Autism
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
a developmental disability significantly affecting verbal and nonverbal communication and social interaction
*generally evident before 3 y/o
**adversely affects child's academic performance
***continuum ranging from mild to severe
behaviorally defined (NO diagnostic testing)
autism characteristics
1. impairment with social communication, interaction, and imagination
2. restrictive interests
3. sensory impairments
(hypo- or hypersensitive)
autism as neurobiological disorder
specific cause of autism is found in 6-10%
has be linked to:
- rubella
- phenylketonuria
- anticonvulsants taken in pregnancy
- tuberous sclerosis
- encephalitis
significant medical history = pronounced learning disabilities
*epilepsy is more common in children with ASD
YES (rate of ASD in siblings is 2-6%)
Does autism have a genetic component?
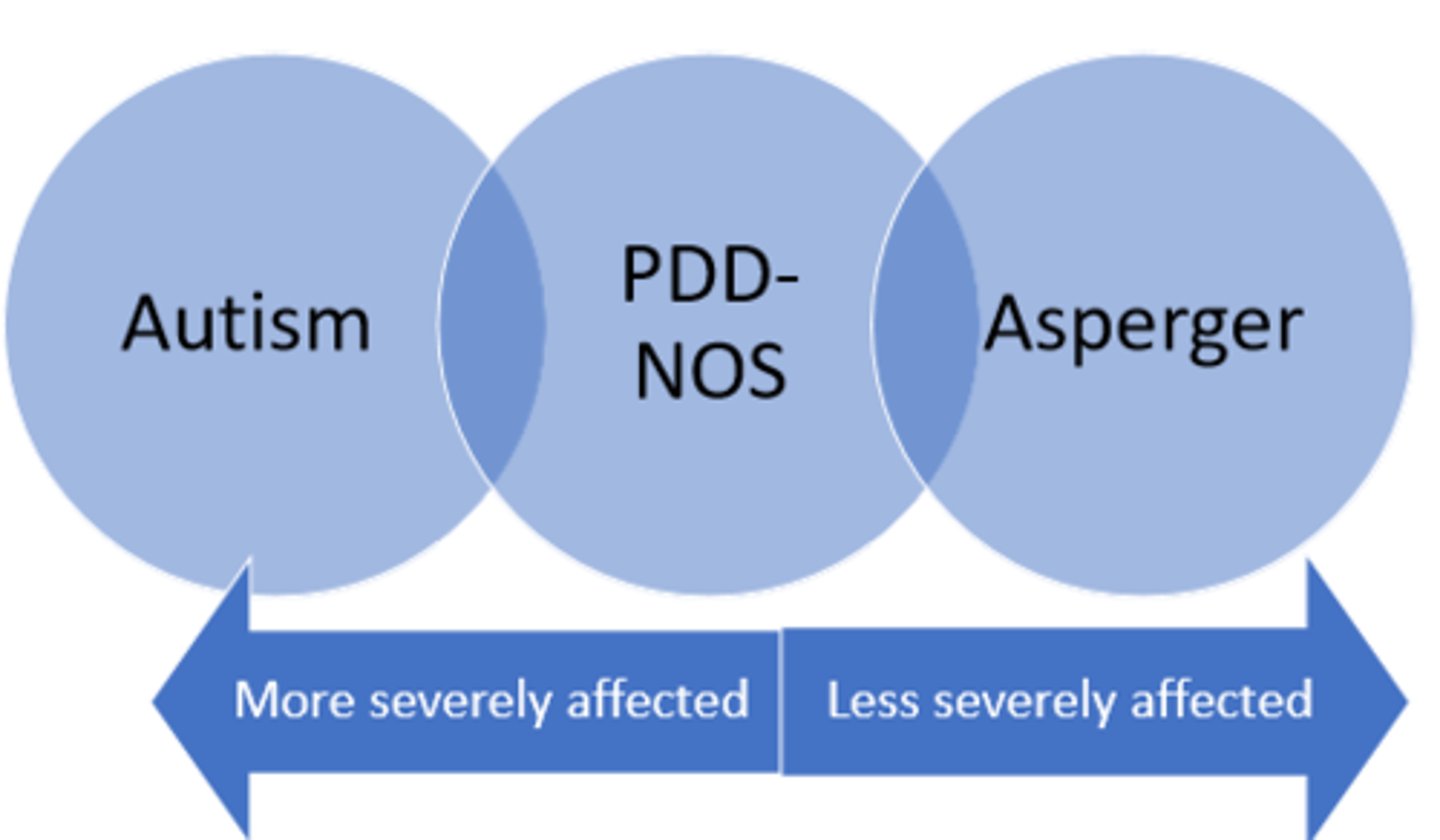
DSM-IV ASD diagnoses
1. autism
2. asperger syndrome
3. pervasive developmental disorder - not otherwise specified
4. rett syndrome
5. childhood disintegrative disorder
DSM-V ASD
SYMPTOMS:
1. persistent deficits in social communication and interaction
2. restrictive, repetitive behavior
3. present in early development period
4. symptoms cause significant impairment in life function
5. symptoms not better explained by intellectual disability
functional levels of ASD
LEVEL 1: requiring support
- difficulty initiating social support
LEVEL 2: requires substantial support
- limited initiation of social interactions
LEVEL 3: requiring very substantial support
- severe deficits in verbal and nonverbal social communication skills
*all categories require some support*
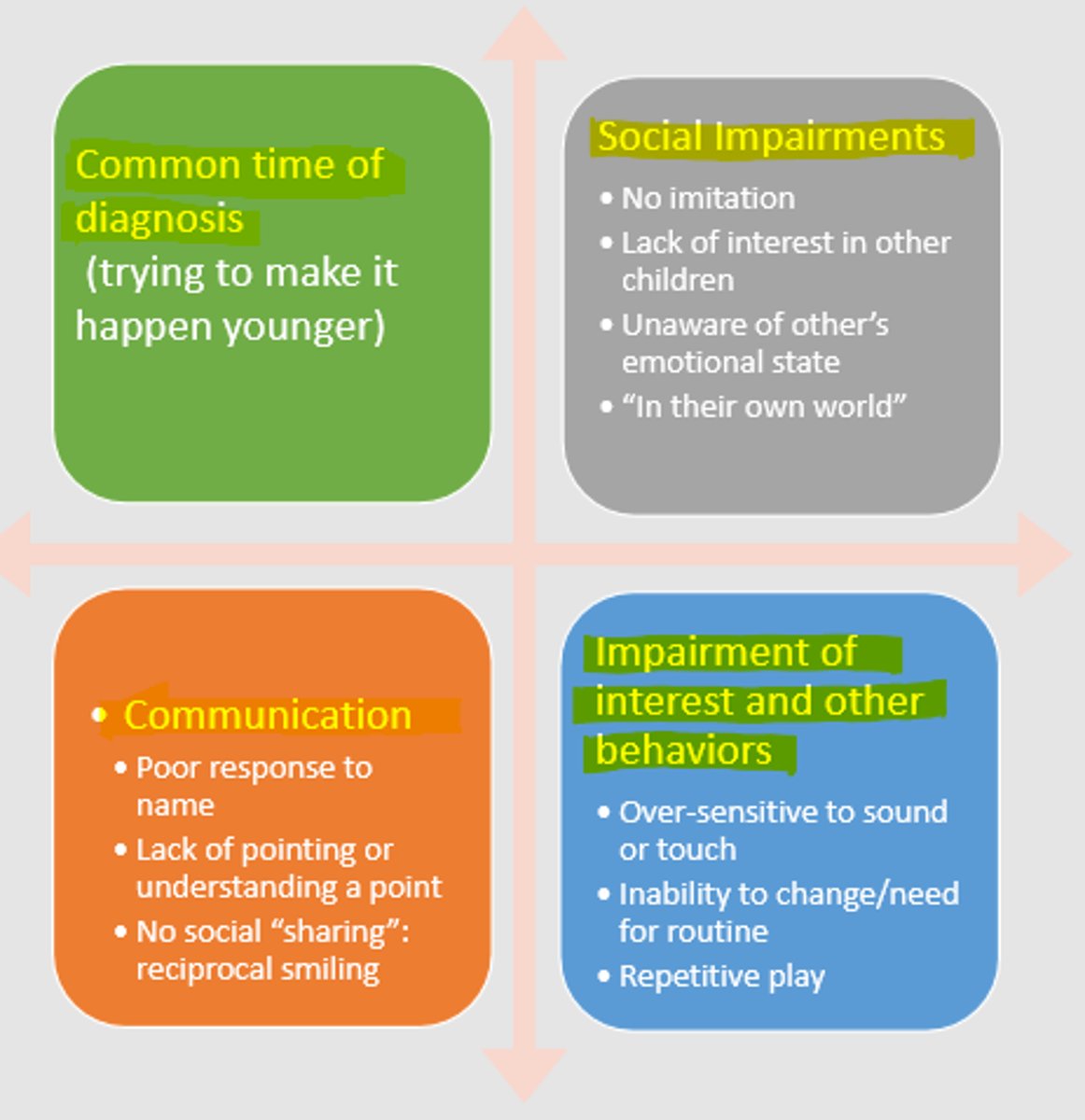
diagnosis under 24 months
DISCRIMINATING FEATURES:
- lack of social smile
- lack of appropriate facial expression
- poor attention
- impaired social interaction
- ignoring people
- preference for aloneness
- lack of eye contact
- lack of appropriate gestures
- lack of emotional expression
- less looking at others
- less pointing
- less showing objects to others
1. communication delay, stagnation, or regression
2. atypical play behaviors
(overfocus on lights, spinning objects)
3. impaired listening skills
parallel play
activity in which play occurs side by side
*less stressful for kids with ASD as eye contact is not forced

preschool
When is the most common time for a child to be diagnosed with ASD?
ASD features in late childhood
COMMUNICATION:
- echolalia
- referring to themselves as "you", "she" or "he" (beyond 3 y/o)
- limited use of language OR excessive language but only about specific topics
SOCIAL:
- doesn't joint in play
- lack of awareness of classroom norms
- extreme reactions to invasion of personal space
- extreme resistance of being "hurried"
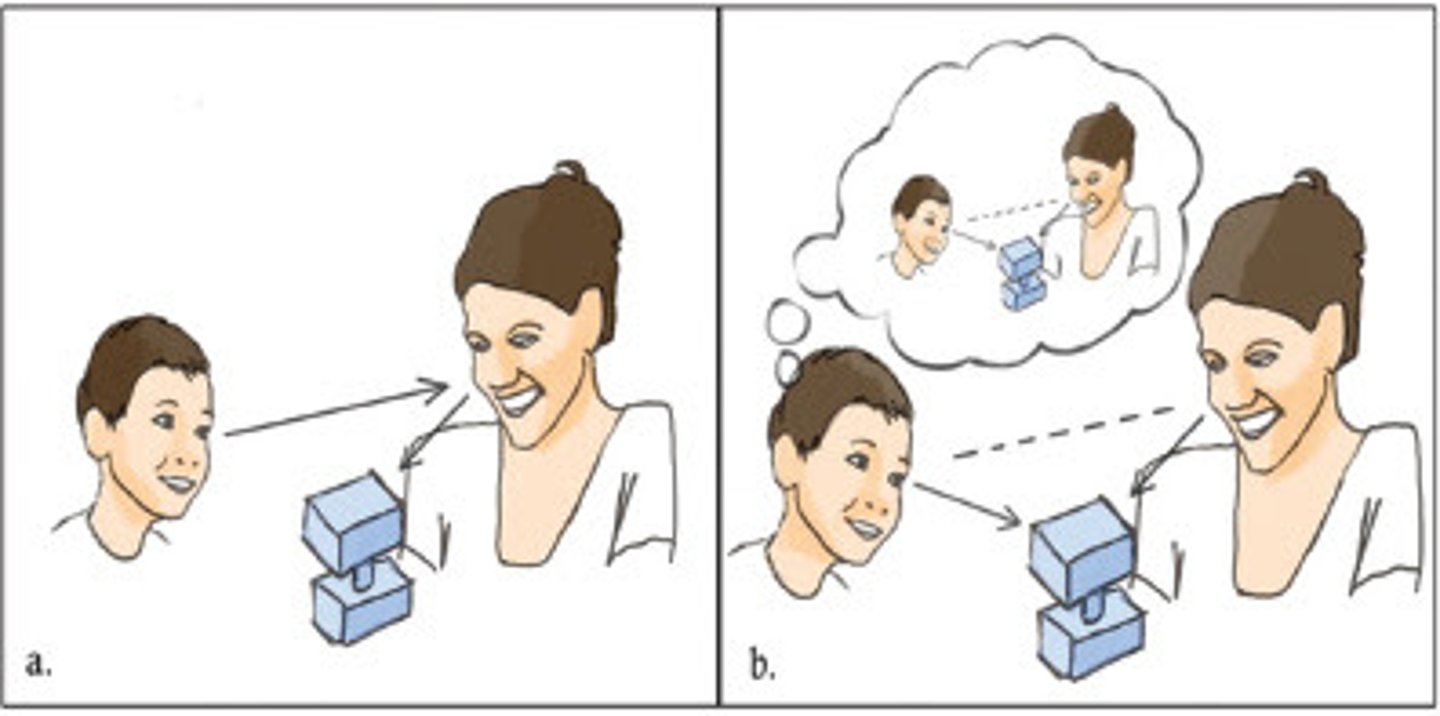
joint attention
an early social-communicative behavior in which two people share attentional focus on an object or event, for the sole purpose of sharing that interesting object with each other
*more recent focus on this concept in kids with ASD
(don't point as much)
presence of motor deficits (delayed development that can impact schooling and socialization)
Why should PTs care about ASD (a communication and social disorder)?
ASD motor impairments
- gross motor coordination
- fine motor coordination
- motor stereotypes (repetitive behavior)
- postural
- imitation and praxis
(motor planning)
COMMON IMITIATION ERRORS:
- reversals
- hand-for-tool errors
(exs. hammer a nail, shoot a gun)
social limitations and joint attention impairments
What causes imitation and praxis impairments in kids with ASD?
postural control impairment
INFANTS & TODDLERS:
- delayed development of head control
- spend less time in postures that require more postural control
*have delayed head and trunk control
SCHOOL-AGE:
- impairment in reactive and anticipatory postural control
- have particular difficulty when vision is removed
early motor delays
INFANTS AND TODDLERS:
- developmental delay
(including delayed onset of walking)
- abnormal muscle tone
(usually hypotonia)
- postural asymmetries
- infants = "jittery" and "irritable"
ASD gait
ADULTS:
- "Parkinsonian gait"
- longer stance duration
- shorter stride lengths
- lack of heel-toe pattern
- reduced upper-limb movement
fine motor delays
- clapping
- reaching
- pointing
- block building
- puzzles
- turning doorknobs
*simultaneous peaking of babbling and rhythmic arm movements NOT seen at typical 9-10 month mark
sensory processing deficits
INFANTS & CHILDREN:
- underresponsiveness
- overresponsiveness
(feeding issues)
- sensory seeking
(rocking, arm flapping, self-stimulation)