Methods Final
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Descriptive Research
Describe nature of thing we are interested in
Easiest to conduct
Explanatory Research
Trying to find the cause behind the event
Hardest to conduct
Predicitive Research
predicting future events
Interviening research
focuses on effectiveness of something
Ethics
Doing what is morally and legally right when conducting scientific research
Research Question
statement answered through research process
is the ‘why’ of your study
Hypothesis
A statement describing the expected result or relationship between dependent and independent variables
Research Hypothesis
A statement of the expected relationship between the variables being analyzed in the current study
Null Hypothesis
A statement that the relationship or difference being tested does not exist
Rival Hypothesis
A statement offering an alternative explanation for the research findings
Theory
As an explanation that offers to classify, organize, explain, predict, or understand the occurrence of specific phenomena
Independent Variable
predictor variable
dependent variable
outcome variable being predicted by IV
Qualitative Research
examining various social settings and the individuals who inhabit these settings
Quantitative Research
Counting and measuring items associated with the phenomena in question
Structured Interview
No deviation from questions (quantitative)
Semi-strucutred interview
interviewer can go beyond basic questions
unstructured interview
Questions are constructed as you go
Full Participant
The researcher becomes a covert participant in the research
Participant Researcher
The researcher becomes a participant in the research, but is known to the study participants
Researcher who participates
The researcher observes study participants and is known among the participants
Complete Researcher
The researcher observes participants without their knowledge
Causality
Behaviors or events that LEAD to other behaviors or events
True Causal Relationship
Time ordering
Correlation
Control for Potential confounders
theoretical relationship
idiographic cause
numerous explanations for why an event occured
Nomothetic Cause
examination of relatively few observations to provide a partial explanation for an event
levels of measurement
nominal
ordinal
interval
ratio
Research Designs
Historical
Descriptive
Developmental/time series
case study
correlation
causal comparative
true experiment
quasi-experimental
Validity
measuring what it claims to measure
face validity
questions are believed to be measuring some concept or construct
content validity
whether the items or questions are representative of possible items c
criterion validity
whether the scores of the new instrument relate to some external standard
construct validity
whether items measure what they intend to
Reliability
over time, questionnaire yields consistent results
Stability
respondents provide same answers at a later point in time
Consistency
questions are strongly related and measure the same concept
Principle of Unidimensionality
Holds that items making up the scale need to represent one dimension befitting a continuum that is supposed to be reflective of only one concept
3 things required for probability sampling
All members of a given population have the same chance of being selected
Selection of each member is independent from the selection of any other member
Selection occurs without replacement
4 types of probability sampling
simple random
stratified random
systematic random
cluster
4 types of non-probabiity sampling
purposive
quota
snowball
convenient
Confidence interval
range of numbers in a normal distribution within which our estimated population parameters fall
Confidence level
estimated probability that our population will fall within a given confidence interval
Survey data collection
mail surveys
self administered
interviews
telephone survey
Data coding
Assigning values to the data for statistical analyses
Univariate Data Analysis
Involves examining the characteristics/attributes of one variable at a time (Descriptive statistics)
Bivariate Data Analysis
Involves examining the relationship between two variables (both comparative and inferential)
Multivariate Data Analysis
Involves examining the relationship between three or more variables (both comparative and inferential)
Absolute frequency distribution
Displays data based on the assigned numbers per category
Relative Frequency Distribution
Displays percentage breakdown of each category as a percentage of the total
Cumulative frequency distribution
every subsequent category is added to the previous value, creating a cumulative total
Cumulative relative frequency distribution
Every subsequent percentage breakdown of each category is added to the previous percentage breakdown, creating a cumulative percentage totalR
Range (Variability)
differences between lowest and highest scores
Standard Deviation (variability)
the distance a score in a distribution is from the meal
Variance (variability)
the standard deviation squared
Leptikurtic
Peaked
Platikurtic
Flat
Measures of association
Pearson’s’ r
Phi Coefficient
Rho
point biserial
polyserial
polychloric
tetreachloric
Crime Rate equation
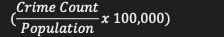
Percentage Change Equation

Inferential Statistical Tests
contingency tables
t-tests
correlation
ANOVAs
bivariate regression
multivariate regression