EXAM 2- KHAN - HIV
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the function of the following enzymes:
integrase
protease
reverse transcriptase
integrase: “integrates” viral DNA into host cell DNA
protease: how proteins become functional
reverse transcriptase: converts viral RNA into double stranded DNA
What is the HIV genome made up of?
-gag for structure
-pol for enzymes
-env for envelope
How is HIV virus transmitted?
IV drug users
sexual
perinatal/vertical
What is the MOA of NRTIs?
inhibits reverse transcriptase
phosphorylated to 5’ triphosphate by HOST cell
(exception: tenofovir already monophosphate)
is incorporated into viral DNA= chain termination
What are the class BBW of NRTIs?
lactic acidosis
hepatomegaly
steatosis (fatty liver)
What is the MOA of NNRTIs?
inhibits reverse transcriptase
binds to ALLOESTERIC SITES on reverse transcriptase
induces conformational change to RT= reduces activity
How does the MOA of NTRIs compare to NNRTIs?
BOTH act on reverse transcriptase—> but in different ways
NRTIs—> compete with nucleoside triphosphates, incorporated into viral DNA, cause chain termination
need phosphorylation
NNRTIs—> bind to allosteric sites on reverse transcriptase, inactivate the enzyme
do NOT need phosphorylation
What are the class ADRs of NNRTIs? drug interactions?
rash
hepatotoxicity
D/I—> CYP3A4 SUBSTATES!!!!!!!!! (1 exception)
What is the MOA of protease inhibitors?
PREVENTS PROTEASE from making functional proteins
prevents protease from cleaving the viral precursor polypeptide and blocks maturation
What are the class ADRs of protease inhibitors? drug interactions?
SEVERE GI—> n/v/d
metabolic syndrome
hyperglycemia
hyperlipidemia
fat redistribution
increased liver enzymes
hypersensitivity
D/I—> CYP3A4 SUBSTRATES
What is the MOA of Integrase Inhibitors?
inhibits catalytic activity of HIV INTEGRASE
Integrase integrates HIV DNA into the host cell genome—> we inhibit this
What are the class ADRs of Integrase Inhibitors?
weight gain
insomnia
rare risk—> depression/psych conditions
How is Abacavir activated?
KNOW: TO BE ACTIVE—> PHOSPHORYLATION THEN DEAMINATION
Abacavir to Abacavir MP using adenosine phosphotransferase
Abacavir MP to Carbovir MP using deaminase
How is Tenofovir activated?
KNOW: ester hydrolysis then diphosphorylated
Tenofovir AF or DF to tenofovir by ester hydrolysis
Tenofovir to Tenofovir diphosphate by HOST CELL
What is an ADR specific to EMTRICITABINE?
hyperpigmentation of the skin
What ADRs are specific to Tenofovir? AF vs. DF?
Tenofovir
reduced renal function
osteomalacia/decreased bone density
AF has less risk than DF
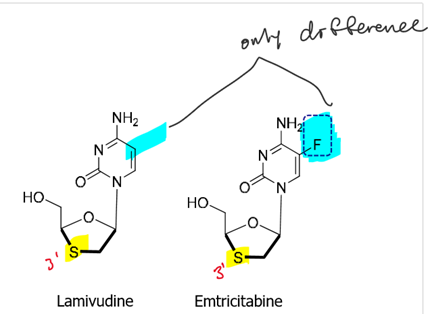
How does the structure of Lamivudine compare to Embrictabine? IDENTIFY STRUCTURES
What mutations are responsible for NRTI resistance?
RT mutations
Which NRTIs are cross resistant to each other? WHY?
LAMIVUDINE AND EMTRICITABINE—> bc of similar structures
How are each of the following effected by food? aka unaltered, no food, take with food
Zidovudine
Efavirenz
Rilipivirine
Atazanavir
Zidovudine- unaltered by food
Efavirenz- take on empty stomach
Rilipivirine- take with food
Atazanavir- absorption is pH dependent, increases in acidic pH
What NRTIs undergo metabolism? What route?
Zidovudine- glucuronidation
Abacavir- 5’ carboxylate derivative and glucuronidation
What NRTIs inhibit mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma?
What adverse reactions are observed?
ABACAVIR AND ZIDOVUDINE inhibit mitochondrial polym of HOST CELLS
causes s/e: mitochondrial TOXICITIY, anemia, granulocytopenia, myopathy, peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis
What NRTI requires HLA*5701 genotype screen prior to use? Because of what BBW?
ABACAVIR!!!!!!
Bc of BBW for hypersensitivity rxns
Is there any advantage of using rilpivirine over other NNRTIs like Efavirez?
NOT A CYP3A4 substrate like the rest of the class
What are specific ADRs of Efavirenz? What’s important about taking it on an empty stomach?
teratogenic in primates
increased cholesterol and TGs
CNS DISTURBANCES (INCLUDES SUICIDALITY)—> WHY WE TAKE ON EMPTY STOMACH TO DECREASE
What are specific ADRs of Rilpivirine? C/I with what?
CNS disturbances—> depression
C/I with antacids, PPIs, and H2RA
NNRTIs are effective against…
a. HIV-1
b. HIV-2
c. both
a.
What is the resistance rate of PI compared to NRTIs and NNRTIs?
resistance rate in between NRTIs and NNRTIs
mutations at active site or secondary mutations
What are the names of the boosters used at subtherapeutic doses to increase the bioavailability of PIs?
Ritonavir and Cobicistat
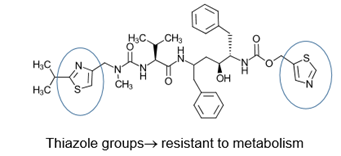
Ritonavir is resistant to what? What group allows this? BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY
resistant to metabolism—> bc of THIAZOLE GROUPS
Ritonavir interacts with many drugs like…
antiarrhythmics
anticoagulants
azoles
hypolipemics
What is a UNIQUE ADR of Atazanavir? What is a UNIQUE ADR of Darunavir?
Atazanavir—> hyperbilirubinemia (whites of your eyes turn yellow)
Darunavir—> Rash/SJS/TEN
What PI should be avoided in sulfa allergy because it has a sulfa group?
a. Ritonavir
b. Atazanavir
c. Darunavir
c
What group does Darunavir have that allows it to have tighter binding at enzyme site?
bis-tetrahydrofuran group

Answer the following about FUSION INHIBITORS:
name
MOA
ADRs
Enfuvirutide
MOA: blocks fusion of host cell and HIV membrane
peptide binds to gp41 of viral envelop protein, prevents conformational changes required for fusion of viral and cell membrane
ADRS:
injection site rxns
erythema, pain
NODULES—> TENNIS BALL SIZED
Answer the following about CCR5 Antagonist:
name
MOA
ADRs
testing before use?
Maraviroc
MOA: Stops HIV binding to CCR5 co-receptor on HOST CELL
prevents interaction of HIV gp120 and CCR5 needed for HIV to enter cells
BINDS TO CCR5 ON HOST CELL MEMBRANE NOT THE VIRUS
ADRS:
BBW—> for hepatoxicity
URI, cough, myopathy, orthostatic hypotension, increased CV risk, rash
trophism testing before beneficial
Answer the following about Attachment Inhibitors:
name
MOA
ADRs
Fostemsavir
MOA: Prevents HIV attachment to CD4
active form Temsavir binds to viral envelope protein gp120—> inhibits attachment to CD4 cells—> inhibits host cell entry
ADRS:
Increases LFT and QTc
Answer the following about Post-attachment Inhibitor:
name
MOA
Ibalizumab
MOA: INHIBITS HIV ENTRY/FUSION
binds to extracellular domain 2 of CD4+ cells
produces steric hinderance for conformational change of gp120 and CD4+ cells—> inhibits HIV entry
note: doesn’t block HIV from binding attaching to host cell, inhibits the fusion/entry of HIV into the host cell
What are the functions of diketoenol group in the structures of integrase inhibitors?
required for drug action
binds to multivalent cations
What is the effect of food on each of the following? no effect, take with, take without, etc.
Raltegravir
Dolutegravir
Elvitegravir
Raltegravir- bioavailability not food dependent, increased fat in food increases absorption
Dolutegravir- take with or without food
Elvitegravir- take WITH food
What should be avoided with integrase inhibitors?
multivalent cations (2hrs before, 6 hrs after)
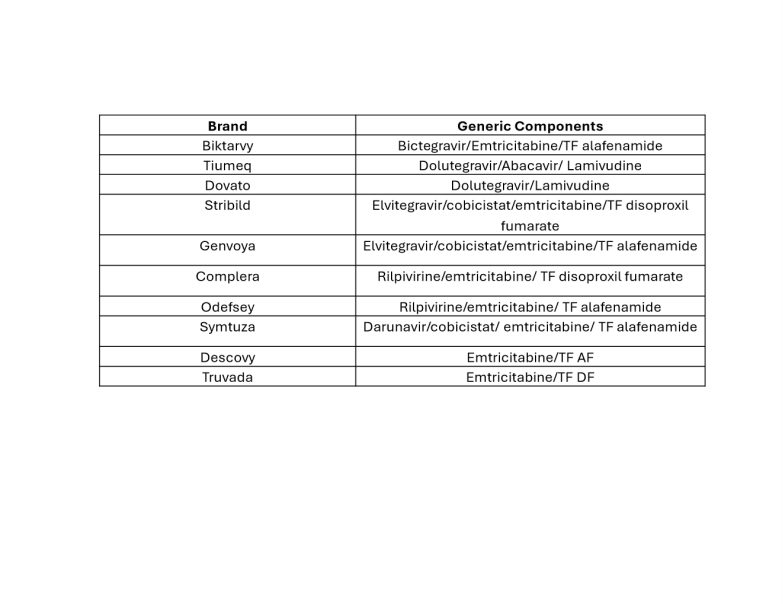
What are the brand names of the agents used for PrEP?
Truvada
Descovy
Apretude (IM Cabotegravir)
What are the brand names of the agents used for oPEP?
Truvada + Tivicay (Dolutegravir)
Truvada + Isentress (Raltegravir)
Know the single agent brand names?