Covalent bonding, periodic trends, structures & VSEPR Quiz
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
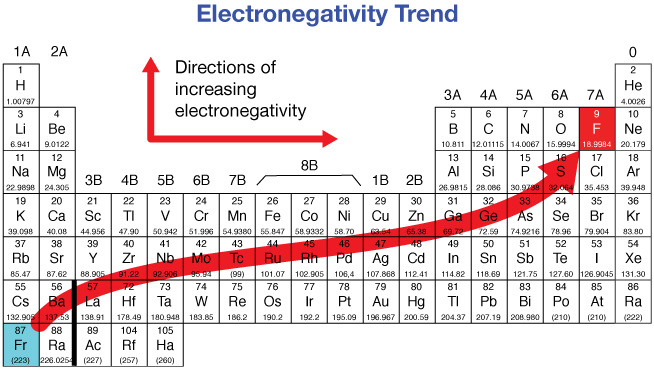
What is electronegativity? How do you find it on a periodic table?
Electronegativity indicates how strongly an element attracts electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. (Noble gases have no EN). Increase towards top right
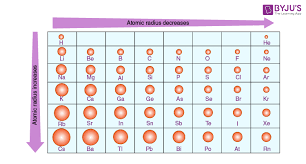
What is atomic radius? How to find it on the periodic table?
Atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost shell of electrons. It generally decreases across a period and increases down a group on the periodic table. Increases towards bottom left.
Which of these atoms would have the highest electronegativity?
Oxygen
Why does Caesium have such a large atomic radius?
Caesium has a large atomic radius because it is located in the lower part of Group 1 of the periodic table, where the number of electron shells increases, leading to greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
Which of the following has the highest electronegativity?
Fluorine
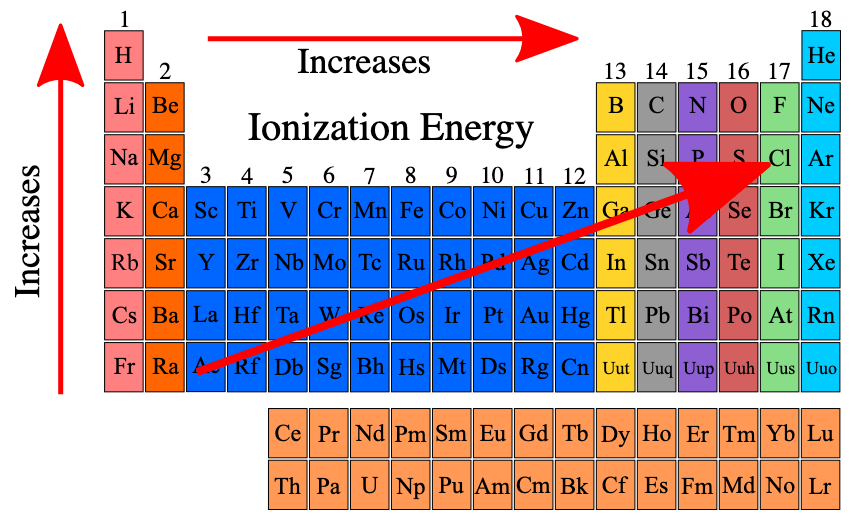
What is ionization energy? How do you find it on the periodic table?
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state. Increases as you move to the top right
Which element has the highest ionization energy?
Helium
Pottasium (0.8) and Bromine (2.8) form a bond. What type of bond do they form?
Ionic
What type of bond do Sulfur (2.5) and hydrogen (2.1) create?
Non-polar covalent
How many electrons make up a full valence shell?
8
Lewis dot diagrams only show the…
Valence electrons
What is the octet rule?
All atoms want a full valence shell, usually made up of 8 valence electrons.
What are the diatomic elements?
The diatomic elements are hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. These elements naturally exist as molecules composed of two atoms.
What do covalent bonds form between?
Two nonmetal atoms that share electrons
What does VSEPR stand for?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
What are valence electrons? How do you find them?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that participate in chemical bonding. To find them, look at the group number of the element in the periodic table.
What are covalent bonds?
Bonds where two non-metal atoms share valence electrons in order to have a full valence shell, forming a molecule.
Naming covalent compounds prefixes (1-10)
1 - mono
2 - di
3 - tri
4 - tetra
5 - penta
6 - hexa
7 - hepta
8 - octa
9 - nona
10 - deca
Across a period, valence electrons _______, atomic radius ________, ionization energy ________, and electronegativity _______.
Increase, decrease, increase, increase.
Properties of covalent bonds (4)
-Generally have lower melting and boiling points than ionic
-Balance between attractive and repulsive forces
-Always optimal distance between nuclei (repel)
-Energy released when the bond forms and absorbed when it breaks
What is bond polarity?
A measure of how equally or unequally the electrons in any covalent bond are shared.
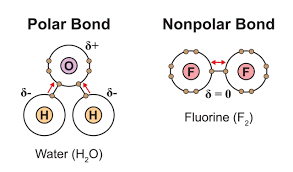
Non-polar covalent bond
A bond in which the electrons are shared equally
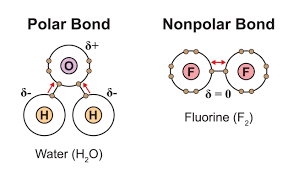
Polar covalent bond
A bond in which one atom has a greater attraction to the shared electrons than the other, resulting in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other.
Ionic bond
A type of chemical bond formed through the attraction between oppositely charged ions. Never polar.
What is Coulumbic Attraction?
The attraction between oppositely charged particles (protons and electrons)
How to calculate bond polarity using electronegativity.
Bond polarity can be calculated by finding the difference in electronegativity values between the two atoms involved in the bond; a larger difference indicates greater polarity.
Down a group, valence electrons _______, atomic radius ________, ionization energy ________, and electronegativity _______.
stay the same, increase, decrease, decrease.