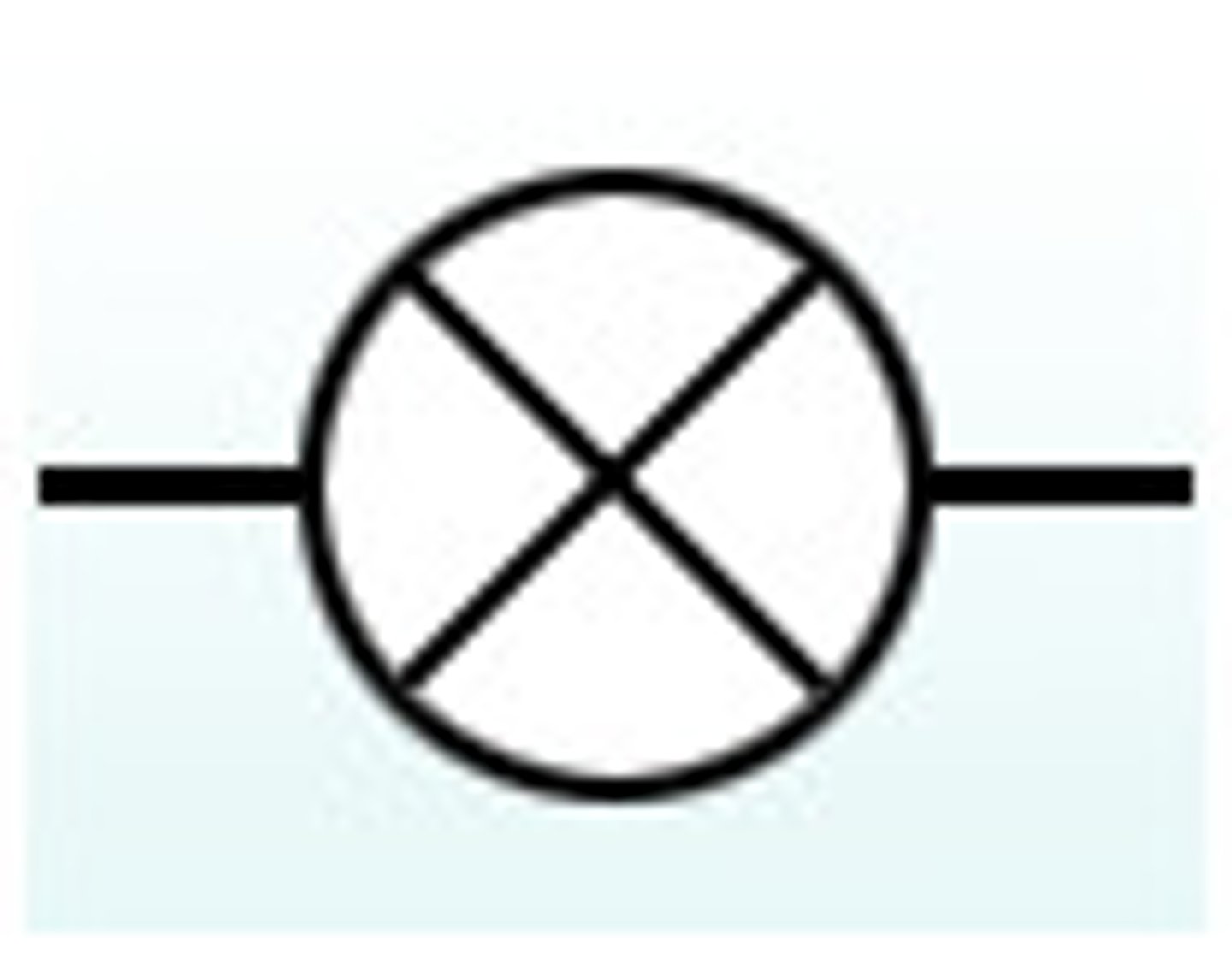
bulb
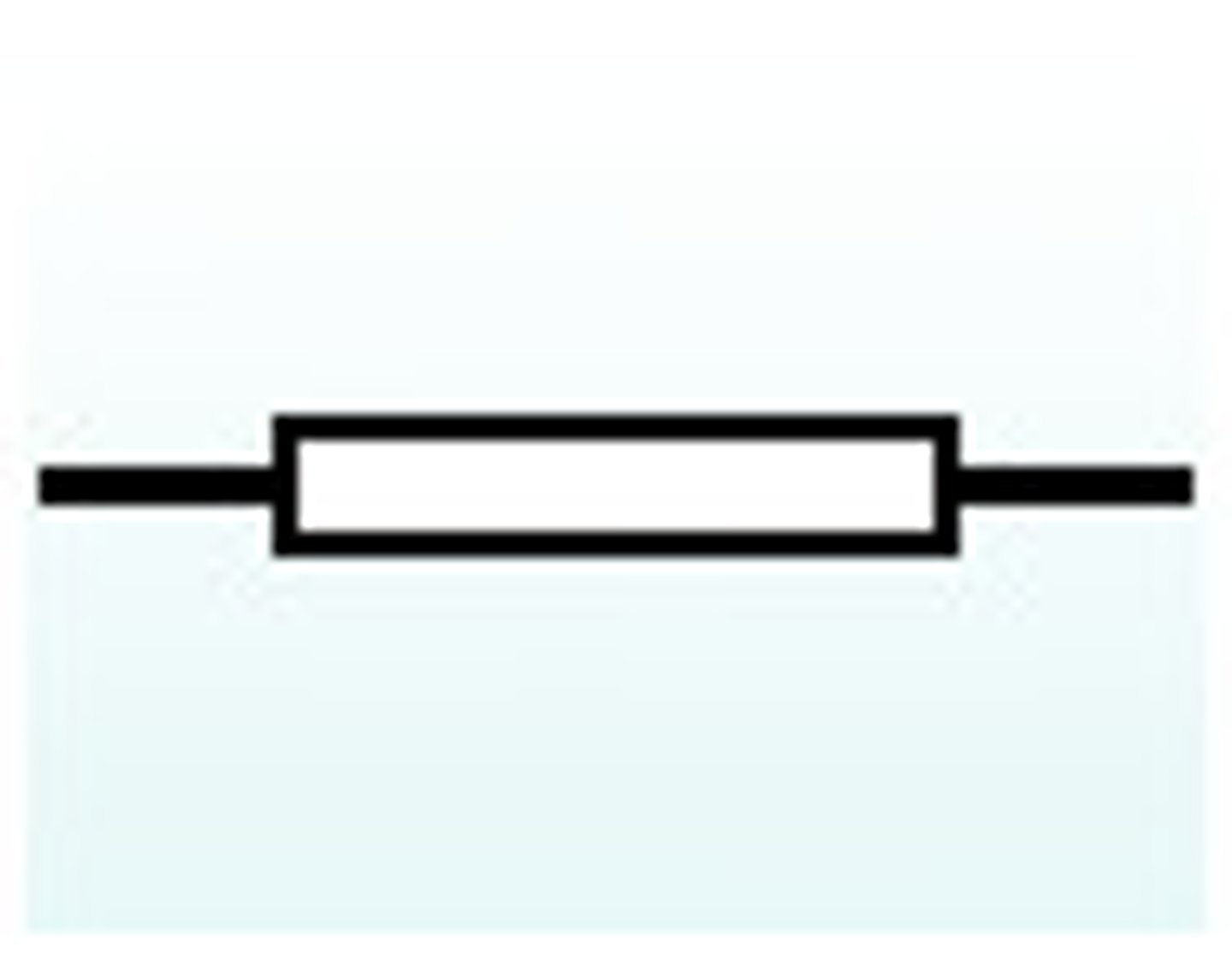
resistor
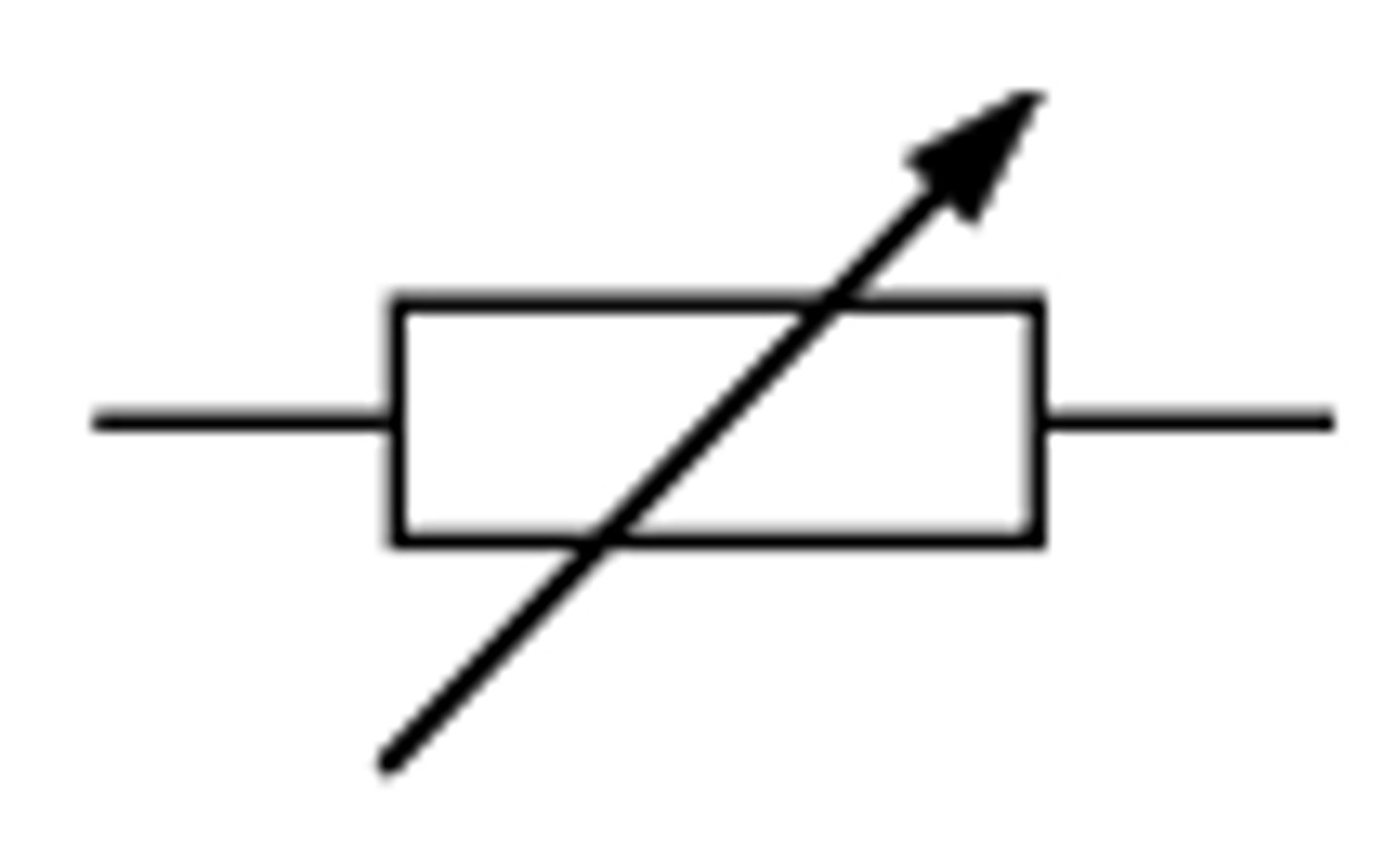
variable resistor
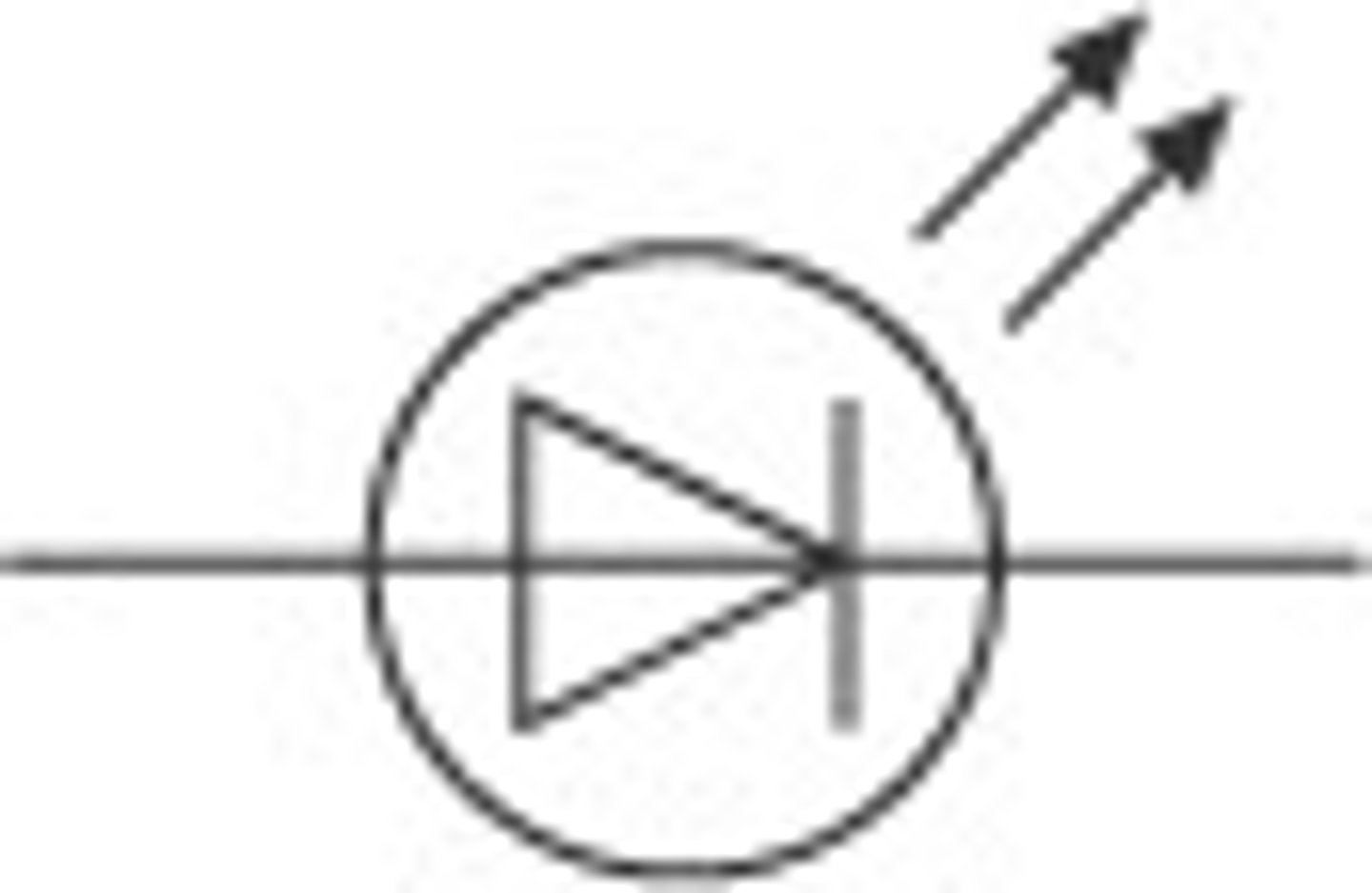
light emitting diode
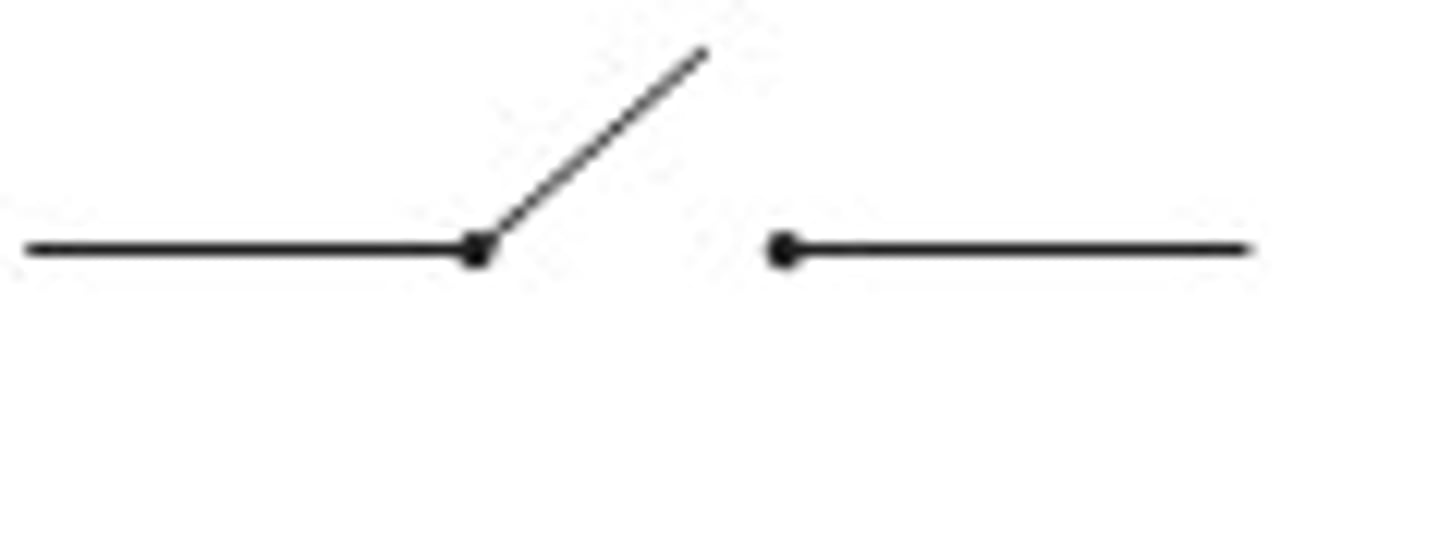
switch
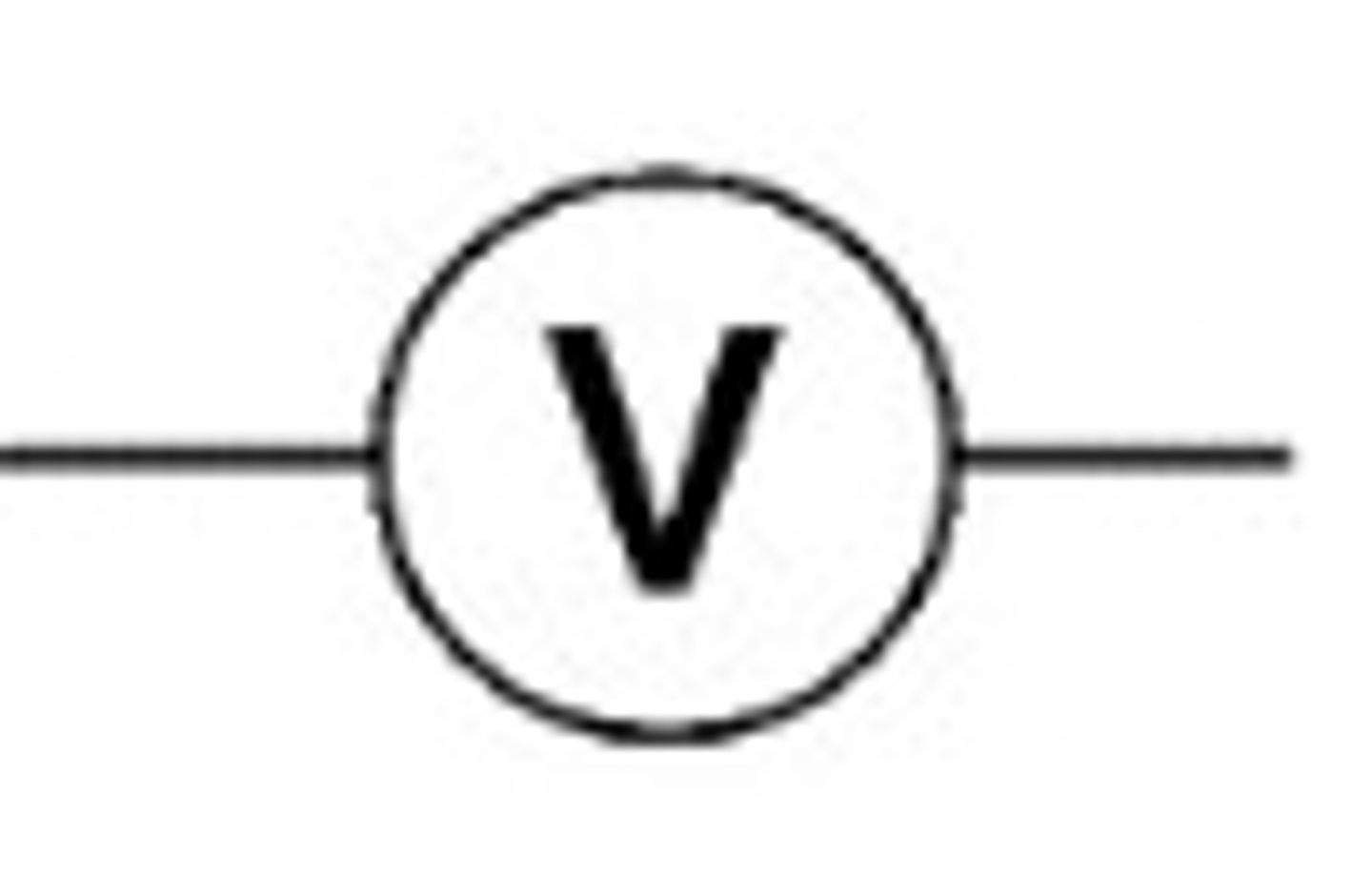
volt meter
measures potential difference
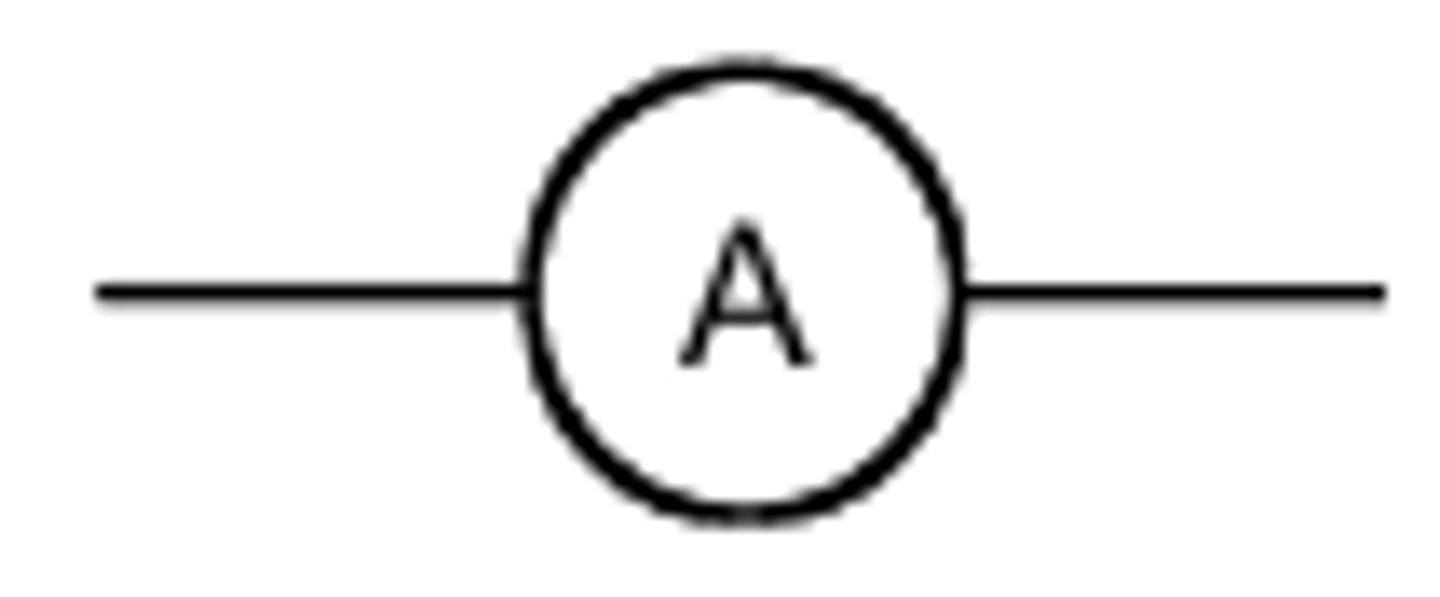
ammeter
measuring the current
resistance
A material's opposition to the flow of electric current.
current
A flow of electric charge.
Density formula
mass/volume
freezing
liquid to solid
melting
solid to liquid
condensing
gas to liquid
boiling
liquid to gas
sublimating
solid to gas or gas to solid
conservation of mass
the principle stating that matter is not created or destroyed during a chemical reaction
physical change
A change in a substance that does not involve a change in the identity of the substance
latent heat
the energy absorbed or released during a change in state
Specific Latent Heat
Amount of heat needed to change the state of 1 kilo of a substance WITHOUT a change in temperature.
specific latent heat equation
energy = mass x specific latent heat
specific latent heat of fusion
the energy needed to change a unit mass from the solid to the liquid phase at constant temperature
specific latent heat of vaporisation
the energy needed to change a unit mass from the liquid to the vapour phase at constant temperature
Pressure equation
P=F/A
pressure change in liquids
pressure increases as you go deeper because you have more liquid pushing down from above.
the greater the density the greater the pressure
Unit of pressure
Pascals, Pa
OR
Newtons per metre squared, N/m^2
upthrust
A force that pushes things up in liquids and gases.
sinking
weight > upthrust
nucleus
the center of an atom
mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
isotopes
atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
why atoms are radioactive
they have too many neutrons and become unstable.
alpha radiation
2 protons and 2 neutrons
alpha calculations
mass number -4 proton number -2
beta radiation
fast-moving electrons
beta calculations
mass number 0 proton number +1
gamma radiation
electromagnetic radiation emitted during radioactive decay and having an extremely short wavelength
ion
atom that has a positive or negative charge
order of ionising power from most to least
alpha > beta > gamma
penetrating power alpha
sheet of paper, couple of cm
penetrating power beta
aluminium
penetrating power gamma
thick lead or concrete
use of alpha radiation
smoke alarm
uses of beta radiation
making paper and aluminium the right thickness
half-life
the period of time in which half of a radioactive substance decays
uses if gamma radiation
find leaks in pipes
carbon dating
a scientific method used to determine the age of an artifact
Plum Pudding Model
The model of an atom in which there is a positively charged ball with electrons dotted through it.
Ernst Rutherford
Gold foil experiment. Most alpha particles passed straight through but some were deflected a little and a lot disproving the plum pudding model.
background radiation
nuclear radiation that occurs naturally in the environment
Sources of background radiation
Radon gas, cosmic rays, rocks, building materials, medical x-rays, food, nuclear industry
nuclear fission
nuclei of isotopes split apart when struck by neutrons produces a large amount of energy.
State two definitions of
radioactive half-life
.
1. The half-life is the (average)
time taken for half of the
radioactive nuclei in a
sample to decay
.
2. The half-life is the time
taken for the activity (or
count rate) of a radioactive
sample to fall to half its
original value.
What is the
difference between the
specific heat capacity and
the specific latent heat of a
material
Specific heat capacity is the energy
needed to raise the temperature
of 1 kg of the material by 1 °C,
with no change of state.
Specific latent heat is the energy
needed to change the state of
1 kg of the material, with no
change in temperature
Complete the gaps
in the sentences.
Choose from:
greater smaller
more less
Beta radiation has a … ionising
power than alpha radiation and
so is … penetrating and has a …
range in air.
A beta source a few metres away
from you is therefore likely
to be … dangerous than an
alpha source at that distance.
Beta radiation has a smaller
ionising power than alpha
radiation and so is more
penetrating and has a greater
range in air.
A beta source a few metres
away from you is therefore
likely to be more dangerous
than an alpha source at that
distance
List the factors that
affect the size of the force on
a current-carrying conductor
in a magnetic field
The magnetic flux density, the
size of the current and the
length of the conductor that is
in (and perpendicular to) the
magnetic field
A magnetic material brought
close to a magnet …
… is always attracted to the
N pole of the magnet.
… is attracted to the
nearest pole of the magnet.
A magnetic material brought
close to a magnet is attracted to
the nearest pole of the magnet.
The strong magnetic field near
either magnet pole makes the
nearby magnetic material an
induced magnet and this
always causes attraction.
State the behaviour of an LDR in
a circuit when the light intensity
falling on it decreases.
An LDR is a light-dependent
resistor. Its electrical
resistance increases when the
light intensity decreases
State the equation
for calculating the
electrical power P of a device
of resistance R, when the
current through it is I, and
state the unit of power.
Power P = I^2 R
The unit of power is the watt,
W (equivalent to J/s)
What is the
equation relating
the potential difference across,
the current through and the
resistance of a component in a
circuit
Potential difference
= current × resistance
True or false?
If all of the electrical
energy supplied to
an efficient kettle is used to
heat the water, this equation
determines the change in
temperature of the water,
∆θ. I V t = m c ∆θ
True.
The electrical energy supplied to
the kettle is power × time = I V t.
The rise in temperature of the
water ∆θ depends on the mass m
and the specific heat capacity c of
the water. Energy change
of water = m c ∆θ.