A&P Chapter 7: Skeletal System
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Bones
Organs composed of many tissues (bone, cartilage, dense connective, blood, and nervous). Vary in size and shape.
Major functions of bones
PROTECTION, support, body movement, blood cell formation, mineral storage
Bone shapes
Long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones
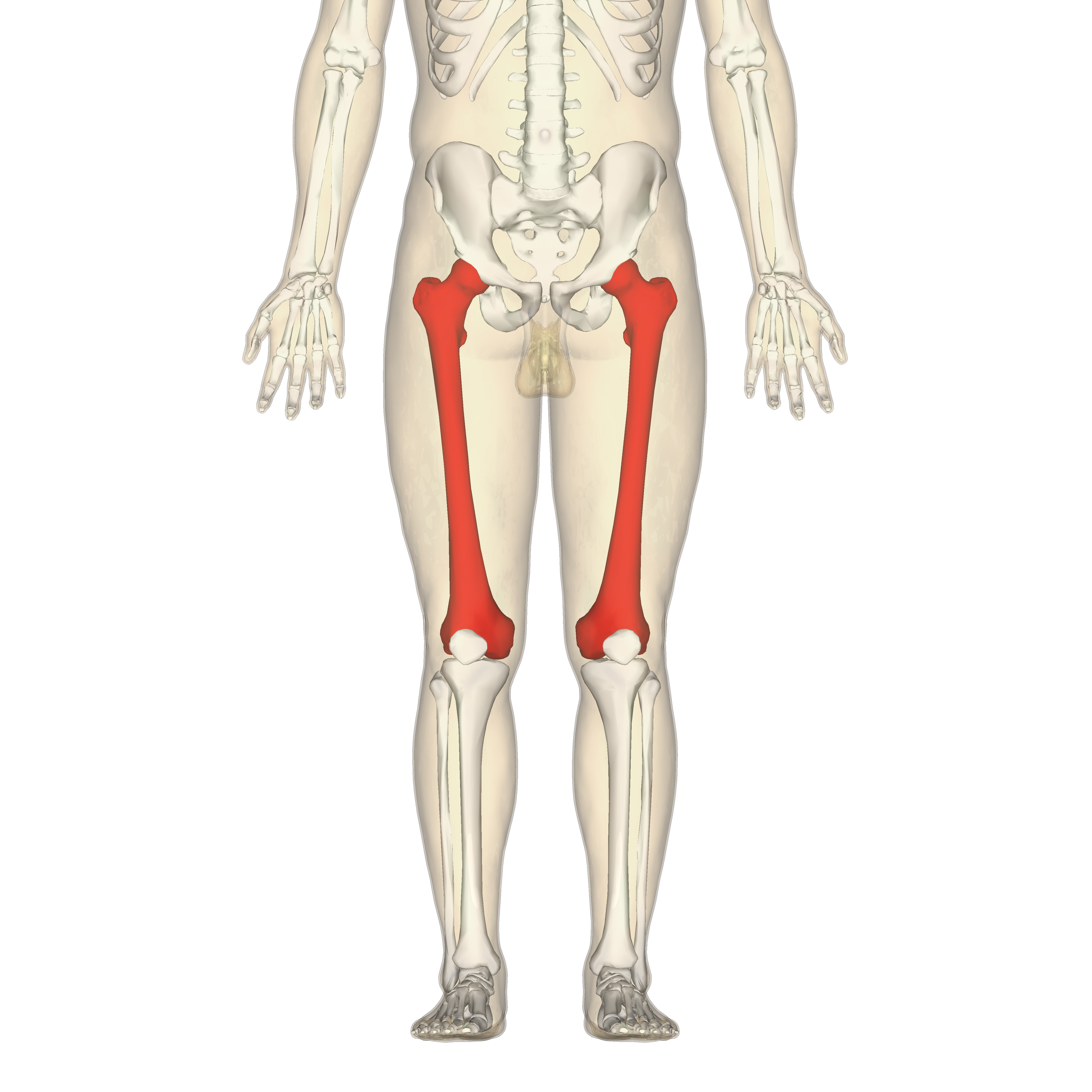
Long bones
Taller than they are wide, have expanded ends
ex. femur
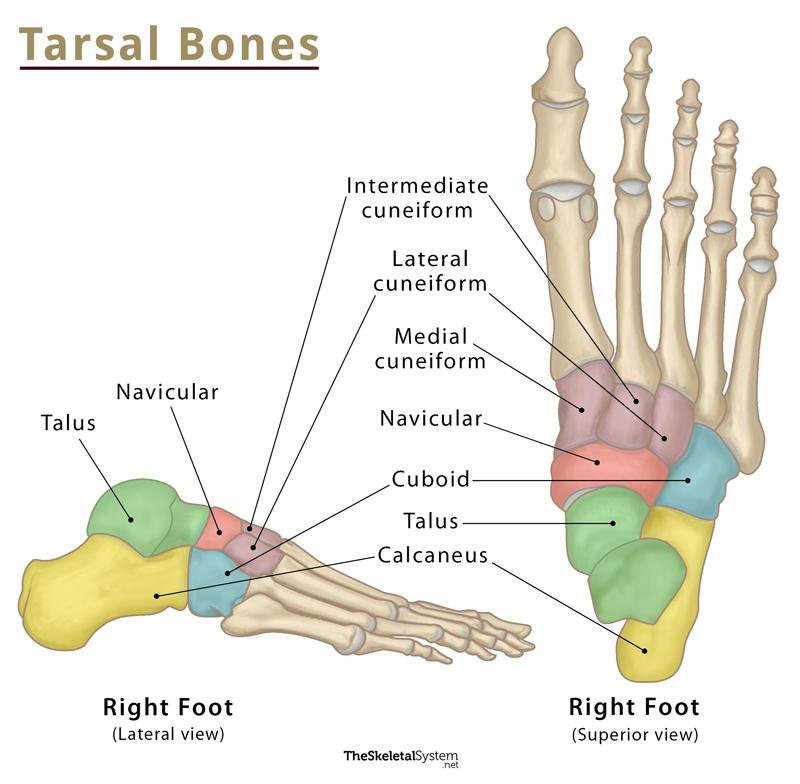
Short bones
Cube-like, length=width. Includes sesamoid (round) bones, which are embedded in tendons
ex. ankle bone, tarsal bones
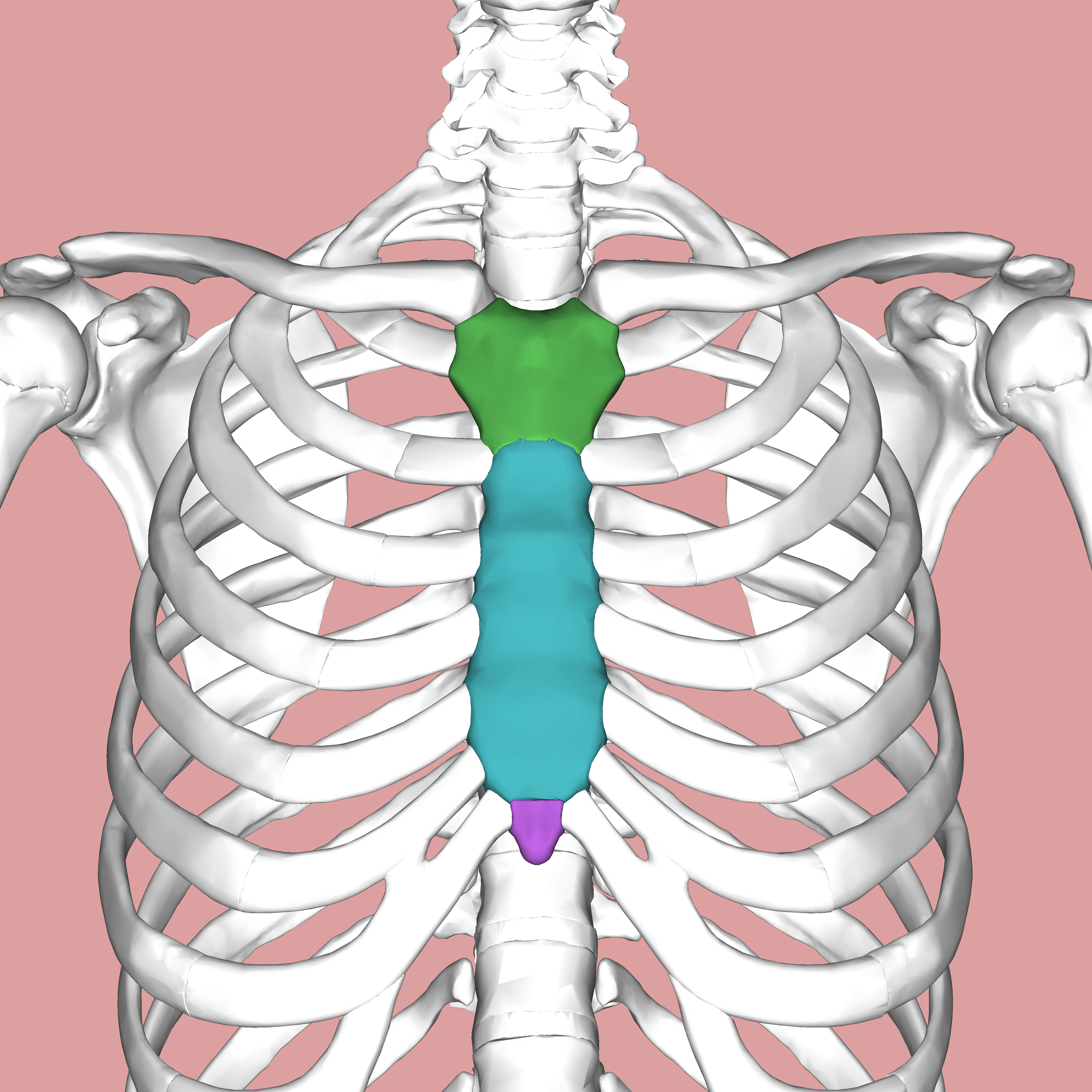
Flat bones
Plate like with broad surfaces
ex. sternum
Irregular bones
Variety of shapes and most are connected to several other bones
ex. vertebrae
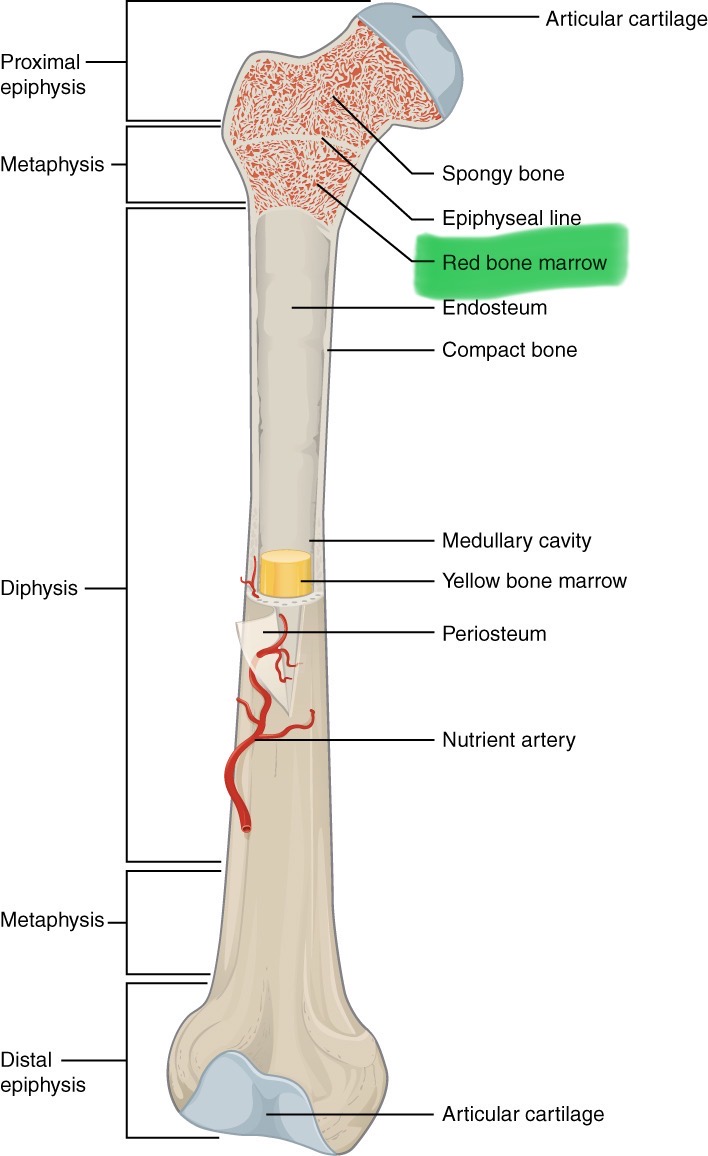
11 parts of a long bone
Epiphysis, Diaphysis, Metaphysis, Articular Cartilage, Periosteum, Compact, Spongy, Traveculae, Medullar cavity, Endosteum, Bone marrow
Epiphysis
End of a long bone
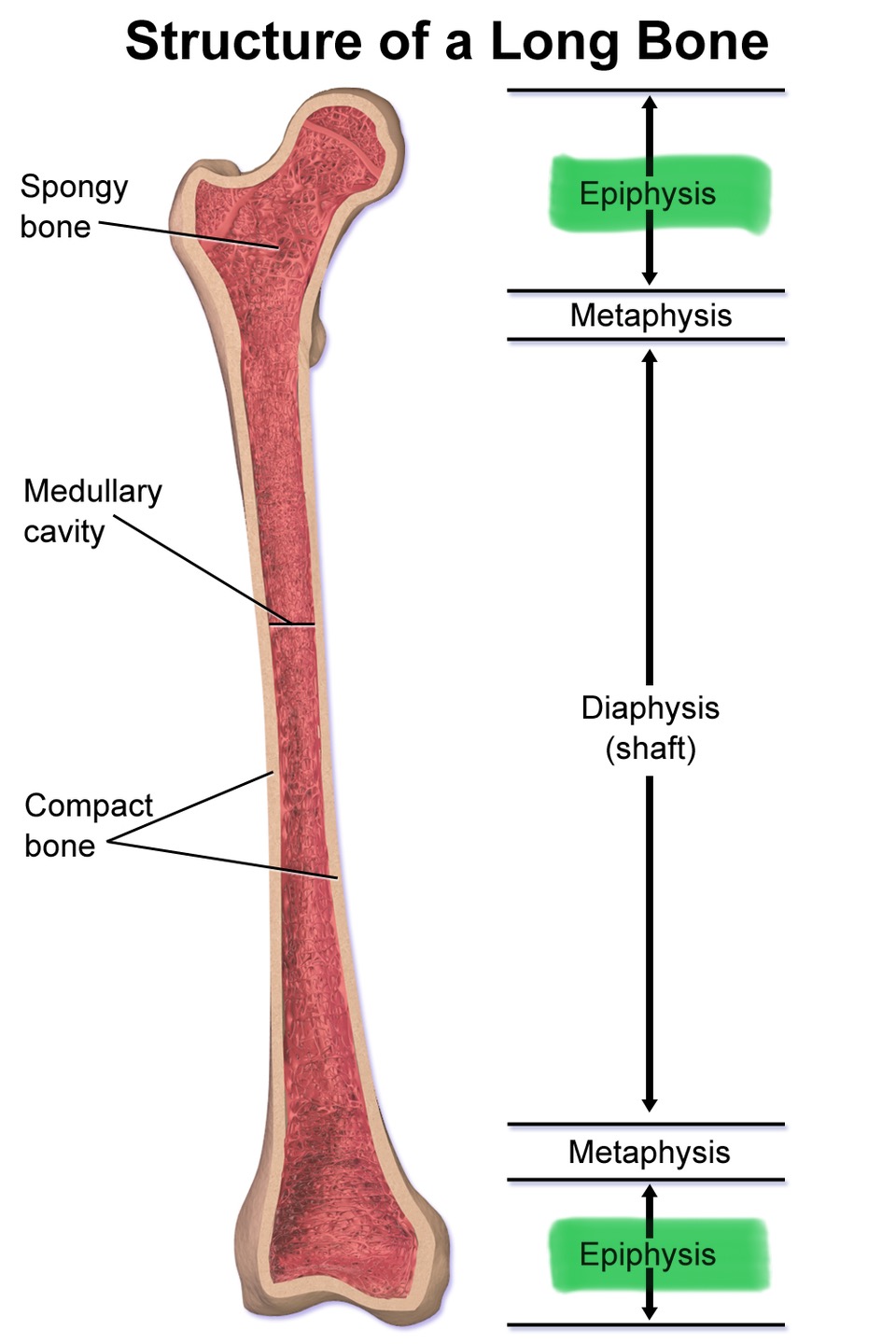
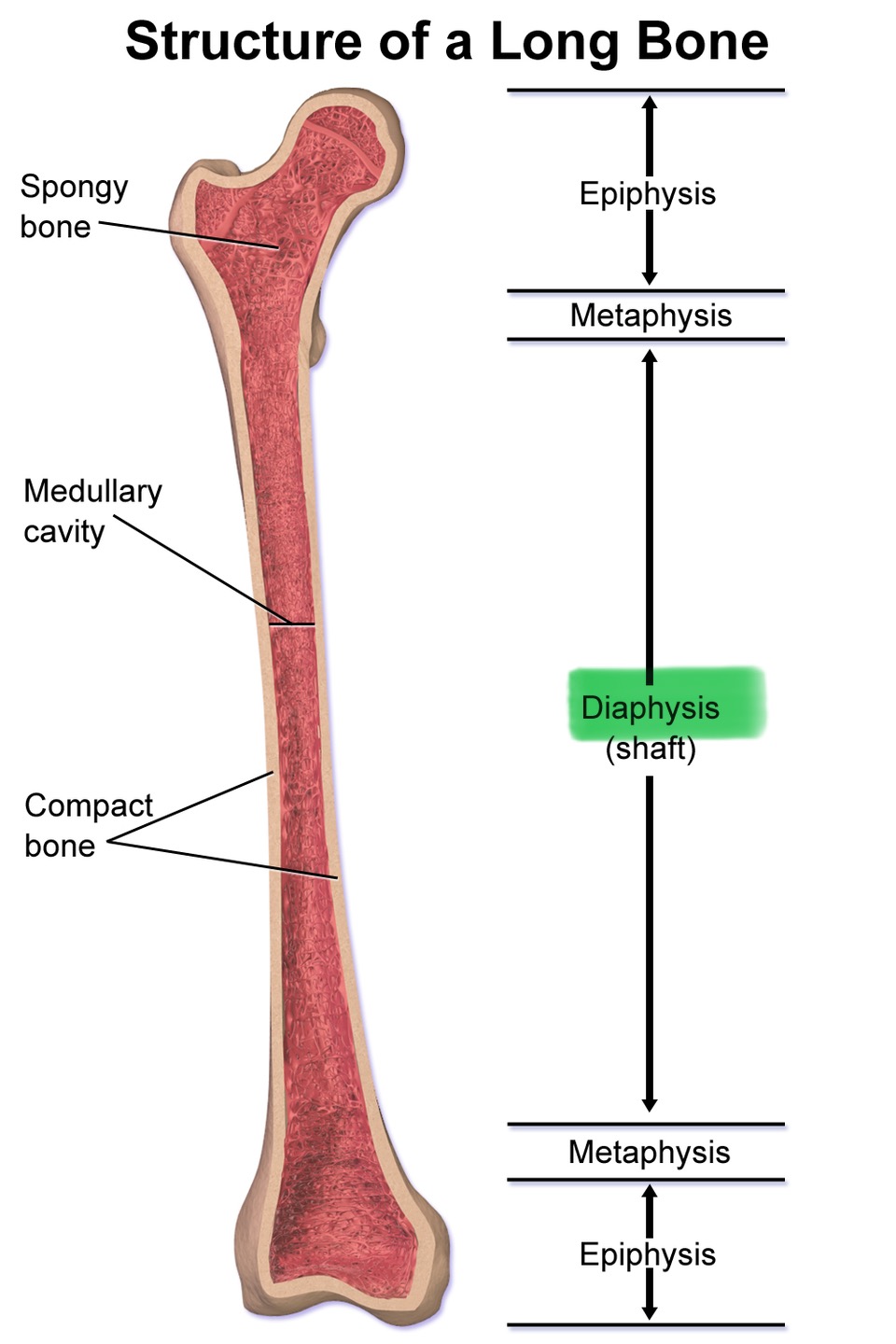
Diaphysis
Middle portion/shaft of a long bone
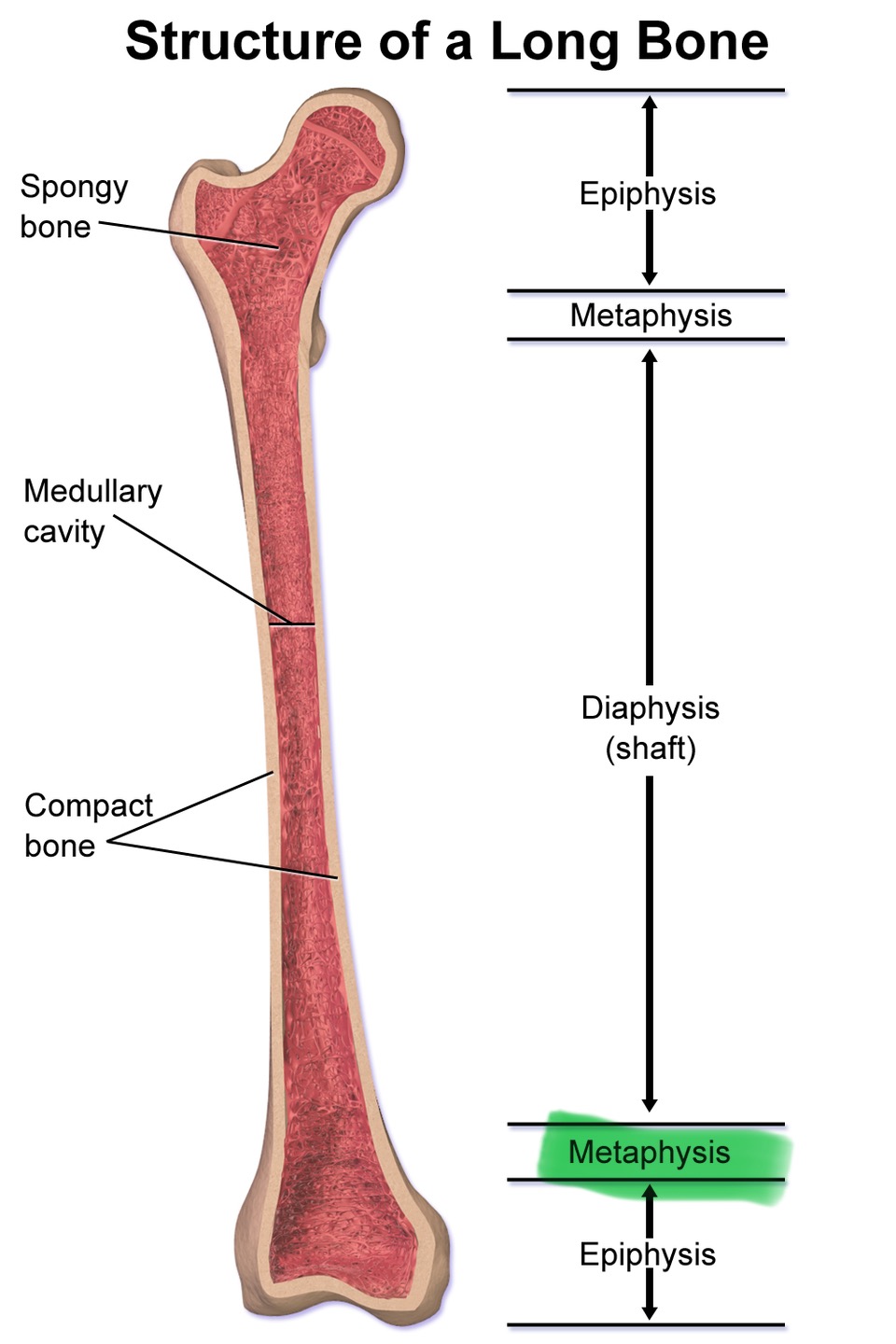
Metaphysis
Between diaphysis and epiphysis, widening part of long bone
Articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage that covers the ends of bones in synovial joints
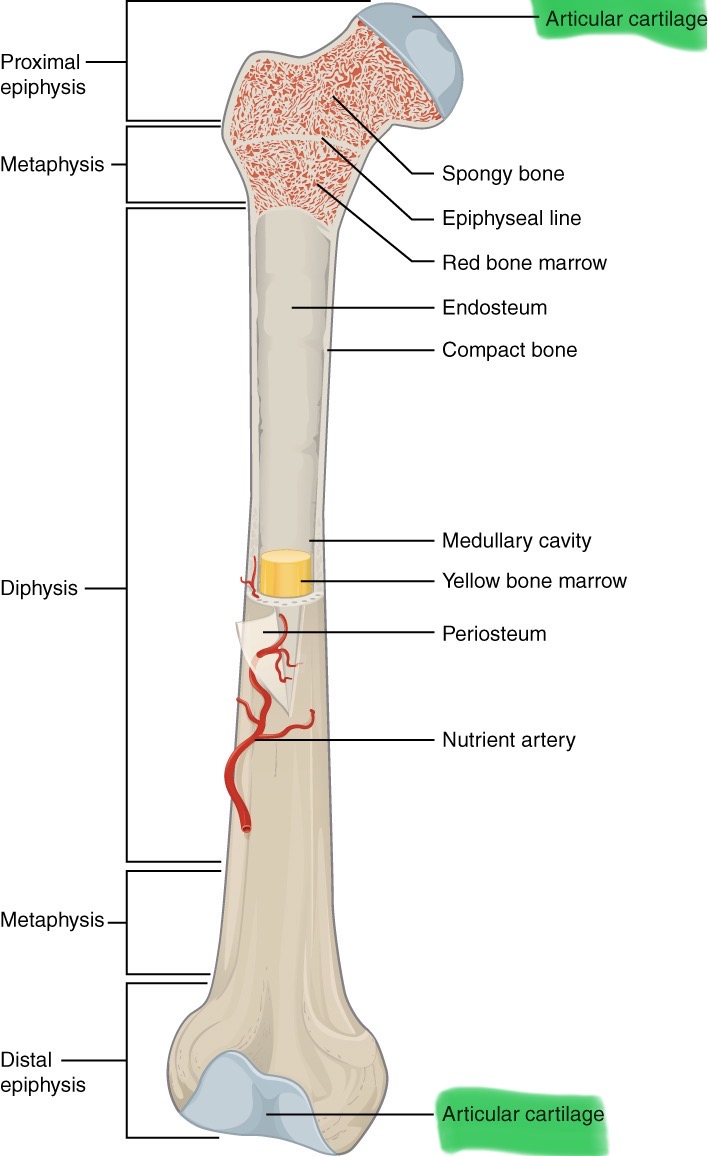
Periosteum
Dense connective tissue covering the surface of a bone.
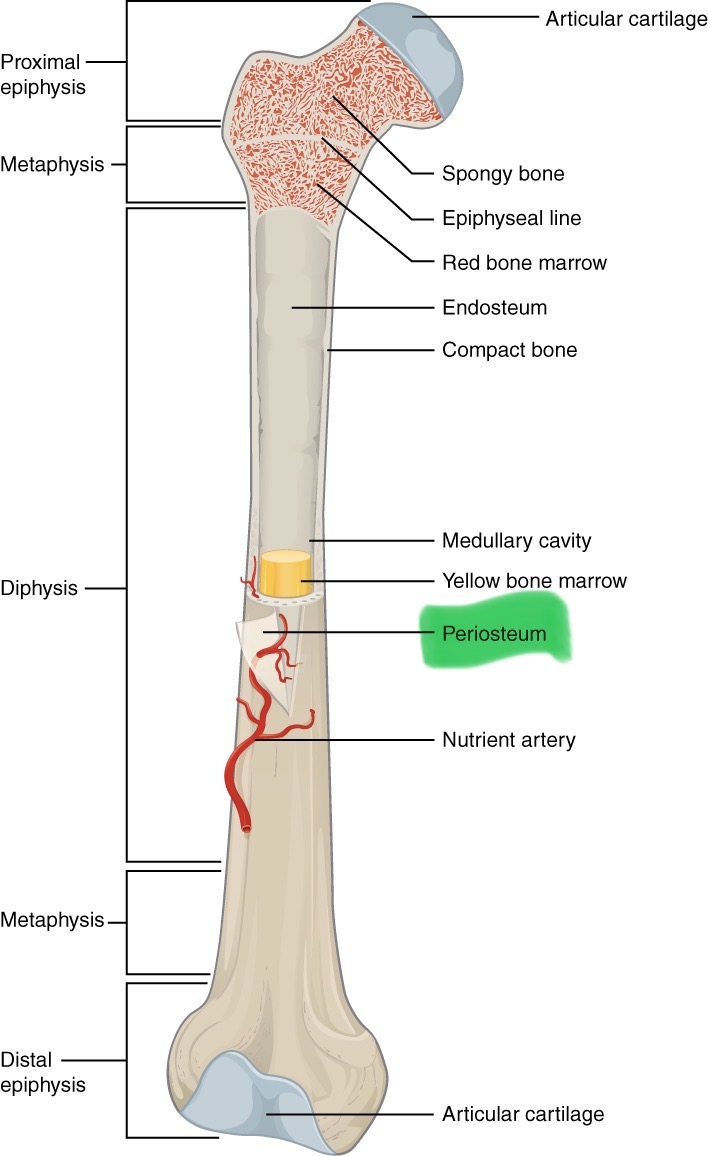
Compact bone
Makes up bone that protects diaphysis; it is the wall of diaphysis
Spongy bone
Makes up epiphysis; has air spaces where red bone marrow is found. Somewhat flexible
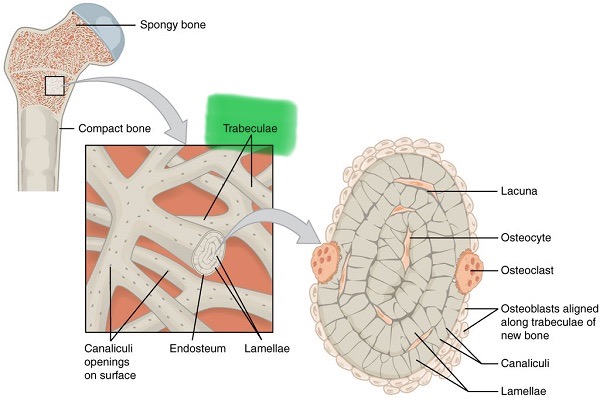
Trabeculae
Branching bony plates that makes up spongy bone. It's spaces reduce the bones weight
Medullar cavity
Hollow chamber in disphysis; contains marrow
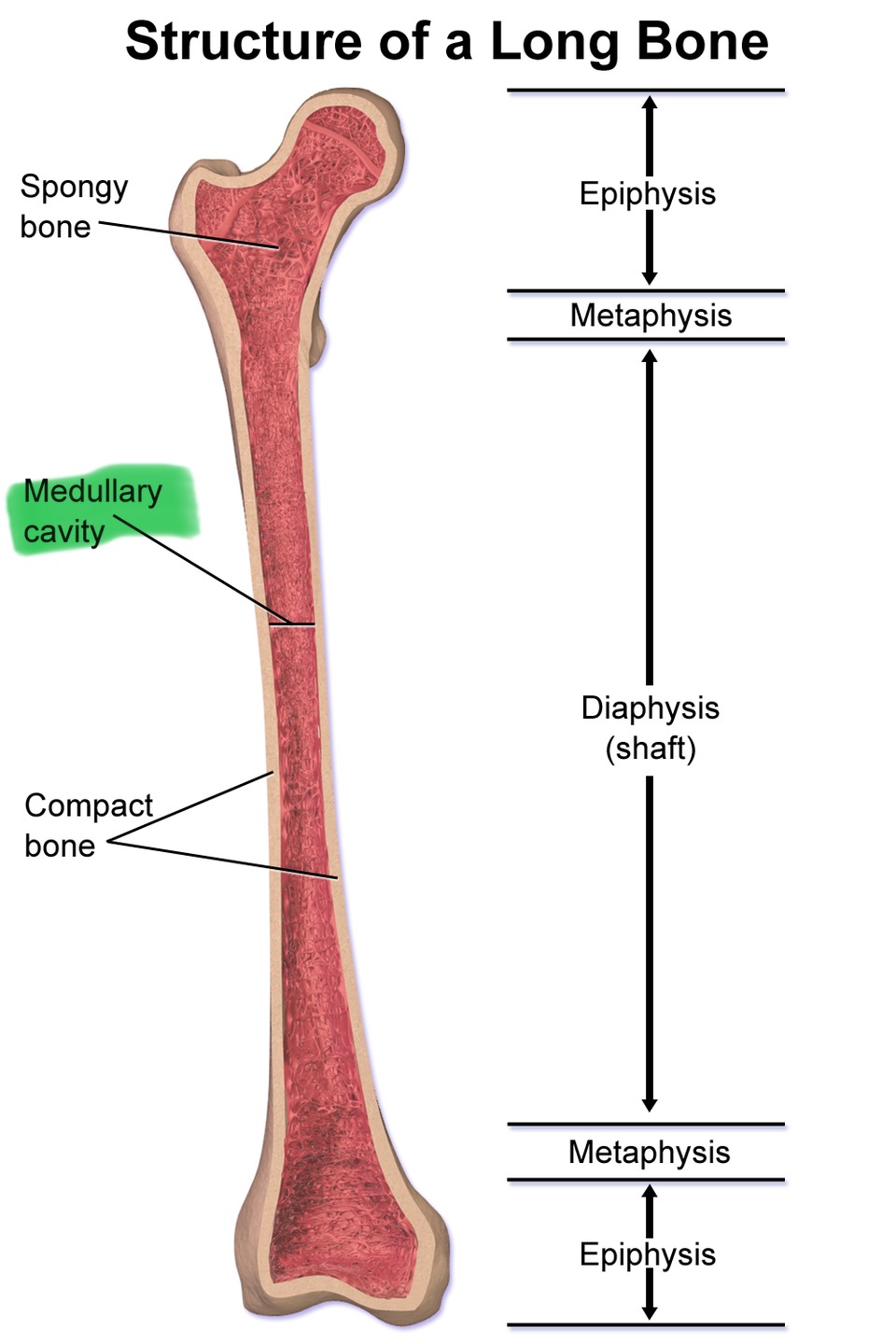
Endosteum
A thin membrane containing bone forming cells. Lines the medullar cavity as well as spaces within spongy bone
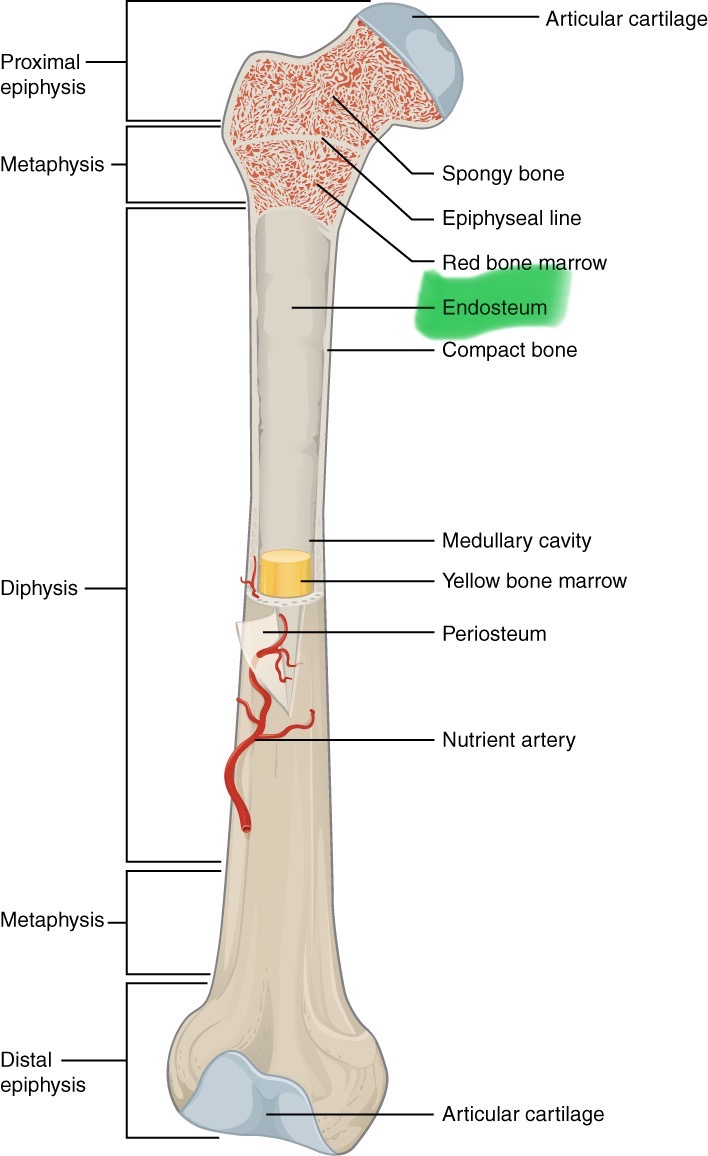
Bone marrow
Red or yellow, lines medullar cavity, found in spongy bone spaces
Appositional growth
Bone gets wider, stronger, and thicker to support excess body weight
Epiphyseal plates
Growth plates; growth/length of long bone
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells
Lacunae
Chambers that contain osteocytes
Canaliculi
Tiny passageways where osteocyte cell processes exchange nutrients and wastes
What is the extracellular matrix of bone mainly composed of?
Collagen fibers- provides resilience (flexibility/strength
Inorganic salts- hardness
Osteons
Cylinder shaped units that make up compact bone
Intramembranous Ossification
Flat skull bones, clavicles, sternum, and some facial bones form between sheets of primitive connective tissue
Endochondrial Ossification
Long bones and most of skeletons are forming from hyaline cartilage models
Intramembranous bones
Broad, flat bones that originate within sheet like layers of connective tissue.
ex. flat bones of the skull, clavicles, sternum, and some facial bones (mandible, maxilla, zygomatic)
Endochondral bones
Begin as masses of hyaline cartilage and is most bones of the skeleton.
ex. femur, humerus, radius, tibia, phalanges, vertebrae
Growth at the Epiphyseal Plate process:
Osteoclasts break down the calcified matrix then osteoblasts invade and replace the cartilage with bone tissue
Bone length growth and when it stops
As long as the cartilage cells in the epiphyseal plate remain active, it can continue to grow. When ossification centers meet, and epiphyseal plate ossifies, bone can no longer grow in length.
How can a bone increase in thickness?
By depositing compact bone on the outside, under the periosteum.
Bone homeostasis
It is continuous bone remodeling throughout life, involving opposing processes of resorption and deposition on the surfaces of the endosteum and periosteum.
How do resorption and deposition maintain bone homeostasis?
Osteoclasts remove old bone (resorption) and osteoblasts form new bone (deposition), replacing 10–20% of the skeleton each year.
Major factors that affect bone development, growth, and repair
Nutrition (vitamins D, A, C), sunlight exposure, hormone levels, and physical exercise
How vitamin D affects bone development, growth, and repair:
Needed for calcium absorption. Deficiency causes rickets/osteomalacia
How vitamin A affects bone development, growth, and repair:
Regulates osteoblast/osteoclast activity; deficiency slows bone development.
How vitamin C affects bone development, growth, and repair:
Required for collagen; deficiency leads to fragile bones
How growth hormones affects bone development, growth, and repair:
Stimulates cartilage cell division; too little=dwarfism, too much= gigantism/acromegaly.
How sex hormones (estrogen & testosterone) affects bone development, growth, and repair:
Promotes bone formation
Fractures
Classified by cause and nature of break
2 types of fractures
Simple (closed): protected by uninjured skin (or mucous membrane)
Compound (open): bone is exposed to the outside through opening of skin (or mucous membrane)
Hematopoiesis
Blood cell formation that occurs in red bone marrow.
Red bone marrow
Produces RBC, WBC, and platelets. With age, some of it is replaced by yellow bone marrow, which stores fat & does not produce blood cells
Inorganic salt storage
About 70% of the bone matrix consists of inorganic mineral salts. Loss of bone mineralization leads to osteoporosis
Fragility fracture
Occurs after a fall from less than standing height and signals low bone density
Prevention of fragility fractures
30 minutes of exercise per day
Get enough calcium and vitamin D
No smoking
Number of bones in body
206; some people have extra, some lack certain bones
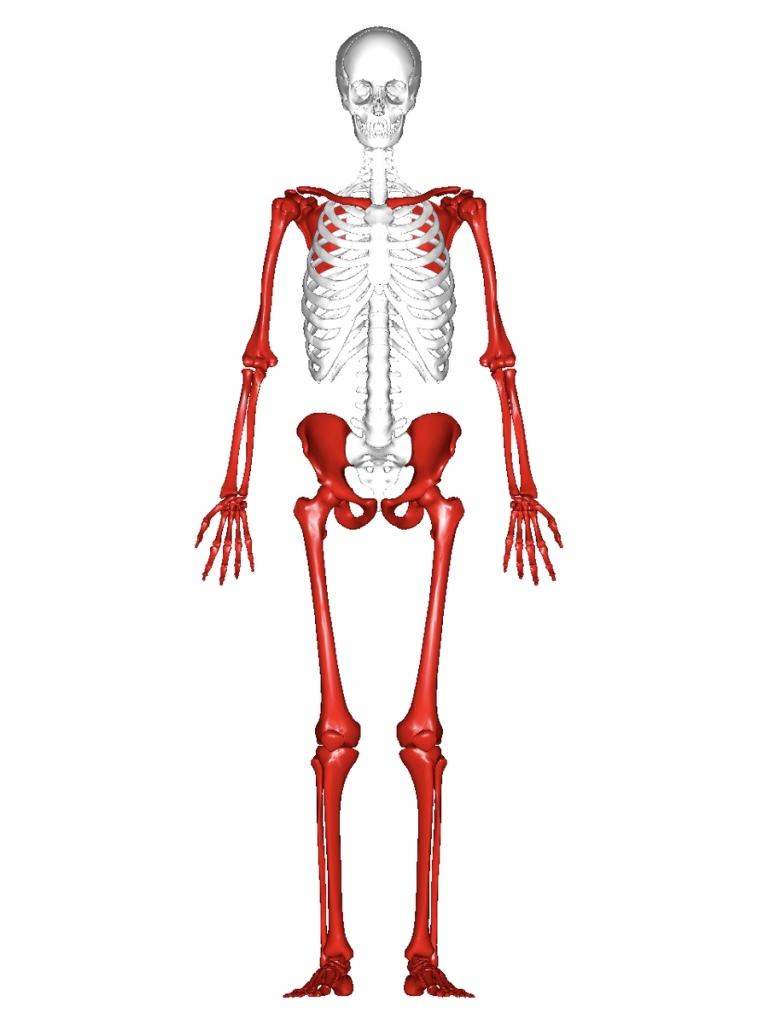
Divisions of the skeleton
Axial & Appendicular
Axial Skeleton
Consists of 80 bones
skull, middle ear bones, hyped bones, vertebral column, thoracic cage
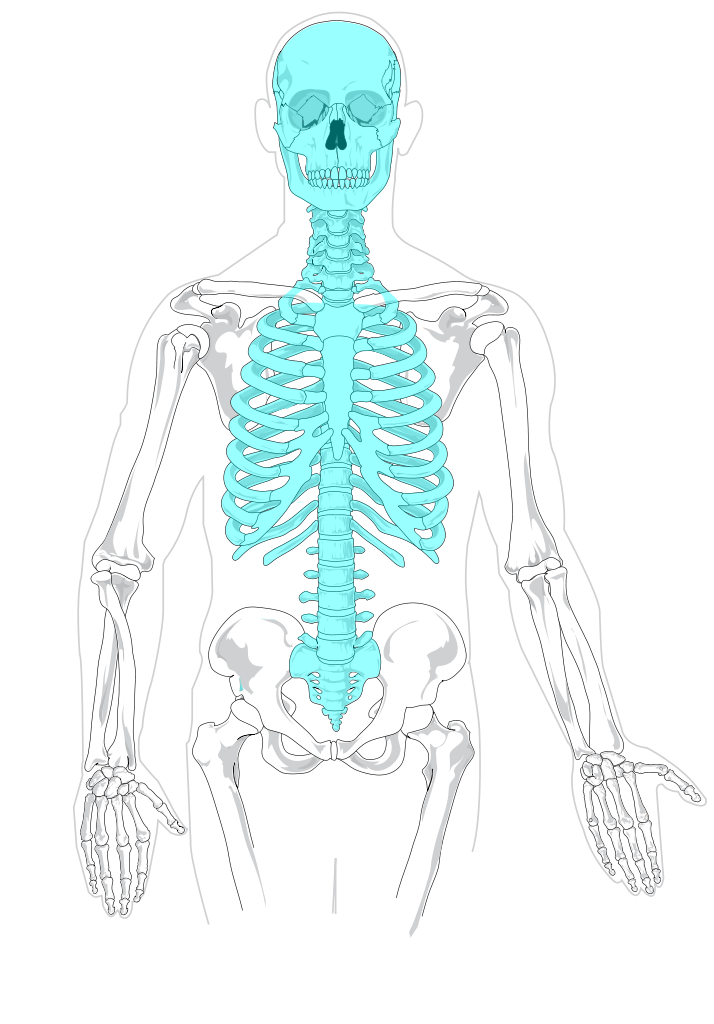
Appendicular Skeleton
126 bones
pectoral girdle, upper limbs, pelvic girdle, lower limbs
Skull
Typically composed of 22 bones. Cranium (8 bones) and facial skeleton (14 bones) make up the skull
cranium enclosed and protects the brain
facial skeleton forms face shape
Fontanels (soft spot of infantile skull)
Fibrous membranes that connect cranial bones where intramembranous ossification is incomplete.
Functions of fontanels
Allow the skull to compress during birth and provide space for the infant’s brain to grow and expand.
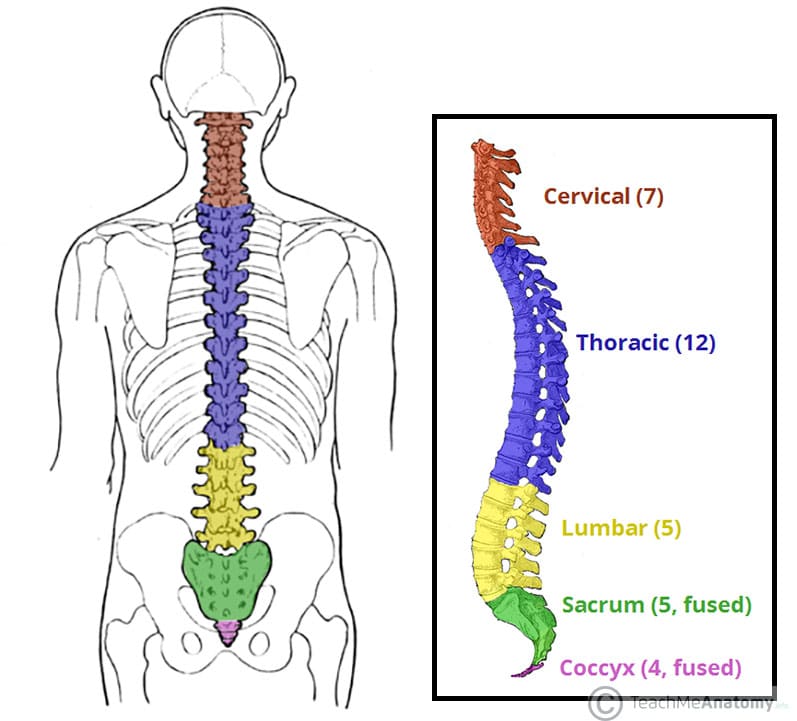
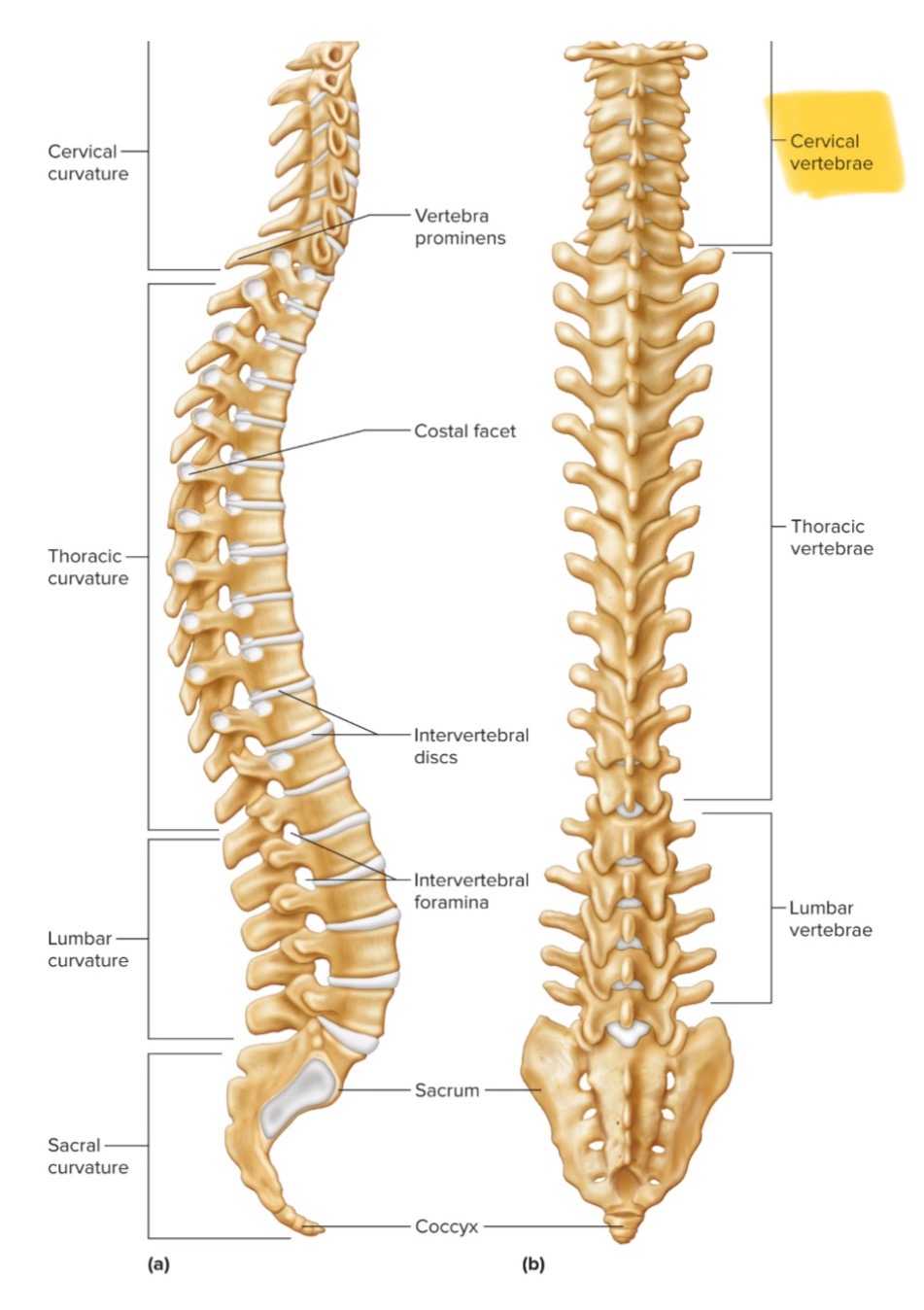
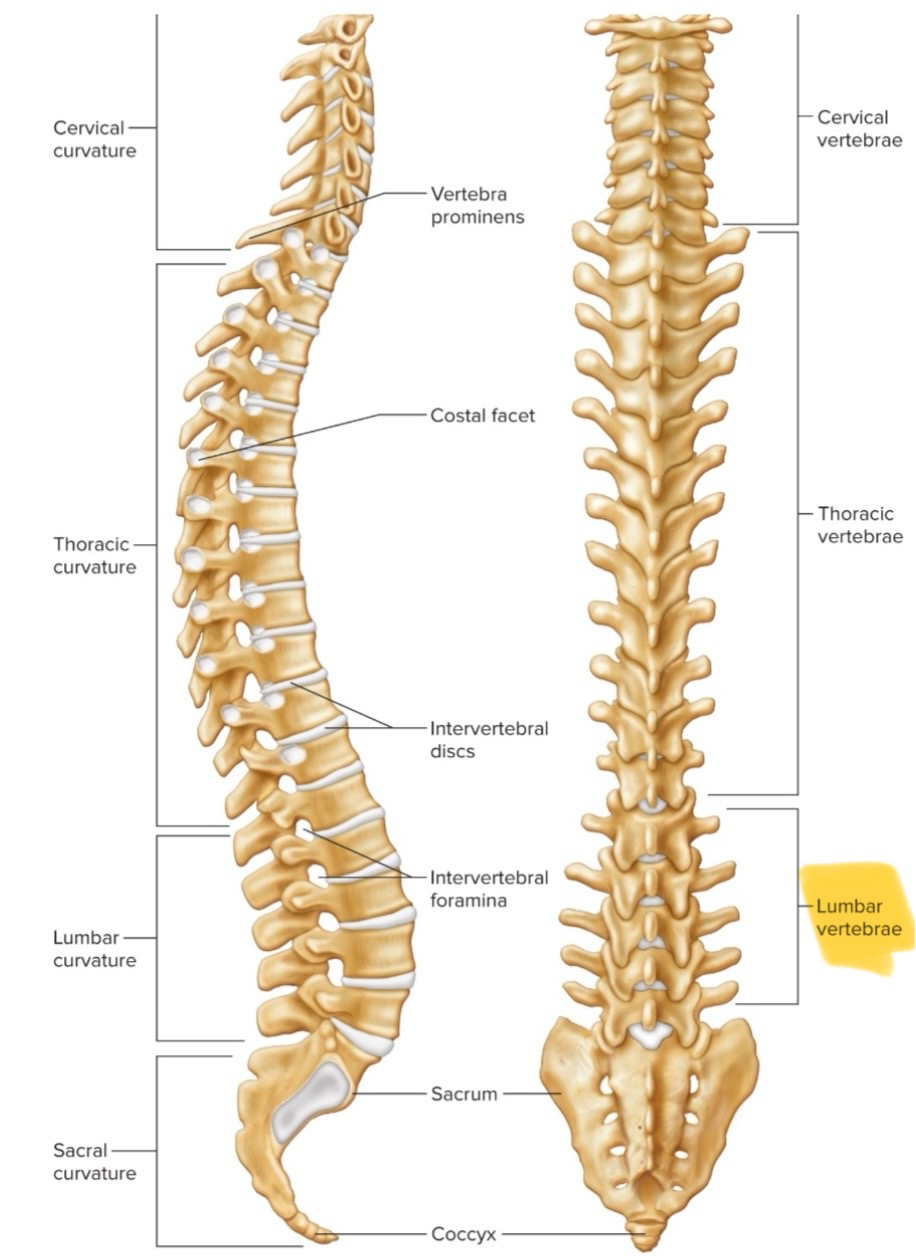
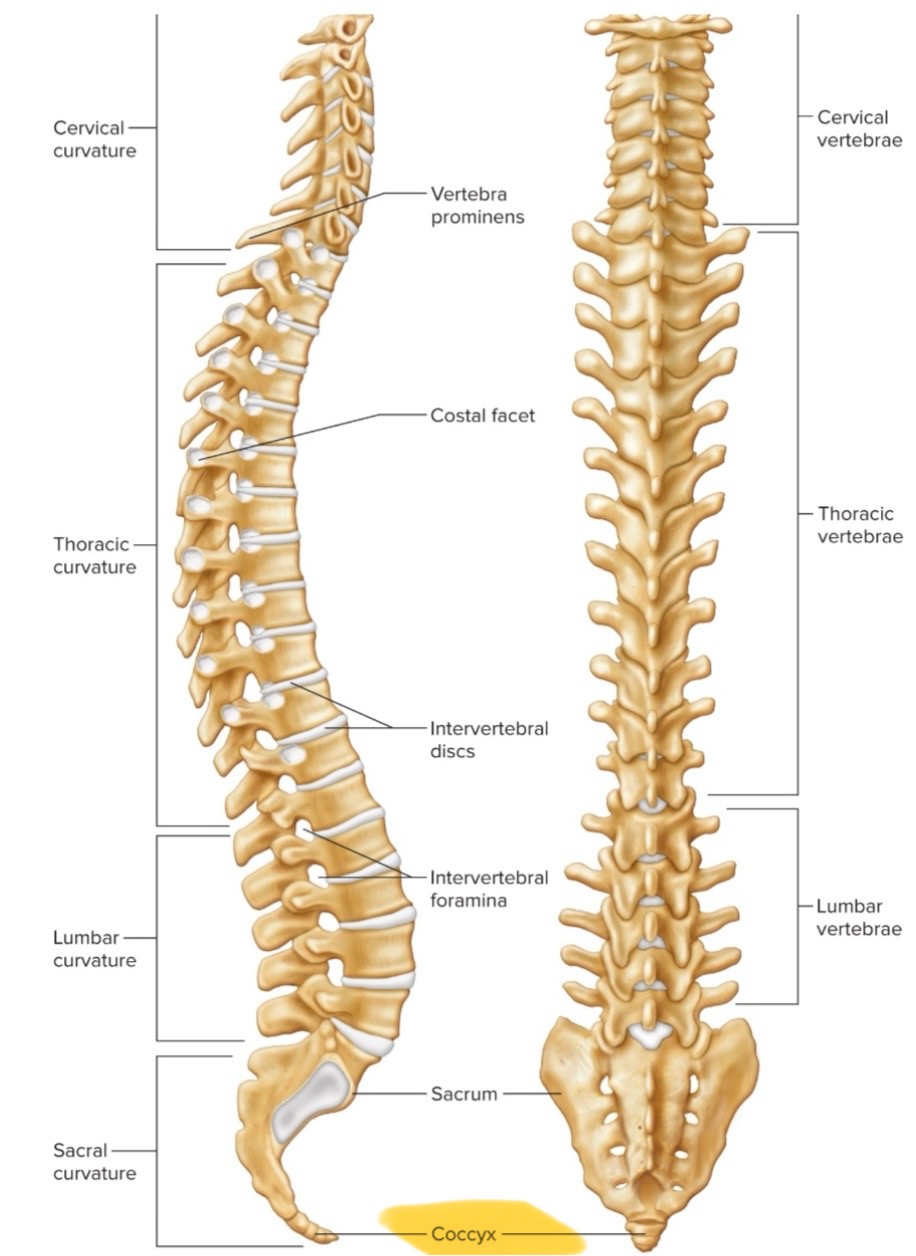
Vertebral Column
Forms vertical axis of skeleton. Consists of many vertebrae separated by cartilaginous intervertebral discs, and connected by ligaments. Supports head, trunk, and spinal cord.
33 separate bones in infant, 26 in adult
4 curvatures of vertebral column
Cervical (secondary, 7), Thoracic (primary, 12), Lumbar (secondary, 5), Sacral (primary, 5)
4 fused coccygeal vertebrae form coccyx

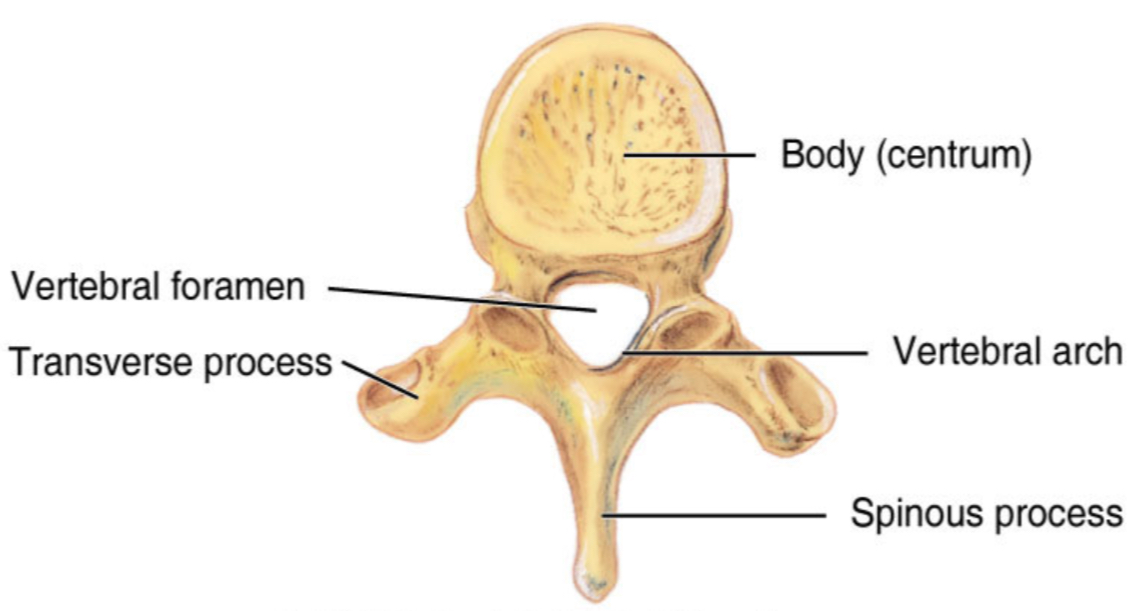
What does a typical vertebra contain?
Body, Pericles, laminae, spinous process, transverse process, vertebral foramen, facets, superior and inferior articular processes
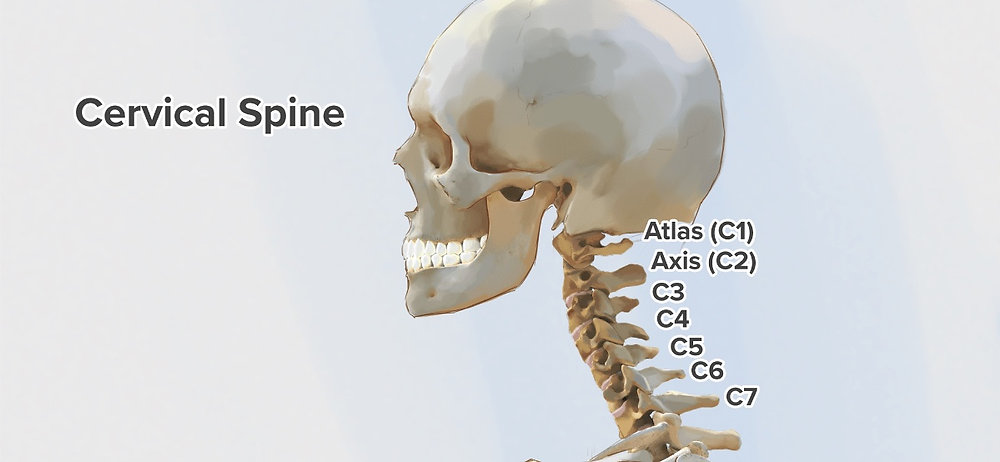
Cervical vertebra
There are 7 cervical vertebrae; they are the smallest, have transverse formamina, and bifid spinous processes on C2-C6. C7 is the vertebral prominens.
Thoracic vertebrae
There are 12 thoracic vertebrae in chest region. Larger than cervical vertebrae, articulate with ribs, long & pointed spinous process.
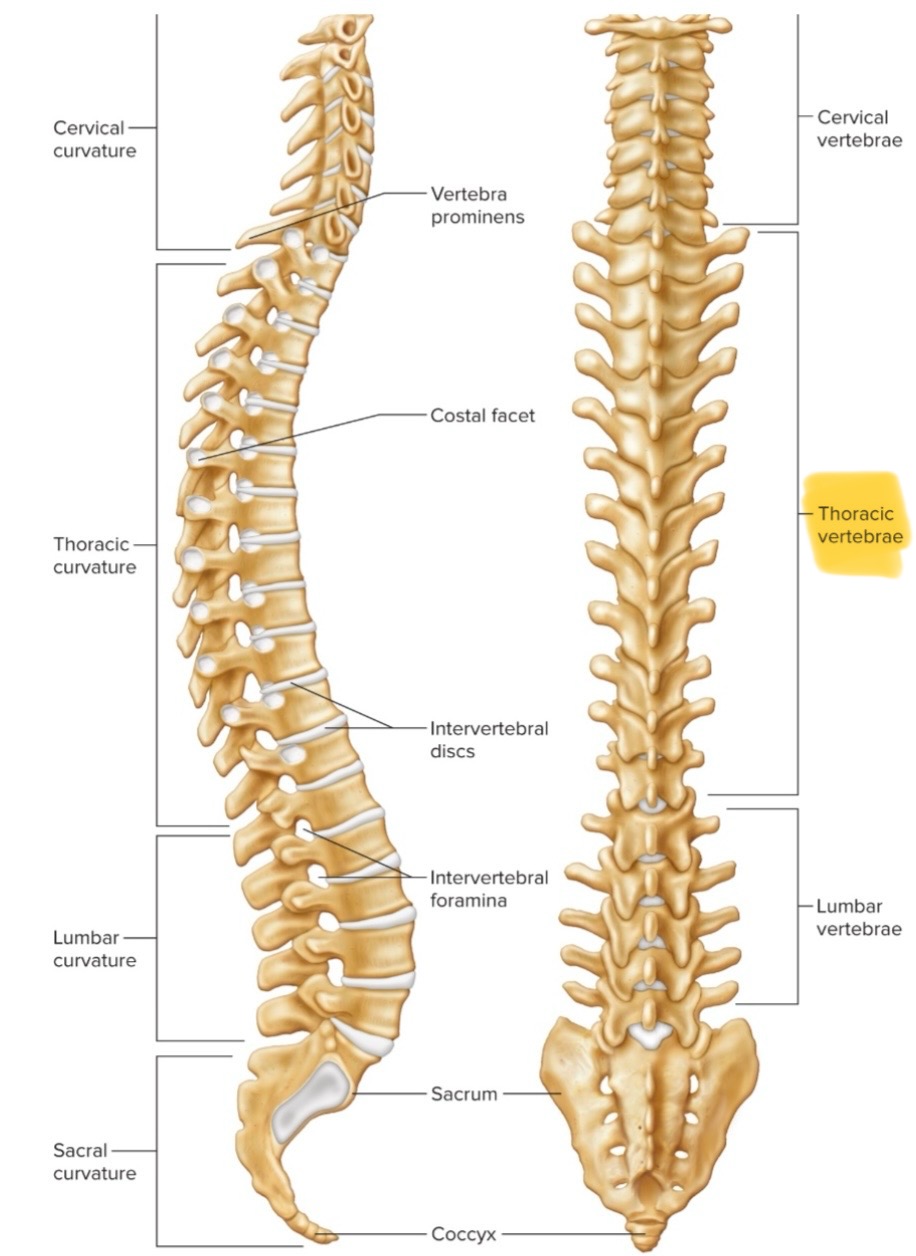
Lumbar vertebrae
There are 5 lumbar vertebrae in small of back. They have large bodies; consist of thick, short, nearly horizontal spinous processes, and are weight bearing
What are the roles of C1 (Atlas) and C2 (Axis)?
Atlas (C1): supports the head.
Axis (C2): allows the atlas (and head) to pivot around the dens.
Sacrum
Triangular structure, at base of vertebral column. Typically 5 fused vertebrae,
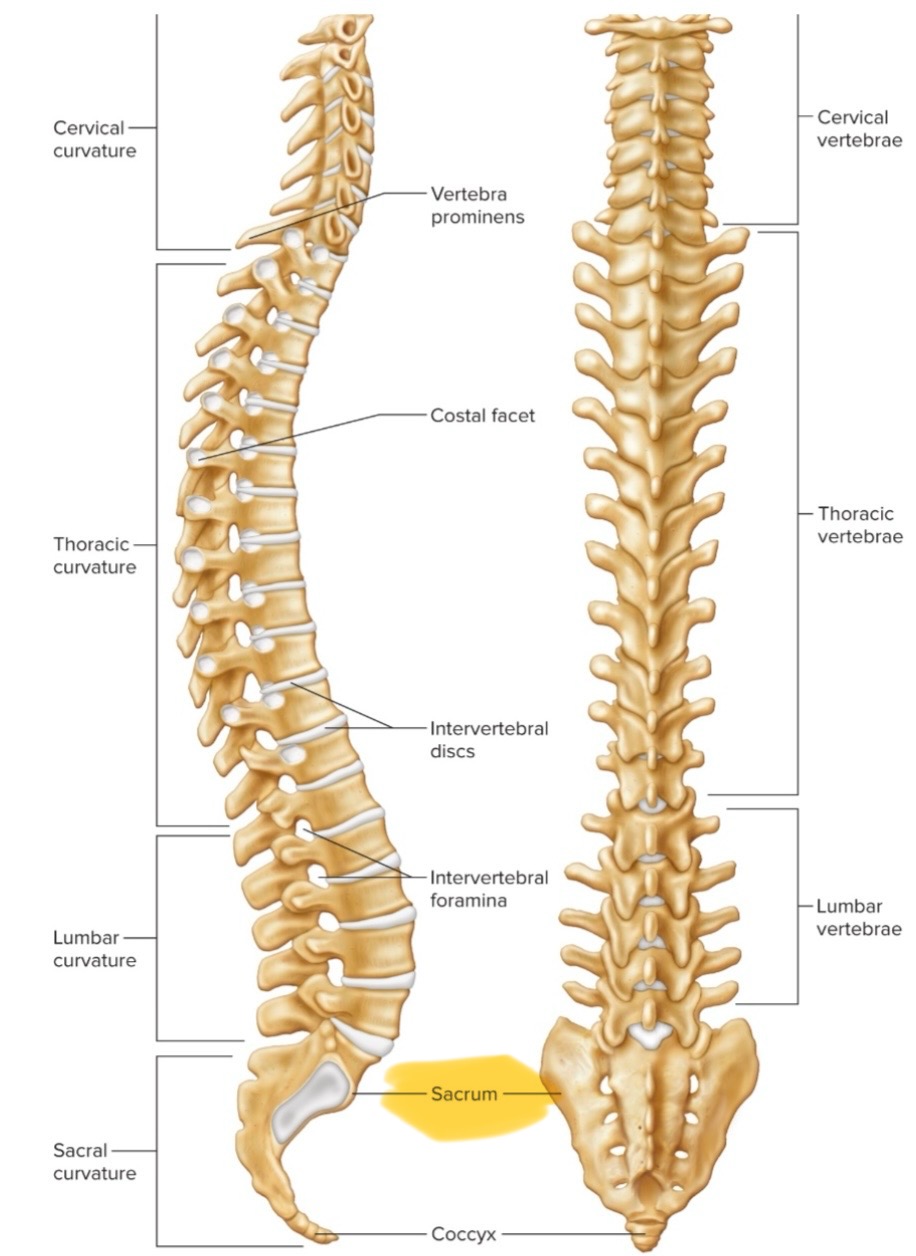
Coccyx
AKA tailbone. Usually consists of 4 fused vertebrae that typically fuse between ages 25 and 30.
Disorders of vertebral column
Herniated or ruptured disc, kyphosis, scoliosis, lordosis, compression fractures
Thoracic cage
Includes the ribs, thoracic vertebrae, sternum, and costal cartilages. It supports the shoulders and arms, protects organs in the chest and upper abdomen, and helps with breathing.
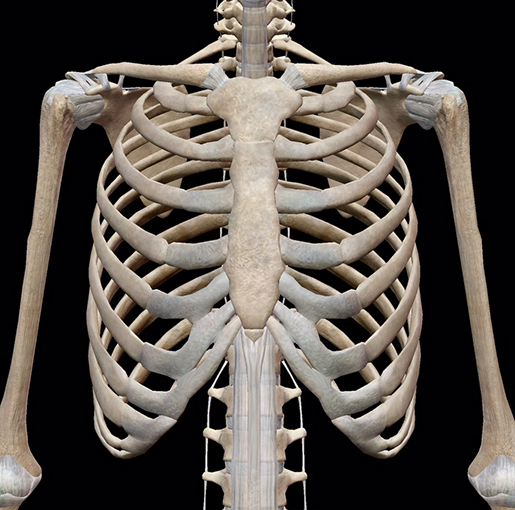
Ribs
Humans have 12 pairs of ribs
True ribs: first 7 pairs; join the sternum directly by their costal cartilages
False ribs: remaining 5 pairs.
vertebrochondral ribs- upper 3 pairs of false ribs
floating ribs- lower 2 pairs of false ribs.
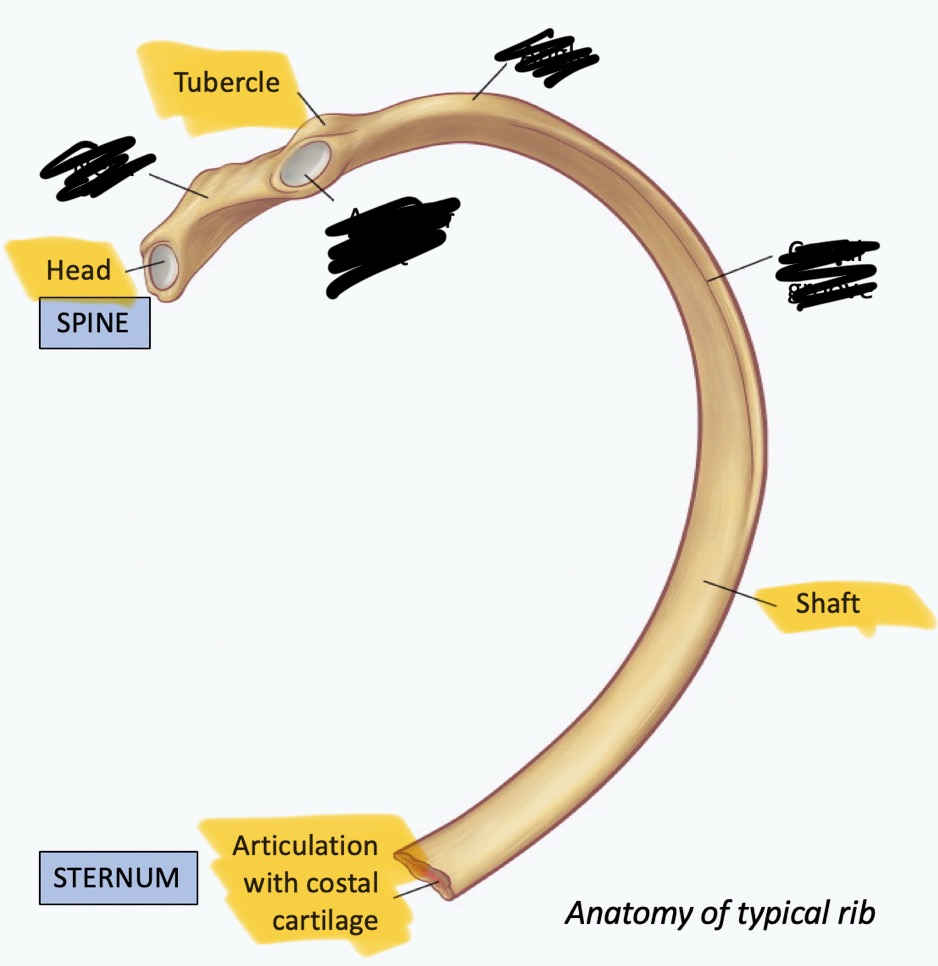
Structure of a rib
Shaft: main portion; long and slender
Head: posterior end; articulates with vertebrae
Tubercle: articulates with vertebra
Costal cartilage: hyaline cartilage; connects rib to sternum
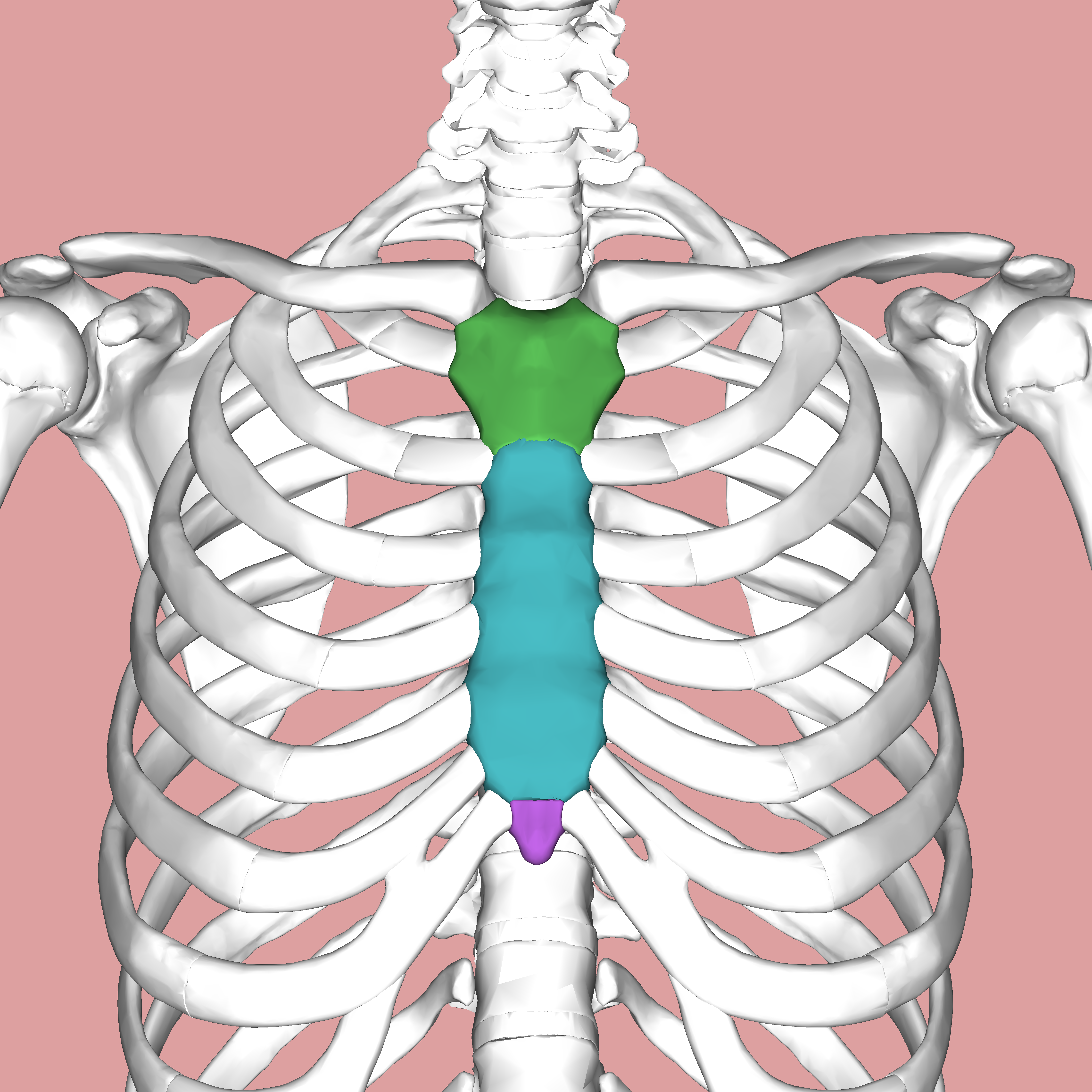
Sternum
AKA breastbone. Articulates with costal cartilages and clavicles. Has 3 parts:
Manubrium: upper part
Body: middle part
Xiphoid process: bottom part
Pectoral girdle
Consists of 2 clavicles (collarbones) and 2 scapulae (shoulder blades). Supports upper limbs
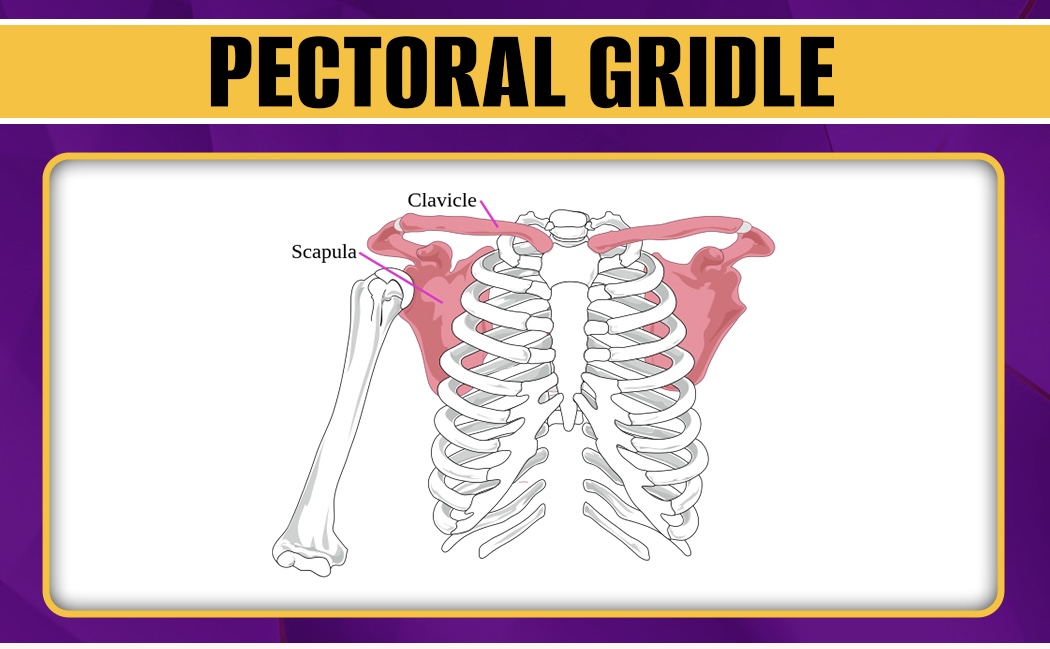
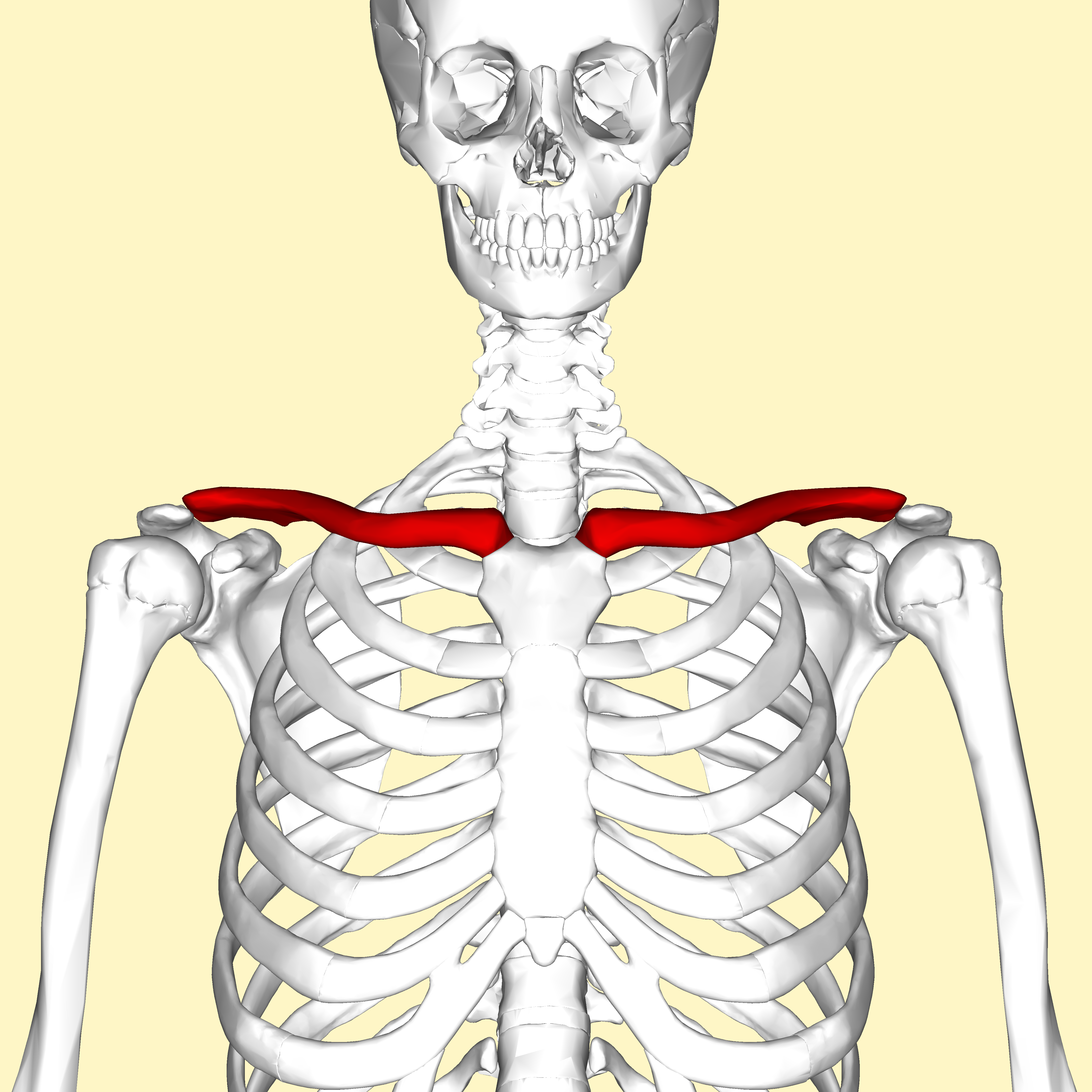
Clavicles
S-shaped bones that connect the manubrium to the scalpulae, keeps the shoulder blades in place while allowing them to move freely
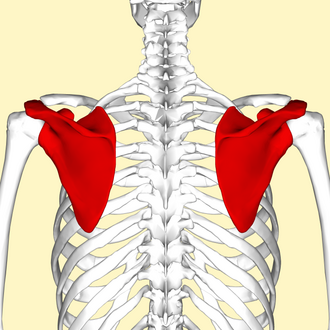
Scapulae
Includes the spine, supraspinous fossa, infraspinous fossa, acromion process, caracoid process, glenoid fossa (cavity) which helps form the shoulder joint
Upper limb
Framework of upper arm, forearm, hand. Includes the humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
Humerus
Only bone in the upper arm. Key parts include the head, anatomical & surgical necks, greater & lesser tubercles, deltoid tuberosity, capitulum (lateral condyle) and trochlea (medial condyle), lateral & medial epicondyles, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa.
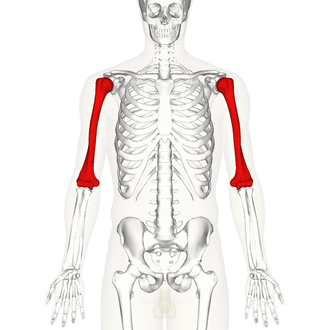
Radius
Lateral bone of the forearm, shorter than the ulnar. Located on thumb side of forearm. Key parts include: head, radial tuberosity, styloid process, and ulnar notch. It helps form the elbow and wrist joints.
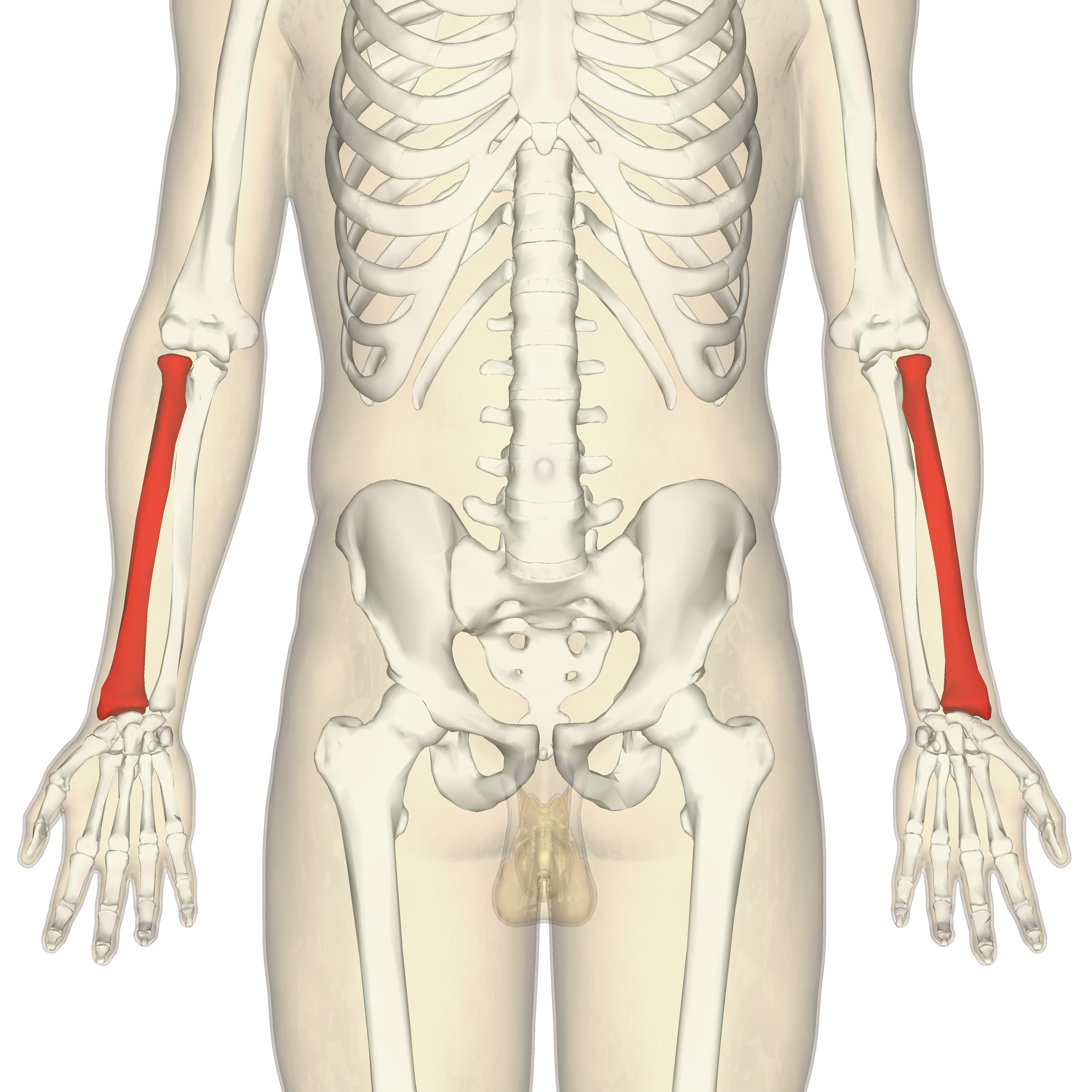
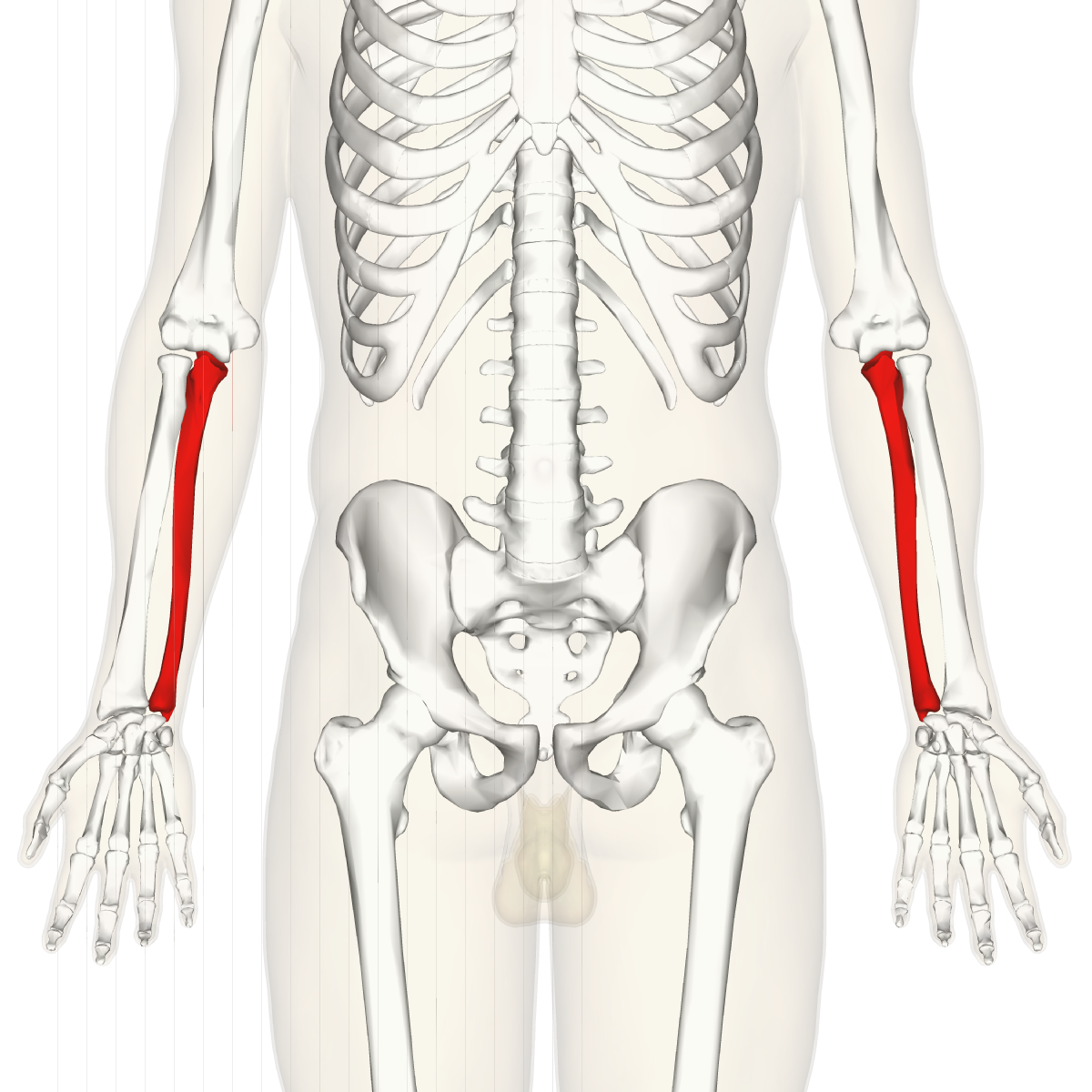
Ulna
Medial bone of the forearm. Includes the OLECRANON PROCESS which helps straighten the arm; aka “funny bone”. It helps form the elbow and supports forearm movement.
Hand
Made up of:
Carpal (wrist) bones (8): Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Hamate, Capitate, Trapezoid, Trapezium
Metacarpals (palm, 5)
Phalanges (fingers bones, 14): Proximal, Middle, Distal
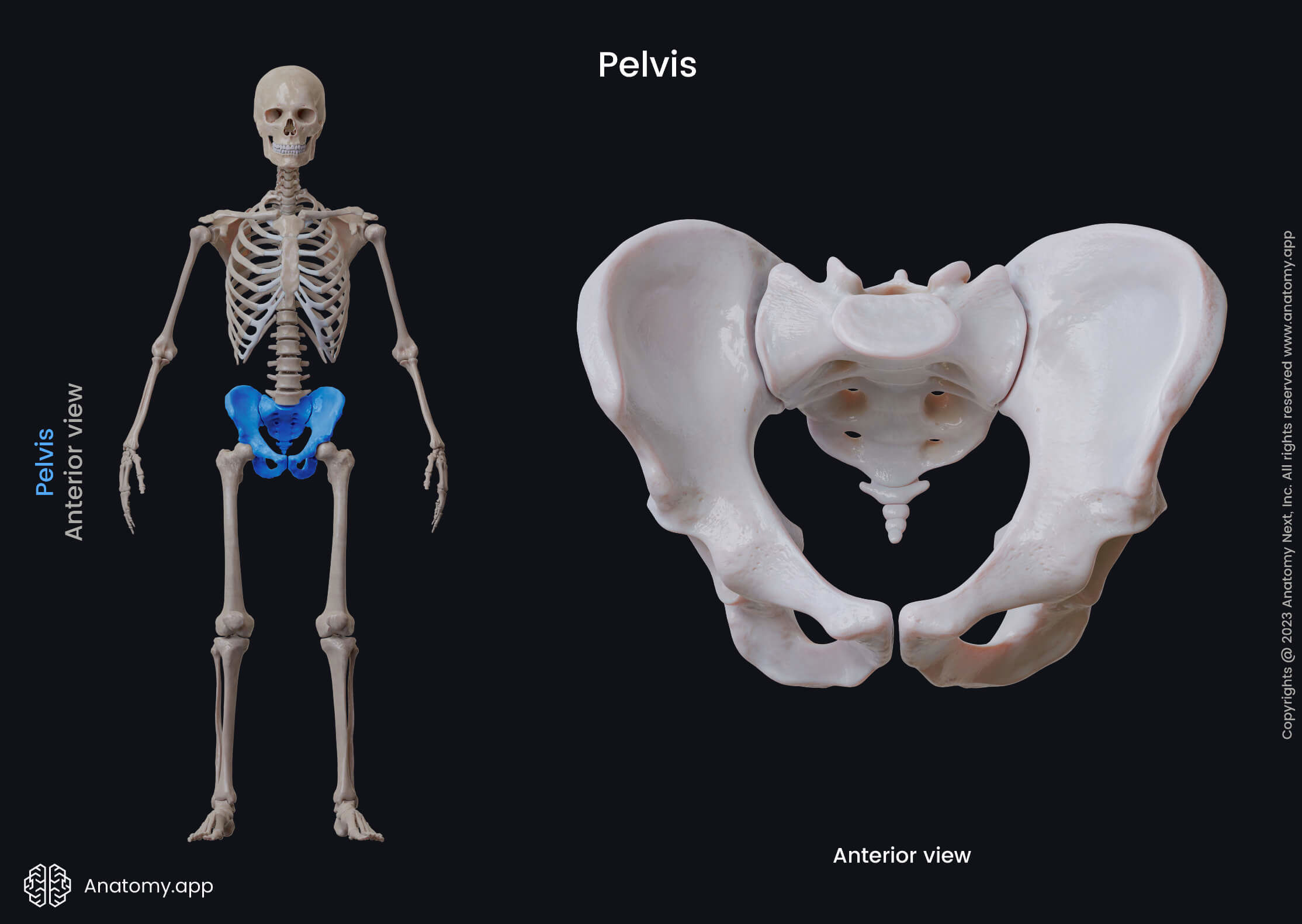
Pelvic girdle
Consists of 2 coxal (hip) bones. The pelvis = pelvic girdle + sacrum + coccyx.
Functions: supports the trunk, protects internal organs, transmits weight to lower limbs, and provides attachment for lower limbs.
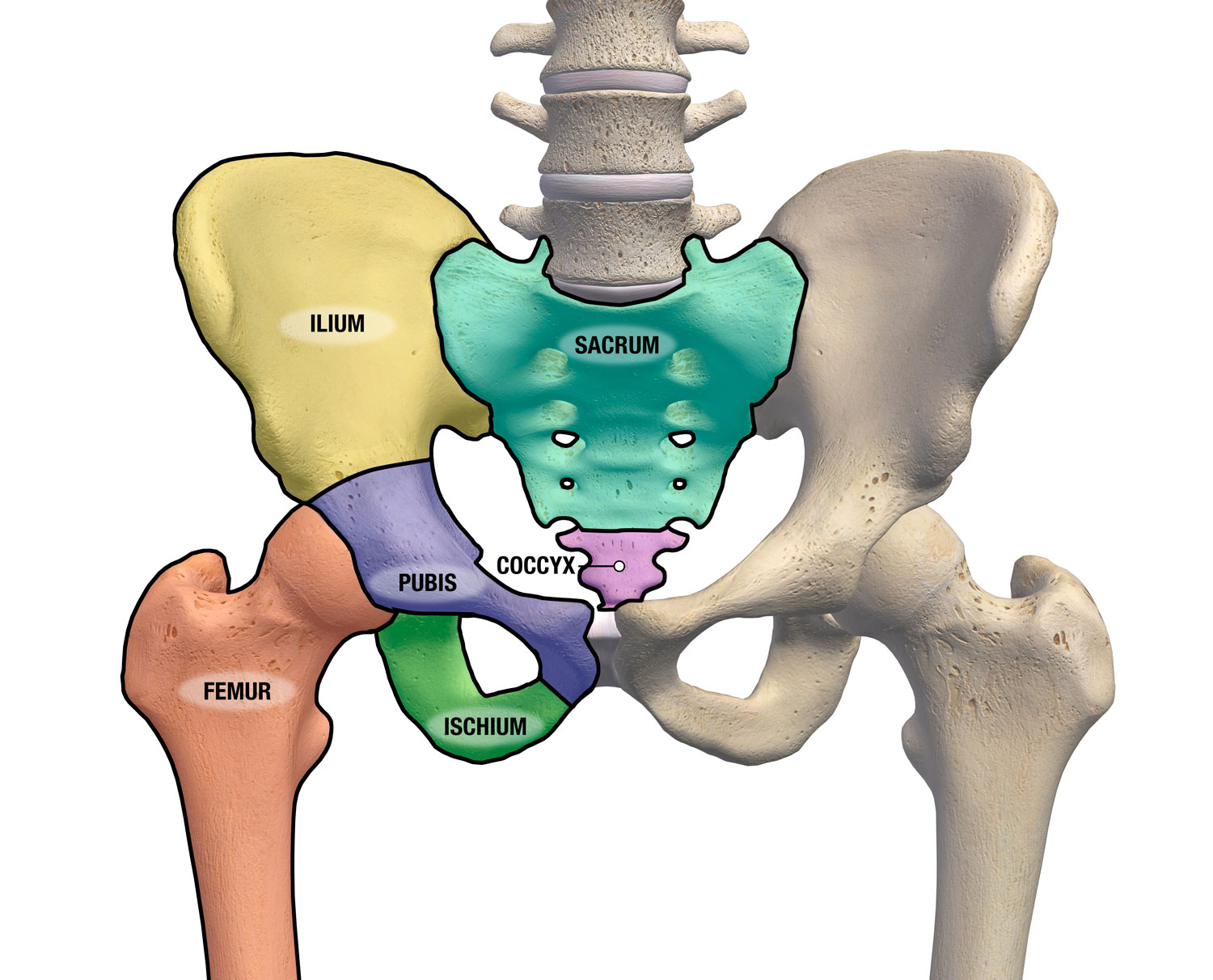
Hip bones
AKA coxal bones. Each hip bone consists of 3 fused bones:
Ilium (largest, top): Iliac crest, iliac spines, greater sciatic notch
Ischium (L-shaped, bottom): Supports weight while sitting, ischial spines, ischial tuberosity
Pubis (front): Pubic symphysis, pubic arch, acetabulum (for femur head), obturator foramen
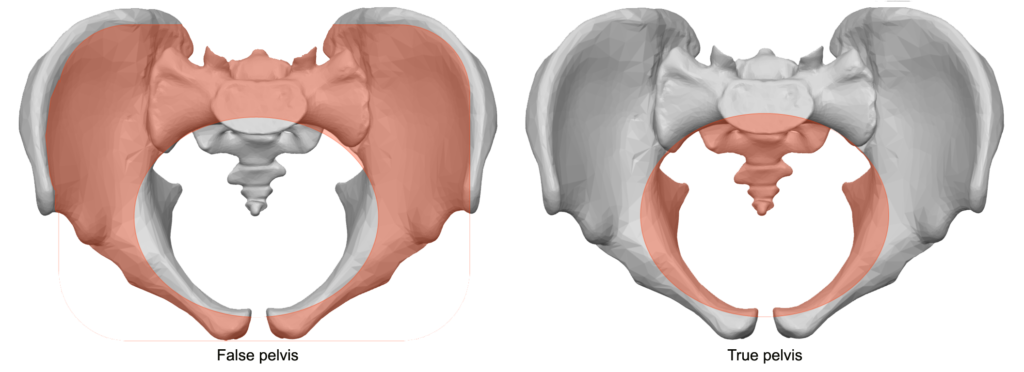
True Pelvis
(lower, lesser). Inferior to pelvis brim. Bounded by sacrum & coccyx (back), lower ilium, ischium, and pubis (sides/front); forms the lower pelvic cavity.
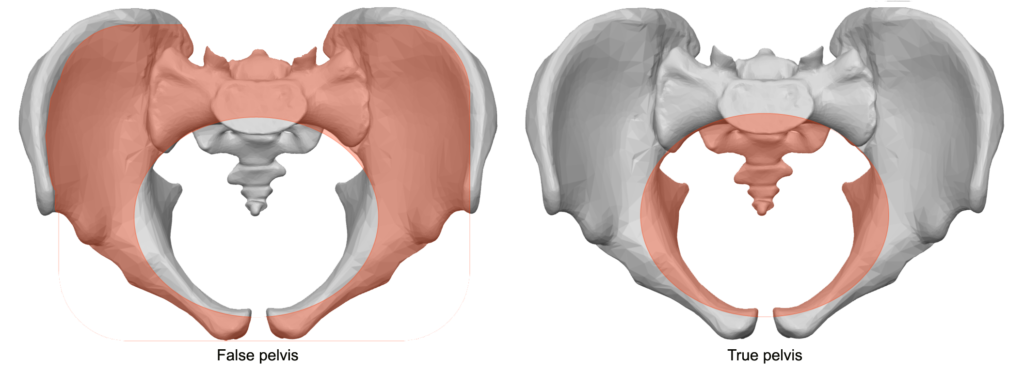
False Pelvis
(greater, upper). Above the pelvic brim; bounded by lumbar vertebrae (back), iliac bones (sides), abdominal wall (front); supports abdominal organs.
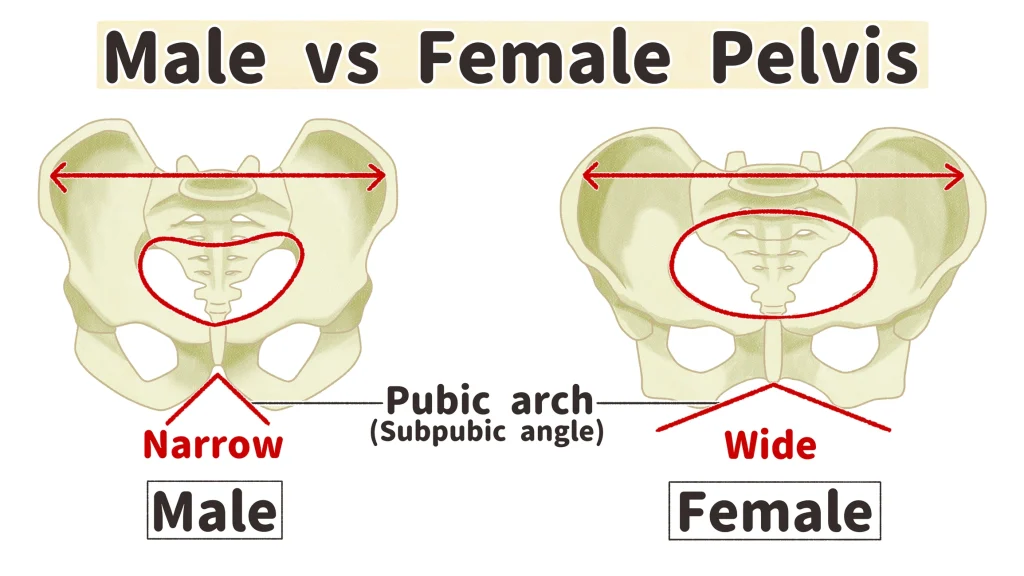
Main differences between the female and male pelvis
Female pelvis: Functions as a birth canal, iliac bones more flared, broader hips, wider pelvic cavity, greater pubic arch angle, more space between ischial spines/tuberosities, sacral curvature shorter and flatter.
Male pelvis: Heavier, less flared, narrower hips and pelvic cavity.
Lower limb
Forms framework of each thigh, leg, and foot. Includes the femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges.
Femur
AKA thigh bone. Longest bone of the body. Key parts include: head, fovea capitis, neck, greater and lesser trochanters, linea aspera, medial & lateral condyles, and medial & lateral epicondyles. It connects the hip to the knee and supports body weight.
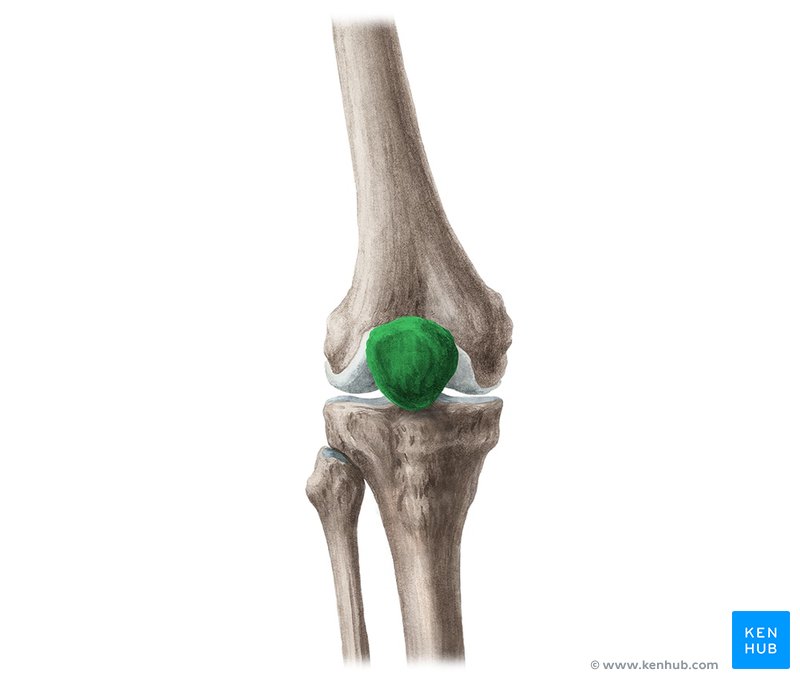
Patella
AKA kneecap. A flat sesamoid bone in the quadriceps tendon, located on the front of the knee. It helps with lever action during lower limb movement.
Tibia
AKA shin bone. The larger leg bone, medial to fibula. Key parts: proximal condyles, tibial tuberosity (for patellar ligament), anterior crest, and medial malleolus.
Fibula
A long, slender bone on the lateral side of the tibia. Key parts: head and lateral malleolus. It is non-weight bearing and provides muscle attachment.
Foot
Tarsals (ankle, 7): Calcaneus, Talus, Navicular, Cuboid, Lateral, Intermediate, Medial cuneiforms
Metatarsals (palm of foot, 5) make up the arch of the foot
Phalanges (toes, 14): Proximal, Middle, Distal
Calcaneus: large heel bone
Talus: lies inferior to the tibia, and allows the foot to pivot up and down
Life span changes
Decrease in height begins at about age 30
Calcium levels fall
Bones become brittle and more prone to fracture
Hip & Vertebral compression fractures become common
Low blood calcium
The parathyroid gland releases parathyroid hormone (PTH), which breaks down bone to release calcium, restoring normal blood calcium levels.
High blood calcium
The thyroid gland releases calcitonin, which stimulates osteoblasts to deposit calcium in bones, lowering blood calcium to normal.