Test 3
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
for physics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
frequency formula
1 / time period
units of frequency
1 sec = hertz
crest
high points of the wave
Troughs
are the low points of the wave. (valley)
Heat depends on
Mass (m) of the objects.
Change in temperature (ΔT)
Type of material defined by the specific heat (C).
Nm (J), kg m2/s2, Calorie, kilocalorie, kilojoules (kJ) , Kilowatt-hour (kwh), foot-pound
Amplitude
distance from the midpoint to the crest.
A measure of the object's resistance to change in temperature. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of mass by 1C.
Temperature scales
Celsius (C) Scale: Freezing 0C, Boiling 100 C
Fahrenheit (F) Scale: Freezing 32F, Boiling 212F
Kelvin (K) Scale: Freezing 273K, Boiling 373K.
Use the equation below to convert temperature in degree Celsius to Fahrenheit. F] = 9/5[C] +32
EX: 200C =? 0F
answer: = 68 F
Use the equation below to convert temperature in degree Fahrenheit to Celsius. [C] = 5/9 [F - 32]
EX: 14F =? C
10 C
1) An iron railroad is 700ft long when the temp is 30C. What is the length when the temp is -10C?
Coefficient of linear expansion for iron is 12 x 10-6 /0c.
Answer: - .336 ft
1) The center span of a steel bridge is 1200 meters long on a winter day when the temp is -50C. How much longer is the span on a summer day when the temp is 350C?
Coefficient of linear expansion for steel is 12x10-6/oc.
Answer: 0.576 m
Pressure (P)
Force per unit area.
Pressure formula
Pressure = Force / area
If a force is applied on less area, then there will be _____
more pressure.
Units for pressure
Metric units of pressure: N/m2 = Pascal (Pa), atmosphere (atm),
Millimeter of mercury (mm of Hg).
British unit of pressure: Pounds per squared inch (psi) = lbs /in2
Pressure due to liquid or liquid pressure
Liquid pressure depends on the depth of the liquid (how deep the liquid is)
Liquid pressure depends on the density of the liquid.
Denser the liquid is more liquid pressure.
Liquid pressure depends on the gravity g = 9.8m/s2
pressure due to liquid formula
D x G x H ( density x 9.8 x depth of liquid )
density
mass per unit volume.
Density formula
mass / volume
Wavelength (λ)
is the distance from the top of the one crest to the next crest or distance between two successive like points
wavelength units
m/wave, cm/wave
Frequency (f)
Number of waves passes any point per second or number of to and for vibrations in a given time.
If given time unit is days, then frequency unit will be _____
1 day
If given time unit is minute, then frequency unit will be _____
1 minute
Period or time period(T)
time to complete one vibration
Unit of period or time period
second, minute, hour, days, year
Wave motion
waves transport energy and not matter.
Wave speed (v)
how fast a disturbance moves through a medium.
Wave speed formula
Wavelength (λ) x Frequency (f)
Wave speed Units
m/s, cm/s , mph, feet/s etc .(same as speed units)
EMW (Electromotive wave)
EMW produced by accelerated charged particles. That means only charged particles like electrons, protons, ions can produce EMW when they accelerate.
Sound waves
Sound waves are longitudinal wave. Speed of sound in air or other gases depend on the temperature.
sounds waves formula
v = 331m/s + 0.6m/s/0C x Temperature in Celsius.
Echolocation
a wave sent out. If it encounters an object, it reflected back. By timing how long it takes for the echo to return, the distance to the object can be determined.
What does the K represent in Coulombs law formula?
K = 9 × 10^9
Echolocation formula
Speed (v) =(2 x distance )/ time
An EM wave traveling through a vacuum has a frequency of 2 x 10^14 Hz. Determine the wavelength of the wave. Speed of light c = 3x10^8m/s
1.5 x 10^-6 m.
A 3500 Hz wave is observed to have a wavelength of 2.3 m/wave.
a) Determine the speed of wave?
8050 m/s
A 3500 Hz wave is observed to have a wavelength of 2.3 m/wave.
b) If a second wave is traveling through the same medium and has a frequency of 55,811Hz. What is its wavelength?
0,144 m.
3. A person stands in front of a cliff and gives a shout. 0.8seconds later the person heard the echo. The speed of sound is 347m/s. How far away is the cliff?
=138.8 m.
You are standing on a canyon edge and give a shout. After 3.7 seconds passed, you heard your echo. The temperature is 20.6 degree Celsius. How far away is the cliff?
V = 343.36 m/s
Doppler Effect
The apparent change in frequency of the sound observed by the observer when there is a relative motion between the source of the sound and the observer
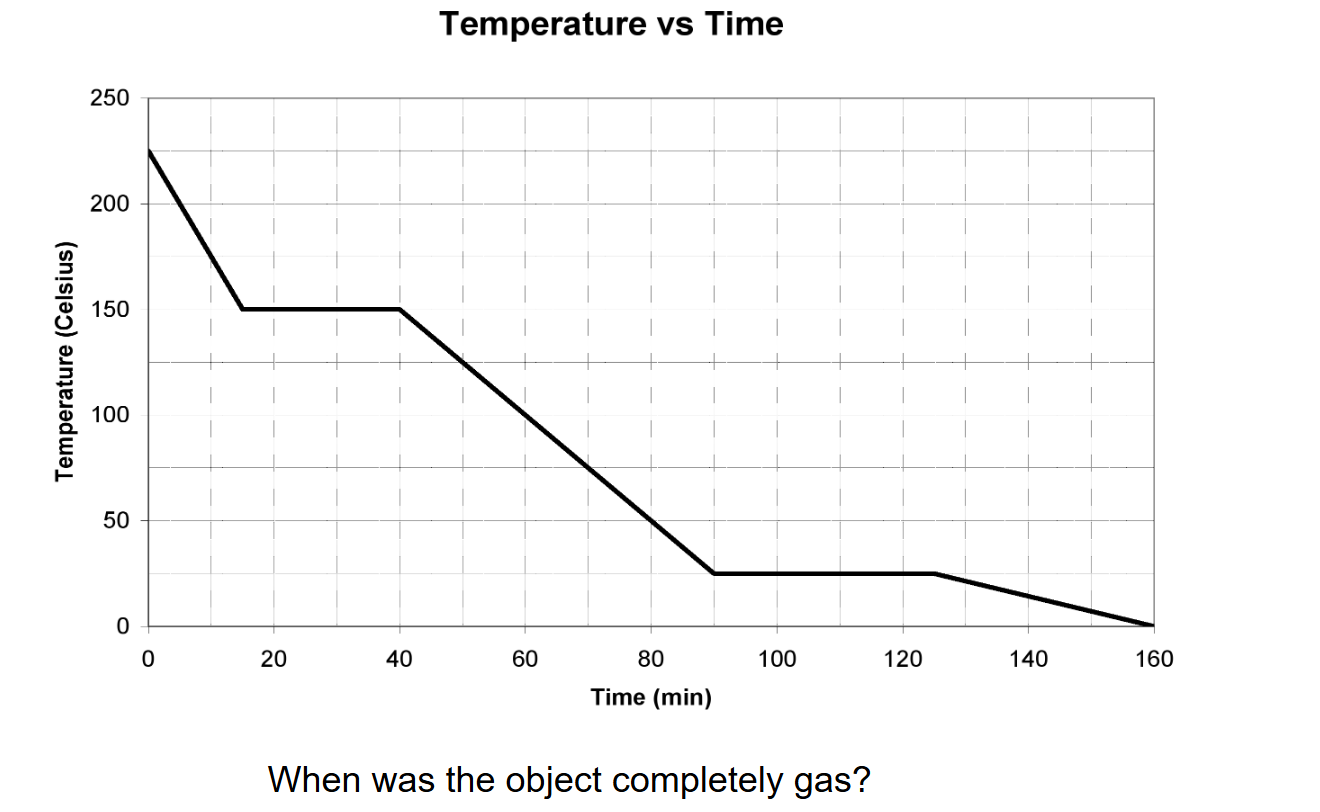
When was the object completely gas?
t = 0 min to 15 min
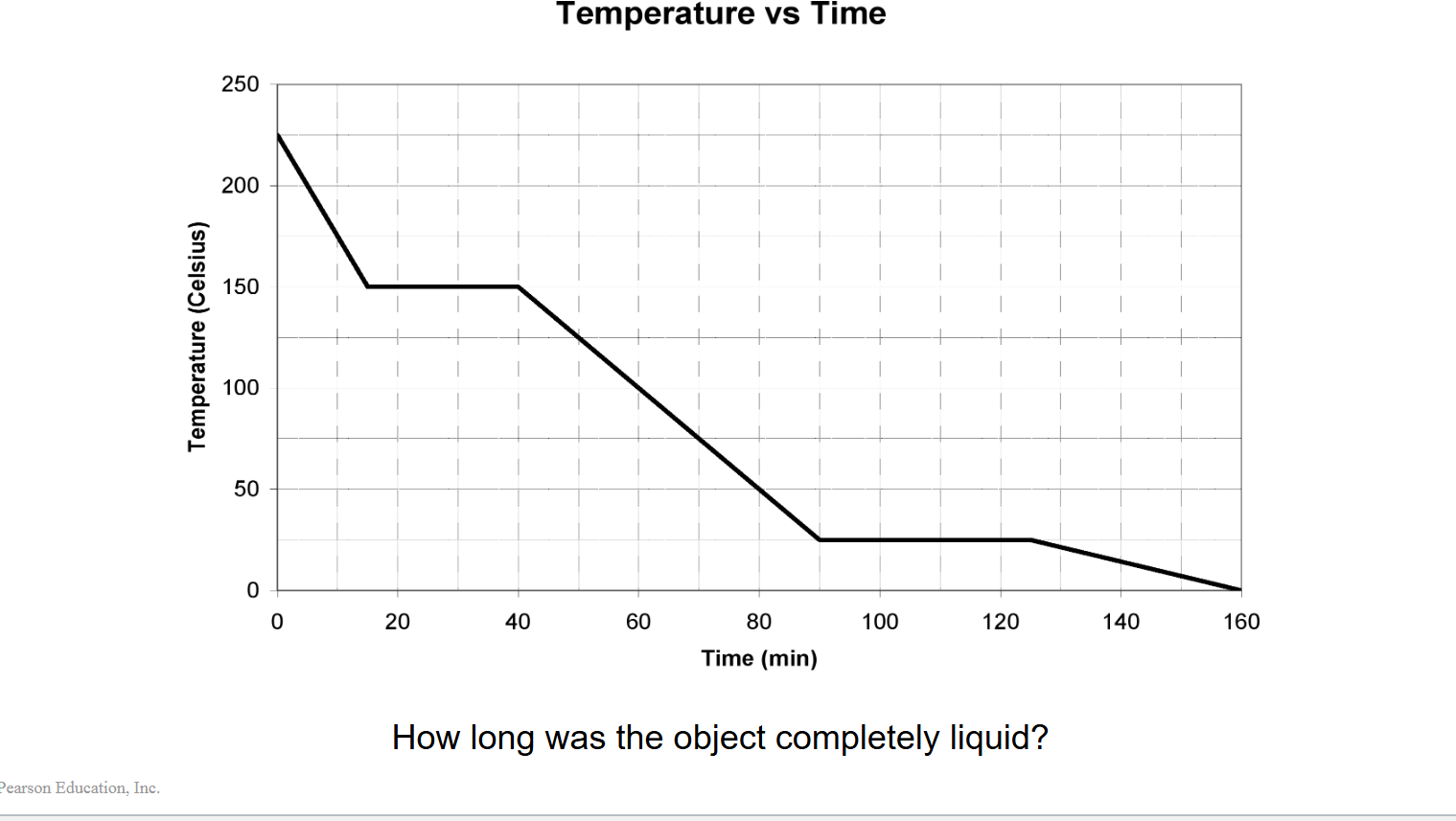
How long was the object completely liquid?
t = 90 min – 40 min = 50 min
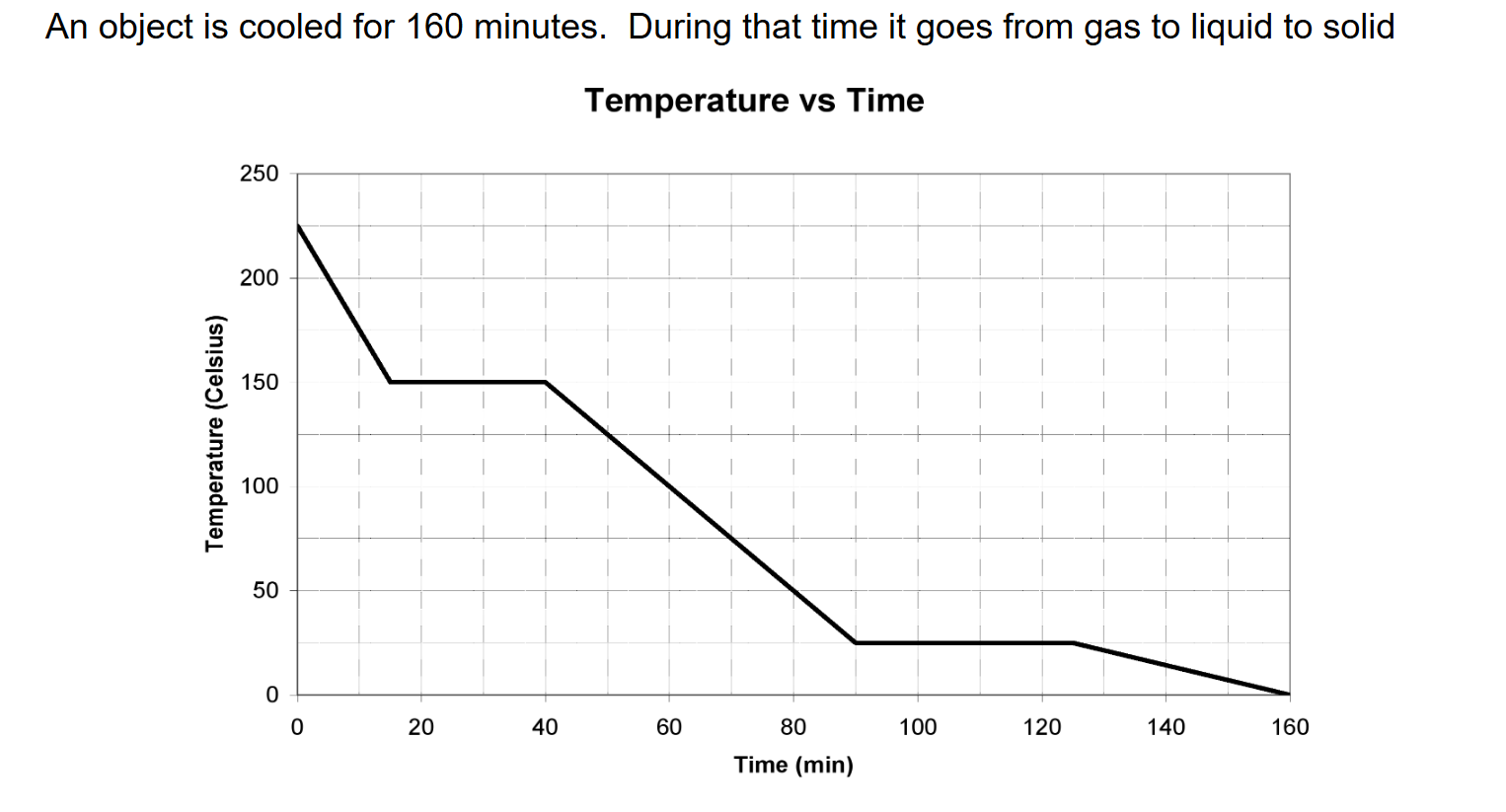
Over what temperature range was the object solid?
25 to 0 degrees Celsius
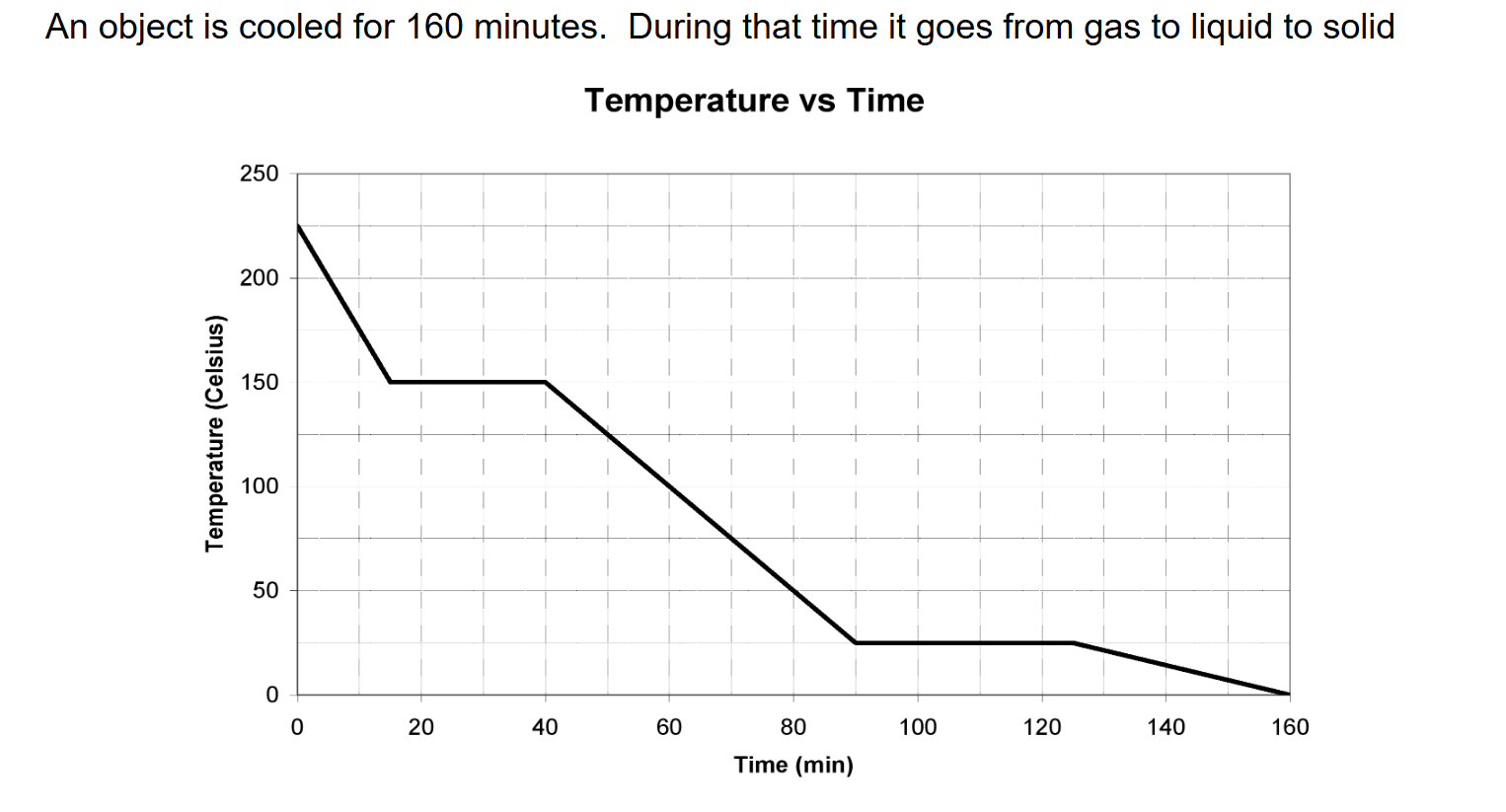
At what temperature did the object freeze?
25 degrees Celsius
Charge (q):
A physical property of certain subatomic particles that is responsible for electl anagnetic phenomena
Charge units
Units: Coulomb (C), micro coulomb (μ C), mill coulomb (m C).
• 1mC = 10 ^ -3 coulomb (C)
• 1μ C = 10 ^ -6 coulomb (C).
Charge on proton is positive
1.6 x10^-19 coulomb
Charge on electrons is negative
- 1.6 x 10^-19 coulomb.
Ionized atom
ue to physical and chemical interactions an atom can gain
one or more electrons or lose one or more electrons. Then atom is said to be
ionized
Positive Ion
atoms lose one or more electrons.
Negative ion:
atoms gain one or more electrons
Coulomb’s law:
electrical force acting between two charged particles is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely
proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Coulomb’s law formula
F= K q1 q2 / d2