APUSH Period 1: 1491-1607 -- The Meeting of Three Peoples
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
4-6% of exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
context for period 1
in the late 1400s to early 1600s, the meeting of American Indians, Europeans, and West Africans on the North American continent led to a broad transformation of much of the world
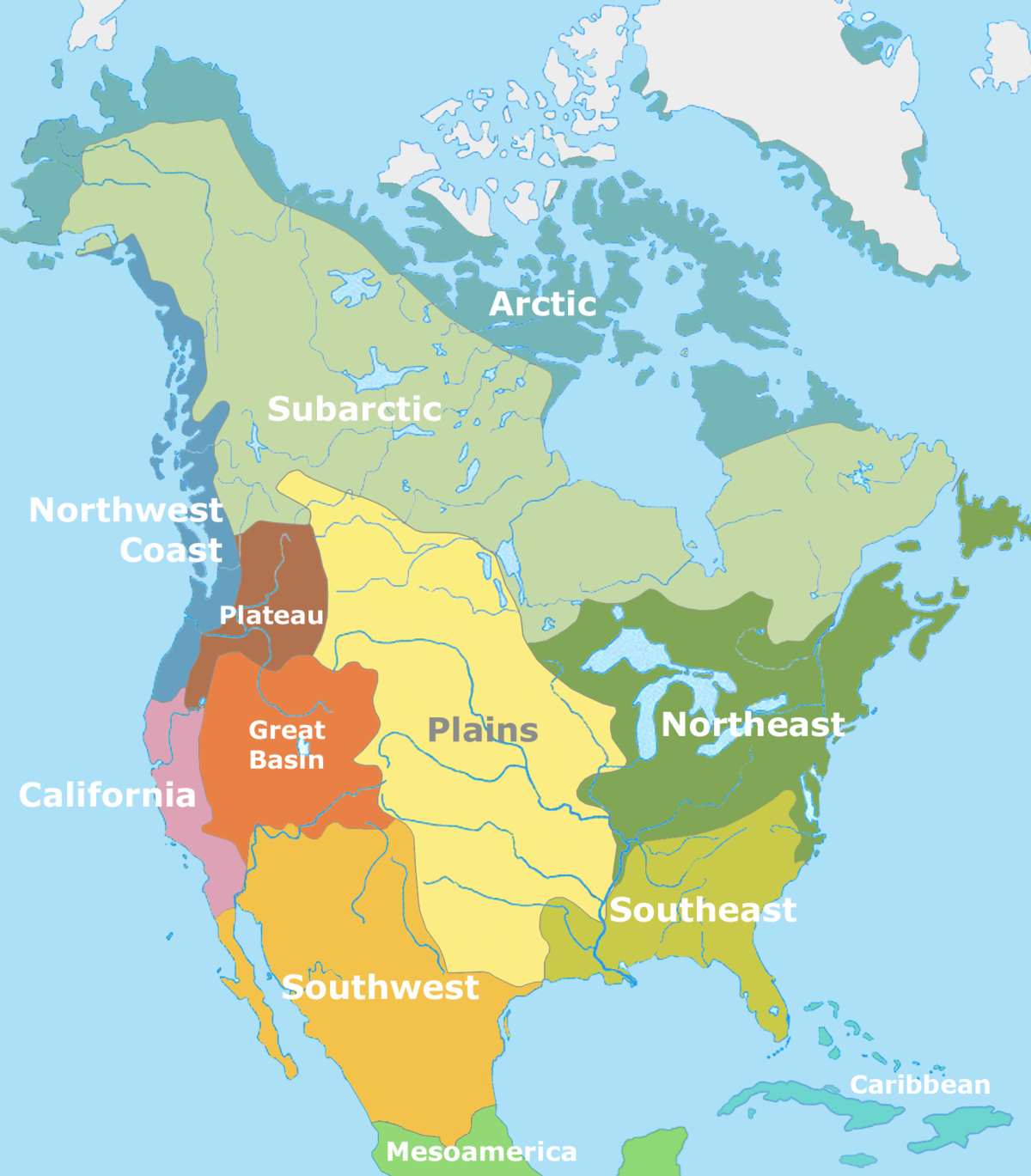
cause for diversity among native peoples
interactions with other native peoples and with the environment
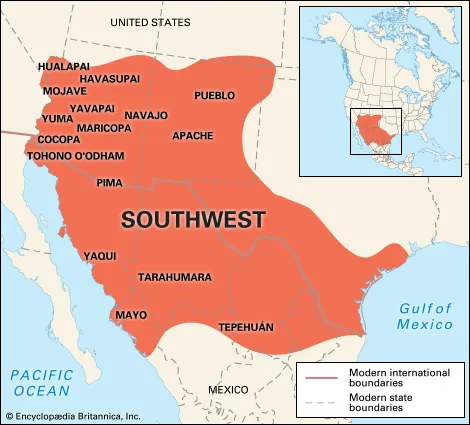
societies of the Southwest
Pueblo people - small towns = “pueblos”
cultivation of maize in settled communities
complex and technologically advanced - architecture
dispersed in 1200s-1300s because of climatic change — weakened on eve of European contact
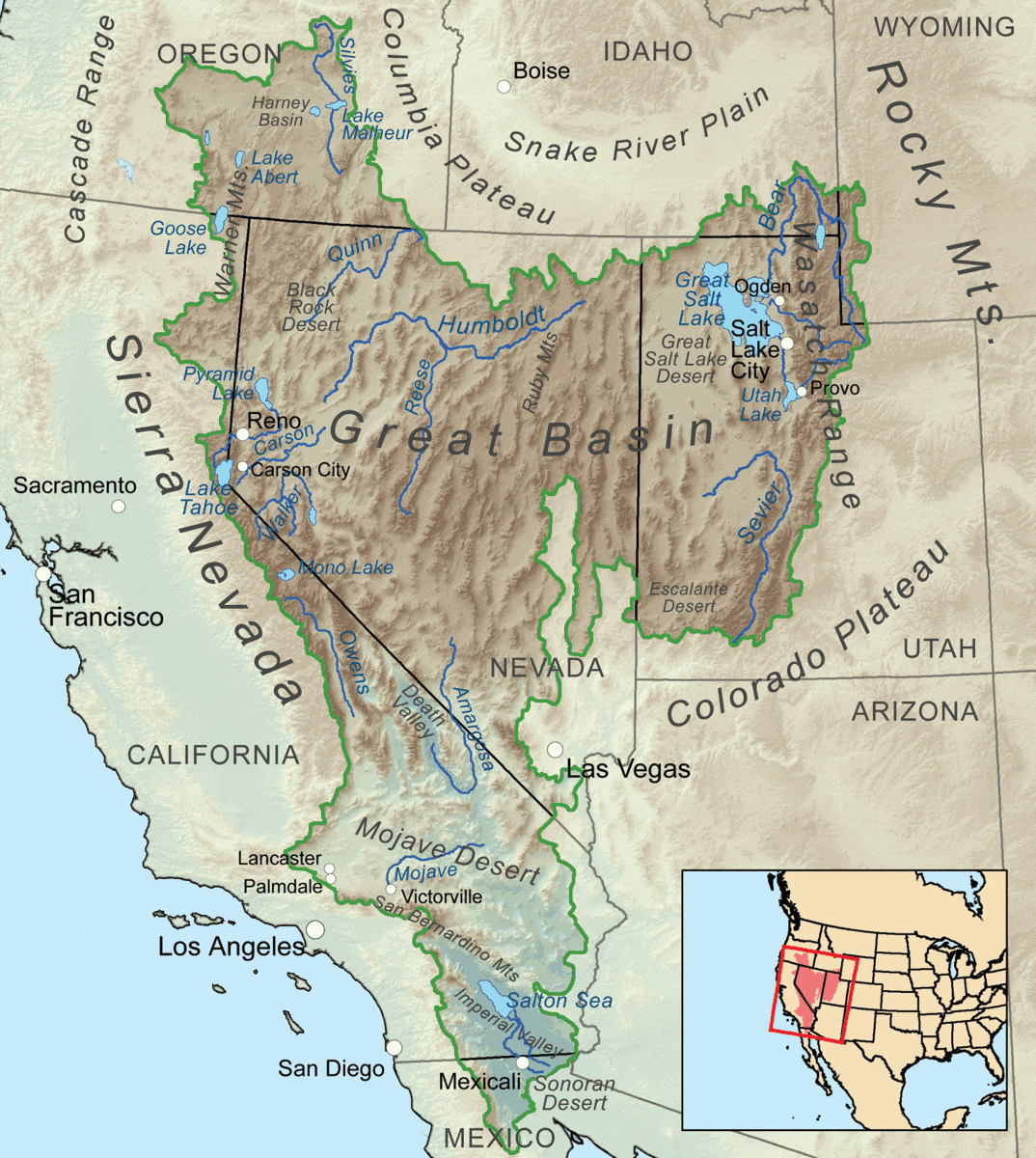
societies of the Great Basin
mobile lifestyles because of lack of natural resources
very few resources in Great Basin
“desert culture” = seasonable mobility (hunters and foragers), basketmaking
Shoshone, Paiute, Ute
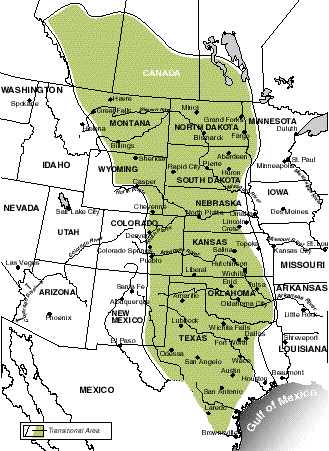
societies of the Great Plains
mobile lifestyle hunting bison
Sioux, Blackfoot, Arapaho
more sedentary, agrarian lifestyles closer to the MS River
Osage, Wichita, Omaha
introduction of horses from Europe changed societies signficantly
societies of the East
mix of agricultural and hunter-gatherer economies
permanent settlements
Algonquian-speaking peoples in northern interior by St. Lawrence River and Great Lakes
hunted, fished, grew maize (less farming in cold New England and upper Great Lakes)
Iroquois League in New York
confederation of Mohawks, Oneidas, Onondagas, Cayugas, Senecas (+ Tuscaroras)
farmed the “3 sisters” — maize, beans, squash
matrilineal society
societies of the Pacific Northwest
mix of foraging and hunting — vast resources of Pacific Ocean and rivers
Chinook people in Washington and Oregon
foraging, hunting, fishing
settled communities
economic development and social stratification
factors contributing to European exploration
God, Gold, Glory:
push for new converts to Christianity
desire for new sources of wealth
competition for power and status
effects of the Crusades
decline in European feudalism
increased interest in trade with Asia
effects of the Black Death
European population down 30-60%
food and land more plentiful
people are more willing to take risks and seek opportunities
undermined stability of feudalism
effects of the Renaissance
spirit of curiosity inspired exploration
humanism caused the spread of knowledge of new discoveries
Johannes Gutenberg’s printing press helped spread information and stimulate interest in discoveries
effects of the Protestant Reformation
renewed religious zeal and desire to spread gospels
Martin Luther and John Calvin broke with the Roman Catholic Church — Lutheranism and Calvinism
English King Henry VIII’s creation of the Church of England didn’t satisfy the Puritans
Counter-Reformation of the Catholic Church — Jesuits sought to spread gospel throughout the world
the Columbian Exchange
the exchange of crops (tobacco, potatoes), disease (syphilis to Europe, smallpox to Americas), precious metals, livestock (horses), people etc. across the Atlantic Ocean
impacts of conquest and the Columbian Exchange on Europe
influx of silver and gold caused Spain to suffer inflation and decline
introduction of new crops (potatoes) and livestock to Europe led to population growth
introduction of new sources of wealth helped faciltiate transition from feudalism to capitalism
impact of technological advances
developments in maritime technology encouraged exploration
compass, astrolabe, quadrant, hourglass, Portulanos, caravels
joint-stock company
model in which shareholders control part of the company in proportion to the number of shares they own
risks spread among multiple investors
funded exploration and colonization
Christopher Columbus
Italian navigator funded by Spanish monarchs Isabella and Ferdinand
sailed to San Salvador in 1492 and called Taino people “Indians”
Treaty of Tordesillas
1494 treaty between Spain and Portugal
settled competing claims by drew longitudinal line through Atlantic Ocean and S. America (Portugal = east, Spain = west)
conquistadores’ conquests
the Spanish took control of much of Central and South America and spread into CA, NM, the area around the MS River, and FL
Hernan Cortes defeated Aztecs 1518-1521
Francisco Pizarro defeated Incas 1532
disease and death in native populations
Old World diseases devastate native populations because they had no immunities to foreign germs
smallpox is especially deadly
50-90% of native population in Americas died 1500-1650
Spanish policies of subjugating natives: warfare, brutal conquest, harsh working conditions —> decline of native populations
impacts of the Columbian Exchange on the Americas
diseases introduced from Europe killed many
sugar, wheat, bananas, goats, cows, chickens introduced
the horse transformed many native cultures
the encomienda system
system in which Spanish encomenderos were granted land and the right to extract labor from Native Americans
resembled Old World feudalism
led to brutal exploitation
impacts of the slave trade in the 1500s
starting in the 1500s, slavery was seen as a permanent and inheritable condition
African slaves were considered property with no rights
entire generations of strong, young people were taken from Africa
the introduction of European manufactured items undermined the traditional African economy
resistance to slavery in the 1500s
cultural resistance attempted to preserve tradition and maintain a sense of autonomy
Maroon communities formed among Africans who escaped slavery and preserved African traditions
the casta system
Spanish caste system in the New World defined by social origin and race — result of racial intermixing
from top to bottom: peninsulares, creoles, mestizos, mulattos, American Indians and Africans
cultural differences between Native Americans and Europeans
many Native American societies were matrilineal
European socieities were patrilineal
many Native Americans saw land as a communal resource
Europeans highly valued individual land ownership
Native American resistance to the Spanish
some Native Americans fled from invading Spaniards — led to population pressures and conflicts elsewhere
both violent and passive resistance
Juanillo’s Revolt 1597 killed several missionaries
Acoma Pueblo people resist conquistador Juan de Onate — 15 Spanish vs. 800 Acoma killed
development of white superiority
Europeans developed racist ideas to justify the subjugation of nonwhite people
Spanish racial hierarchy based on traditional notions about “pure blood”
Bartolome de Las Casas
Spanish priest who criticized Spanish treatment of Native Americans in the encomienda system
wrote A Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies (written 1542, published 1552)
initially advocated transition to enslavement of Africans
Juan Gines de Sepulveda
Spanish theologian who defended Spanish treatment of Native Americans
asserted that Native Americans were “natural slaves” and insisted that battles of New World conquest were “just wars”
“Black Legend”
the anti-Spanish propaganda written by English, Italian, Dutch, and other European writers
English writers may have tried to demonize Spanish behavior to portray English behavior in a more favorable light
animism
the belief that the natural world is suffused with spiritual power
influenced gender roles and rituals in many Native American societies
civic humanism
an ideology praising public virtue and service to the state
celebrated in the Italian Renaissance
influenced European and American ideas of government
primogeniture
a practice where the eldest son receives all of his father’s land
predestination
idea that God chooses certain people for salvation before they are born and condemns the rest for eternal damnation — preached by John Calvin
Identity (theme)
American Indians and Africans in the New World adapted to European culture, but were able to maintain some elements of their own cultures
Work, Exchange, Technology (theme)
maize cultivation was very important to the economic development of North American Indians
the Portuguese and Spanish intiated the transatlantic slave trade, working with some Africans to acquire slave labor
the Spanish developed the encomienda system with Native Americans and African slaves
Peopling (theme)
Native Americans migrated throughout N. America and developed diverse and complex societies
NA societies that depended on agriculture and hunting tended to live in permanent settlements
the Columbian Exchange brought significant changes to native peoples and to Europeans in the New World and Europe — disease, slavery
Politics and Power (theme)
Native Americans and Africans attempted to maintain autonomy despite European efforts to control them
America in the World (theme)
European arrival in the 1400s-1500s led to demographic and social change
Spanish and Portuguese conquests led to epidemics, racial mixing, and a caste system
the Spanish introduced new crops and domesticated animals to the W. Hemisphere — economic, political, and social change
Spanish and Portuguese explorers had little understanding of Native Americans
Environment and Geography (theme)
Native Americans and Europeans adapted to and transformed varied evnrionments
due to a scarcity of natural resources, Native Americans in the Plains and Great Basin were largely mobile
Ideas, Beliefs, and Culture (theme)
Europeans came to the New World to spread Christianity (as well as to gain wealth and power)
European exploration and settlement of the W. Hemisphere contributed to the end of feudalism in Western Europe
European exploration and contact with Native Americans led to debate over the definition of “civilized” and the treatment of native peoples