6.4 Uncertainty, Expectations, Shock
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Why are expectations important in macroeconomics?
They influence current behavior and investment decisions, and unmet expectations can lead to economic shocks.
What is a shock in economics?
An unexpected event that disrupts expectations—can be positive or negative.
What is a demand shock?
An unexpected change in the demand for goods and services.
What is a supply shock?
An unexpected change in the supply of goods and services.
What does a positive demand shock mean?
Actual demand is higher than expected.
What does a negative demand shock mean?
Actual demand is lower than expected.
Why are sticky prices a problem during demand shocks?
Prices don’t adjust quickly, so output and employment must change instead.
What are sticky prices?
Prices that are inflexible or slow to change in response to market conditions.
How do firms respond to demand shocks when prices are sticky?
By adjusting output and employment rather than prices.
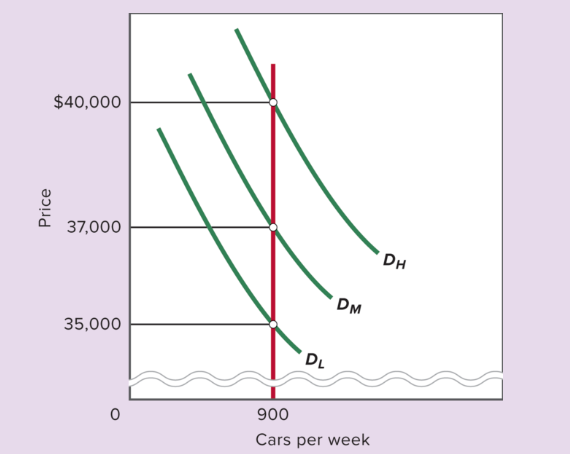
What does Figure 6.1a illustrate?
With flexible prices, output stays constant and price adjusts to match demand.
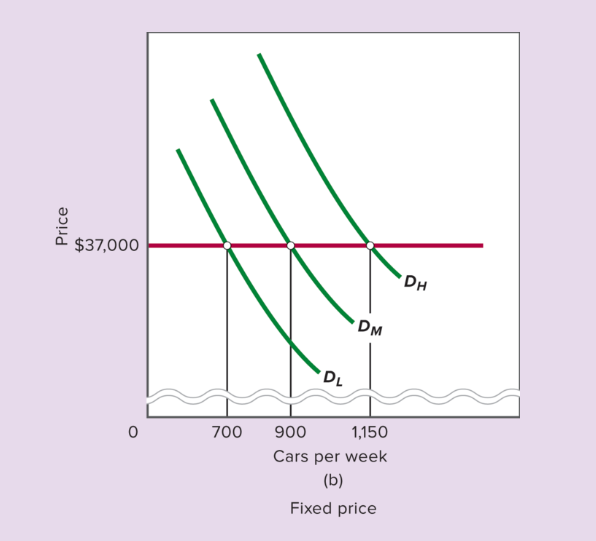
What does Figure 6.1b illustrate?
With fixed prices, quantity demanded changes, causing fluctuations in output and employment.
What is the optimal output rate for Buzzer Auto?
900 cars per week.
What happens if demand is unexpectedly low and prices are fixed?
Quantity demanded falls below output, inventories rise, and firms may cut production.
What happens if demand is unexpectedly high and prices are fixed?
Quantity demanded exceeds output, inventories fall, and firms may increase production.
Why do firms maintain inventories?
To smooth production and respond to short-term demand fluctuations without changing output levels.
What happens if inventories rise for many weeks due to low demand?
Firms may cut production and lay off workers, increasing unemployment.
What happens if inventories fall for many weeks due to high demand?
Firms may increase production and hire more workers, decreasing unemployment.
What causes short-run fluctuations in real GDP and unemployment?
Unexpected changes in demand combined with sticky prices.
What are sticky prices?
Prices that are slow to adjust to changes in supply or demand in the short run.
Why are sticky prices problematic during demand shocks?
They prevent prices from adjusting quickly, so firms must change output and employment instead.
What causes prices to be sticky?
Menu costs (costs of changing prices)
Long-term contracts
Social norms and customer expectations
How do sticky prices affect short-run economic fluctuations?
They amplify changes in output and unemployment when demand shifts unexpectedly.
What is an economic shock?
An unexpected event that disrupts market expectations—can affect demand or supply.
What is a demand shock?
An unexpected change in the demand for goods and services.
What is a supply shock?
An unexpected change in the supply of goods and services.
What is a positive demand shock?
Actual demand is higher than expected.
What is a negative demand shock?
Actual demand is lower than expected.
How do shocks contribute to business cycles?
They cause short-run fluctuations in output and employment when expectations are unmet.
What are flexible prices?
Prices that adjust quickly to changes in supply or demand.
How do flexible prices help stabilize the economy?
They allow quantity demanded to match quantity supplied without changing output or employment.
What happens in a market with flexible prices during a demand shock?
Price adjusts to maintain equilibrium; output stays constant.
Why don’t all markets have flexible prices?
Real-world frictions like contracts, regulations, and adjustment costs slow price changes.