BIO100 Nutrition Lecture #1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Carbohydrates
The primary cellular fuel that provides structure to cells.
A common source of dietary energy for animals and important building blocks of plants.
- C, H, O
- energy along with lipids/fats
What does it mean when a word ends with "ose"?
Its a sugar
Sarccharides
Simple Sugarrs
Monosarccharides (monomer)
Individual saccharide molecules that are simple sugars.
Polysaccharide
Consist of one or more monosaccharide joined together like carbohydrates
Fates of "Blood Sugar"
1. fuel for cellular activity
2. Glycogen for temporary storage
3. Fat for long-term energy storage
4 Important Polysaccharide
1. Starch (potatoes, etc) - s
2. Cellulose (glucose)
3. Glyocogen (animals)
4. Chitin (anthropods)
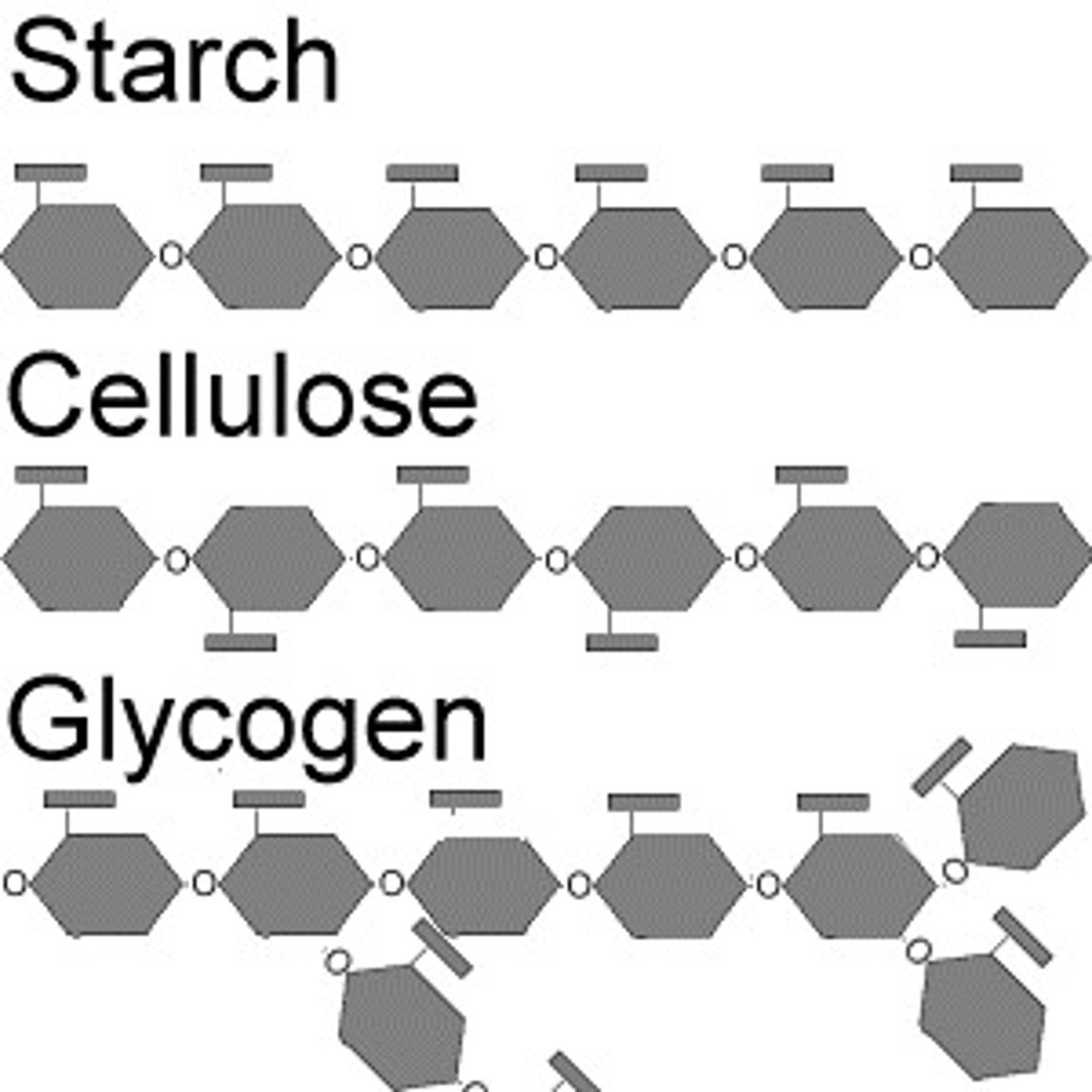
Starch
An important polysaccharide found in plants (like potatoes) that stores glucose in plants.
Cellulose
An important polysaccharide that is formed of starch chains linked together with hydrogen bonds. Makes wood and "fiber" in diet.
Glyocogen
An important polysaccharide similar to starch. Consists of a branched chains of glucose molecules. Stored in liver and muscles for up to 24 hours.
Chitin
An important polysaccharide that forms the outer skeleton of arthropods. and many fungi. Similar to cellulose except that the glucose monomer. has nitrogen.
Digestion and Use of Carbs
Sugars are converted to glucose, then metabolized and converted.
Complex Carbohydrates
Many are time-released packets of energy
1. Carbohydrates are polymers composed of monosaccharides
2. Disaccharides (lactose, sucrose)
3. Polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates like starch)
Short-term vs. Long-term Energy
Depending on their structure, dietary carbohydrates can lead to quick-but-brief or slow-but persistent increases in blood sugar.
A polysaccharide takes longer to absorb.
Cellular Respiration
Breaks down glucose into Carbon dioxide to supply energy to the cell (ATP)
1. Glycolysis
2. Citric Acid Cycle (output carbon dioxide)
3. Electron Transport Chain (input oxygen, output water)
Diabetes
Type 1: not diet related. Destruction of pancreatic B cells that produce insulin.
Type 2: desensitization of insulin receptors due to high consumption of simple sugars. Lack of exercise and poor quality diet
What normally happens after a meal?
1. Stimulus: rising blood glucose
2. Pancreases increases insulin
3. Body cells take up glucose or live store glucose as glycogen
4. Blood glucose level falls
5. Homeostasis of normal blood glucose.
What normally happens when one is hungry?
1. Stimulus: declining blood glucose
2. Pancreas increases glucagon
3. Liver breaks down glycogen
4. Blood glucose level rises.
5. Homeostasis normal blood glucose level
How is glucose absorbed into the body?
Diffusion
A tendency for molecules to spread out evenly to the available space.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across selectively permeable membrane.