Geol 101 - Ch. 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TEXTBOOOK RAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAH
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is a volcano?
A vent or opening from which melt that originates inside the Earth emerges onto the planet’s surfaces.
What is magma?
Underground melt; molten rock beneath the Earth’s surface.
What is lava?
Emerged melt'; molten rock that has flowed out onto Earth’s surface.
What is extrusive igneous rock?
Forms when lava that freezes above ground comes into contact with air/water after it erupts.

What is pyroclastic debris?
Fragmented material that sprayed out of a volcano and landed on the ground/seafloor in solid form.
What is volcanic ash?
Tiny glass shards from lava sprays.
What is intrusive igneous rock?
Rock formed by the freezing of magma underground; solidification of magma.

What are causes of melting?
Decompression
Addition of Volatiles
Heat Transfer
What is decompression?
Decrease in pressure triggers melting as long as temperature stays the same.
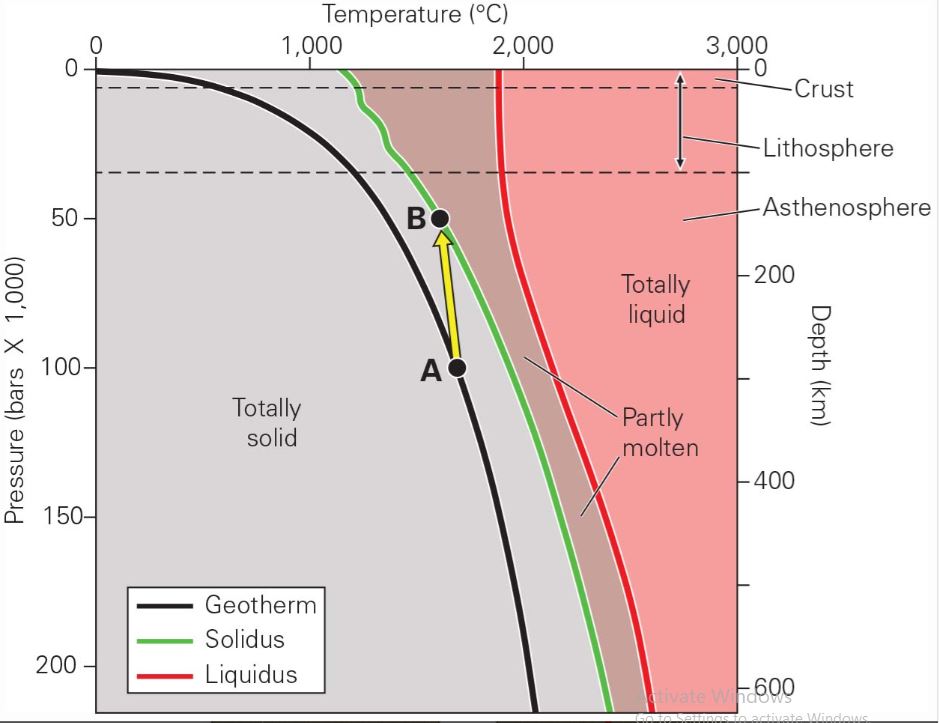
What is the addition of volatiles?
Substances that evaporate really easily; decreases a rock’s melting temperature.
What is melting due to heat transfer?
Hot magma from the mantle rises into the crust and it’s heat raises the temperature of surrounding crustal rock.
What do all molten rocks include?
Silica (SiO2)
What are dry melts?
They do not contain volatiles.
What are wet melts?
They contain volatiles.
Mafic Melts
Contain a relatively high proportion of magnesium oxide/iron oxide with silica
Ultramafic Melts
An even higher proportion of magnesium oxide and iron oxide.
Intermediate Melts
Composition between the mafic and felsic melts.
Source-rock Composition
Reflects the composition of the solid from which it was derived.
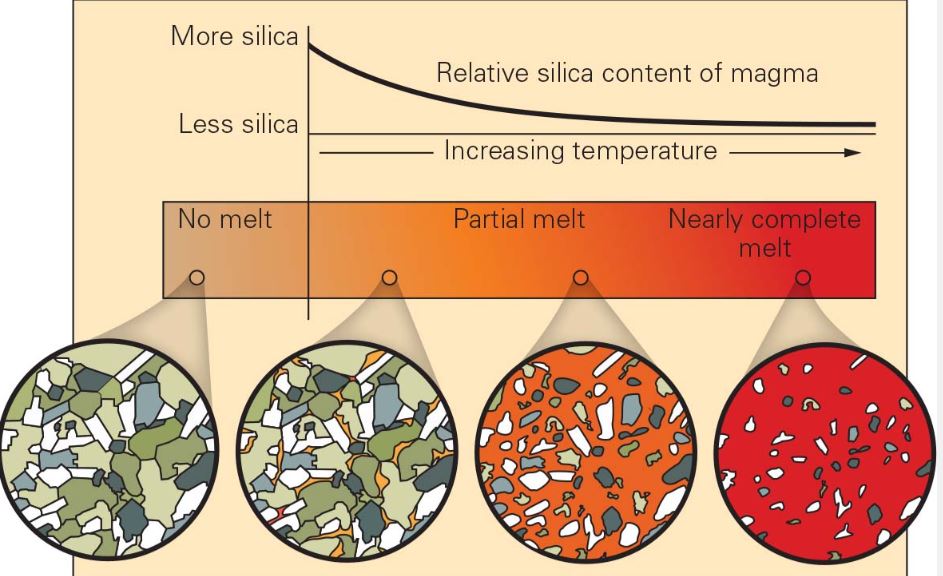
Partial Melting
Lowest temperature materials melt while higher temperature remain solid.
Assimilation
The incorporation of chemicals that dissolved from the wall rock/from blocks that detached from the wall and sank into magma.
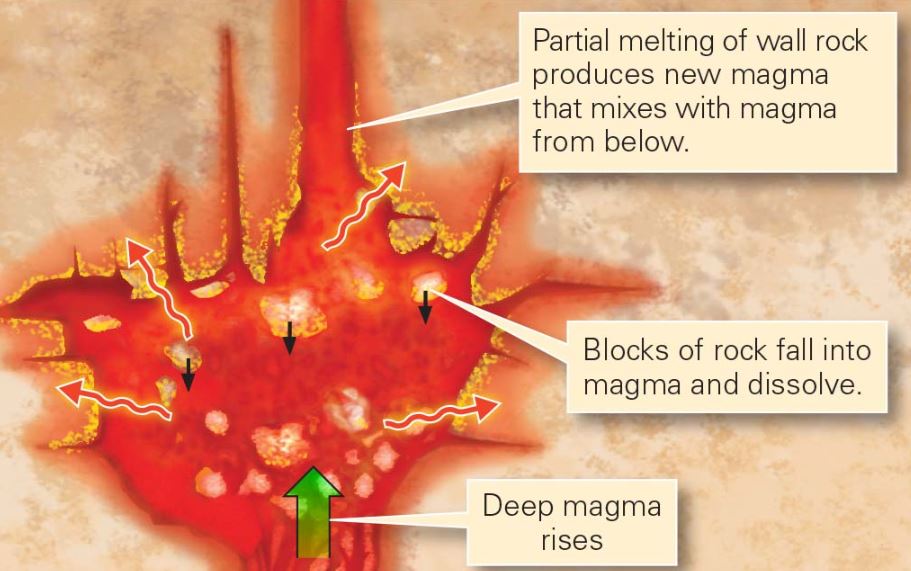
Magma Mixing
Formed in different locations from different sources that may come into contact underground.
Why does magma rise?
Buoyancy
Magma Pressure
What controls the speed of magma flow?
Viscosity; The resistance of material to flow
Which is more viscous?
A dry melt is more viscous than a wet melt.
What are the three factors the cooling time of magma?
Depth of intrusion
The shape and size of a magma body
The presence of circulating groundwater.
What is fractional crystallization?
The process by which a magma becomes progressively more silicic as it cools, because early-formed crystals settle out.
What is a magma chamber?
A space below ground filled with magma; does not contain melt, rather a “mush”
Extrusive Igneous Settings
When this lava freezes; it forms a thin lava flow which takes days-months to cool.
Intrusive Igneous Settings
Roughly planar and have a fairly uniform thickness; forms when magma injects into cracks underground.
What is a dike?
A tabular intrusion that cuts across pre-existing layering.
What is a sill?
A tabular intrusion that injects between layers; parallel
Laccolith
A blister-shaped igneous intrusion that forms when magma injects between layers underground
Plutons
Blob-shaped intrusions that range in size from tens of meters to tens of kilometers across; form when magma in a magma chamber solidifies.
Batholith
Resulting immense mass of igneous rock
Where do dike intrusions exist?
In regions where the crust stretches horizontally happens in a rift; magma forces it way a vertical crack → walls of crack move apart sideways.
How is the space of plutons developed?
Rose upward though the crust as light-bulb-shaped blobs of magma that pierced overlying rock and pushed it aside as they rose.
Stoping
A process during which magma assimilates wall rock, and blocks of wall rock break off and sink into the magma.
Xenolith
A relict of wall rock surrounded by intrusive rock when the intrusive rock freezes
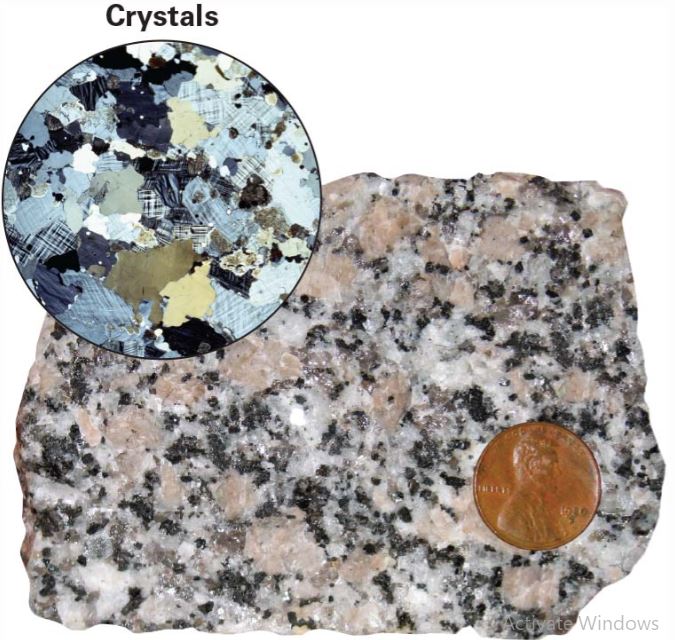

What texture is this?
Crystalline Texture
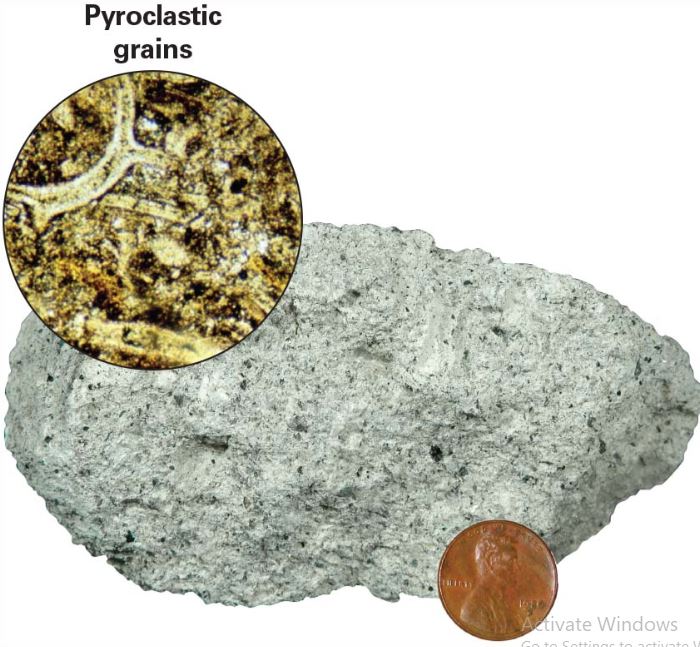

What texture is this?
Fragmental Texture
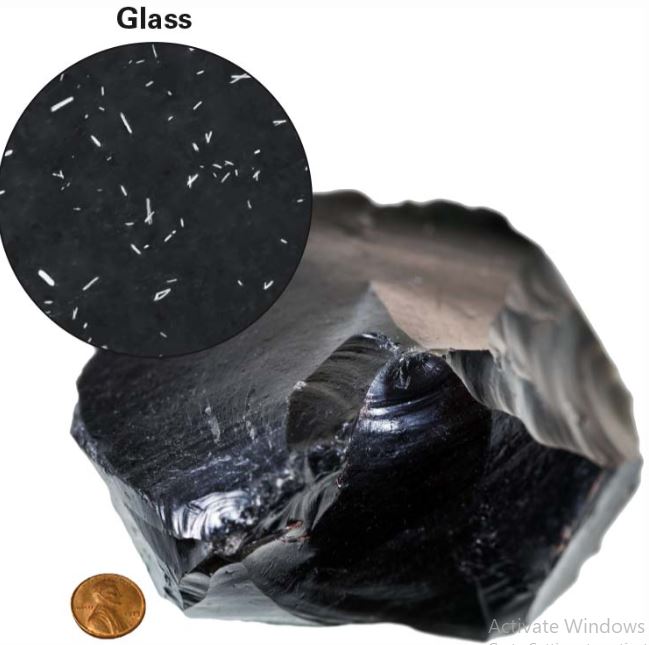

What texture is this?
Glassy Igneous Rocks
What are hot spots?
Igneous activity with mantle plumes rising from deep in the mantle.
Volcanic Arc
Forms on the overriding plate adjacent to the deep-sea trenches that mark convergent boundaries.
How does subduction trigger melting?
Volatiles are bonded to other elements within mineral crystals
Large Igneous Province (LIP)
A region in which huge volumes of lava/ash erupted over a relatively short interval of geologic time.
Flood Basalts
Vast sheets of basalt that spread from a volcanic vent over an extensive surface of land; formed by rifting above a continental hot spot.