2.5 economic growth
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
define the term “Positive output gap”
when actual economic output exceeds the potential output of an economy, indicating that the economy is operating above its full capacity, often leading to inflationary pressures.
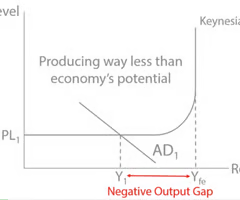
Define the term “Negative output gap”
occurs when actual economic output is below the economy's potential output, indicating underutilization of resources and often leading to higher unemployment and lower inflation.
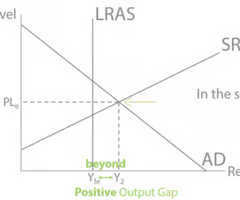
what happens to an output gap if actual growth is slower than trend growth
the output gap becomes negative. This means the economy is operating below its potential, leading to underutilized resources, higher unemployment, and typically lower inflation.
characteristics of an economic boom
5
Strong GDP Growth: Rapid increase in economic output.
Low Unemployment: High demand for labor as businesses expand.
Rising Consumer Spending: Increased consumer confidence and spending.
Higher Investment: Businesses invest in new projects, equipment, and expansion.
Inflationary Pressures: Rising demand can lead to higher prices.
list the characteristics of a recession
5
Declining GDP: Negative growth in economic output over two consecutive quarters or more.
Rising Unemployment: Increased job losses as businesses cut back on production.
Decreased Consumer Spending: Reduced confidence leads to lower spending.
Lower Business Investment: Companies postpone or reduce investment due to economic uncertainty.
Deflationary or Low Inflation: Weak demand leads to downward pressure on prices.
recession
a period of declining economic activity marked by negative economic growth for two consecutive quarters or more
explain the benefits of actual growth on consumers
Increased income:leads to higher wages, improving consumer purchasing power.
More employment opportunities: Economic growth typically creates more job openings,
Better standards of living: As economies grow, consumers generally experience higher living standards, with better access to healthcare, education, and housing
Costs of actual economic growth on consumers
4
Inflation: rising demand, causing inflation and higher prices
Income inequality: Growth may disproportionately benefit higher-income individuals, widening the gap between rich and poor.
Environmental: Increased production and consumption can lead to negative environmental impacts, affecting consumers' quality of life.
Resource depletion: Rapid economic growth may strain natural resources
what is the crowding out effect
- When increased government spending, often financed by borrowing, reduces private sector investment and spending.
- This happens because government borrowing can drive up interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow money, thus discouraging private investment.
what is the crowding in effect give an example too
When government spending increases private investment. This happens because public spending can stimulate economic growth, creating more profitable investment opportunities for businesses.
(e.g. The government builds a new high-speed rail line. This improves transport links between cities, making it faster and cheaper to move goods and people. As a result, private companies are more willing to invest in factories, offices, and logistics in those areas, because they expect higher productivity and profits)
Impact of actual economic growth on firms
Increased Revenue: Growth often leads to higher sales and more demand for products or services.
Higher Profits: With growth, firms can scale operations, improve efficiency, and reduce costs, boosting profitability.
Enhanced Investment: Growth attracts investors,
Job Creation: Economic growth often leads to hiring more employees,
Cost for firms of actual economic growth
Increased Operating Costs: Growth often requires more resources, such as raw materials, energy, and labor, which can raise operational expenses.
Higher Labor Costs: Expanding a workforce can increase payroll expenses.
Capital Investment: Firms may need to invest in new equipment, facilities, or technology to, which involves significant upfront costs.
white elephant projects (evaluation for gov spending)
Projects that are poorly constructed without adequate cost-benefit analysis - can be used as an evaluation to crowding in (what if the gov project is poorly planned or collapses? May drive private investors away)
disadvantages of export led growth
- Susceptible to shock, what if there is a war, or pandemic, or the trading partner enters recession
- Exchange rate risks (exporting firms often earn revenue in foreign currencies. If the domestic currency strengthens (appreciates), the value of those foreign earnings falls when converted back, reducing profits.)
Benefits of actual growth on the government
Increased Tax Revenue: Economic growth leads to higher business profits, higher wages, and more consumption, more tax income for the government.
Improved Public Services: With increased tax revenue, the government can fund services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure
Lower Unemployment Rates: Economic growth creates more job opportunities, reducing unemployment which can reduce welfare costs.
Costs of actual growth on the government
Inflationary Pressures: Rapid economic growth can lead to inflation, which may require the government to implement monetary policies to stabilize the economy.
Income Inequality: Economic growth may disproportionately benefit certain sectors or income groups, exacerbating income inequality
Environmental Costs: Increased production and consumption can lead to environmental degradation ,
causes of short run growth
Driven by increases in any component of Aggregate Demand (AD: C + I + G + (X–M)), shifting AD rightward in AD/AS diagrams
Can also be shown on the PPF as movement from inside towards the curve
causes of long run growth
Caused by improvements in the quality or quantity of the factors of production:
Land: new resource discoveries (e.g., oil) .
Labour: larger or more skilled workforce (immigration, education, participation)
Capital: higher investment in machinery, technology, infrastructure
Benefits on living standards actual growth
Higher Incomes: Actual economic growth often leads to increased wages and employment opportunities
Improved Public Services: With increased tax revenues generated from economic growth, governments can invest more in public services, "fiscal dividend"
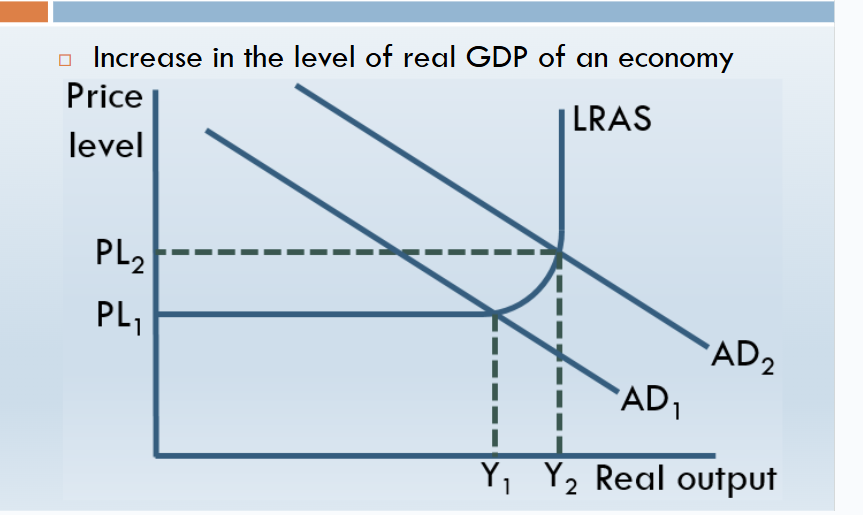
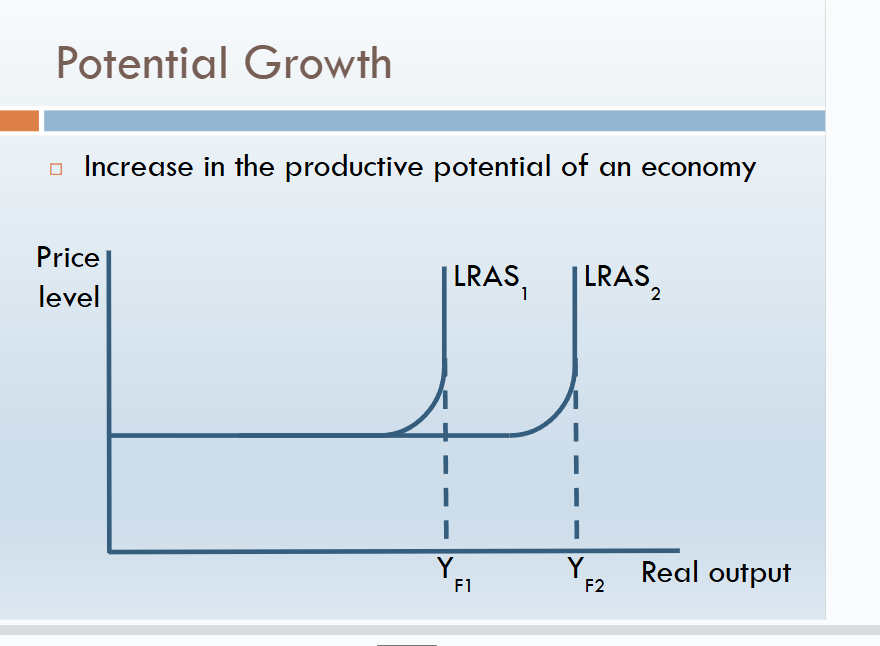
actual VS potential growth
Actual Growth
An increase in real GDP, showing the economy is producing more goods and services.
Potential Growth
An increase in the economy’s capacity to produce, from improvements like technology or more skilled workers.
Actual growth diagram
Potential growth diagram
Trade cycle diagram
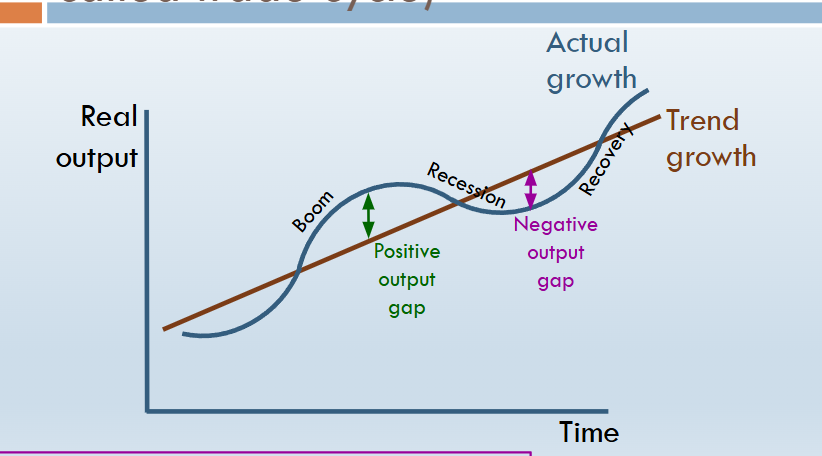
why would investment not lead to economic growth
1) Administrative costs, if the investment is poorly spent or goes towards administrative costs, then it may not cause a multiplier or increase economic growth
2) Opportunity cost, could the money have been better spent elsewhere?
3) Time lag, it may take months or years for the effects of the investments to be visible
What are automatic stabilisers
Automatic stabilisers are fiscal mechanisms that naturally adjust government tax revenues and welfare spending in response to changes in the economic cycle, without any deliberate policy changes by the government.
They help smooth out fluctuations in aggregate demand (AD), moderating the effects of booms and recessions.
features of automatic stabilisers
Automatic: No new legislation or discretionary decisions required.
Counter-cyclical: They work against the direction of the economic cycle.
examples of automatic stabilisers
Progressive income tax system
Unemployment benefits
Means-tested welfare programs
purpose & benefits
Reduces volatility in real GDP.
Helps maintain macroeconomic stability.
Reduces the need for constant discretionary fiscal policy interventions.
capital expenditure
Capital expenditure is government investment spending on long-term assets like:
Infrastructure (roads, schools, hospitals)
Technology
Transport systems
It differs from current spending, which is day-to-day (like wages and benefits).
output gap
The output gap is the difference between actual output (real GDP) and potential output (the economy’s maximum sustainable output).
Negative output gap = spare capacity, unemployment.
Positive output gap = economy overheating, inflation pressures.
inflation on government
- national debt improves
- balance of trade worsens
- increased inequality (people on fixed incomes suffer)
when is inflation good for a firm
f it is caused by an increase in demand (signals there is profit to be made)
wage spiral
When demand-pull inflation drives workers to demand higher real wages, causing cost push inflation.
For example, the cost of living crisis in 2023
deflationary trap
The spiral begins with deflation which is where there is a sustained fall in the general price level. Consumers notice the falling prices and decide to delay their purchases and wait for prices to fall further. This causes a reduction in AD as consumption is a component of AD. The fall in AD lowers the price level again and so consumers further delay their purchases. And the cycle repeats.
benefits and consequences of high inflation
- protects economy from deflationary spiral
- real value of debt decreases, improving inequality
- decreases real wages, lowering costs for firms and the government
but
- inflationary spiral leads to higher wages and more inflation... could lead to hyperinflation
- decreases real value of savings, effecting those who rely on their savings
- may decrease investment due to uncertainty of future prices
disadvantage of increasing corp tax
Firms have to pay more tax on their profits.
This leaves them with less money to invest in new machinery, technology, or buildings.
If firms invest less, their productivity grows more slowly.
Over time, this can mean lower economic growth (GDP falls)
what is quantitative easing
When the central bank electronically generates money and uses it to buy bonds and other securities from high-street banks. This gives high-street banks more cash to lend more to businesses and consumers
benefits of quantitative easing - how might it lead to economic growth
) QE -> More cash for highstreet banks = more loans to companies and consumers -> more Consumption and Investment -> AD increases -> GDP increases
Kaa 2) QE -> supply of money increases -> value of money decreases -> Weak pound = imports expensive, exports cheap -> exports cheap = international competitiveness increases -> exports increase -> (x-m) increases -> AD increases -> GDP increases (These chains-of-reasoning show you understand QE also effects the UK on a global scale)
evaluate quantitative easing
Could be inflationary if it leads to demand-pull inflation, this can lead to an increase in poverty and inequality as savings decrease and the cost of living increases. Consequently, the government may have to spend more on benefits, leading to an increase in the government debt.
2) Depends on animal spirits and consumer confidence - there may be no demand for loans if investors fear recessions or the MPC of consumers is low
how may government spending lead to an increase in real gdp
Government spending -> crowding in -> positive multiplier effect -> AD increases as Gov spending is 25% of AD -> Real GDP increases -> incomes rise -> tax revenue rises further -> government spends more and the cycle repeats.
ricardian equivalence theory
- Government spending will not boost GDP because consumers will reduce their consumption as they know the government will raise tax rates in the future (This is a very impressive theory to mention)
why may increasing national minimum wage not be bad
Wage efficiency theory (Very impressive to use). Higher wages can incentivise workers to become more efficient because the opportunity cost of them losing their job is now greater than it previously was. The firm can now fire some of their workers as they need less workers than previously to maintain the same output, this will reduce costs, rather than increase them, leading to an increase in profit.
increasing spending on infrastructure and education is good
Government spending on education -> higher levels of human capital -> more efficient workforce -> increased quality of labour -> LRAS shis outwards
BUT
Brain drain - Skilled workers will leave the economy and go to other countries where they can progress their careers further than their native country. E.g. Poland spends money on education and training yet many Poles leave the country afterwards to work in the West where salaries are higher
advantages and disadvantages of increasing benefits
Advantage - Workers have more disposable income --> increase consumption --> increased aggregate demand
Disadvantage - little incentive to work --> more unemployment --> decrease GDP , also known as the 'benefits trap'
what is monetary policy
When central banks control the base interest rates and money supply in order to influence aggregate demand
why do we want 2% inflation
Stability firms can predict future costs and prices to help with financial
forecasting
• Encourages investment
• Helps protect the real value of savings
• Keeps goods and services internationally competitive increasing /
maintaining level of exports
• High inflation tends to be unsustainable
fiscal policy
The policy that controls the level of government spending and tax
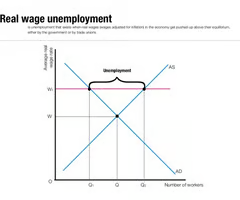
real wage unemployment
excess supply of labour bc wage is above equillibrium because of national minimum wage or trade unions
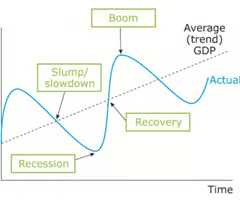
trade cycle
what is a demand side policy
Are attempts to increase or decrease aggregate demand to affect output, employment, and inflation
advantages and disadvantages of removing minimum wage
Lower costs of production as firms can, in theory, have little to no wage costs
2) Increased AD and AS (perhaps as more firms invest because they are more profitable)
Disadvantage:
1) 1.9million workers get minimum wage so they will consume less, reducing AD
2) Workers may emigrate elsewhere causing a decrease in the labour supply which will shift long-run aggregate supply to the left
3) Increase in unemployment as workers stop working due to lower incomes
the phillips curve + what does it show
indicates a short-run inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment rates
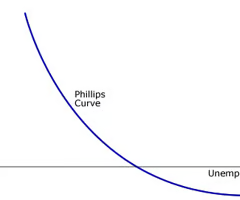
explanation of the phillips curve
Low unemployment = high employment -> more people earning incomes -> consumption increases -> AD increases -> raises price level from PL to PL1 (inflation)
When unemployment is low, firms compete for scarce workers → wages rise → higher costs → more inflation.
When unemployment is high, wages grow slowly (or fall) → less inflationary pressure.
Remember this when mentioning the conflict between macroeconomic objectives! Inflation/Unemployment