A Level Pearson Edexcel Physics Topic 8 Nuclear & Particle Physics
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What is the nucleon number
The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
(mass number)
What is the atomic (proton) number
The total number of protons in the nucleus
Outline Rutherford's alpha scattering experiment
High speed alpha particles were fired at a very thin sheet of gold foil. The deflections of the particle's were measured and conclusions were drawn
What was observed in the Alpha scattering experiment
-Most alpha particles passed straight through the gold atoms
-Some were deflected
-A few of them were deflected backwards
What is thermionic emission
Thermionic emissions is the release of electrons due to heating
Explain why electrons are released from a heated filament
As the filament heats up , free electrons inside the metal gain kinetic energy. When the surface electrons gain sufficient energy, they are released from the surface
What will happen to a beam of electrons if it passed through a potential difference
The beam of the electrons will be accelerated since work is done by the potential difference
How do we calculate the energy transferred to an electron, when it is accelerated across potential difference
Energy = Charge * Potential Difference
E = eV
What happens when a beam of electrons is directed into a magnetic field
The electron beam will be deflected, since magnetic fields apply forces on moving charges.
What is the magnitude of the force experienced by a moving electron in a magnetic field
Force = Magnetic Flux density Charge Velocity
F = BeV
If the electrons are moving perpendicular to the field lines, which direction will the magnetic force act
The force will act perpendicular to both the electron and field directions
Describe the shape of the path of a beam of electrons passing through a magnetic field
The beam will produce a circular path since the magnetic force always acts perpendicular to the electrons motion. This means it acts as centripetal force and produces a circular path
What are the two kinds of particle accelerators
-Linear accelerator (LINAC)
-Circular accelerators
What is a Linear accelerator (LINAC)
It is a particle accelerator that is used to accelerate charged particles (such as electrons or protons) along a straight path using alternating electric fields
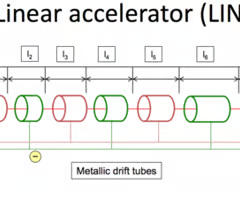
Describe the composition of a Linear accelerator (LINAC)
LINAC consists of several cylindrical electrodes called drift tubes, arranged in a series, with increasing lengths along the path
These electrodes are connected to alternating voltages, which create electric fields between them
There is a particle source at the beginning of the accelerator where the particles are released
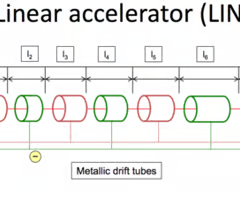
How does a Linear accelerator (LINAC) work
Charged particles are released from a source and accelerated toward the first electrode.
Alternating electric fields between the electrodes accelerate the particles each time they pass through a gap.
The polarity of the electric field switches at the right moment, ensuring the particles continue accelerating through the successive gaps.
This process repeats until the particles reach the desired speed as they exit the accelerator.
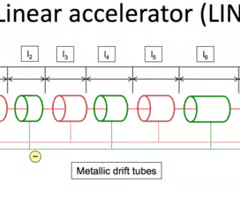
What does a Linear accelerator (LINAC) use
Uses an alternating electric field
What are two kind of circular particle accelerators
Cyclotrons
Synchrotrons
What is a Cyclotron
Is a particle accelerator that uses magnetic fields to accelerate particles in circular paths. This allows higher speeds to be reached, without the limitations of the accelerator's length.
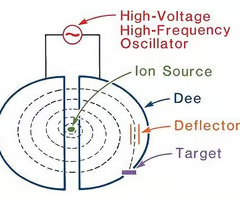
Describe the composition of a Cyclotron
Cyclotrons consist of two D-shaped paths which are separated by a small gap
An alternating potential difference is applied across the gap
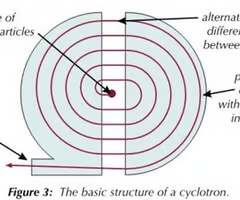
How does a Cyclotron work
An electron beam(particle) is passed into the cyclotron, where it is deflected into a circular path by a perpendicular magnetic field.
When the beam(particle) reaches the gap, it's accelerated by a potential difference.
This increases the speed of the beam, causing the radius of the path to increase.
This process repeats every half circle.
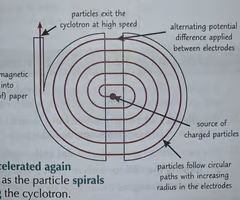
What does a Cyclotron use
Uses a magnetic field and an alternating electric field
What is the force like that is exerted by a magnetic field on a charged particle
The exerted force must be perpendicular to its motion of travel
State the equation used to calculate the circular radius of an electron beam deflected in a magnetic field
Radius = mv/BQ
What two equations must be used if you want to derive Radius = mv/BQ (the radius equation)
Centripetal force = mv^2 / r
Magnetic field = BQv
Derive Radius = mv/BQ (the radius equation)
Centripetal force = Magnetic field
mv^2 / r = BQv
Rearange:
mv^2/BQv = r
Cancel v:
mv/BQ = r
Why do we use r = mv/BQ
To find the radius of curvature of tracks
Why do we find the radius of curvature of tracks
This allows us to find out certain characteristics of particles that are being observed
How can you simply r = mv/BQ further by using the fact that p =mv
r = mv/BQ
So p =mv hence substitute it in:
r = p/BQ
What are the three properties that must always be conserved during particle interactions
Charge
Energy
Momentum
What are ways we can view charged particles
By using a particle track
What are two kinds of particle tracks
Bubble chamber
Cloud chamber
What is a bubble chamber
A tank filled with superheated liquid hydrogen.
Forms bubbles around ionized particles from the movement of charged particles.
How does a bubble chamber work
By observing the path created by visible bubbles, you can see the path taken by moving, charged particles.
The tank is placed in a magnetic field, causing charged particles to take circular paths.
What is a cloud chamber
A cloud chamber is a device used to visualise ionising radiation. It contains supersaturated alcohol vapor that forms visible tracks when charged particles pass through and ionize the vapor. These trails reveal the paths of subatomic particles.
How does a cloud chamber work
Alcohol vapour supersaturated into chamber and cooled
Particle interacts with alcohol vapour
This results in "clouds" being seen
What must you always do when investigating an object
Must use waves with wavelengths similar in size
How to find wavelengths
Use de Broglie relation (λ = h/p)
de Broglie relation
λ = h / p
λ is Broglie wavelength
h is planks constant
p is the momentum of a particle
What can we see by using de Broglie relation
The smaller the de Broglie wavelength needed, the higher energy (/momentum) of the particle is required
State the mass-energy equation
E = mc^2
m = mass
c = speed of light
What is matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
What is antimatter
Has exactly the same mass as the normal particle
Has opposite charges (if the normal particle is charged)
What happens when antimatter and matter meet
Annihilation
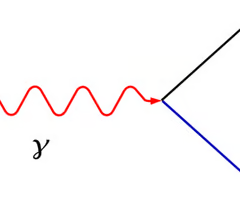
What is pair production
Where a photon is converted into an equal amount of matter a and antimatter
What is Annihilation
When a particle and its corresponding antiparticle collide.
This results in their masses being converted into energy. This releases two photons into opposite directions
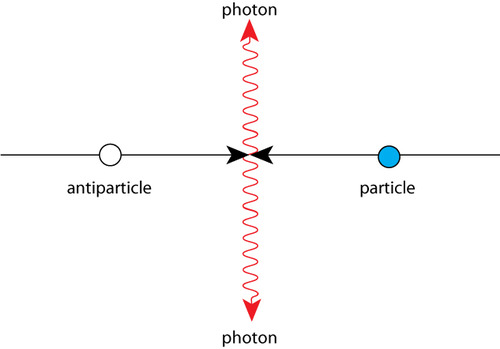
Why must the mass be converted into energy during annihilation
This is to conserve momentum
What happens to a photon in Particle production
photon -> electron + positron
How is a photon created in Particle annihilation
electron + positron -> photon(s)
What does eV stand
electron Volt
What is eV
1 eV, is the kinetic energy of an electron accelerated across a potential difference of 1V
What is 1 eV into joules
1 eV = 1.6 * 10^-19 J
What does MeV stand for
Mega electron Volts
What does GeV stand for
Giga electron Volts
In a quark-lepton model, what are the four main categories of a particle
Baryons
Mesons
Leptons
Photons
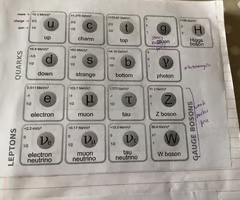
What is the quark composition of a baryon
Baryons are made up of three quarks
What is the quark composition of a meson
Mesons are made up of a quark and a antiquark pair
Which category of particles are classed as fundamental particles
Leptons
Give two examples of leptons
Electrons
Neutrinos
What category do pions belong to
Mesons
Give two examples of baryons
Protons
Neutrons
What did the symmetry of the quark-lepton model predict the existence off
The top quark
What is a antiparticle
An antiparticle is one that has the same mass but opposite charge and conservation numbers to its corresponding particle
What is the antiparticle of a proton
An antiproton
What is the antiparticle of a electron
A positron
Name four things that are always conserved in a particle interaction
Mass/Energy
Baryon number
Lepton
Charge
Describe the conservation of lepton number
The lepton number for each specific type of lepton must be the same before and after the interaction