Crying with chem
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/58
Last updated 2:47 PM on 1/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
3 reasons for big bang
the measured abundances of elements, the observed expansion of space, and the discovery of the cosmic microwave background
2
New cards
Red shifted
moving away
3
New cards
Blueshifted
moving towards
4
New cards
atomic emission spectra
the set of frequencies of the electromagnetic waves emitted by atoms of the element
5
New cards
protons
positively charged particles in the nucleus of an atom
6
New cards
Proton mass
1 amu
7
New cards
Neutron mass
1 amu
8
New cards
Neutron
no charge, in nucleus
9
New cards
Electron mass
0 amu
10
New cards
Electron
negatively charged particle outside the nucleus
11
New cards
nuclear decay
a process that occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus changes into another more stable nucleus by emitting radiation
12
New cards
Half life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
13
New cards
How to find half life on decay graph
Take half of the initial mass go across until the line meets the curve. Then go down to find the time that corresponds to the half life.
14
New cards
isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
15
New cards
average atomic mass
the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element
16
New cards
how to calculate average atomic mass
Divide percents of naturally occurring isotopes by 100, multiply percent by mass, add all together.
17
New cards
Subscripts
number of electrons in a given sublevel
18
New cards
Number and letters in electron configuration
two of the electron's four quantum numbers., tell us more information about the properties of electrons and their orbitals.
19
New cards
three rules to follow when drawing an energy level diagram
Aufbau Principle, Pauli-exclusion Principle, and Hund's Rule
20
New cards
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it
21
New cards
Pauli-exclusion Principle
An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin direction
22
New cards
Hund's Rule
electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as large as possible
23
New cards
Matter breaks down into
pure substances and mixtures
24
New cards
Mixture breaks down to
Homo and Heterogenious mixtures
25
New cards
homogeneous
of the same kind
26
New cards
heterogeneous
(adj.) composed of different kinds, diverse
27
New cards
Pure substances breaks into
Compound and elements
28
New cards
chemical chage
substance combines with another to form a new substance
29
New cards
physical change
a change of matter from one form to another without a change in chemical properties
30
New cards
four pieces of evidence for a chemical reaction
color change, formation of a precipitate, formation of a gas, odor change, temperature change
31
New cards
5 kinds of chemical reactions
single displacement, double displacement, combustion, synthesis, and decomposition
32
New cards
single displacement
A + BC --\> AC + B
33
New cards
double displacement
AB + CD --\> AD + CB
34
New cards
combustion
the process of burning something
35
New cards
synthesis
combining parts into a whole
36
New cards
decomposition
AB-\>A+B
37
New cards
Four Intermolecular Forces (weakest to strongest)
dispersion force.
38
New cards
Dipole-dipole force.
ttractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.
39
New cards
Hydrogen bond.
a weak bond between two molecules resulting from an __electrostatic__ attraction between a __proton__ in one molecule and an __electronegative__ atom in the other.
40
New cards
Ion-dipole force.
an attractive force that results from the electrostatic attraction between an ion and a neutral molecule that has a dipole
41
New cards
dispersion force
attractions between molecules caused by the electron motion on one molecule affecting the electron motion on the other through electrical forces; these are the weakest interactions between molecules
42
New cards
Dipole-dipole force
attractions between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules
43
New cards
Hydrogen bond.
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
44
New cards
Ion-dipole force.
an intermolecular force between an ion and the oppositely charged end of a polar molecule
45
New cards
Gas laws
the laws that state the mathematical relationships between the volume, temperature, pressure, and quantity of a gas
46
New cards
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
47
New cards
second law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
48
New cards
Specific heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius
49
New cards
How to find Neutrons
Mass-atomic number
50
New cards
How to find protons
Equal to the atomic number
51
New cards
How to find electrons
Electrons are equal to number of protons
52
New cards
What is the 6
Atomic number

53
New cards
12\.011
Atomic mass

54
New cards
WHat is the 7
protons+neutrons
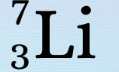
55
New cards
What is the 3
Protons
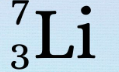
56
New cards
Polar
uneven distribution of electron density
57
New cards
Nonpolar
one whose charge distribution is spherically symmetric when averaged over time
58
New cards
Ionic
***compounds made up of ions that form charged particles when an atom (or group of atoms) gains or loses electrons***
59
New cards
Covalent
***chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms***