Overview of the Nervous System and Muscle Physiology
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
What are the primary functions of the nervous system?
The nervous system coordinates and controls body functions, processes information, and determines appropriate responses to stimuli.
How does the nervous system differ from the endocrine system in terms of communication?
The nervous system communicates using electrical and chemical signals, while the endocrine system uses chemical messengers (hormones) secreted into the blood.
What are the three basic steps the nervous system uses to carry out its tasks?
1. Sense organs receive information and transmit coded messages to the CNS. 2. The CNS processes this information and relates it to past experiences. 3. The CNS issues commands to muscles and glands to execute a response.
What are the main organs of the nervous system?
The main organs include the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
What types of cells make up nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue is made up of neurons and glial cells.
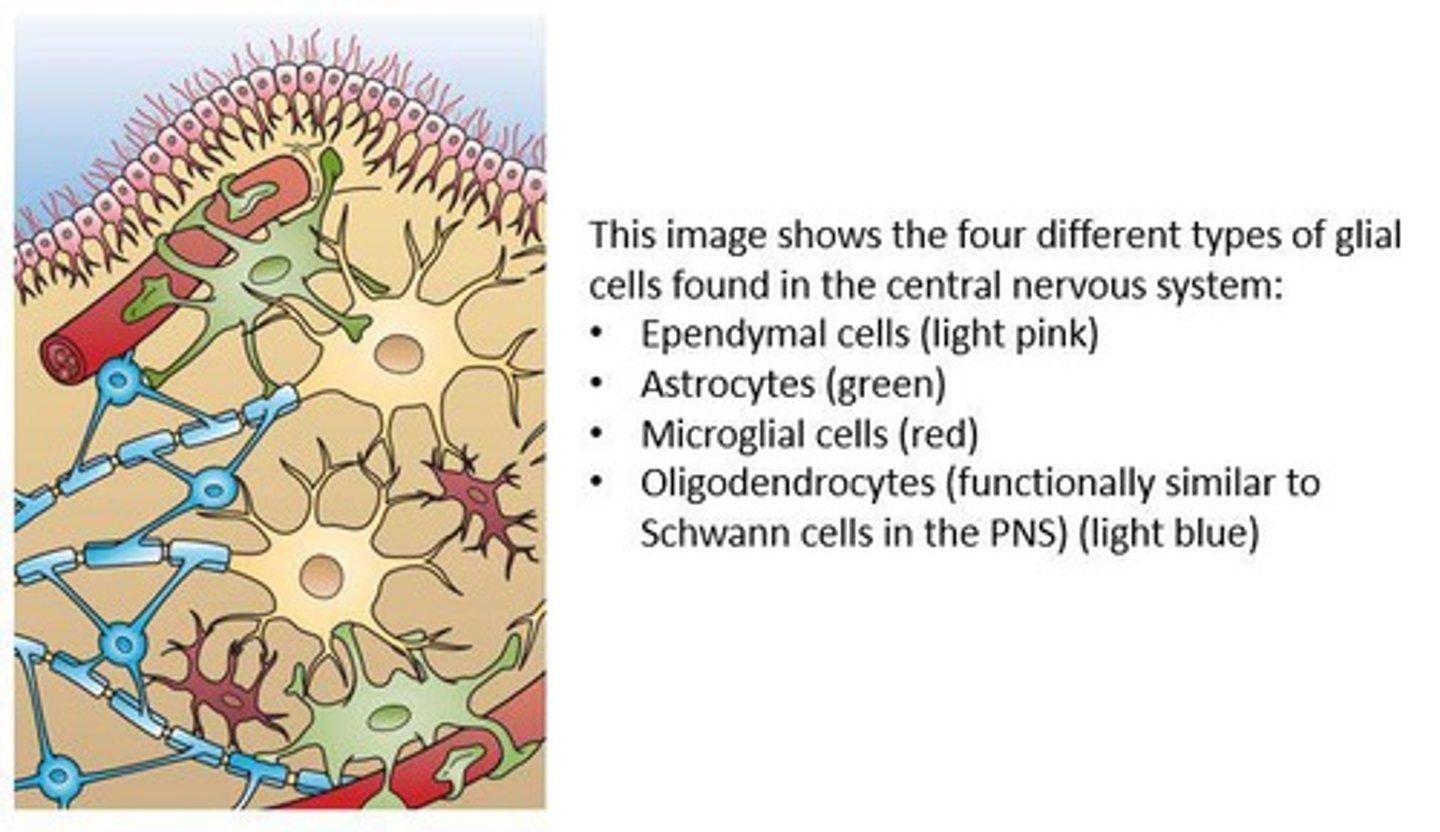
What are glial cells and what are their functions?
Glial cells support and protect neurons, provide insulation, and assist in the maintenance of the nervous system.
How can neurons be categorized?
Neurons can be categorized by function (sensory, motor, and interneurons) and by structure (unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar neurons).
What are the two main types of cells found in nervous tissue?
Neurons (excitable cells) and Glial cells (support neurons, non-excitable).
What are the main parts of a neuron?
Dendrites (receive signals), Cell body (soma, control center), Axon hillock, Axon (sends signals away), Myelin sheath (insulation), Nodes of Ranvier (gaps in myelin), Axon terminals (forms synapse).
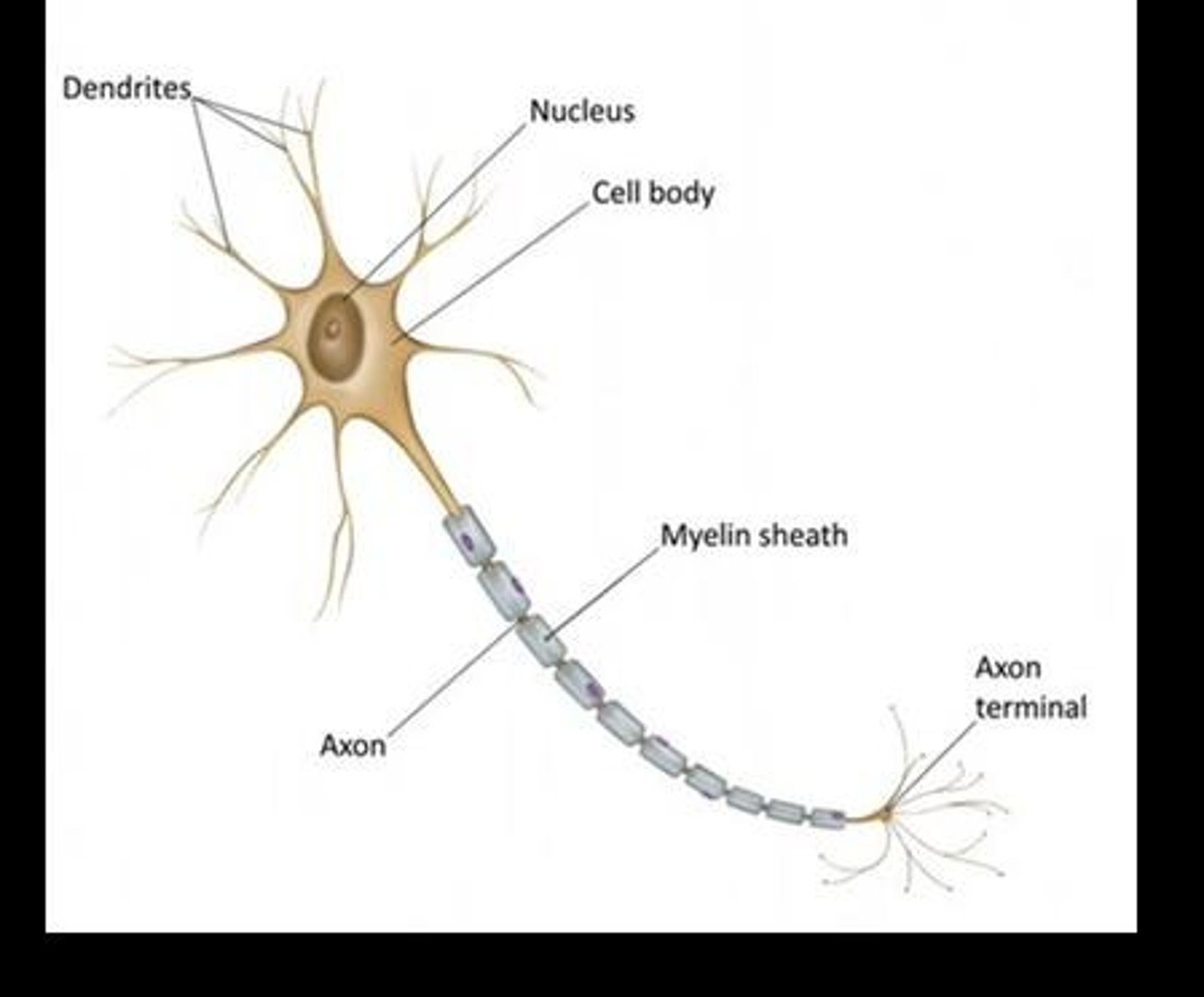
What is the function of dendrites in a neuron?
Dendrites receive signals.
What is the role of the axon in a neuron?
The axon sends signals away from the cell body.
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
The myelin sheath provides insulation for the axon.
What are astrocytes and their function?
Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells that form the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
What do oligodendrocytes do?
Oligodendrocytes myelinate neurons in the central nervous system (CNS).
What is the role of ependymal cells?
Ependymal cells form cerebrospinal fluid and have cilia that help move the fluid.
What is the function of microglia?
Microglia are small cells that carry out phagocytosis and prune unneeded processes of neurons during brain development.
What do Schwann cells do?
Schwann cells myelinate axons of peripheral nerves.
What is the function of satellite cells?
Satellite cells support neuronal cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What are the three functional types of neurons?
Sensory (afferent) neurons, Interneurons (integration), and Motor (efferent) neurons.
What is the most common type of neuron?
Multipolar neuron.
Where are bipolar neurons typically found?
Bipolar neurons are found in special sense organs.
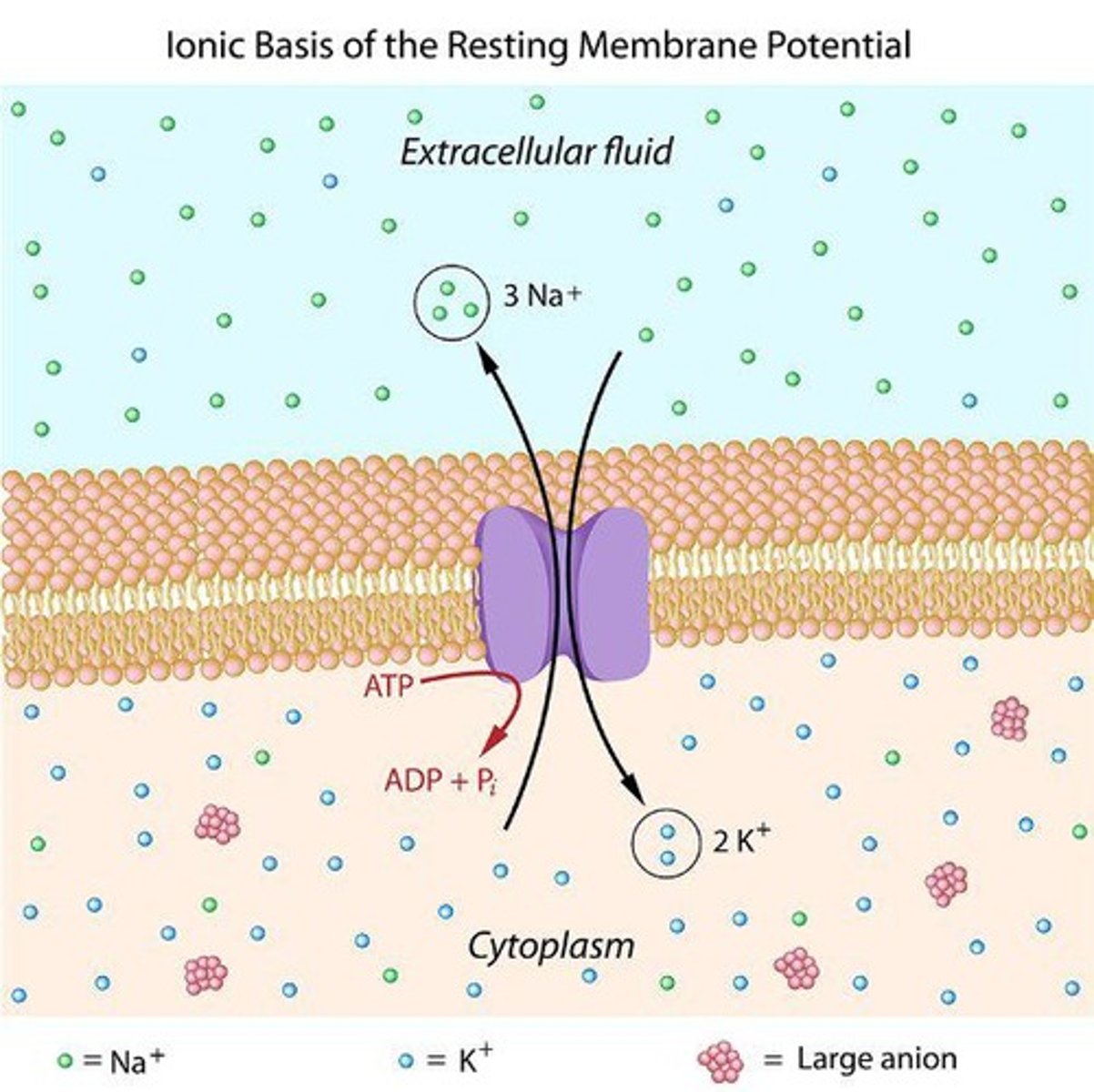
What is resting membrane potential?
The difference in ion concentrations across a membrane at rest, typically around -70mV.
What ions are primarily involved in resting membrane potential?
Sodium (Na+) outside and Potassium (K+) inside the cell.
What is a local potential?
A shift away from resting membrane potential at a specific region of the plasma membrane.
What occurs during depolarization?
Sodium (Na+) enters the cell.
What happens during hyperpolarization?
Potassium (K+) exits the cell.
What is an action potential?
An influx of ions causing an electrical fluctuation that travels along the surface of a neuron's plasma membrane.
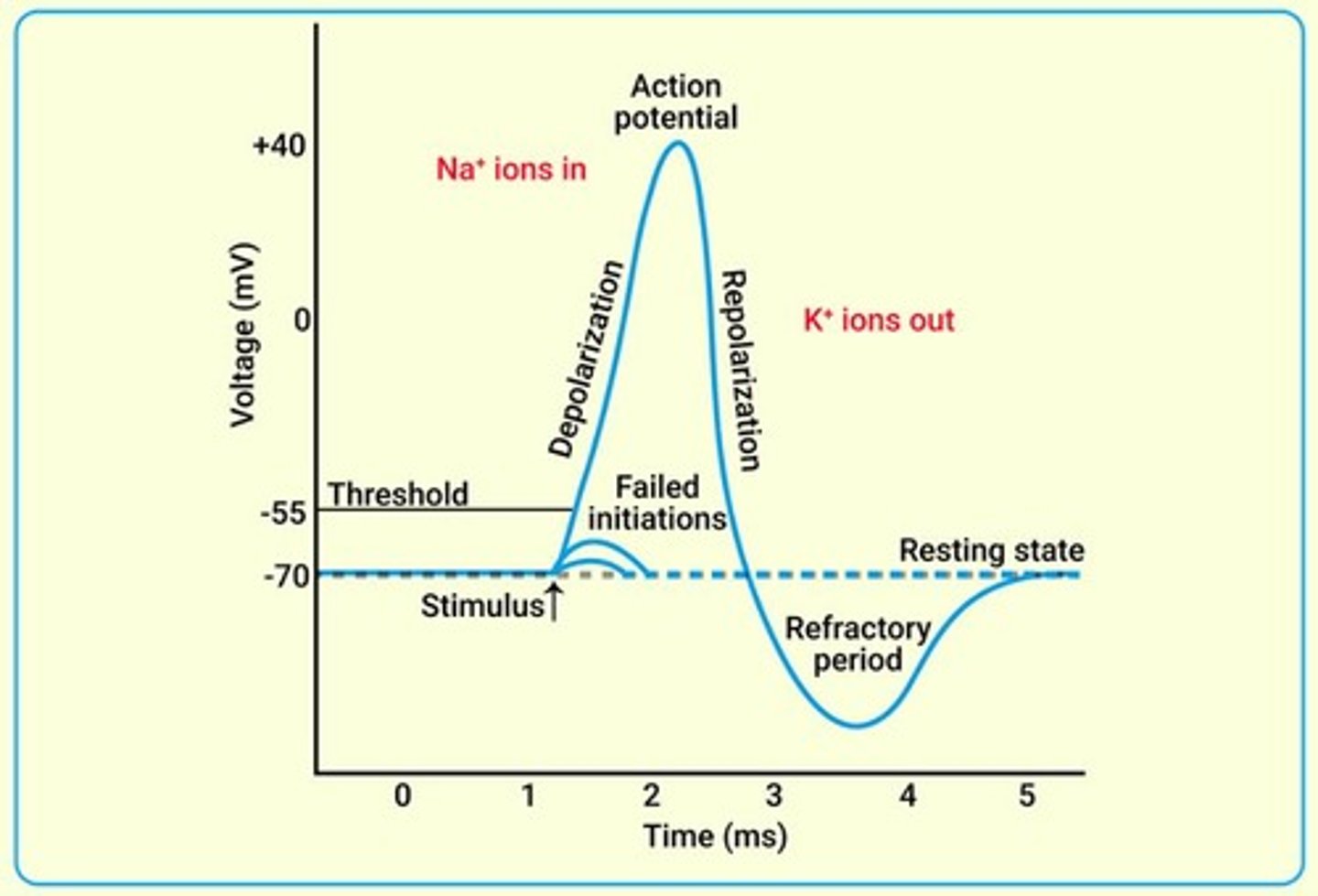
What is the threshold for initiating an action potential?
Approximately -55mV.
What are the two types of conduction of action potentials?
Continuous conduction (unmyelinated axon) and Saltatory conduction (myelinated axon).
What are the fates of neurotransmitters in synaptic transmission?
Neurotransmitter degradation (e.g., acetylcholinesterase), reuptake into the axon terminal, or diffusion away from the synapse.
What are the structural classifications of neurotransmitters?
Acetylcholine, amino acids (e.g., GABA, glutamate), amines (e.g., epinephrine, dopamine, serotonin), purines (e.g., adenosine, ATP), gases (e.g., nitric oxide, carbon monoxide), and neuropeptides (e.g., endorphins, CCK).

What is temporal summation?
Rapid succession of stimuli on one neuron.
What is spatial summation?
Multiple stimuli on the same nerve.
What are the functions of skeletal muscle tissue?
Producing movement, posture and support, metabolism (energy storage), and generating heat.
What are the properties of muscular tissue?
Electrical excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity.
What is contractility in muscular tissue?
The ability of the muscle to shorten or contract.
What is extensibility in muscular tissue?
The capacity of a muscle to stretch beyond its resting length.
What is excitability in muscular tissue?
The ability of muscle tissue to respond to a stimulus.
Which types of muscle tissue have striations?
Skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle.
How are skeletal muscles formed?
Skeletal muscles are formed by the joining together of myoblasts, which fuse to create immature skeletal muscle fibers that mature into muscle fibers.
What is the role of tendons in skeletal muscle?
Tendons attach skeletal muscles to bones.
What is a fascicle in skeletal muscle?
A fascicle is a bundle of muscle fibers within a muscle, enclosed in a fibrous perimysium.
What is the epimysium in skeletal muscle?
The epimysium is a fibrous layer that encloses the entire skeletal muscle and separates it from neighboring muscles.
What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscle control?
Skeletal muscle is under voluntary control, while cardiac and smooth muscles are involuntary.
What is the histology of skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle is characterized by long, parallel cells (muscle fibers) that are striated.
What is the significance of electrical excitability in muscle tissue?
It allows the muscle to change its resting membrane potential and respond to stimuli.
What happens to muscle fibers during contraction?
Muscle fibers shorten, generating force.
What is the primary function of smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle controls involuntary movements within internal organs.
What is the primary function of cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
What encloses muscle fibers in skeletal muscle?
Muscle fibers are enclosed in a specialized plasma membrane called the sarcolemma.
What are myofibrils?
Myofibrils are densely packed bundles of contractile protein myofilaments.
What surrounds each myofibril?
Each myofibril is surrounded by sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria.
What is the function of the endomysium?
The endomysium is a thin, fibrous sleeve that encloses each muscle fiber.
What is a sarcomere?
A sarcomere is the contractile unit of muscle from one z-disc to another z-disc.
What proteins are found in thick filaments of a sarcomere?
Thick filaments are primarily composed of myosin.
What proteins are found in thin filaments of a sarcomere?
Thin filaments are primarily composed of actin.
What is the role of troponin and tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
Troponin and tropomyosin regulate the interaction between myosin and actin.
What is the function of the Z-disc in a sarcomere?
The Z-disc provides anchorage for actin and titan filaments.
What is the A-band in a sarcomere?
The A-band is the region from the beginning of one thick filament to the end of the same thick filament, creating a dark band.
What is the I-band in a sarcomere?
The I-band is the region from the end of one thick filament to the beginning of the next thick filament, creating a light band.
What is the H-zone in a sarcomere?
The H-zone is the region from the end of one thin filament to the beginning of the next thin filament.
What is the M-line in a sarcomere?
The M-line is the line found at the center of the thick filament, providing an anchor for the thick filament.
What is the sliding filament theory?
The sliding filament theory explains that muscle contraction occurs when myosin pulls on actin, causing thin filaments to slide inward.
What is a motor unit?
A motor unit consists of a somatic motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates.
What neurotransmitter is involved in the neuromuscular junction?
Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter involved in the neuromuscular junction.
What is the role of acetylcholine esterase?
Acetylcholine esterase breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft.
What triggers the interaction between myosin and actin during muscle contraction?
The release of calcium ions triggers the interaction between myosin and actin.
Which protein blocks myosin-binding sites on actin in a relaxed state?
Tropomyosin blocks myosin-binding sites on actin in a relaxed state.
What defines the boundaries of a sarcomere?
The boundaries of a sarcomere are defined by Z-lines.
Which region contains only thick filaments?
The H-zone contains only thick filaments (myosin).
What initiates muscle contraction at the neuromuscular junction?
A nerve impulse reaches the neuromuscular junction.
What neurotransmitter is released to facilitate muscle contraction?
Acetylcholine (ACh) is released into the synaptic cleft.
What role does calcium play in muscle contraction?
Calcium binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to move away from actin binding sites.
What is the sequence of events that occurs after calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Calcium ions are released into the sarcoplasm, allowing myosin heads to attach to actin and form cross-bridges.
What happens during the power stroke of muscle contraction?
Myosin performs a power stroke, pulling actin filaments toward the center of the sarcomere.
What resets the myosin head for another contraction cycle?
ATP binds to myosin, causing it to detach from actin and reset.
What are the three methods by which muscles create ATP for contraction?
1. Creatine phosphate conversion, 2. Anaerobic glycolysis, 3. Aerobic respiration.
How long does ATP generated from creatine phosphate last?
About 15 seconds.
What is the energy yield of anaerobic glycolysis?
Generates two ATPs and provides energy for about two minutes.
What is the energy yield of aerobic respiration?
Generates 30 to 32 ATPs, sufficient for several minutes to hours.
What is muscle fatigue?
The inability to maintain force production.
What are some factors that influence muscle fatigue?
Inadequate release of Ca2+, depletion of creatine phosphate, insufficient O2, depletion of glycogen/nutrients, buildup of lactic acid & ADP, and not enough ACh.
What characterizes isotonic contractions?
Contraction with a change in length but no change in tension.
What characterizes isometric contractions?
Contraction where there is no change in length.
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle contraction?
It releases calcium ions into the sarcoplasm.
What is the function of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
It blocks actin binding sites until calcium binds to troponin.
What happens to calcium after muscle contraction?
Calcium is pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What is the significance of cross-bridges in muscle contraction?
Cross-bridges form when myosin heads attach to actin, enabling contraction.
What is the role of action potential in muscle contraction?
It travels along the sarcolemma and down the T-tubules, triggering calcium release.
What is the result of ATP depletion during muscle contraction?
It prevents myosin from detaching from actin, leading to muscle fatigue.
How does lactic acid affect muscle performance?
Buildup of lactic acid contributes to muscle fatigue.
What is the relationship between creatine phosphate and ATP?
Conversion of creatine phosphate helps catalyze the conversion of ADP into ATP.
What are the three types of skeletal muscle fibers?
Slow oxidative, Fast oxidative glycolytic, Fast glycolytic.
What type of contraction involves the muscle shortening as it generates tension?
Concentric contraction.
What is the first step of ATP production during exercise?
Stored ATP in the muscle is used for the first 1-2 seconds of activity.
What follows the use of stored ATP in ATP production during exercise?
The phosphagen system replenishes ATP by using creatine phosphate for up to 10-15 seconds of high-intensity activity.
What is the dominant source of ATP for sustained, long-term muscle activity?
Aerobic respiration.
What is muscle hypertrophy?
An increase in muscle size due to exercise.
What is muscle hyperplasia?
An increase in the number of muscle fibers.
What happens to muscle tissue between the ages of 30-50?
10% of muscle is replaced by fibrous connective tissue and adipose tissue.