P.E - A0S 1 - Chapter 1
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hard
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Functions Of Skeletal System
Body movement
Framework
Protection
Mineral Storage
Production of red blood cells
Type Of Bone Tissue
Compact bone, Cancellous bone
Hemoglobin
Protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen around the body
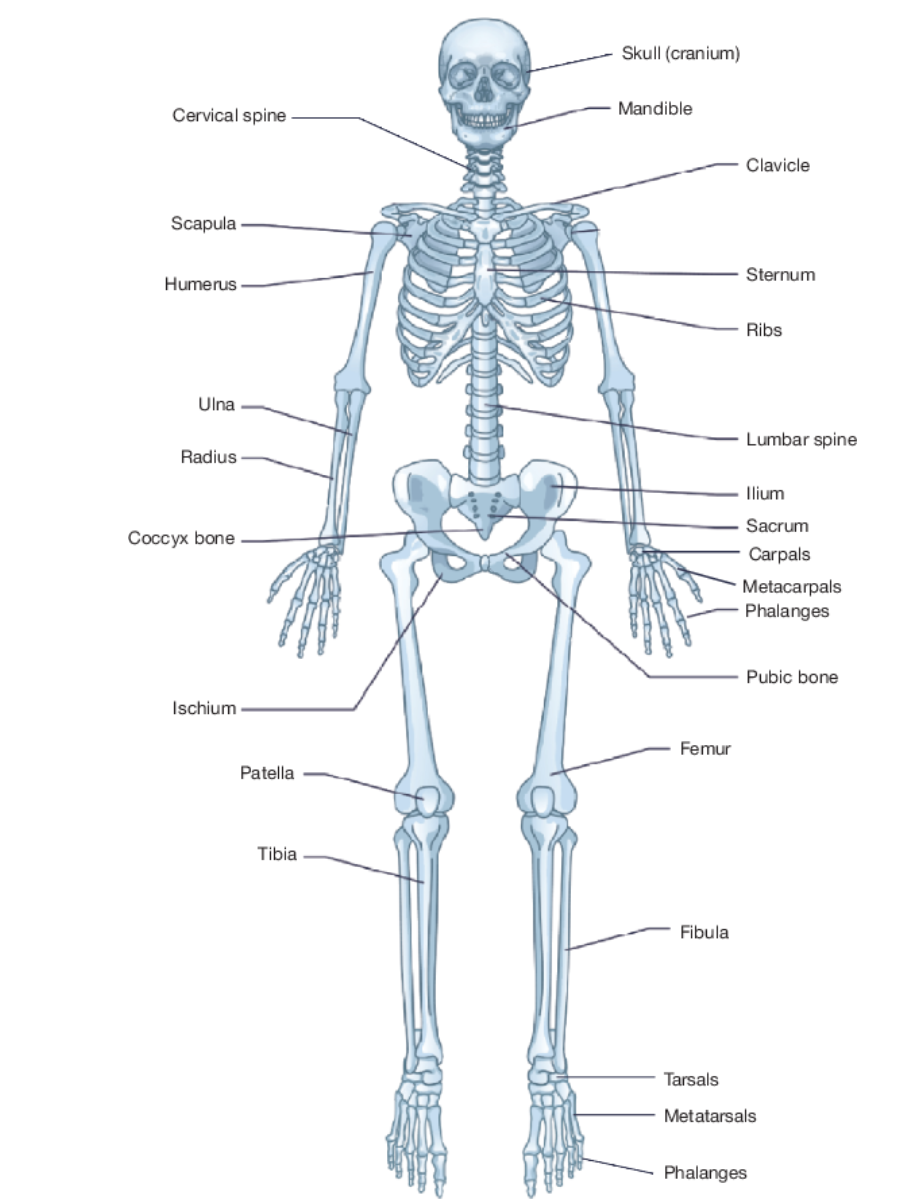
Bones in the body
Types of bones
Short bones (cubical bones)
Long bones (bones longer than their width)
Sesamoid bones (Small bones developed around tendons in some joints)
Irregular bones (no specific structure)
Parts of vertebrae
Cervical (supports the head and neck) - 7 bones
Thoracic (supports ribcage and vertebral column) - 12 bones
Sacrum (pelvis bones) - 5 bones
Coccyx (Bottom of vertebrae - tailbone) - 4 bones
Lumbar (Supports the overarching weight of the body) - 5 bones
Epiphyseal plates
Growth plates/centers for bone growth
Classification of joints (3 types)
Fibrous (immovable joints eg.skull)
Cartilaginous (slightly moveable joints eg. vertebrae)
Synovial (freely moveable joints)
Cartilage
Connective tissue at end of joints that absorbs impact preventing damage to occur onto bones.
Ligament
Holds two or more bones or cartilage (only bones)
Tendons
Attaches muscle to bones
Synovial Joints
Freely moveable joint + joint capsule
Ball Socket Joint
Allows a wide range of motion
Hinge joint
Allows movement in only one direction
Pivot joint
Where one bone rotates about another
Gliding joint
Only allows gliding or sliding movements
Flexion
Decrease in angle or joint
Extension
Opening up the angle of the joint
Abduction
Movement away from the body
Adduction
Movement of a limb coming back to the midline of the body
Circumduction
Movement of the end of the bone in a circular motion
Supination
Rotation of the hand so that the thumb moves away from the body.
foot rolling outward
Dorsi flexion
Lifting up ankle, closer to leg
Plantar flexion
Pushing toes to the floor, pushing foot away from leg
Voluntary Control
Having conscious control upon the muscle
3 muscle types
Smooth, Cardiac, Skeletal
Smooth Muscle
In hollow organs, and are involuntarily controlled - eg. intestinal walls in stomach
Cardiac muscles
Muscles found in the heart
Skeletal muscle
Muscle that allows the body to move (voluntary) - eg. bicep, quadriceps
Common features of muscles
Nervous control (voluntarily moved)
Excitability
Contractility
Extensibility
Elasticity
Atrophy - muscles decrease in size upon illness or injury
Hypertrophy
Fusiform muscles
Run across tendon, and produce low force
Types of pennate muscles
Unipennate - Fibres only on one side of tendon
Bipennate - Fibres on both sides of the tendon
Multipennate - Fibres branch out from several tendons (most force generated)
Epimysium
Layer of connective tissue
Fasiculus
Bundle of muscle fibres
Endomysium
Connective tissue that binds the muscle fibers together
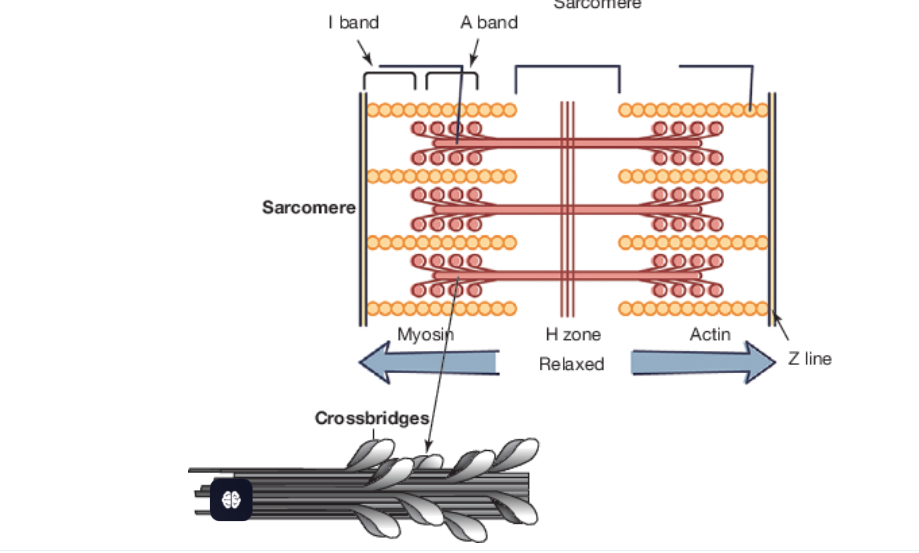
Sacromere
Smallest unit of muscle contraction
Sliding filament theory
Actin (thin filaments) is pulled by mysoin (thick filament), and causes a contraction in the sacromere.
Muscle Fiber Types
Type 1, Type 2A, Type 2B
Type 1 muscle fibres
Slow twitch fibres
Are for longer duration and aerobic work
Type 2A
Fast twitch fibres
For anaerobic and aerobic parts
Type 2B
Very fast-twitch
For short duration of aerobic work
Motor Unit
One motor neuron and the muscle fibre it stimulates
“All or nothing” principle
If the stimulation is less than threshold, no action is taken, but if stimulation meets the threshold then an action is taken. Intensity is dependent on the frequency of the signal.
Size principle / Henneman principle
Any action irrelevant of intensity starts from small motor units, and then progresses towards larger motor units if required.
Types of muscular contractions
Concentric, Eccentric, Isometric
Concentric contraction
Muscle shortens, causing joint movement to induce in contraction
Eccentric contraction
Muscle opens up, and returns to its original state, becoming on par with gravity.
Isometric Force
Muscle length remains unchanged, but generates force (highest of any contraction)
Agonist
Prime muscle mover
Antagonist
The muscle that relaxes and allows the opposite muscle to engage.
Synergist
Muscle that assists the agonist
e.g. tricep during pushuip
Stabiliser
Group of muscles that stabiles the joint during the exercise.
e.g. rotator cuff, trapezius (shoudler)
Reciprocal Inhibition
When one muscle engages in the movement, while the other relaxes.
Third Class lever
Force is located between axis or resistance of load to be moved.
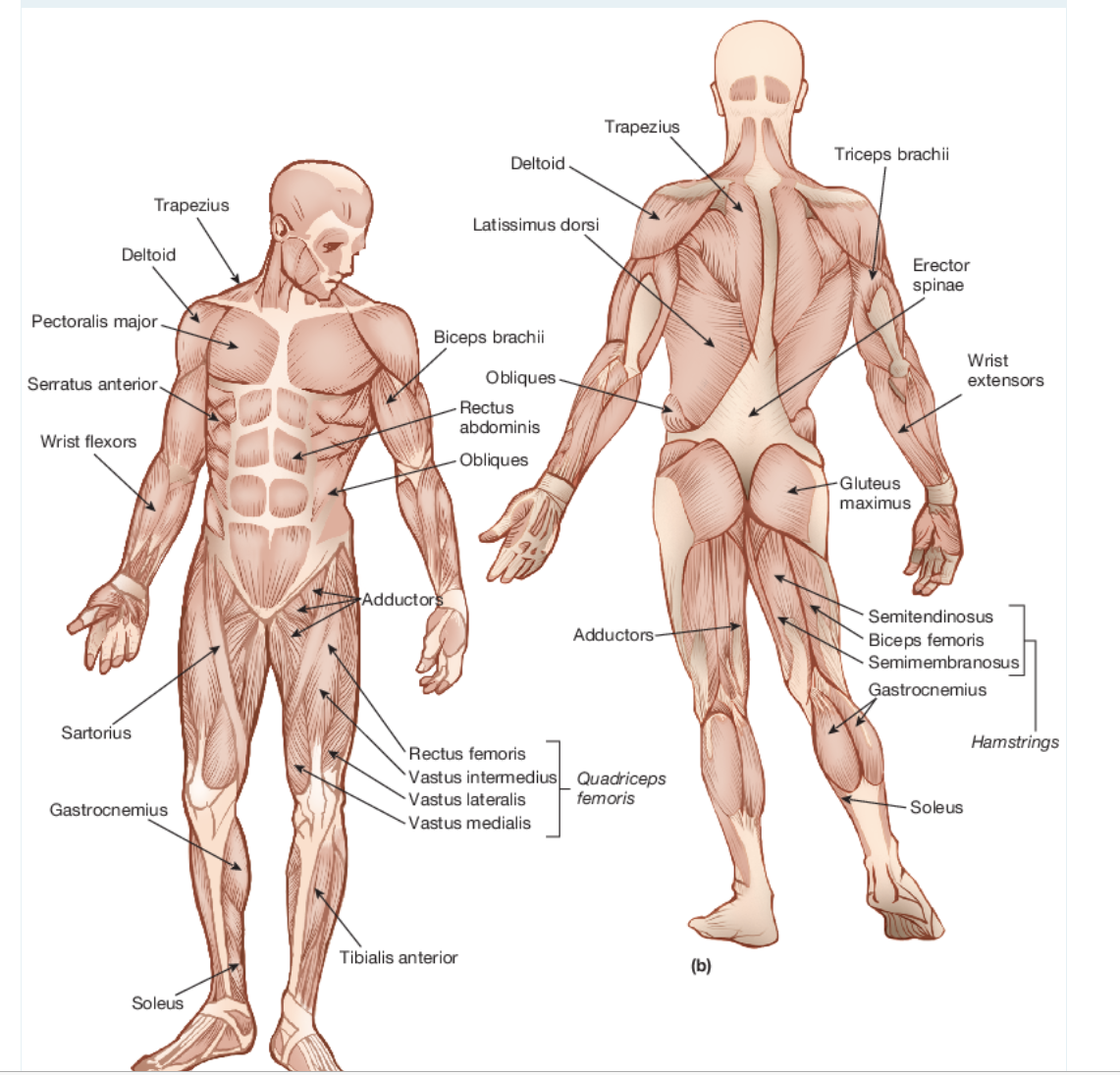
Main Muscles Of The Body
Coats ends of bones in synovial joints
Hyaline Cartilage
Seperate the vertebrae of the spine
Disc Cartilage
Attach to the sternum via cartilage
Ribs
Hard part of the ear and the tip of the nose
Cartilage
Types of synovial joints
Gliding, ball and socket, hinge, pivot, saddle joint, condyloid joint
Why are third class levers made in the body
To amplify speed
Examples of third class levers
Rackets, hockey stick, cricket bat
Sliding Filament Thoery
In the presence of calcium, the actin attaches to the myosin
The myosin then pulls onto the actin and the ‘H’ zone disappears, because the myosin is stronger than the actin
Then the sarcomere contracts. This causes a translation effect upon all sarcomeres within the muscle, hence causing the muscle to contract.