APUSH 1+2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
encomiendas
spanish labor system: king gives land in exchange for protection and conversion of natives--natives abused anyway
Quebec
first french colony in new world
new amsterdam
first dutch settlement in new world; replaced by new york with no struggle
social mobility
a change in position within the social hierarchy
chesapeake colonies
maryland and virginia, farmed tobacco
virginia company
An english joint-stock company based in Virginia
jamestown
first successful english colony, major colony of virginia
house of burgesses
Elected governing assembly in colonial Virginia
powhatan
Indian chief and founder of the Powhatan confederacy of tribes in eastern Virginia
bacon's rebellion
Nathaniel Bacon and other western Virginia settlers were angry at Virginia Governor Berkley. The frontiersmen formed an army, with Bacon as its leader, which defeated the Indians and burned the Jamestown. The rebellion ended suddenly when Bacon died of an illness.
indentured servant
Colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a certain number of years
pilgrims
English Puritans who left Britain because of religious persecution and founded Plymouth colony in 1620, led by John Winthrop
puritans
believe in purification of Anglican church
salem witch trials
19 women accused, tried, executed for witchcraft in salem, massachusetts
rhode island
colony of puritan outcasts started by roger williams and anne hutchinson
roger williams
pilgrim who disagreed with the lack of separation of church and state in puritan colonies, founded colony of providence in RI with anne hutchinson
anne hutchinson
pilgrim who disagreed with role of women in puritan church, founded colony of providence in RI with roger williams
middle colonies
New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware; most diverse + tolerant, cereal crop farming
pennsylvania + maryland religions
pennsylvania: quakers, maryland: catholics then protestants
william penn
founded Pennsylvania for religious freedom (Quakers)
slave songs
carried messages about African culture, escape; allude to biblical Israelites escaping slavery in Egypt
autonomy
(n.) self-government, political control; independence
syncretism
a blending of beliefs and practices from different religions into one faith: mix of African + Christian religion, voodoo etc.
british west indies
plantation agriculture, dominated by planter elite, grew tobacco and rice, similar to southern colonies
town meetings
system of local self-governance prominent in new england colonies influenced by puritan values--discussed/mixed church and state
massachusetts legislature (massachusetts general court)
massachusetts version of house of burgesses; modeled after parliament, elected officials vote on colonial matters
transatlantic trade
aka triangular trade, three pointed Atlantic economy that emerged with the New world
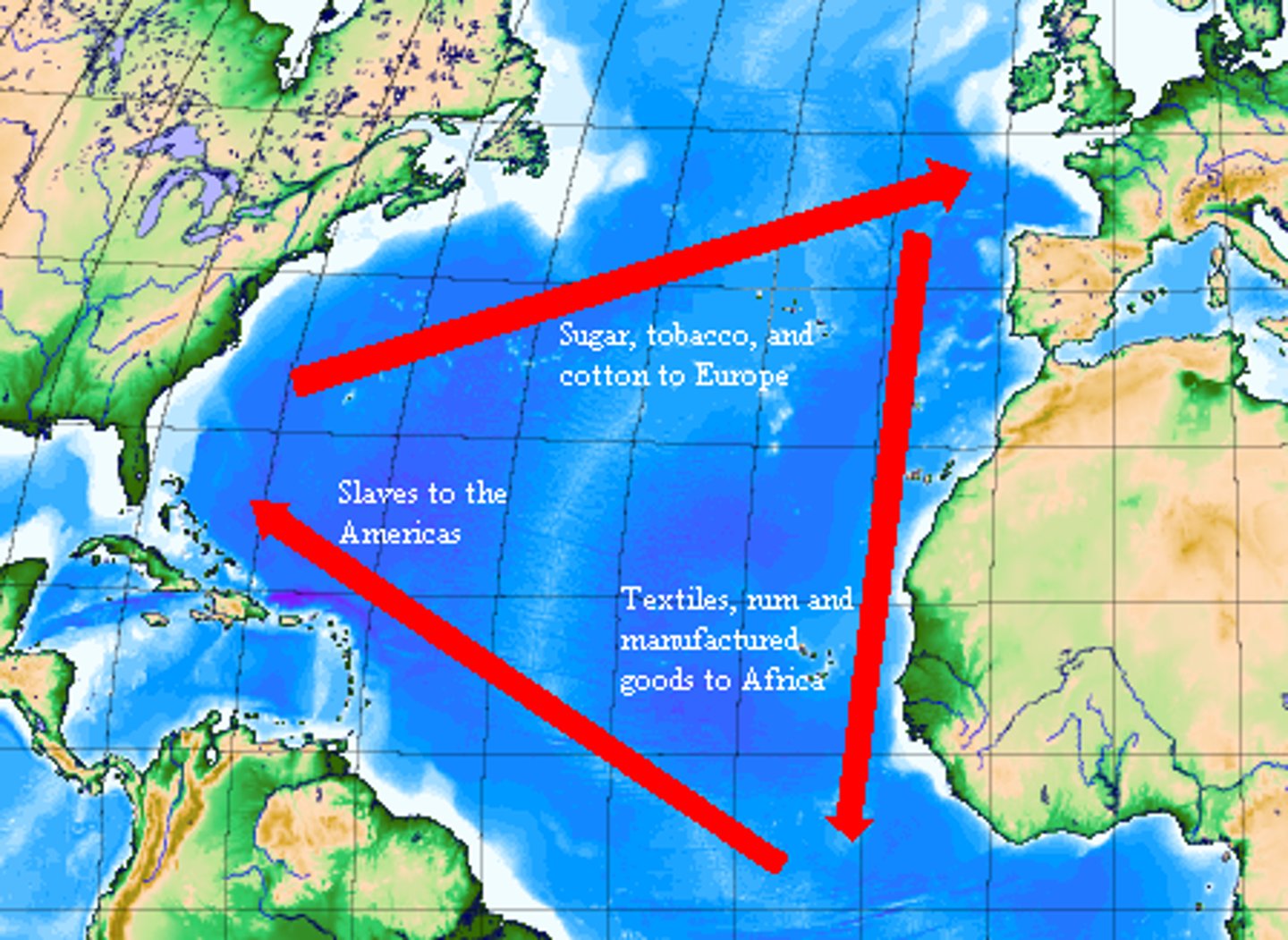
middle passage
portion of transatlantic trade from africa to the new world, notoriously brutal slave trade route
destruction of the huron
20,000-40,000 to 12,000 population loss of Huron tribe because of smallpox and measles epidemics brought by Europeans
beaver wars
Iroquois and British fought the French and Huron for control of the fur trade in the east and the Great Lakes region
chickasaw wars
War in the 1700s between the Chickasaw, allied with the British, against the French, who were allied with the Choctaw and Illini. The war was fought over land, primarily for control of the Mississippi River.
king williams war
The first of a series of colonial struggles between England and France; these conflicts occurred principally on the frontiers of northern New England and New York between 1689 and 1697.
queen anne's war
Second of the North American wars waged by the British vs French and natives over land, little help from King
massachusetts becomes a royal colony
King takes control of Massachusetts, they had a illegal mint, voting issues and discrimination against Anglicans.
dominion of new england
king frustrated with new england colonists, merges all of new england colonies into one; lots of revolts, dominion only lasts three years
examples of mercantilist policies controlling colonists
molasses act, navigation acts, wool acts
navigation acts
british tell colonists that they must use british ships, british sailors, british ports, etc.
wool acts
british tell colonists that they can only sell wool to british territories
molasses act
british law: colonists must pay a tax if purchasing molasses from anyone other than british territories, forced to purchase from british exclusively
king philips war (metacom's war)
war between wampanoags led by metacom (king philip) and puritan colonists angered by praying towns
pequot war
The Bay colonists wanted to claim Connecticut for themselves but it belonged to the Pequot. The colonists burned down their village and 400 were killed.
yamasee war
war between the South Carolina settlers and the local natives who did not like being used for slavery and threatened for their land
praying towns
puritan towns for natives to live, convert to christianity, learn english culture; abusive
pueblo revolt
Native American revolt led by Pope (pope-ay) against the Spanish missions; expelled the Spanish for over 10 years; Spain began to take an accommodating approach to Natives after the revolt
spanish mission system
a more peaceful (still forceful) replacement for encomiendas, similar to praying towns but larger/harsher
pluralism
presence of multiple distinct groups ideas in societies (ex. diverse middle colonies)
great awakening
colony-wise religious re-awakening, promoted individual salvation + removed need for clergy; protestant evangelism; led by john locke and george whitfield
enlightenment
A movement that advocated the use of reason and logic, contradicted church, spread from europe to americas
protestant response to enlightenment
great awakening
anglicization
process of colonies becoming more english-like (due to print culture), govt modeled after parliament, enlightenment, language, attire inspired by english
trans-atlantic print culture
spread of ideas, and goods via trade and newspapers; guttenbergs printing press anglicization
protestant evangelism
Christianity based on emotionalism and spirituality. It was part of the First Great Awakening. Evangelism was a reaction to the Enlightenment priority of rationalism over emotionalism and spirituality.
salutary neglect
king's hands-off approach for colonies, led to self-governing in colonies, less work + more money for king
chattel slavery
slaves viewed as property (different from forms of slavery like trafficking)
interracial marriage laws
prohibited interracial marriage in maryland, virginia, pennsylvania; associated with chattel slavery since slaves were legal property
perpetuity of slavery
slavery designed to last forever; children of slave mothers were to be slaves regardless of father
overt resistance by slaves
breaking tools, running away, working slowly, blatant rebellion (stono rebellion)
covert resistance by slaves
surrogate families, retaining culture, language, music, syncretic religion
surrogate family
an adoptive family of slaves to help reserve culture and tradition
stono rebellion
south carolina, one of the first major slave rebellions
examples of syncretic religion (african religions mixed with christianity)
voodoo, santeria, rastafari
maize
An early form of corn grown by Native Americans especially in mexico
atlantic seaboard
north american east coast
columbian exchange
exchange of ideas, culture, goods, disease, etc. between old and new world
mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought; country focused on gold/money
feudalism
A political system in which nobles are granted the use of lands that legally belong to their king, in exchange for their loyalty, military service, and protection of the people who live on the land
Capitalism
an economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state (new world economy)
sextant
measures lattitude
joint-stock companies
multiple investors in a company; developed in new world
epidemics brought to north america
smallpox, measles
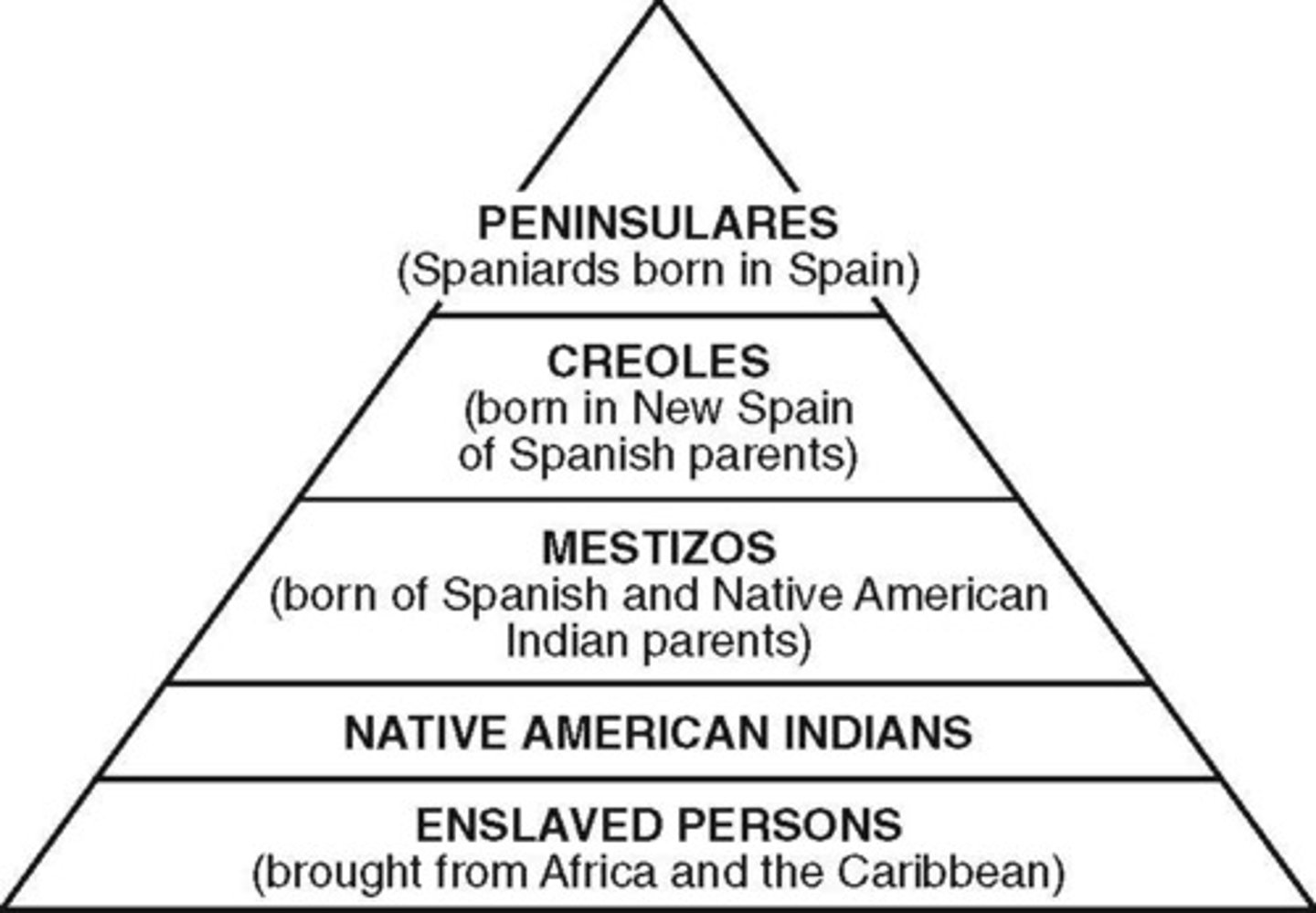
casta system
A system in colonial Spain of determining a person's social importance according to different racial categories.
subjugation
the act of conquering or bringing under control; enslavement
valladolid debates
debates about spanish treatment of natives in new world (encomiendas)
bartolome de las casas
argued that native americans should be treated humanely, former encomienda owner
juan de sepulveda
Argued that the Native Americans needed the rule and "civilization" that Spain could provide, ("saving their souls") which justified their treatment at the hands of colonizers.
Never left Spain
casta system
A system in colonial Spain of determining a person's social importance according to different racial categories.