OMIS 327
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Quantitative Analysis
scientific approach to managerial decision making
Business analytics
data driven approach to decision making that allows companies to make better decisions.
3 categories of business analytics
Descriptive - study and consolidation of historical data for a business and industry to measure how it is performing
Predictive - aimed at forecasting future outcomes based on patterns in the past data
Prescriptive - involves the use of optimization methods to provide new and better ways to operate
Quantitative Analysis Approach (QAA)-
scientific approach to managerial decision making in which raw data are processed and manipulated to produce meaningful information.
Steps to QAA -
Develop a clear, concise statement of the problem
Must be specific and measurable objectives
Develop a model (model = mathematical representation of a situation)
Model = realistic, solvable, and understandable mathematical representations of a situation.
Controllable inputs = decision variables
Uncontrollable inputs = pareteres; things outside of their control.
Deterministic models = a of the values used in the model are known with complete certainty
Probabilistic models = variables used in the model are estimates based on probabilities.
Acquiring input data
GIGO Rule - input data must be accurate.
Can come from a variety of sources
Developing a solution
Manipulating the model to arrive at the best (optimal solution)
Ex: solving equations, trial and error, complete enumeration (trying all [possible values.)
Testing the solution
Both input data and the model should be tested for accuracy and completeness before analysis and implementation.
Analyzing the results and sensitivity analysis
Determining the implications of of the solution
Sensitivity analysis - postoptimality analysis determines how much the results will change if the model or input data changes.
Implementing the results
Incorporates the solution into the company
Change takes place over time, so even successful implementations must be monitored to determine if modifications are necessary
Mathematical model-
set of mathematical relationships, expressed in equations and inequalities
Variable
a measurable quantity that may vary or is subject to change, can be controllable or uncontrollable
Parameter
a measurable quantity that is inherent in the problem
Profit
= revenue - (fixed cost + variable cost)
= (selling price per unit) (number of units sold)
= sX - [f + vX]
S = selling price price per unit
f = fixed cost
v = variable cost per unit
X = number of units sold
Advantages of mathematical modeling
Models can accurately represent reality
Models can help a decision maker formulate problems
Models can give us insight and information
Models can save time and money in decision making and problem solving
A model may be the only way to solve some large or complex problems in a timely fashion
A model can be used to communicate problems and solutions to others
Possible problems in quantitative analysis approach
Defining the problem
Conflicting viewpoints
Impact on other departments
Beginning assumptions
Solutions outdated
Developing a model
Acquiring input data
Developing a solution
Testing the solution
Analyzing teh results
6 steps in decision making
Clearly define the problem at hand
List the possible alternatives
Identify the possible outcomes or states of nature
List the payoff (typically profit) of each combination of alternatives and outcomes
Select one of the mathematical decision theory models
Apply the model and make your decision
Types of decision making environments
Decision making under certainty - decision maker knows with certainty the consequences of every alternative or decision choice
Decision making under uncertainty - the decision maker does not know the probabilities of the various outcomes
Decision making under risk - there are several possible outcomes for each alternative, and the decision maker knows the probability of occurrence of each outcome.
Decision making under uncertainty criteria
maximax - find maximum max
maximin - find the maximum of all minimum
minimax regret - (calculated by column vertically not horizontally by row)
Then pick smallest minimax by row (want the least regret)
difference between the optimal profit and the actual payoff for a decision
Decision making under risk criteria
Selecting the alternative with the highest expected monetary value

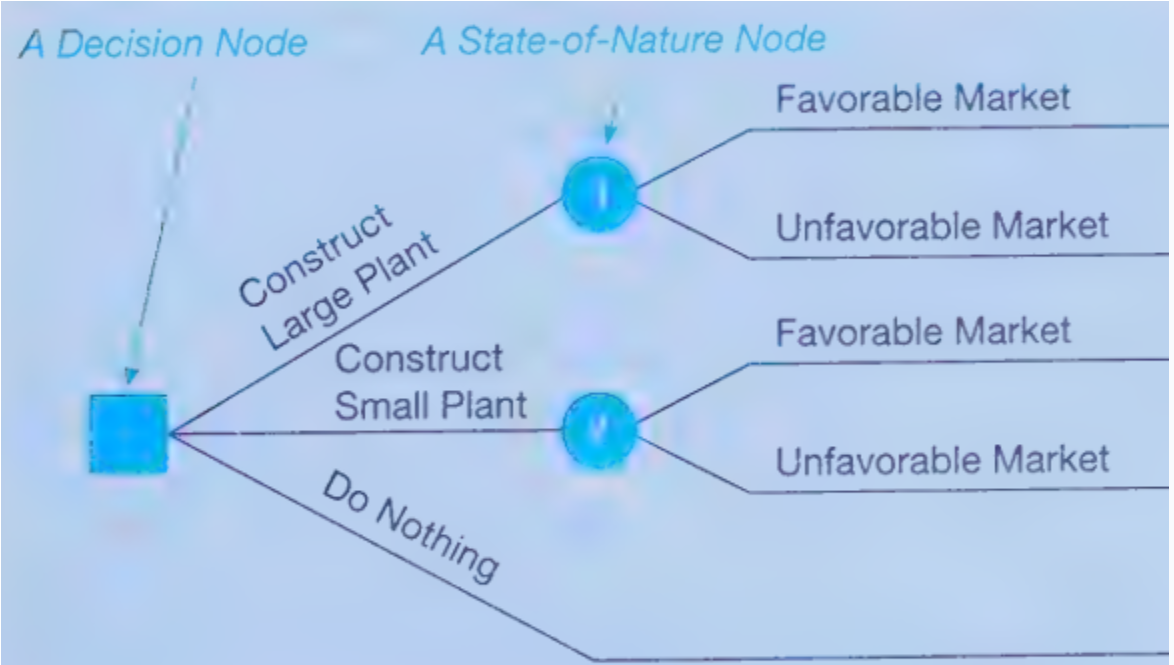
5 Steps of Decision Tree Analysis
Define the problem
Structure or draw the decision tree
Assign probabilities to the states of nature
Estimate payoffs for each possible combination of alternatives of nature
Solve the problem by compound EMVs for each state of nature node. This is done by working backwards, that is, starting at the right of the tree and working back to the decision nodes on the left. Also at each decision node, the alternative with the best EMV is selected.
All decision trees contain
Decision nodes - one of several alternatives may be chosen
Decision points
State of nature nodes - out of which one state of nature will occur
State of nature points
Expected monetary value (EMV)
long run average value of that decision. The sum of possible payoffs of the alternative, each weighted by the probability of that payoff occurring
EMV (alternative i)
= ΣXiP(Xi)
Xi = payoff for the alternative in state of nature i
P(Xi) = probability of achieving payoff Xi (i.e., probability of state of nature i)
Σ = summation symbol
Expected value with perfect information (EVwPI) =
Σ(Best payoff in state of nature 7 i) (probability of state of nature 7 i)
EPVI
= expected value of perfect information
EVwPI — Best EMV
Expected value of sample information (EVSI)
increase in expected value resulting from the sampling information.
= (EV with SI + cost) — (EV without SI)
Efficiency of sample information =
(EVSI/ EVPI)100%
Business Analytics
a data driven approach to decision making
Profit Function (px) =
revenue - total cost
Expected opportunity loss (EOL)
Σ(opportunity loss)*(probability)
Decision alternatives
different possible strategies the decision maker can employ
States of nature
refer to future events, not under the control of the decision maker, which may occur.
States of nature should be defined so that they are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive
Payoff
consequence resulting from a specific combination of a decision alternative and a state of nature
Linear programming (LP) is a widely used
mathematical modeling technique designed to help managers in planning and decision making relative to resource allocation.
Requirements of Linear programming
Problems seek to maximize or minimize an objective
Constraints limit the degree to which the objective can be obtained
There must be alternatives available
Mathematical relationships are linear
Properties of linear programs
One objective function
One or more constraints
Alternative courses of action
Objective function and constraints are linear—proportionality and divisibility
Certainty
Divisibility
Nonnegative variables
The steps in formulating a linear program follow:
Completely understand the managerial problem being faced.
Identify the objective and the constraints.
Define the decision variables.
Use the decision variables to write mathematical expressions for the objective function and the constraints.
Slack
(Amount of resource available) — (Amount of resource used)
Surplus
(Actual amount) — (Minimum amount)
Maximax (optimistic) criteria
find the maximum payoff for each alternative, pick the maximum out of the list of maximum
Locate the maximum payoff for each alternative
Select the alternative with the maximum number
When there are several possible states of nature and
the probabilities associated with each possible state are known
Most popular method - choose the alternative with the highest expected monetary value (EMV) similar to expected value
For each alternative the emv is calculated by

EMV definition
( Expected Monetary Value) A higher, positive EMV signifies a more profitable, lower-risk decision or investment.
Minimax regret
Best payoff in each state – (x individual payoff of alternative)
(calculated by column vertically not horizontally by row)
Then pick smallest minimax by row (want the least regret)
Difference between the optimal profit and the actual payoff for a decision
How to solve for minimax regret
Calculate opportunity loss by subtracting each payoff in the column from the best payoff in the column (i.e. under each state of nature)
Find the maximum opportunity loss for each alternative and pick the alternative with the minimum number.
Optimization (mathematical) model includes:
Objective function - mathematical expression that describes the problems objective, such as maximizing profit or minimizing cost
Constraints - a set of restrictions or limitations, such as production capacities
Uncontrollable inputs - factors that are not under the control of the decision maker
Decision variables - controllable inputs, decision alternatives specified by the decision maker, such as the number of units of a product to produce
Linear programming problem -
both the objective function and the constraints are linear
Functions in which each variable appears in a separate term (ex: +, -, , *) raised to the first power and is multiplied by a constant (which could be 0)
Separate term -> x + y good, xy bad, x/y bad
Nonlinear format = bad (ex: √z) (ex: x-1)
Its okay to have a single variable ex: 1 + x
Linear constraints
linear functions that are restricted to be “≥”, “=”, “≤” or a constant
Nonnegativity constraint
X, Y ≥ 0
*basically just saying that your answer can’t be negative
Algebraic model
AX + BY ≤ 0
Ex: 20x + 30y ≤ 0
Linear constraint note-
usually (but not always) the linear function is on the left hand side of a constraint, and a constant on the right hand side
Hint phrases for linear constraint
>= constraint : at least, no less than , minimum requirement, etc
< = constraint: at most, no more than, maximum requirement, availability, capacity, budget etc
= constraint = exactly, equal to etc
Maximin
(pessimistic) - find all the minimums, find the largest minimum out of all mins
(find the max minimum)
Linear functions cannot have
variables multiplied together or raised to powers.
Limitations of LP
forces the decision maker to state one objective only
Integer programming
model that has constraints and an objective function identical to that formulated by the LP. (Only difference is that one or more of the decision variables has to take on an integer value in the final solution).
3 Types of integer programming problems
Pure integer programming problems - cases in which all variables are required to have integer values
Mixed integer programming problems - cases in which some, but not all, of the decision variables are required to have integer values
Zero-one integer programming problems - special cases in which all decision variables must have integer solution values of 0 or 1
Steps for integer programming
Defining the problem
Developing a model
Acquiring input data
Testing the solution
Analyzing the results
Implementing the results
Binary variable
0-1 decision; 0 if the condition is not met and 1 if the condition is met
In order for a break-even quantity to exist in the presence of positive fixed costs, sales price must
exceed variable cost per unit
a controllable variable is also called a:
a. decision variable.
b. mathematical model.
c. parameter.
d. measurable quantity.
a. decision variable.
A optimistic decision-making criterion is
a. decision making under certainty
b. maximax
c. maximin
d. equally likely.
b. maximax
Which of the following is not one of the steps in the quantitative analysis approach?
a. Defining the Problem
b. Observing a Hypothesis
c. Developing a Solution
d. Testing a Solution
b. Observing a Hypothesis
To be linear
all variables should be in separate terms and only raised to the power of 1.
An objective function is required for
any optimization problem, maximization or minimization.
In an LP problem
both objective function and constraints must both be linear.
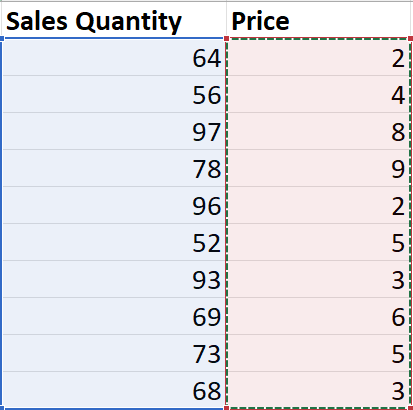
=SUMPRODUCT
multiplies 2 categories of rows (arrays) against each other
So 64 x 2, 56 x 4 etc. Need to have same number of values for both arrays so everyone gets multiplied against something
Slack
any unused resource of r an =<
Slack equation
(Any amount of resource available) -( amount of resource used)
Binding constraints
constraints with zero slack or surplus, meaning these constraints are binding at the optimality (bottleneck constraint we need to look out for)
Nonbinding constraints
constraints with non-zero slack or surplus
General build of constraint equation
Functional (actual amt) on the left side
Constant (max / min) on the right side
Ex: 5x + 7y ≤ 30
Surplus
excess amount for a >= constraint.
Surplus equation
(actual amt) - (minimum amt)
Sensitivity analysis
(aka post optimality analysis) used to determine how the optimal solution is affected by changes (w/ specific ranges in:) (used for dynamic changes)
Objective function coefficients
Right hand side (RHS) values in the constraints