Session 7: Introduction to the Endocrine System and Pancreatic Hormones
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Control system in the body maintains
homeostasis
What variables are regulated at an optimal level in homeostasis
Blood
Glucose levels
Body temperature
A ___ point is established for each variable which is monitored accordingly
set
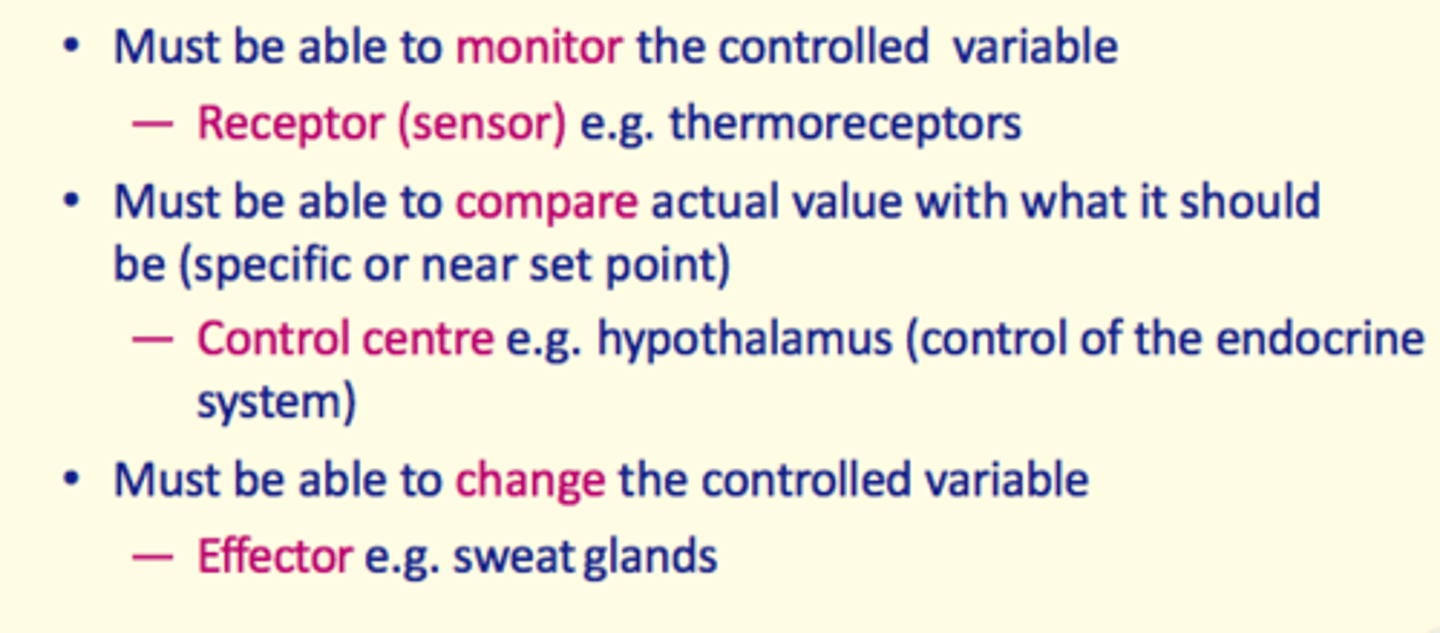
What three parts does the control system of the body consist of?
1) Receptor
2) Control centre
3) Effector
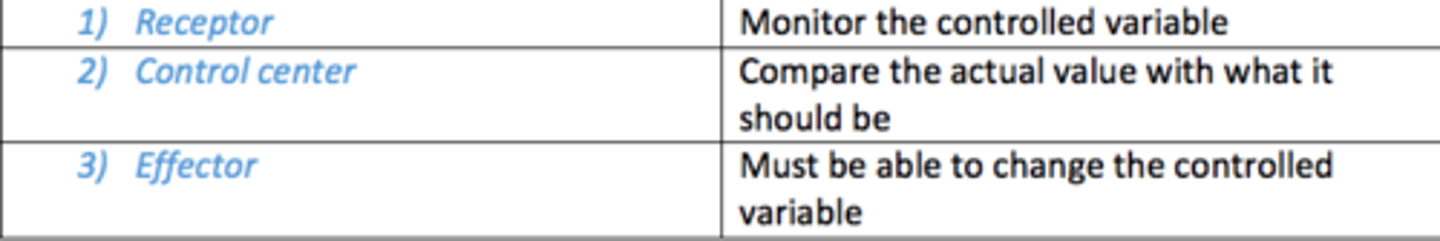
Control system requirements
- Receptor e.g., thermoreceptor
- Control centre e.g., hypothalamus
- Effector e.g., sweat glands
Circadian rhythm
the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle
What two hormones affect the circadian rhythm
- Melatonin
- Cortisol
The set point can vary over a 24h period due to what?
Circadian rhythm
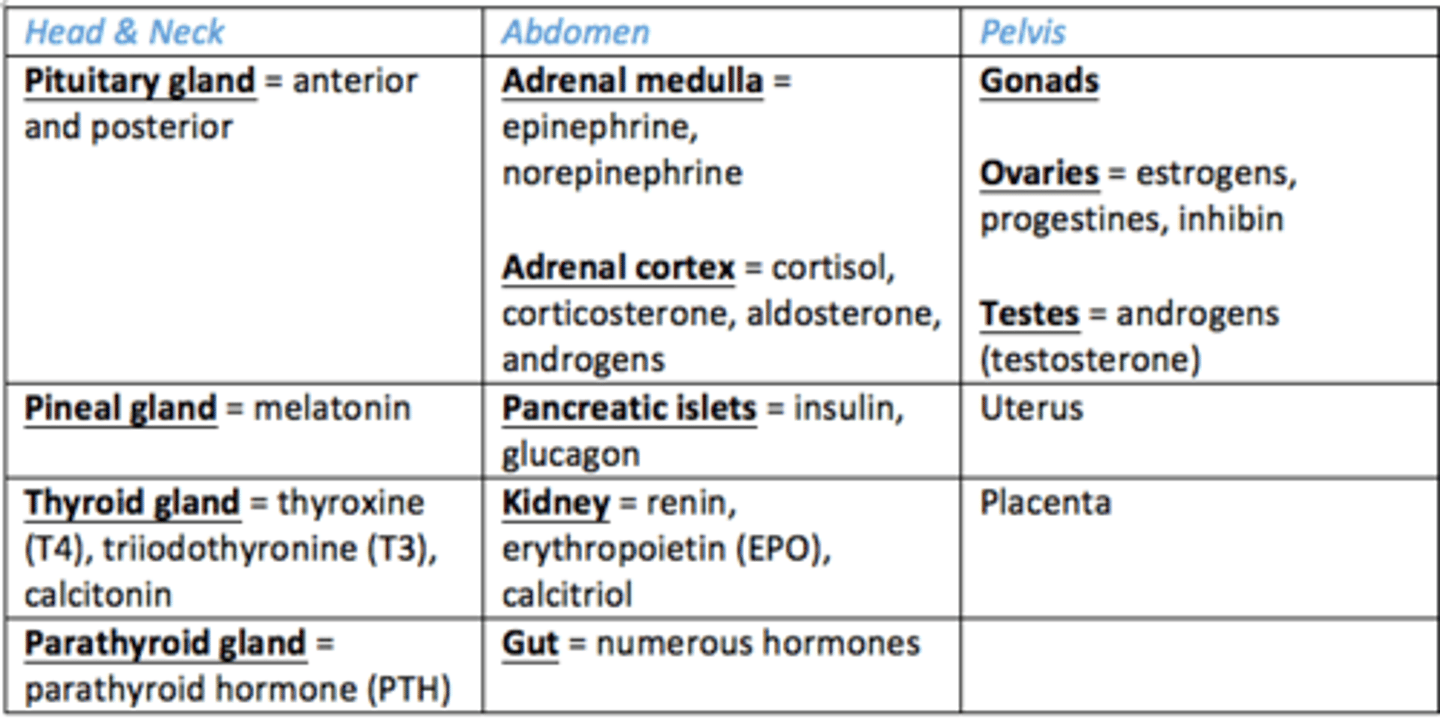
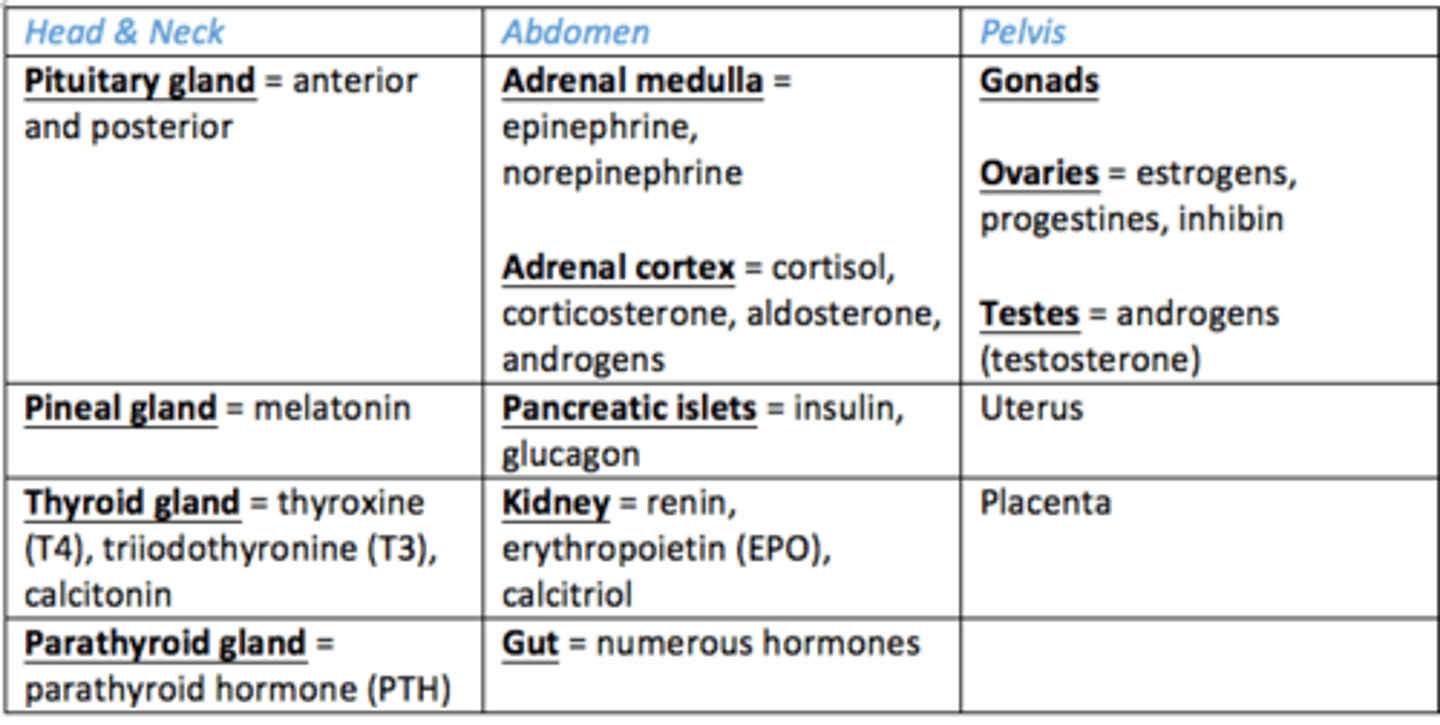
Endocrine glands in head and neck
1) Pituitary gland
2) Pineal gland
3) Thyroid gland
4) Parathyroid glands
What is the role of the hypothalamus?
Links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland
Endocrine glands in the abdomen?
- Adrenal glands: cortex and medulla
- Pancreas
- Kidney
- Gut
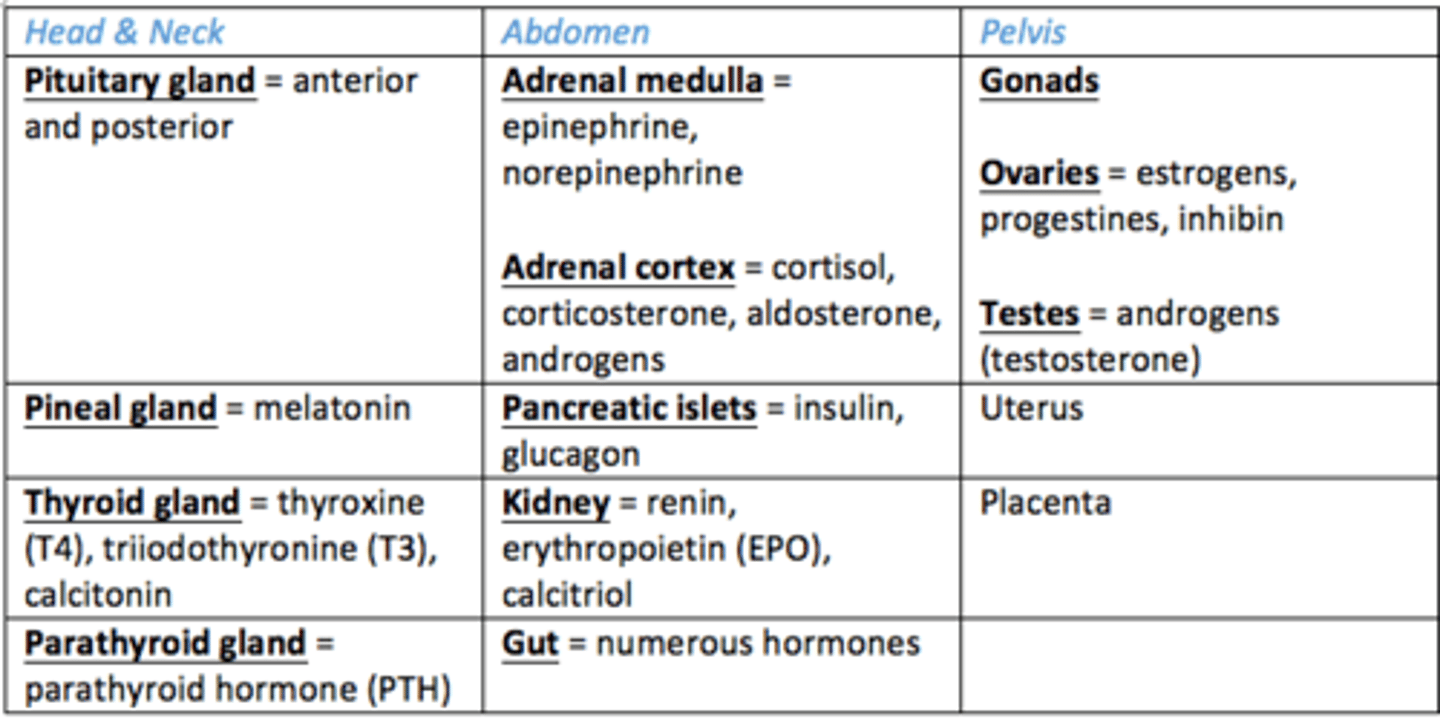
Endocrine glands in the pelvis
- Gonads (ovaries, testes)
- Uterus
- Placenta
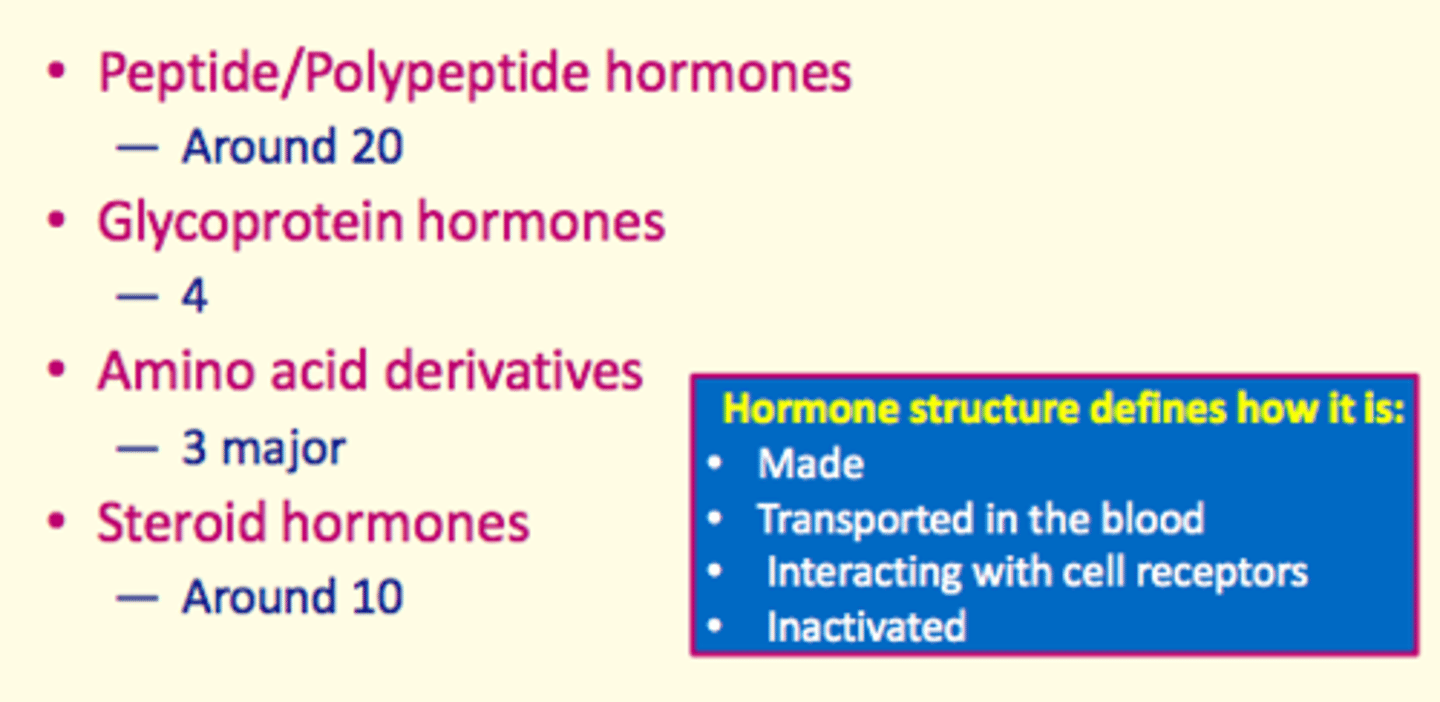
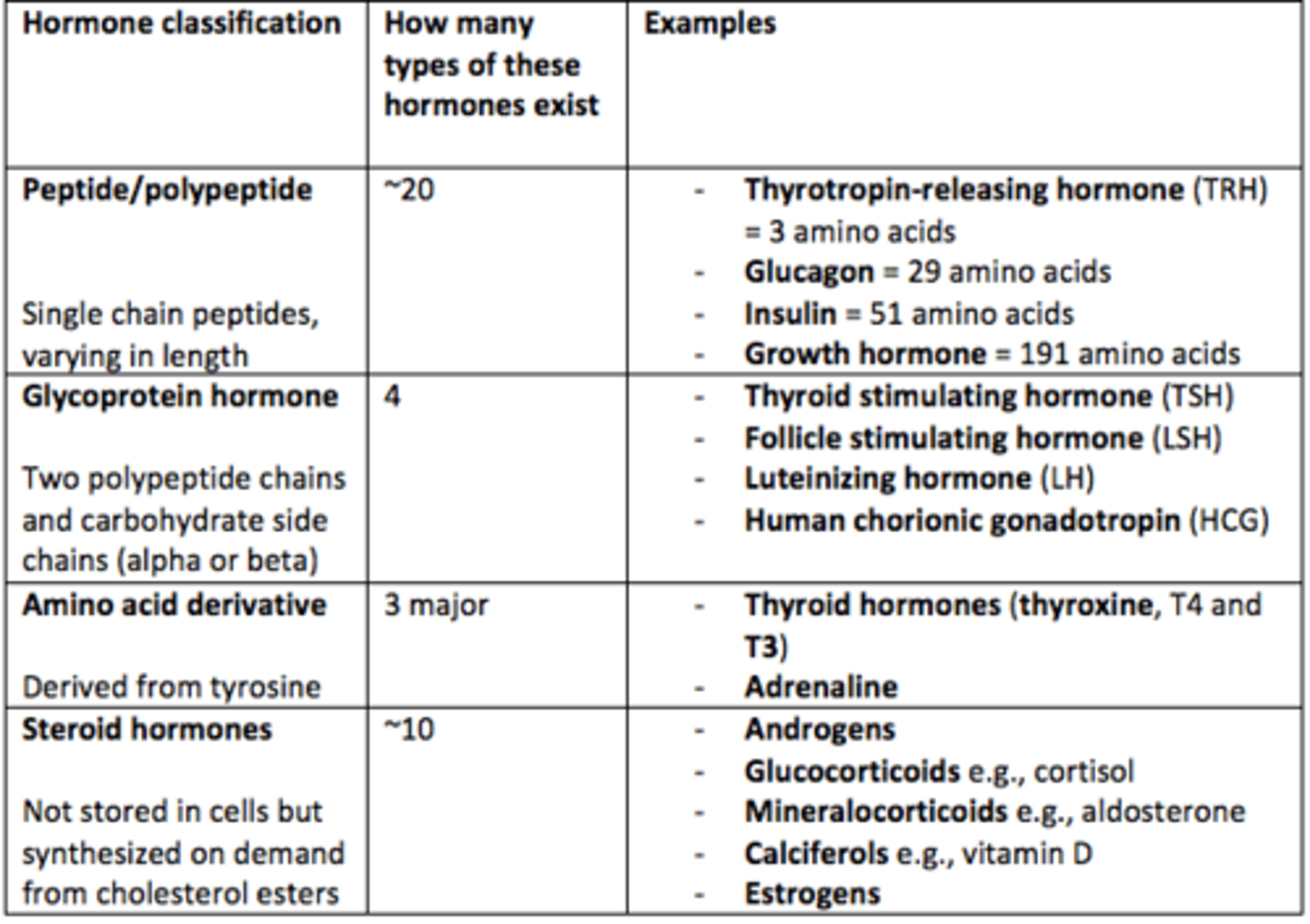
Classification of hormones (what are the four groups of hormones)?
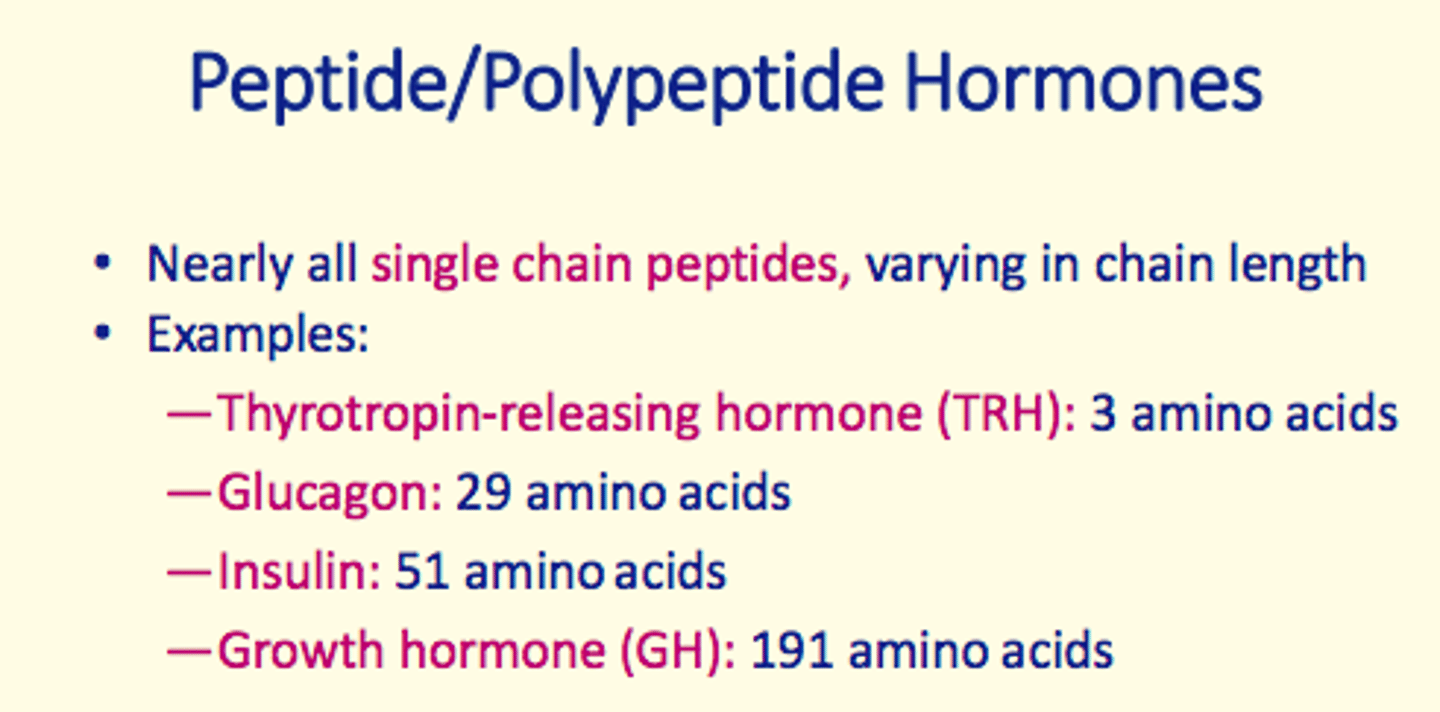
1) Peptide/polypeptide hormones
2) Glycoprotein hormones
3) Amino acid derivatives
4) Steroid hormones
The control system uses a ___ loop to maintain levels for homeostasis
feedback
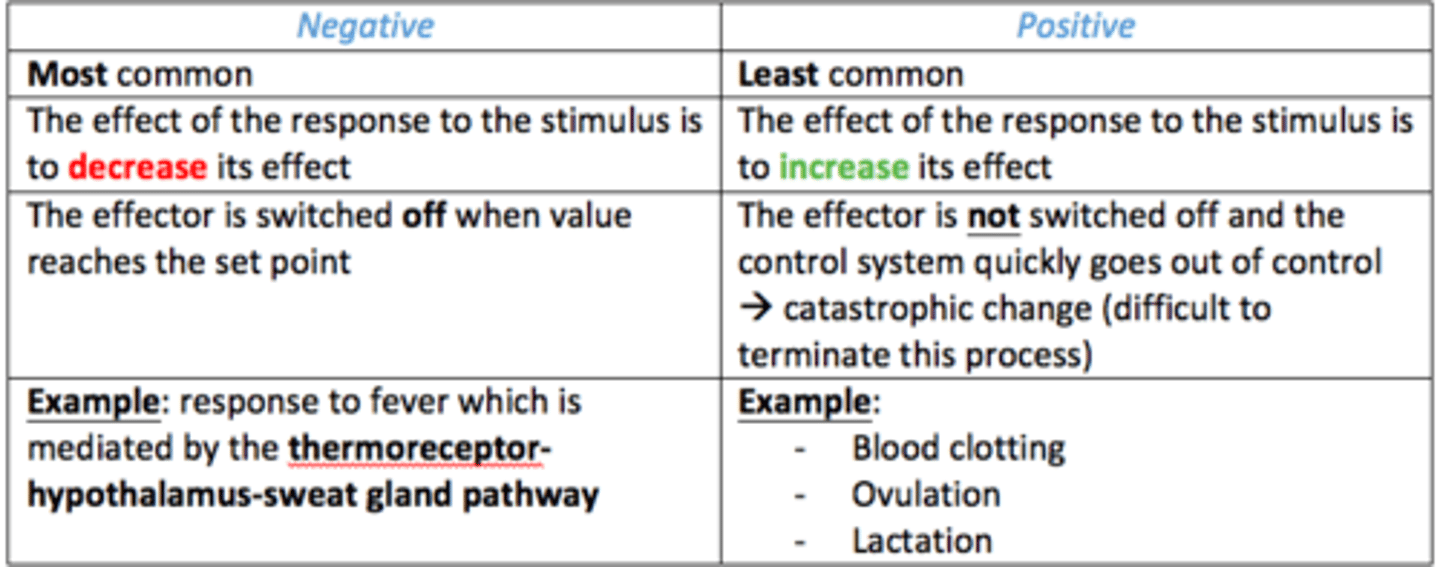
Most common type of feedback loop
Negative feedback
Negative feedback loop
- The effect of the response to stimulus = is to decrease its effect
- The effector is switched off when value reaches the set point
Example of a negative feedback loop in the human body
Thermoreceptors-hypothalamus-sweat glands = body temperature regulation
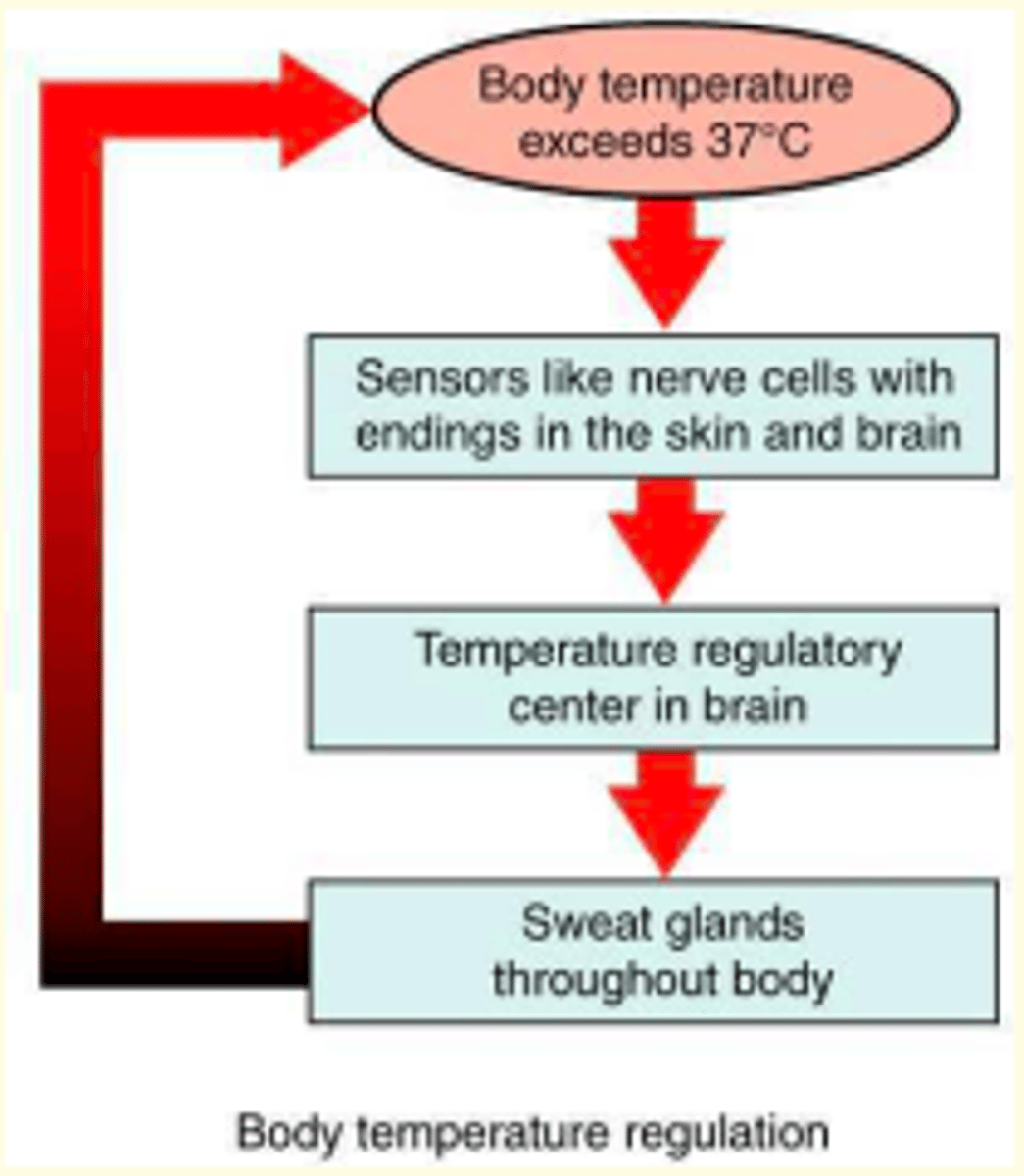
Body temperature regulation negative feedback loop
1) Body temperature exceeds 37 degrees celsius
2) Thermoreceptors in the skin and brain sense this
3) Temperature regulatory centre in hypothalamus detects this
4) Sweat glands throughout body activated
5) Decrease of temperature back to optimum set point (37 degrees celsius)
Positive feedback loop
- Effect of the response to stimulus = increase its effect
- The effector is not switched off
- Control system goes out of control leading to = catastrophic change
Examples of positive feedback loops in the body
- Blood clotting
- Ovulation
- Lactation
A control system only works effectively if there is good communication between its components. Communication can occur through 3 routes...
1) When they come into contact = cell surface chemicals
2) When they are close = local diffusion
3) When they are far apart = hormones/neurotransmitters

Hormones are chemical signals produced in ___ glands
endocrine
Hormones travel in the ___ to affect other tissues
bloodstream

Endocrine
Endocrine signaling uses the circulatory system to transport ligands
Paracrine
signals diffuse to and affect nearby cells (paracrine = proximity)
Autocrine
Referring to a secreted molecule that acts on the cell that secreted it.
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
- Peptide/polypeptide hormone
- 3 amino acids long
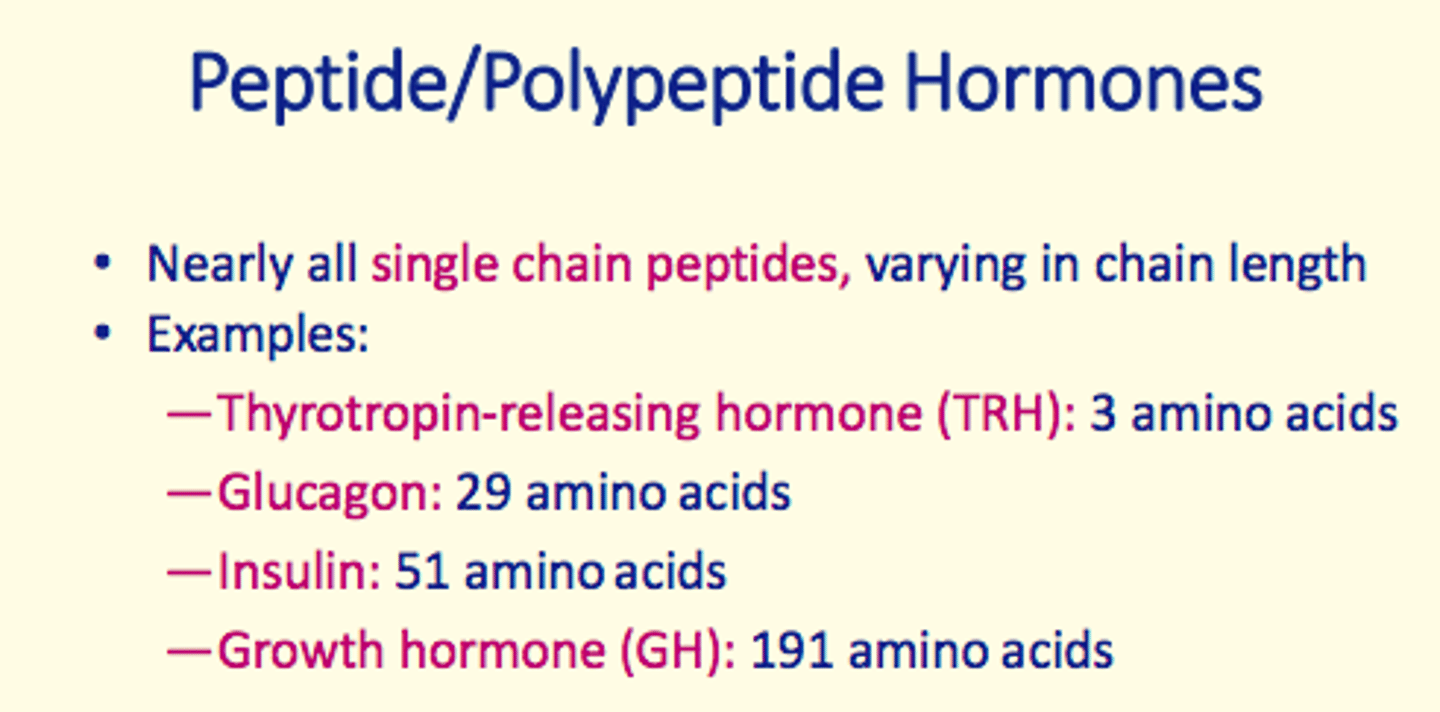
Glucagon
- Peptide/polypeptide hormone
- 29 amino acids long
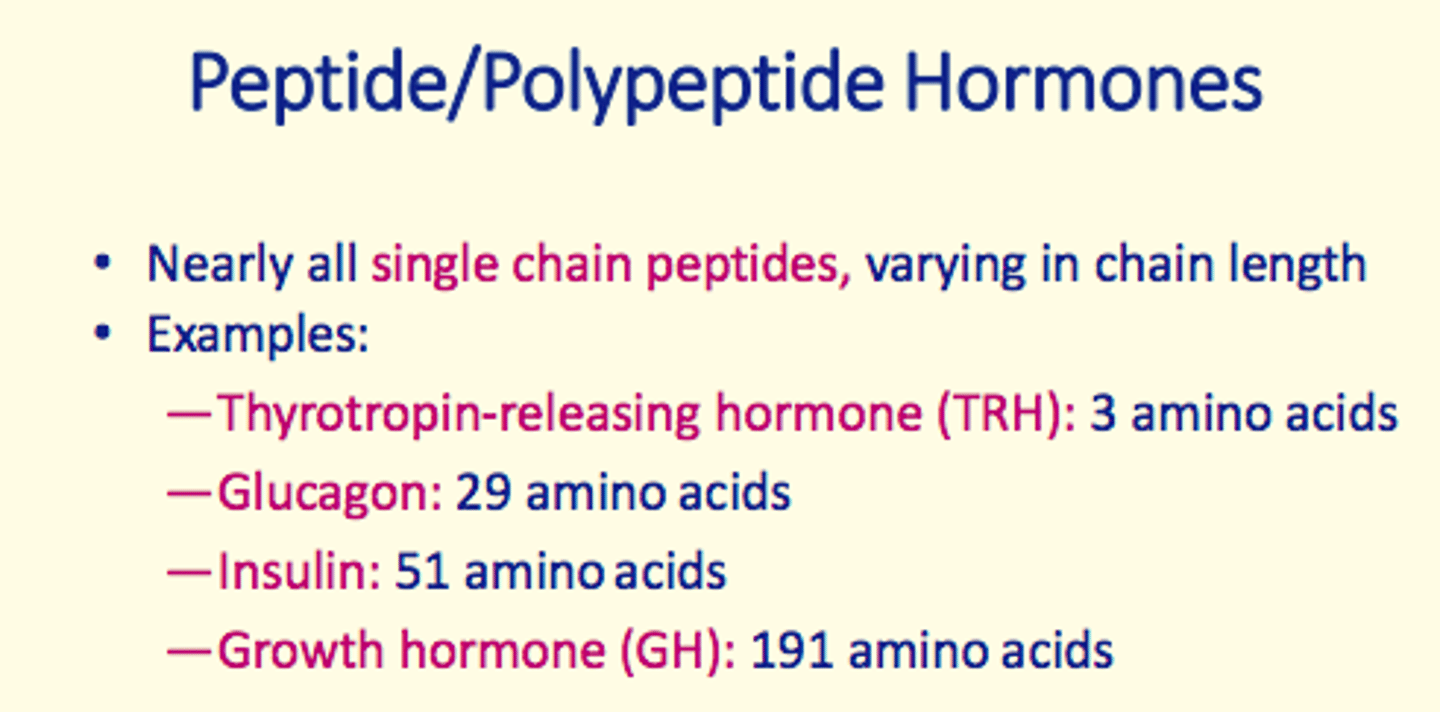
Insulin
- Peptide/polypeptide hormone
- 51 amino acids long
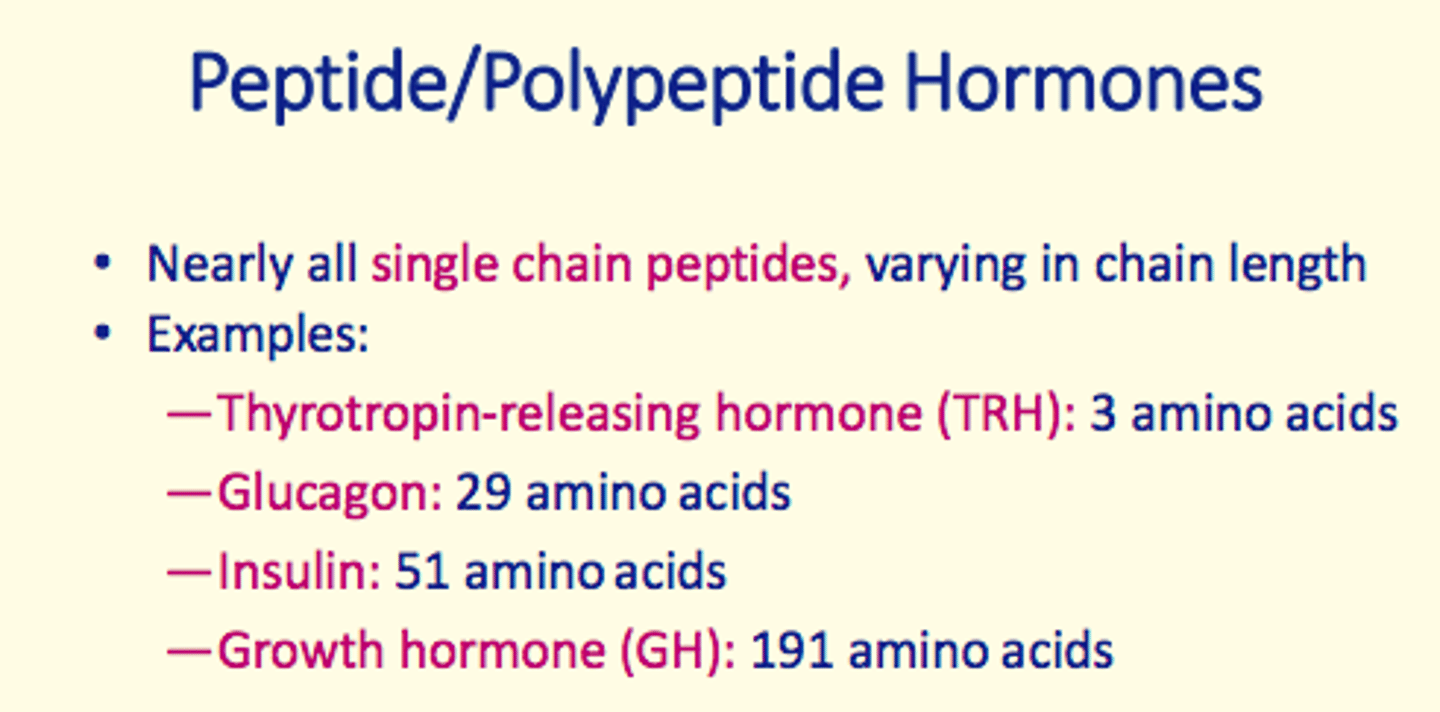
Growth hormone (GH)
- Peptide/polypeptide hormone
- 191 amino acids long
Glycoprotein hormones all have ___ polypeptide chains with carbohydrate side chains (α and β chains)
two
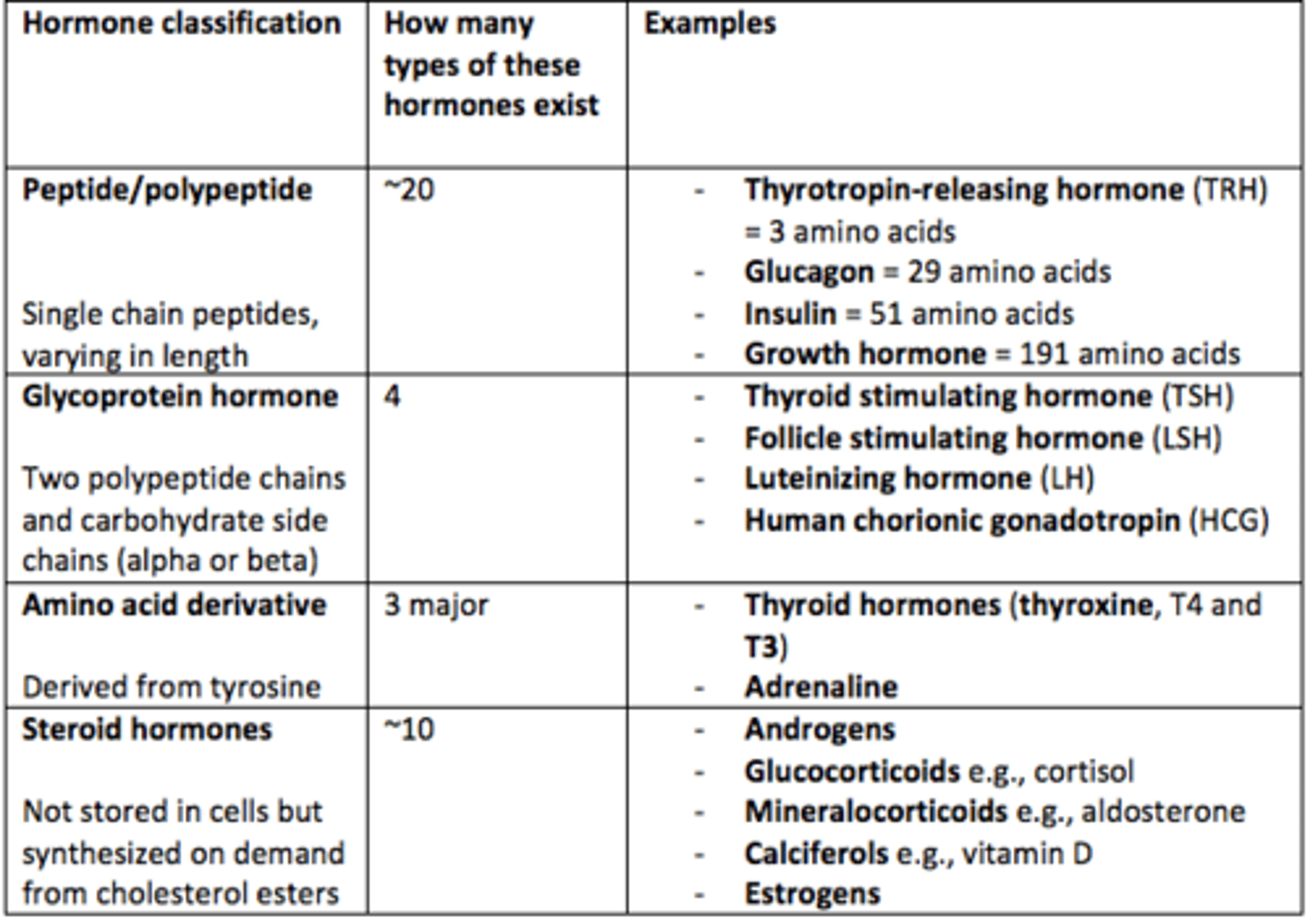
Give four examples of glycoprotein hormones
1) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
2) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
3) Luteinizing hormone (LH)
4) Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)
Brief overall description of how peptide/polypeptide and glycoprotein hormones are synthesised and secreted
1) Synthesised as larger precursor molecules = prepro-hormones and pro-hormones
2) Pro-hormones stored in secretory vesicles before release
3) Cleaved to → active hormone and released from vesicles
4) Hydrophilic

List the three amino acid derivative hormones
1) Thyroid hormones (T4 or Thyroxine) and T3
2) Adrenaline
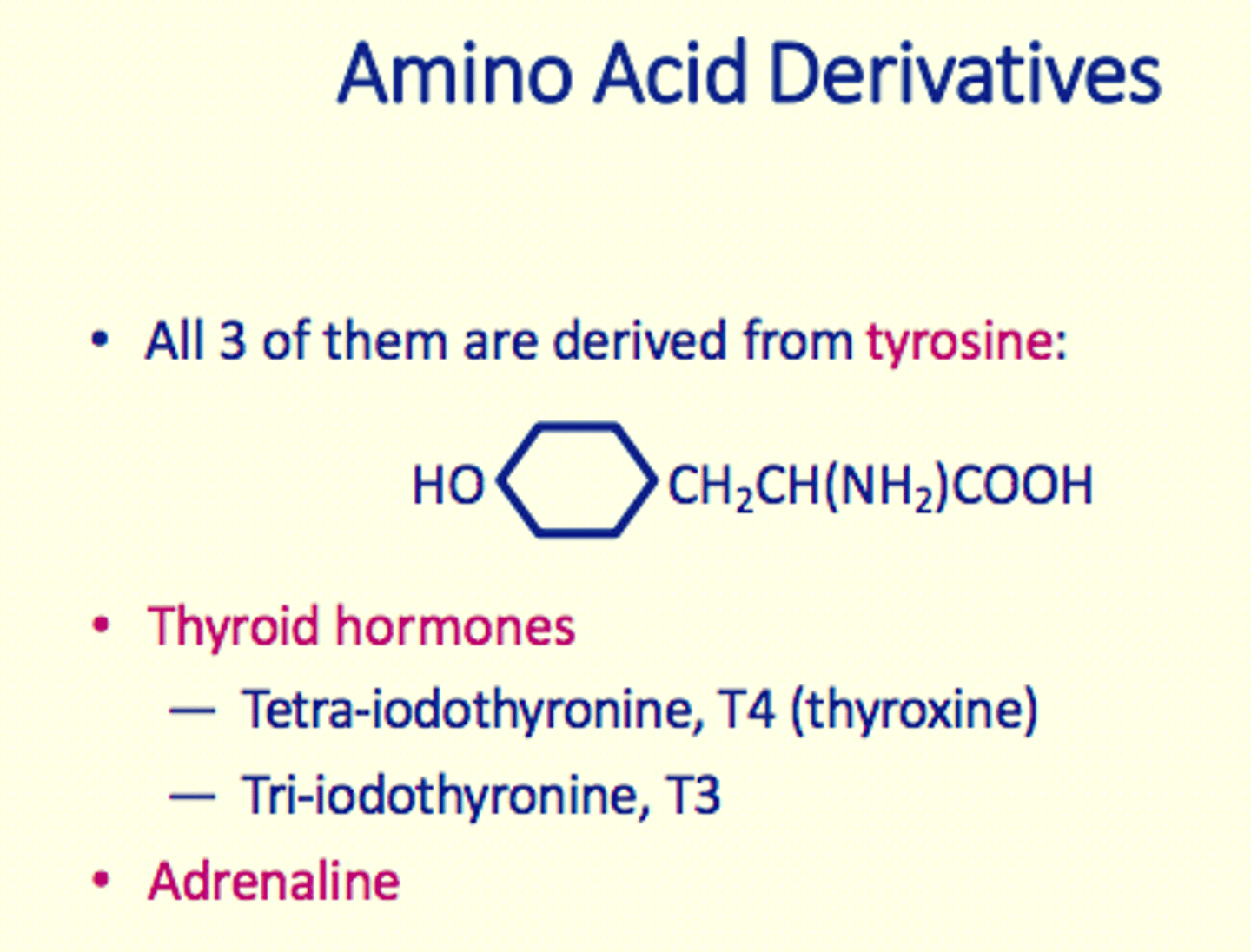
All three of the amino acid derivative hormones are derived from ___
tyrosine
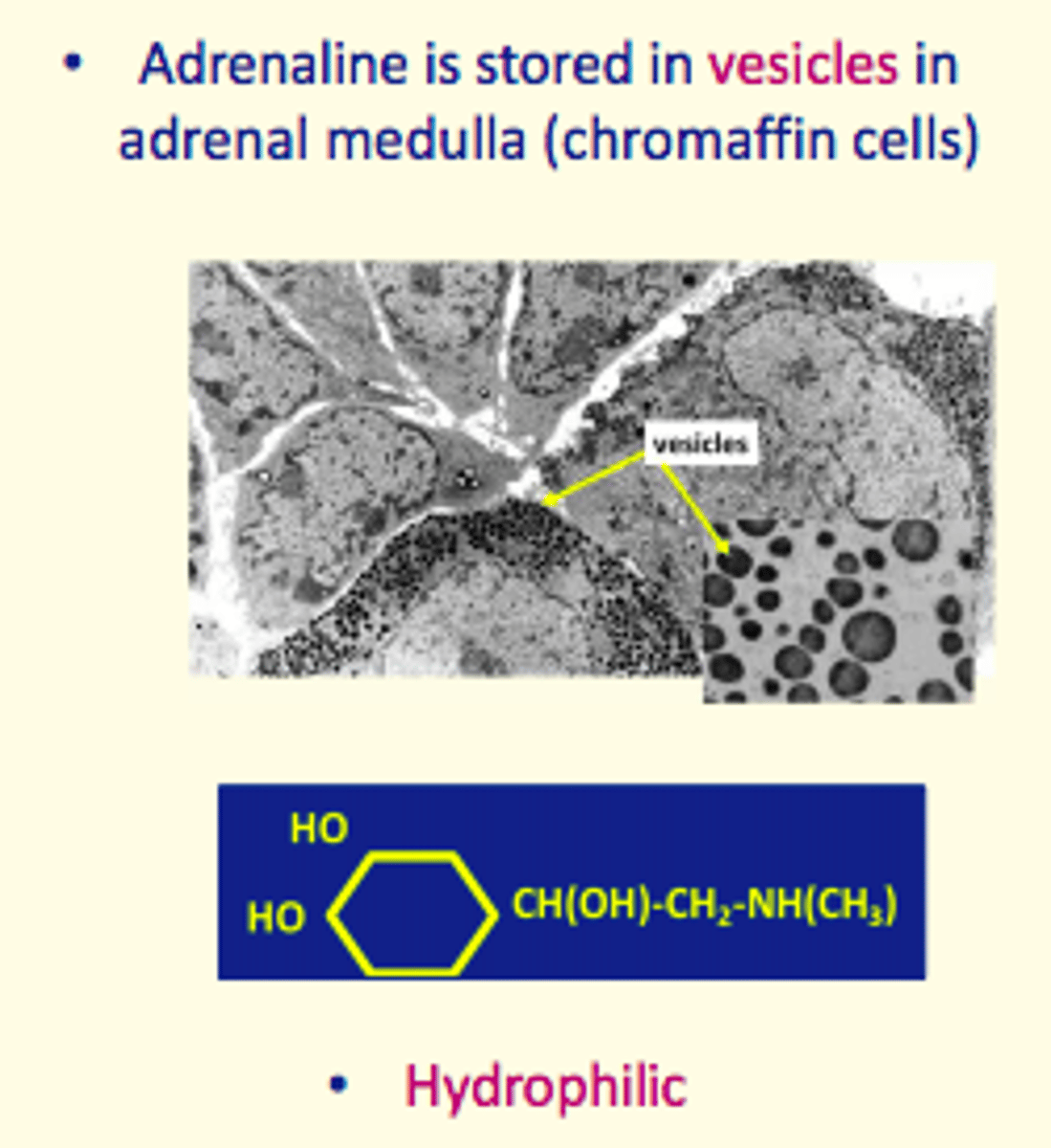
Adrenaline is stored in ___ in the adrenal medulla in ___ cells
vesicles, chromaffin cells
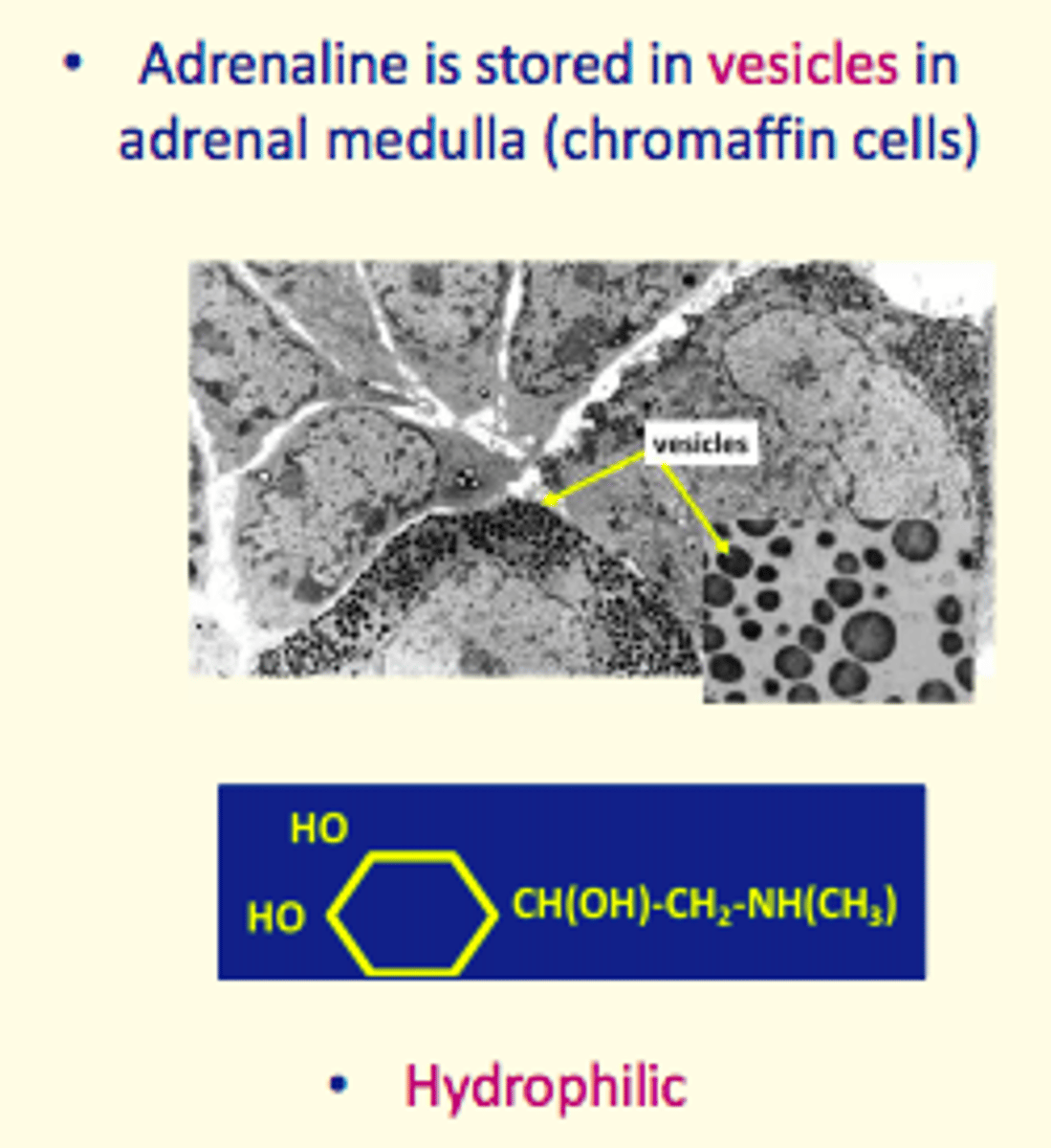
Is adrenaline hydrophilic or hydrophobic
Hydrophilic
Name of the cells in which adrenaline hormone vesicles are stored in (in the adrenal medulla)?
Chromaffin cells
Thyroid hormones are stored as ___ (prohormone) extra-cellularly in follicles in the thyroid gland as ___
thyroglobulin, colloid
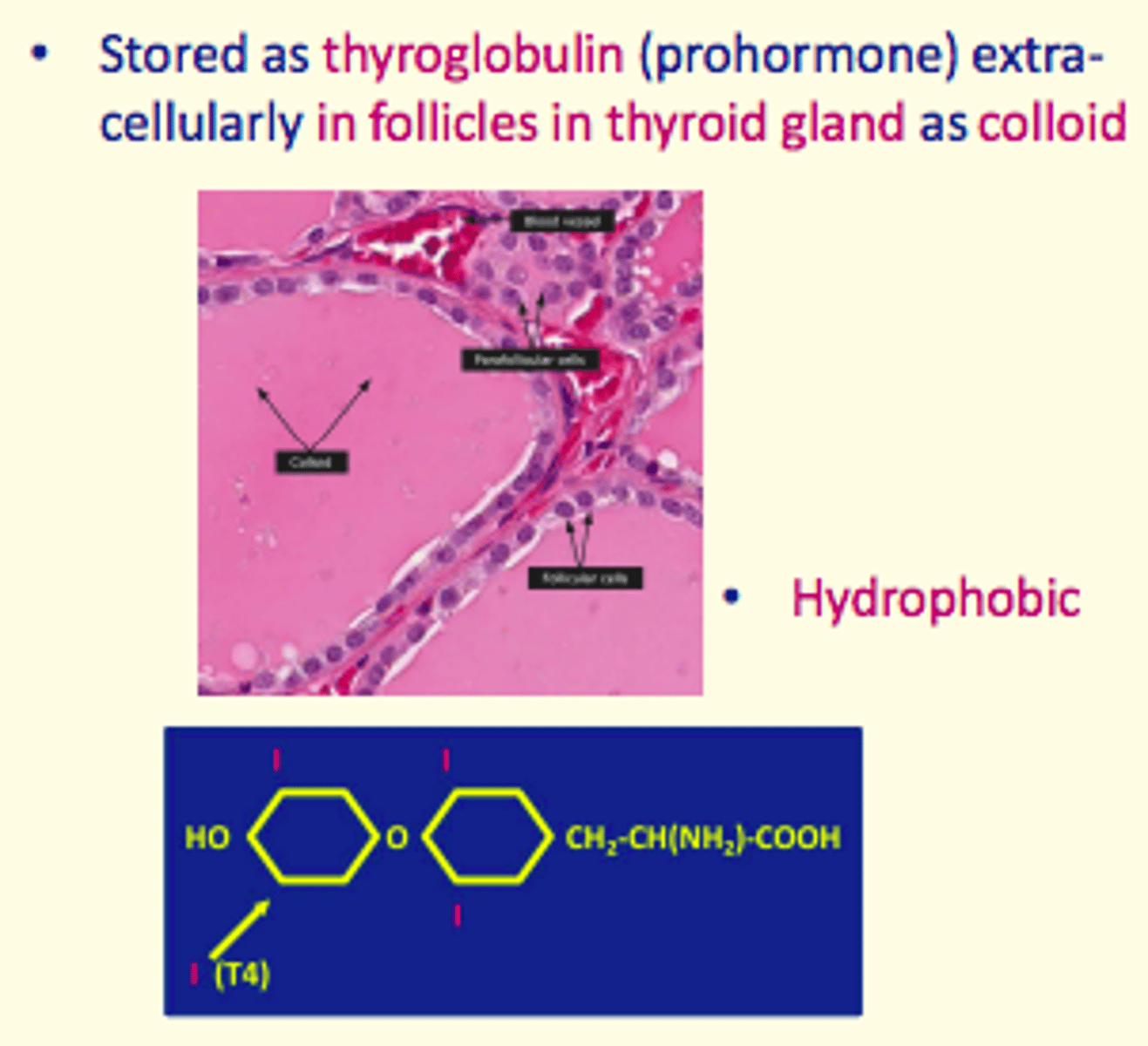
Are thyroid hormones hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophobic _
Are steroid hormones stored by cells?
No
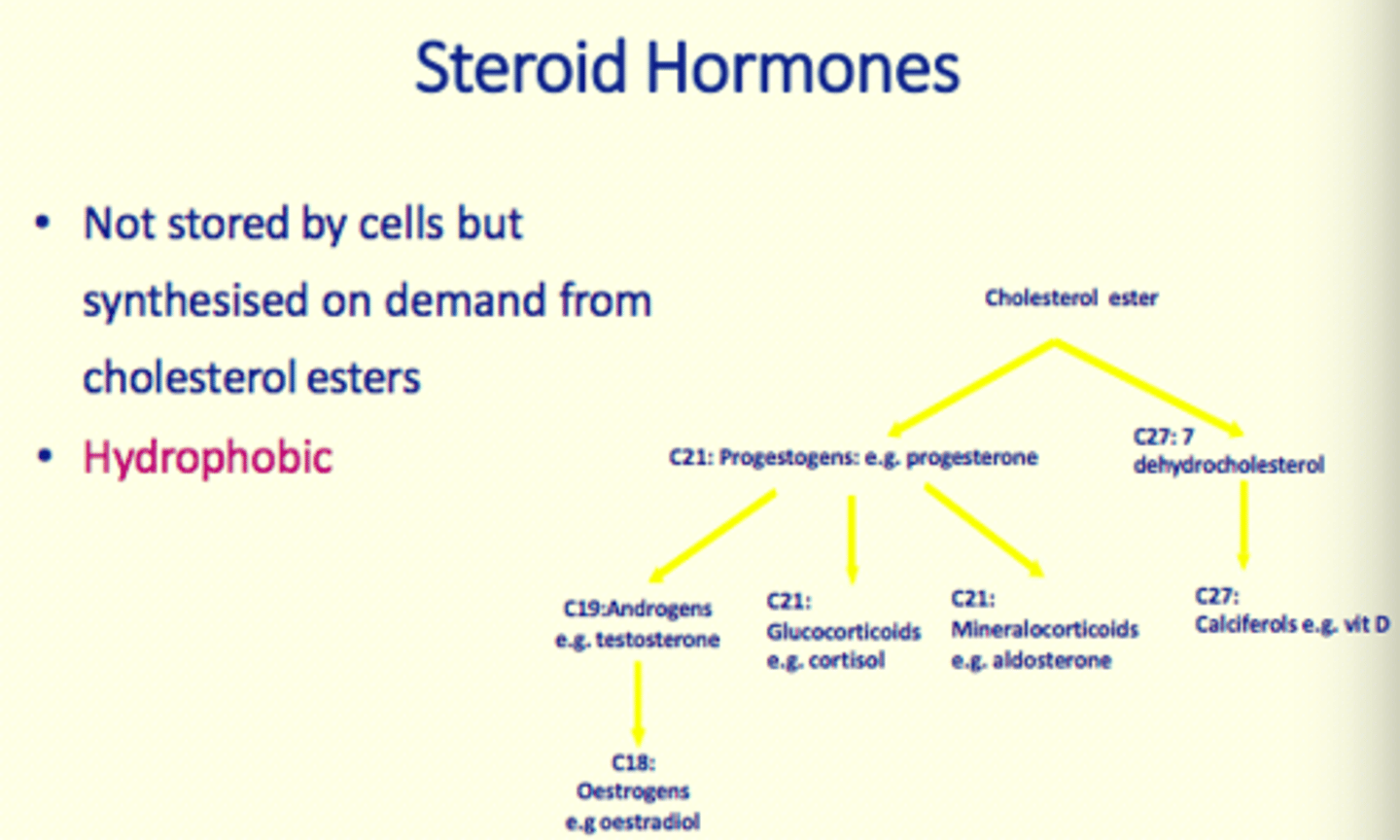
Steroid hormones are ___ on demand from ___ esters
synthesised, cholesterol
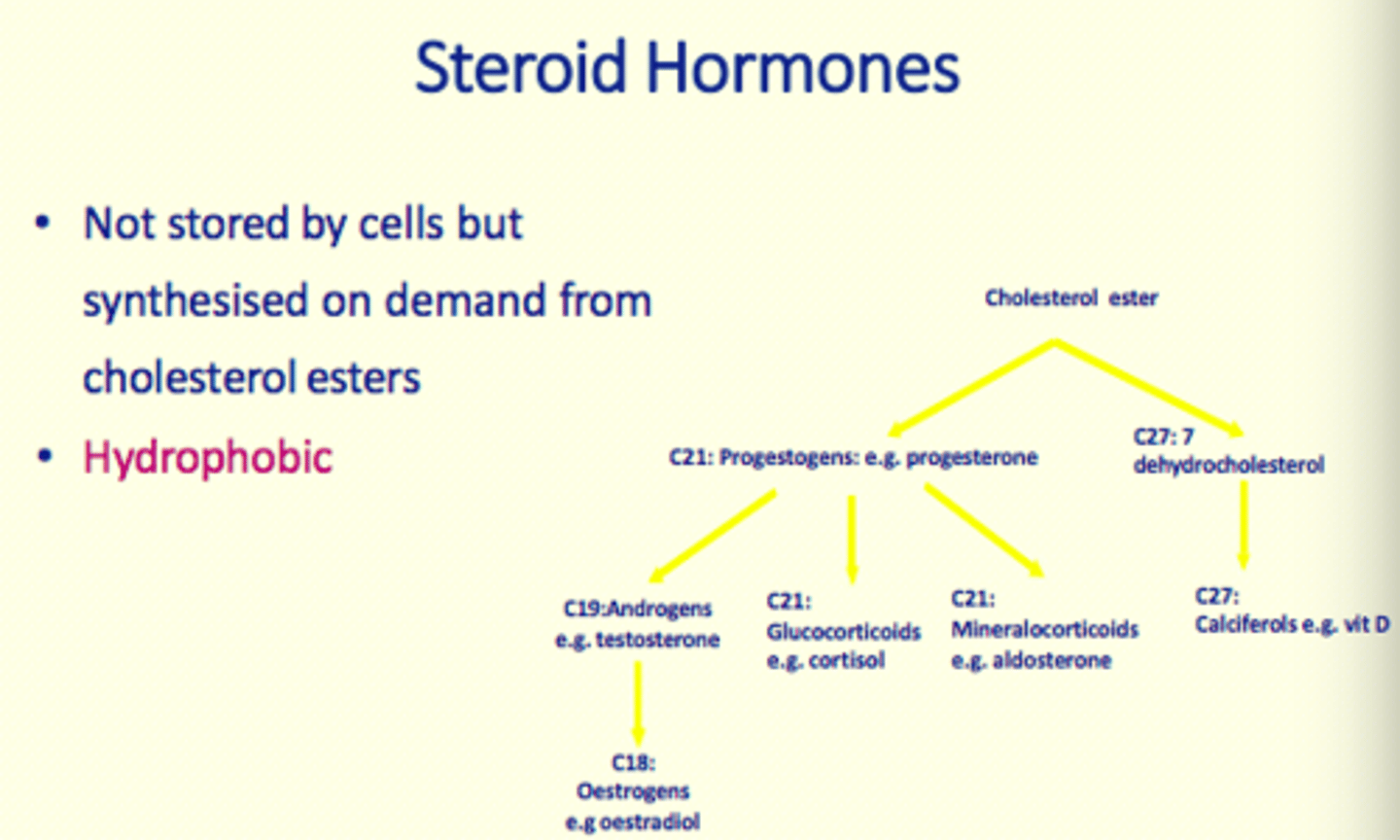
Are steroid hormones hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic_2
The rate of hormonal secretion is controlled by a ___ feedback loop
negative
Explain parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion negative feedback loop briefly
1) PTH secretion is stimulated by decreased blood calcium level
2) PTH acts on bone and kidney to increase blood calcium level
3) Increased blood calcium level reduces PTH's own secretion
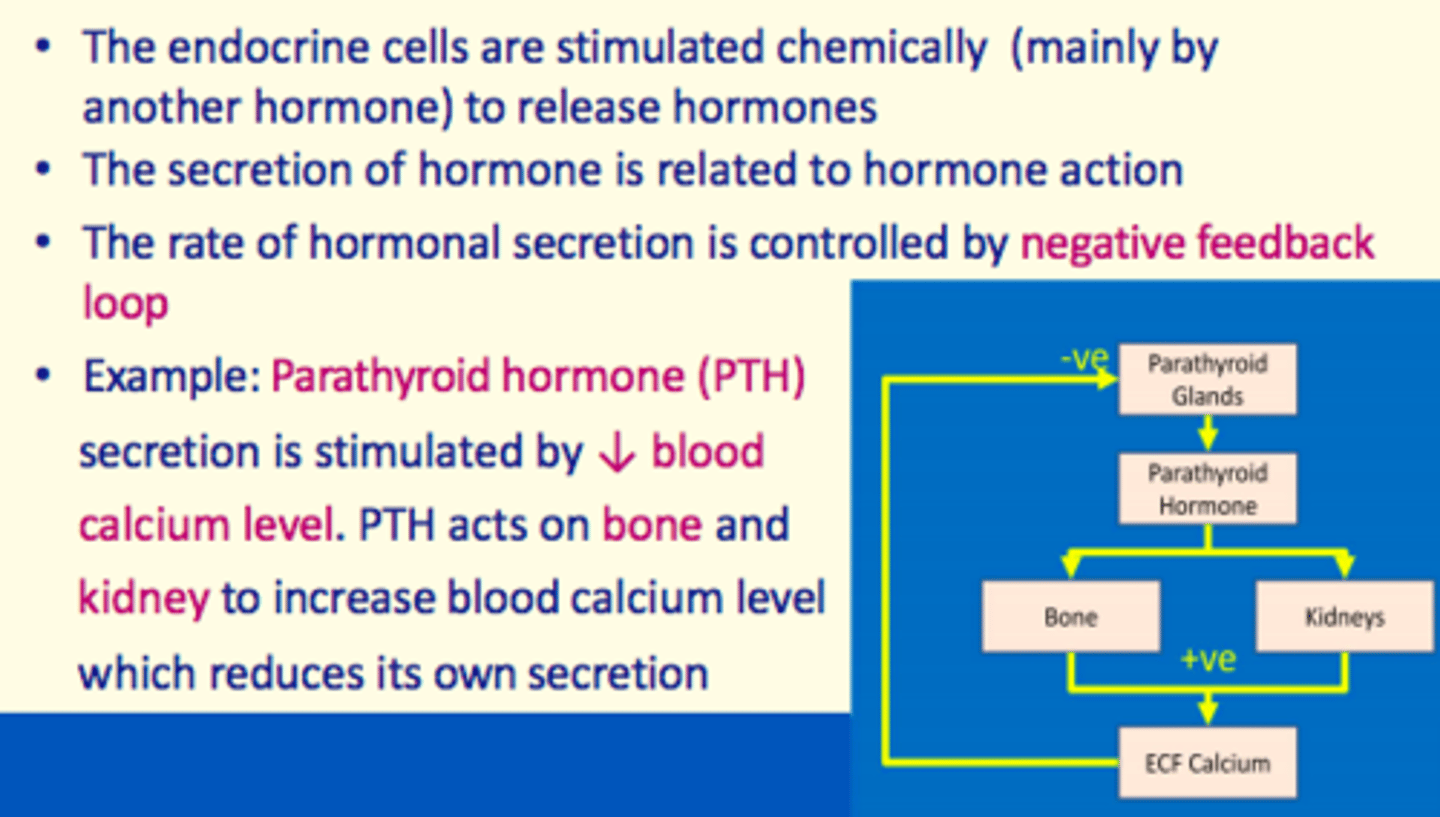
PTH secretion is stimulated by a decreased ___ level in the blood
calcium
PTH acts on ___ and ___ to increase blood calcium level
bone, kidney
Tropic hormone
hormone that stimulates the secretion of another hormone
Give example of tropic hormone
TSH is a tropic hormone (thyroid-stimulating hormone) which is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormones
- Tyrotropin
Hypothalamus stimulates or inhibits ___ gland hormone secretion via hypothalamic releasing hormones
pituitary
Hypoglycaemia
'Four to the floor'
Hyperglycaemia (fasting)
>7
Hyperglycaemia (random)
>11
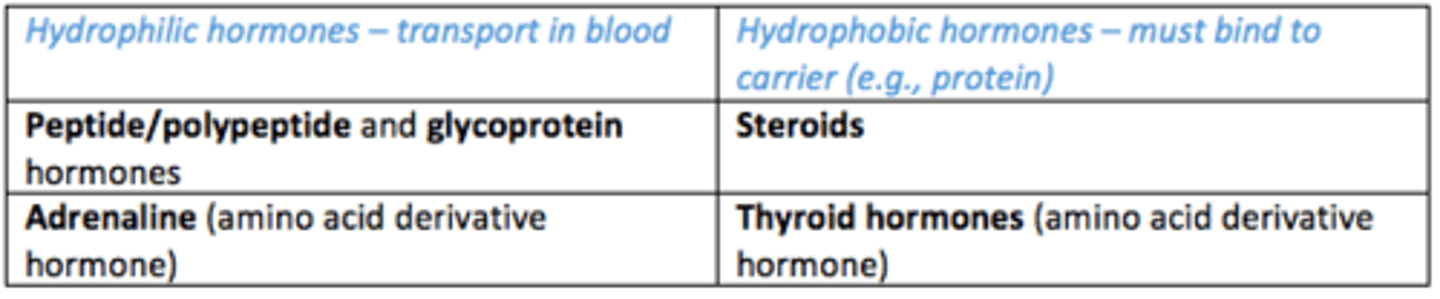
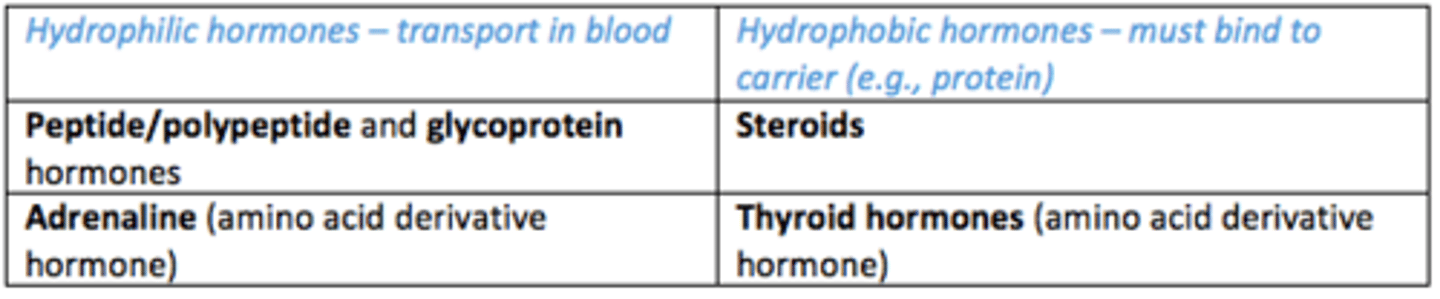
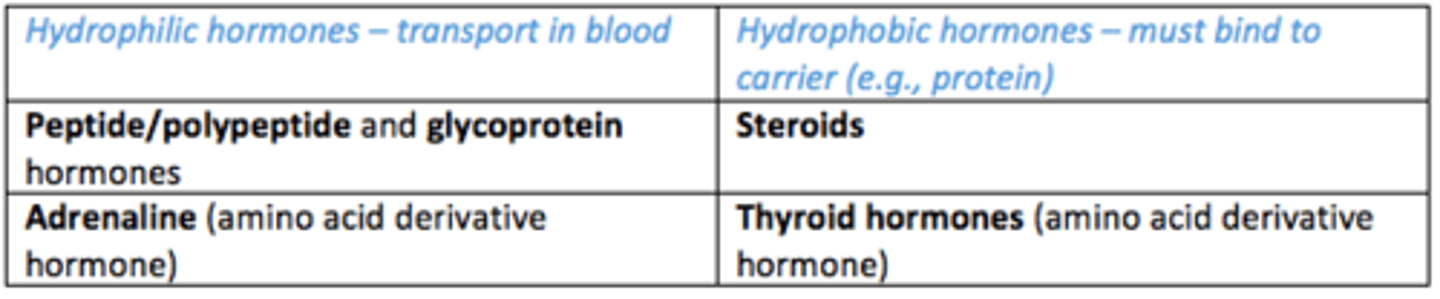
Which hormones are able to travel in the blood? (hydrophilic)
- Peptide/polypeptide hormones
- Glycoprotein hormones
- Adrenaline (amino acid derivate hormone)
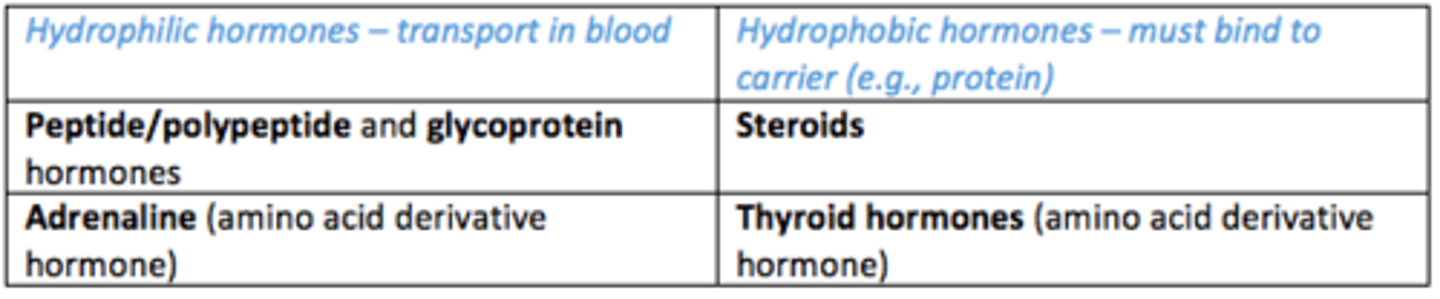
Which hormones must bind to carrier (e.g., protein) to be transported in blood due to being hydrophobic
- Steroid hormone
- Thyroid hormone

Inactivation of hormones usually occurs in the
liver
Peptide, polypeptide and glycoprotein hormones are inactivated by being...
- Degraded to amino acids
- Reused for protein synthesis

Steroid hormones and amino-acid derivative hormones are inactivated by undergoing...
- Small changes in their structure
- Recycled or excreted

Pancreas
Organ of digestive (exocrine) and endocrine systems
How large is the pancreas in a healthy adult (weight and length)?
weight ~200-300g
length ~15-20cm
The pancreas is anatomically divided into three parts...
1) Head
2) Body
3) Tail
The pancreas is functionally and histologically divided into two parts...
1) Endocrine = 2% (Insulin, Glucagon)
2) Exocrine = 98% (digestive enzymes)
A majority of the pancreas has ___ function
exocrine (98%)
A minority of the pancreas has ___ function
endocrine (2%)
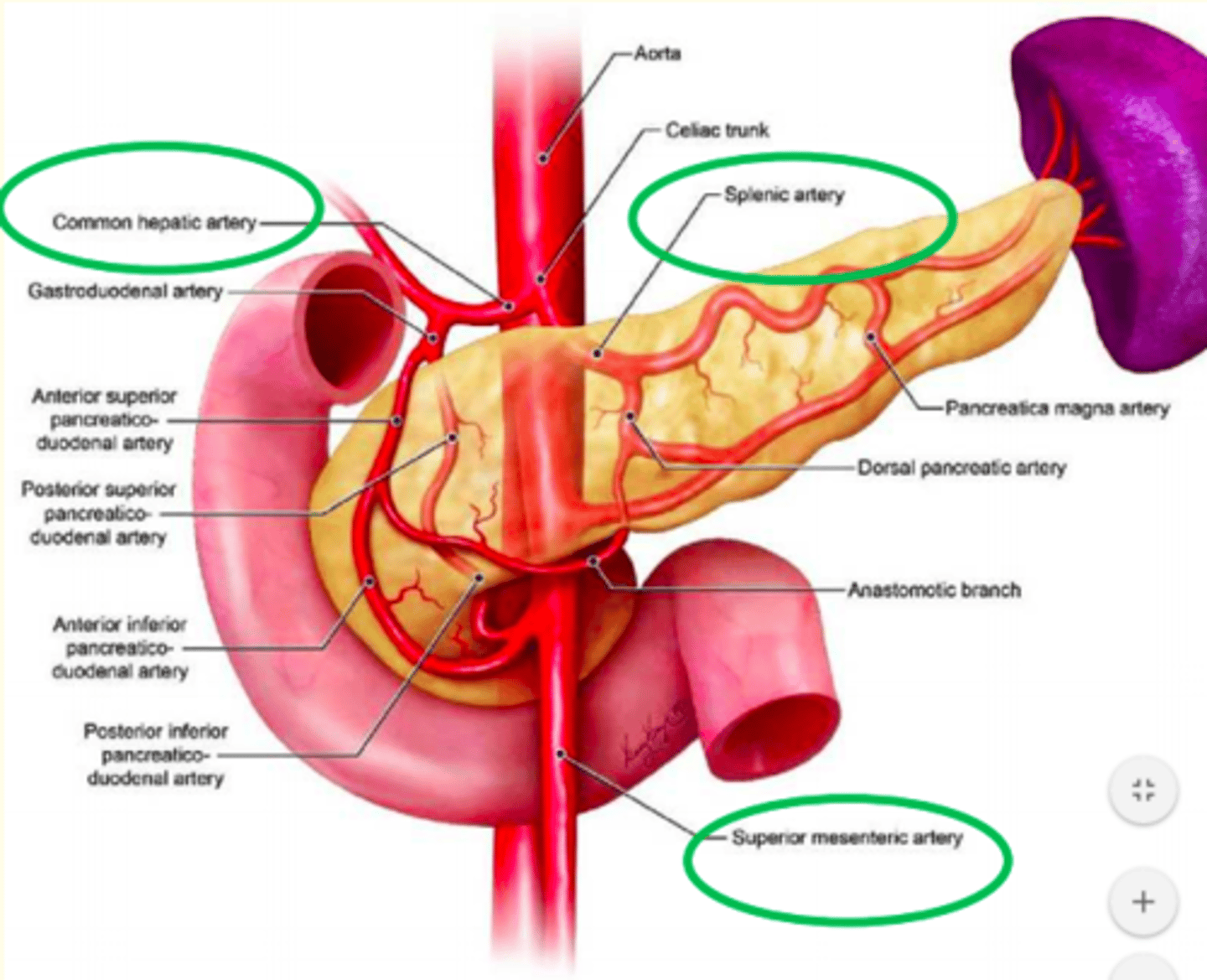
Anatomy and vasculature of the pancreas
Artery near duodenum = common hepatic artery
The artery inside pancreas = splenic artery
Artery exiting pancreas = superior mesenteric artery
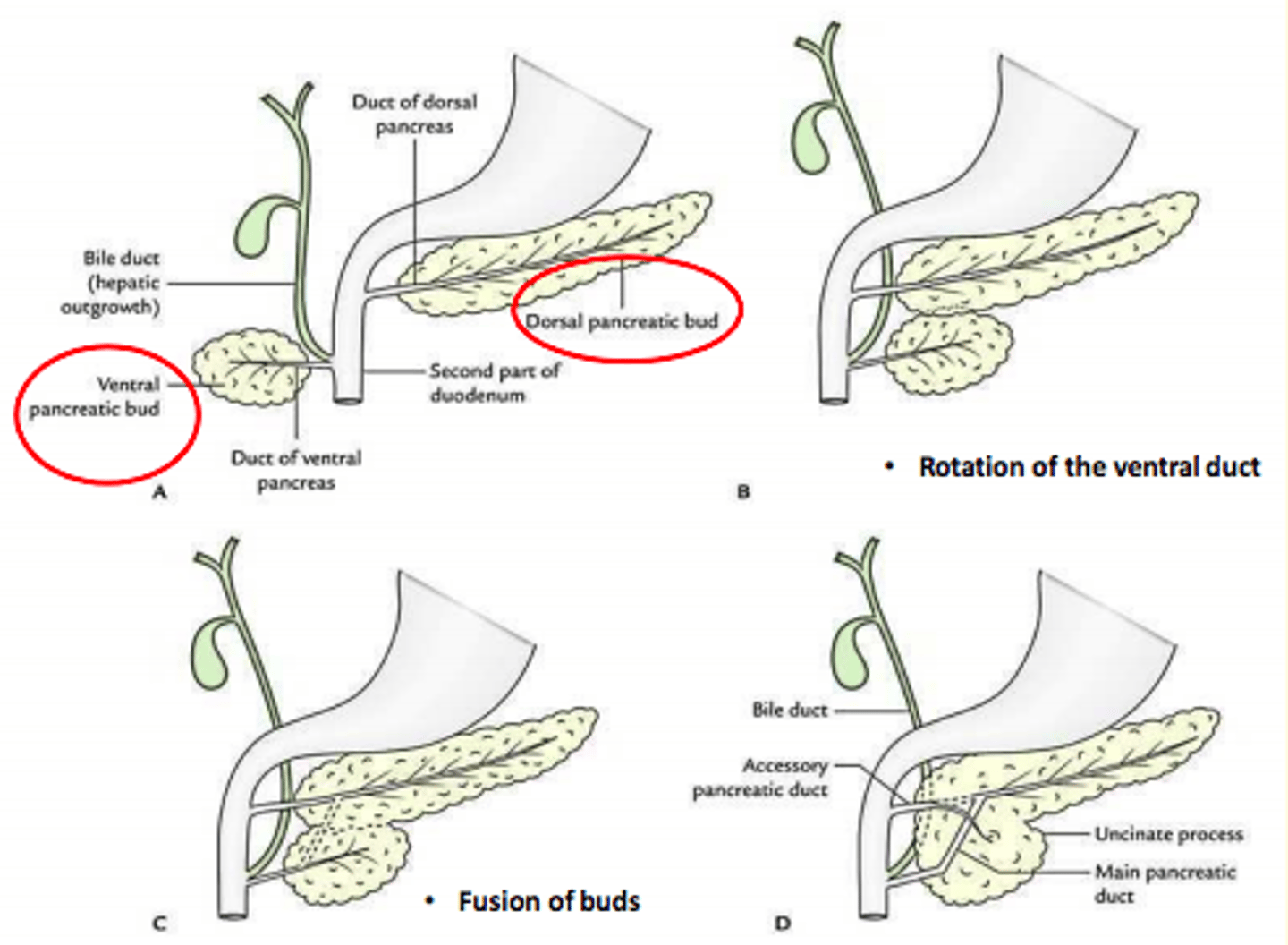
How does the pancreas develop?
- Ventral pancreatic bud and dorsal pancreatic bud
- Rotation of the ventral duct (bud)
- Fusion of the buds
Functions of the pancreas
1) Exocrine
2) Endocrine
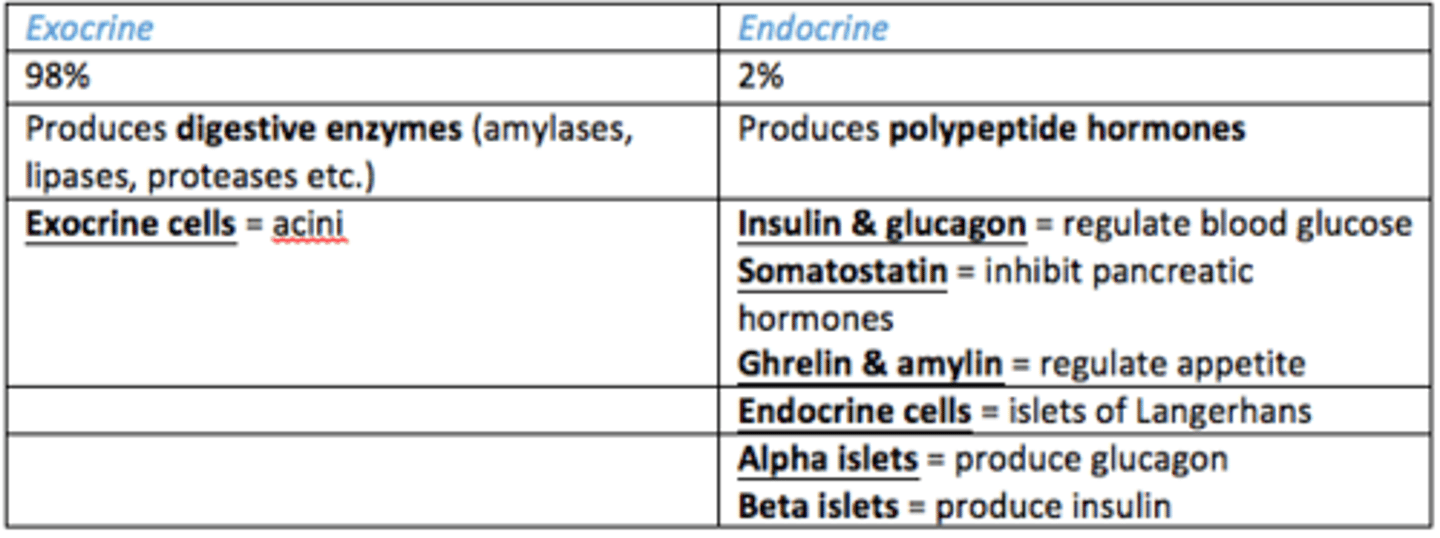
What does the exocrine pancreas do?
Secretes digestive enzymes (amylases, lipases, proteases etc)
What does the endocrine pancreas do?
Produces polypeptide hormones
What polypeptide hormones does the endocrine pancreas produce?
1) Insulin & Glucagon = regulate blood glucose
2) Somatostatin = inhibits pancreatic hormones
3) Ghrelin and amylin = regulate appetite

Histology of the pancreas
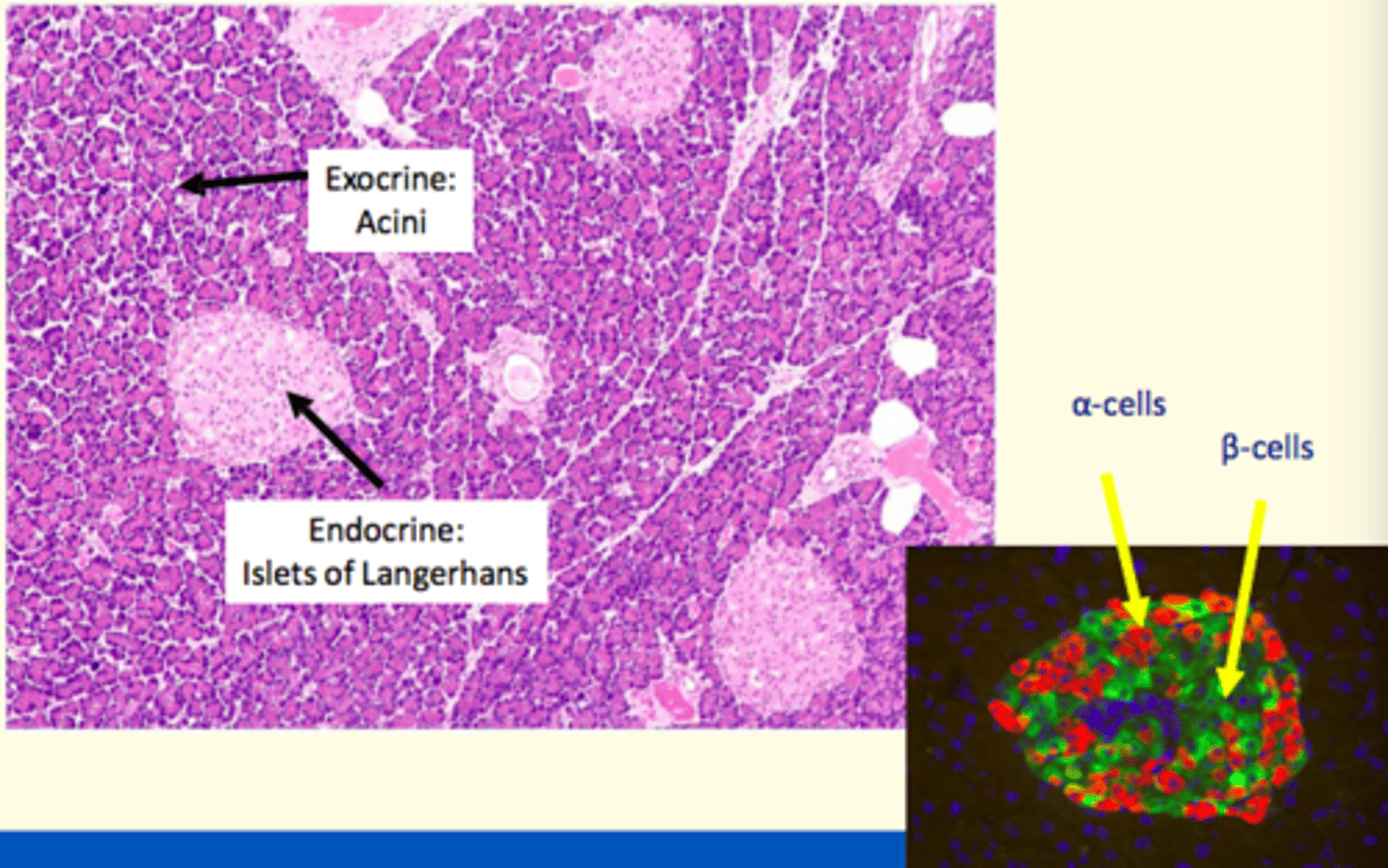
What endocrine cells found in pancreas
Islets of Langerhans =
- Alpha
- Beta
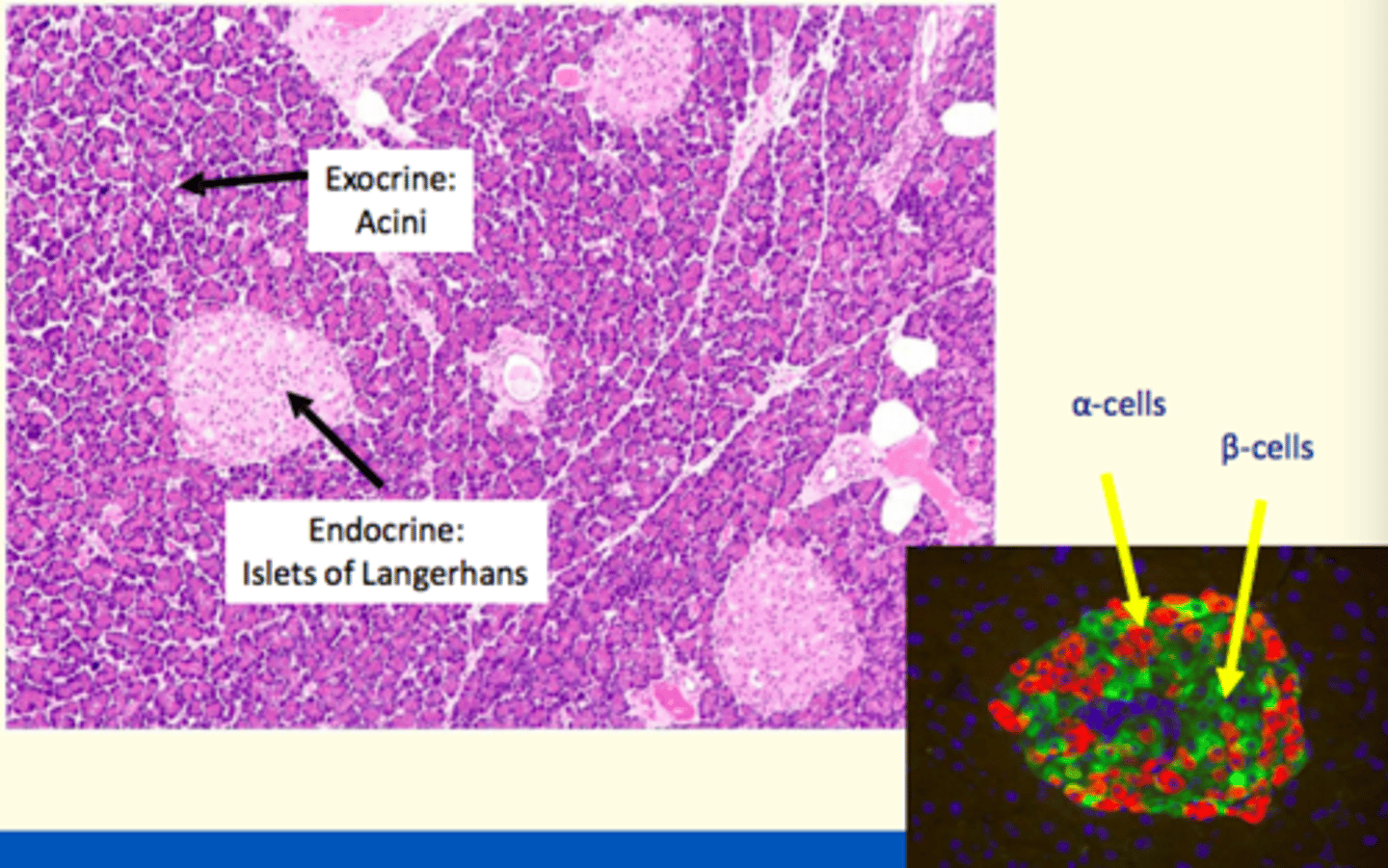
What exocrine cells found in pancreas
Acini
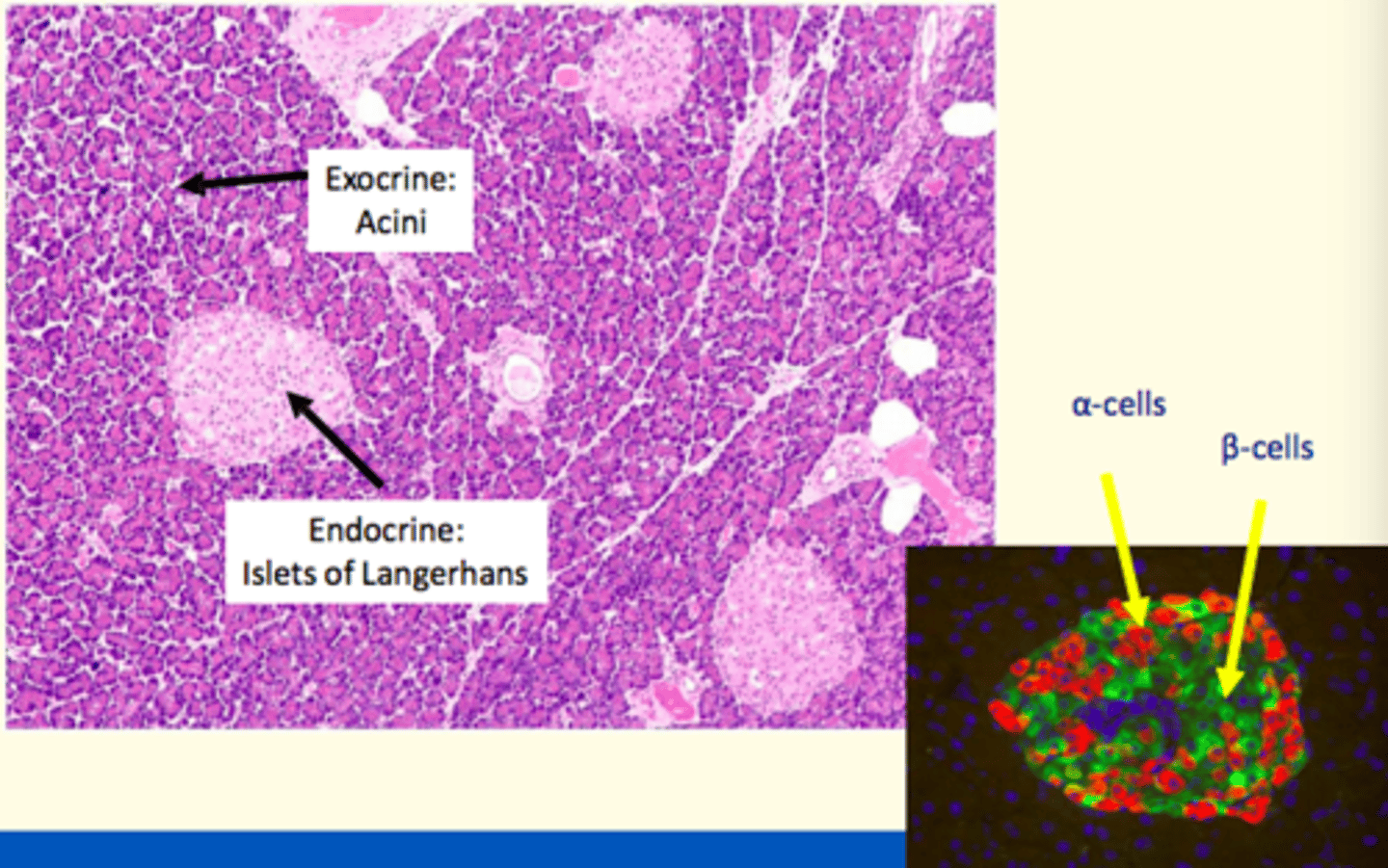
What are the cells of the islet of Langerhans in the pancreas that function to regulate glucose homeostasis
1) Alpha-cells = glucagon-secreting
2) Beta-cells = Insulin-secreting
3) Delta-cells = Somatostatin-secreting

What cells of the islet of Langerhans in the pancreas function to regulate appetite?
- Ghrelin-secreting cells (<1%)
- Pancreatic polypeptide-secreting PP cells (>1%)

Insulin
Hormone produced by beta-cells that lowers blood glucose
Glucagon
Hormone produced by alpha-cells that increases blood glucose
What tissues are insulin-sensitive?
Adipose, skeletal muscle and liver
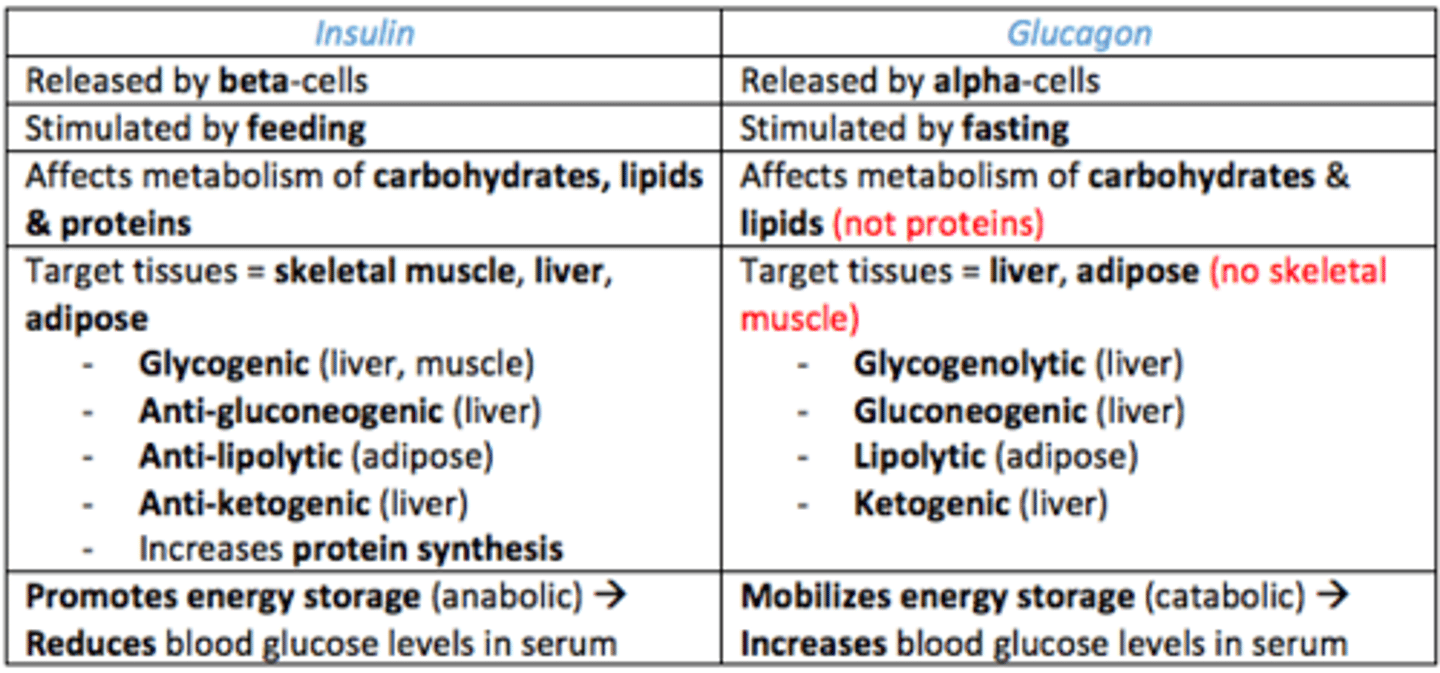
Compare and contrast actions and metabolic effects of insulin and glucagon
Briefly describe how insulin is synthesised?
1) Preproinsulin gene transcribed to m-RNA in nucleus.
2) Preproinsulin m-RNA moves to cytoplasmic ribosomes where N-terminal peptide is formed. N-terminal peptide allows transport of ribosomes with m-RNA to RER
3) Preproinsulin m-RNA translated to preproinsulin
4) N-signal peptide is cleaved forming = proinsulin
5) Proinsulin transported to the Golgi where it is cleaved into insulin and C peptide
6) Insulin and C-peptide are packaged into secretory vesicles for storage
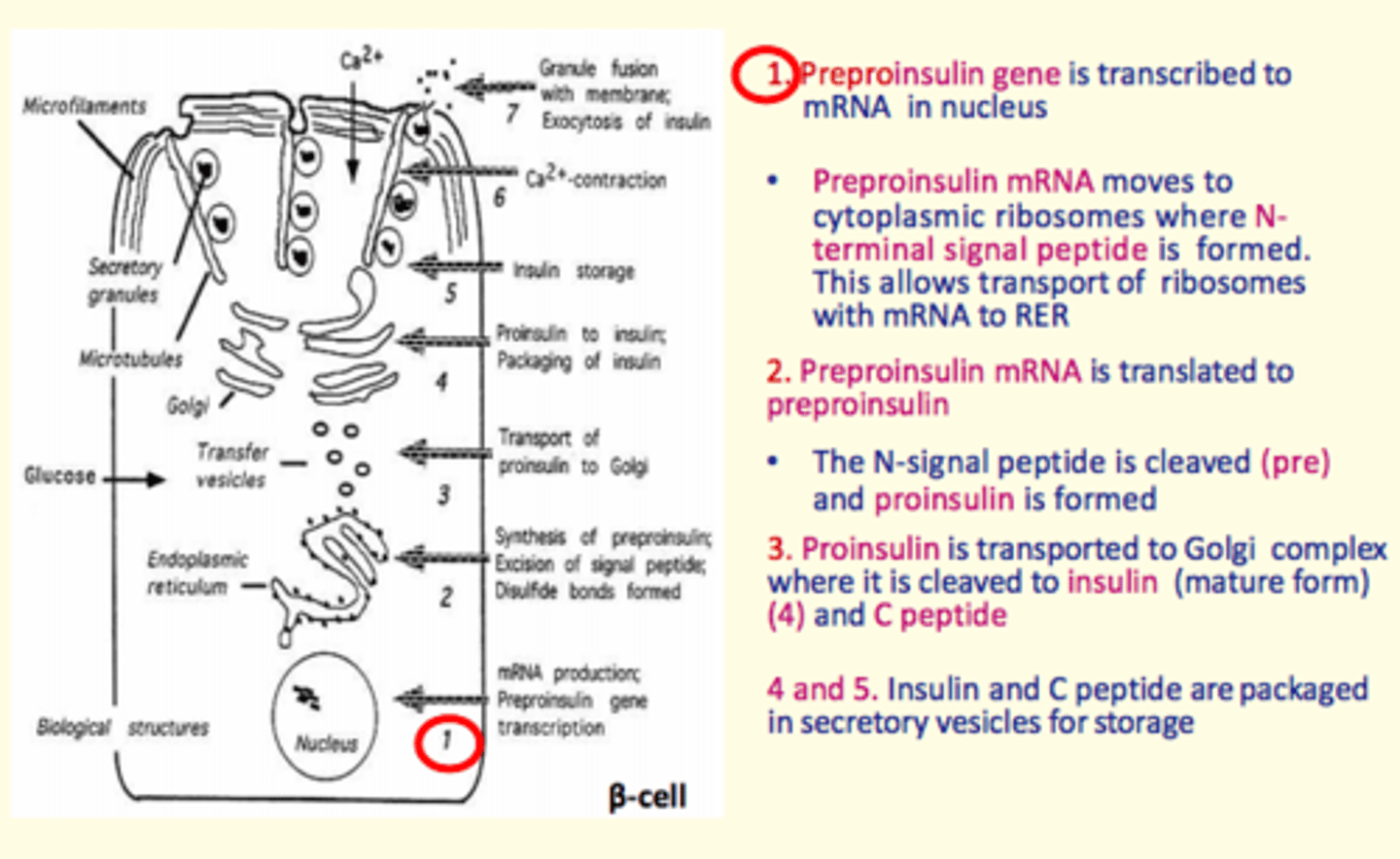
Insulin secretion process
1) Margination = secretory vesicles move along microtubules towards plasma membrane of beta-cell
2) High blood glucose means glucose transported into beta cell by facilitated diffusion (GLUT2).
3) Influx of calcium into beta cell
4) Increased intracellular calcium leads to contraction of microfilaments
5) Vesicle membranes fuse with the plasma membrane
6) Insulin and peptide C are released from the vesicle via exocytosis
Difference between negative and positive feedback loop
Hormone
chemical signaling molecules produced by the endocrine glands and secreted directly into the bloodstream.
Three key features of hormones
1) Must be able to travel to all parts of the body in 30 seconds
2) Different effects in different places
3) Effect of the hormone on the target cell depends on its concentration in the blood
The structure of a hormone defines how it is...
(name four things)
1) Produced
2) Transported in the blood
3) Interacting with cell receptors
4) Inactivated
Margination (secretion of insulin)
Secretory vesicles move along microtubules towards the plasma membrane of the beta-cell
What is the name of the glucose transporter on beta cells?
GLUT2
How does Insulin exert its effects?
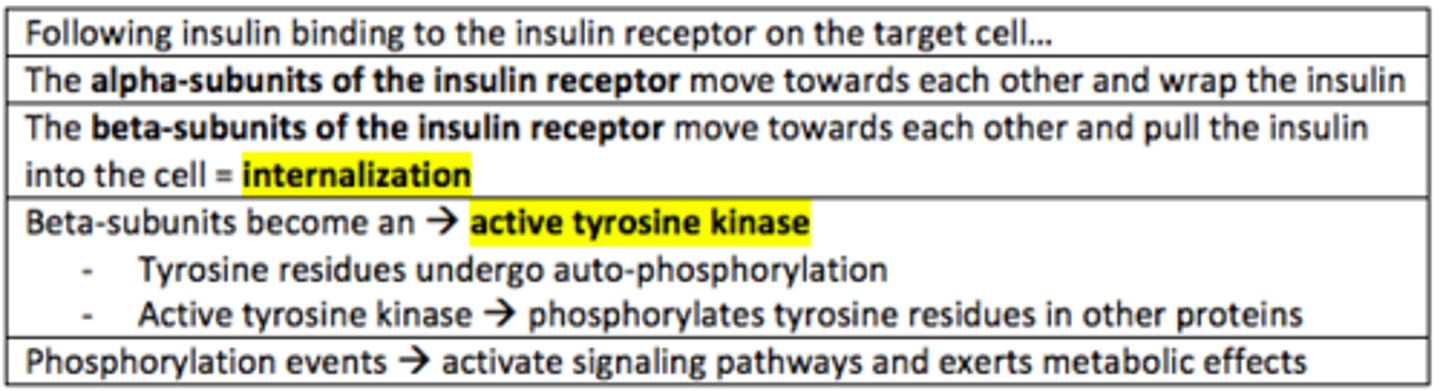
Insulin receptors are
tyrosine kinase receptors
Insulin receptors have alpha-units and ___-units
beta
How is Glucagon synthesised in alpha cells?
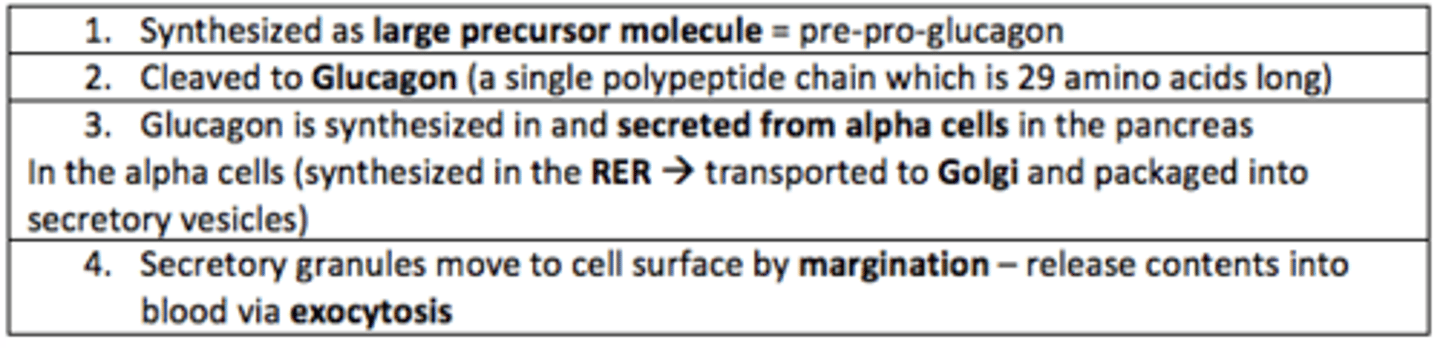
Glucagon is synthesised as a large precursor molecule known as...
pre-pro-glucagon
Secretory granules of glucagon move to the cell surface of alpha-cells in the pancreas by a process known as...
margination
Secretory granules of glucagon are released from alpha-cells via a process known as...
exocytosis
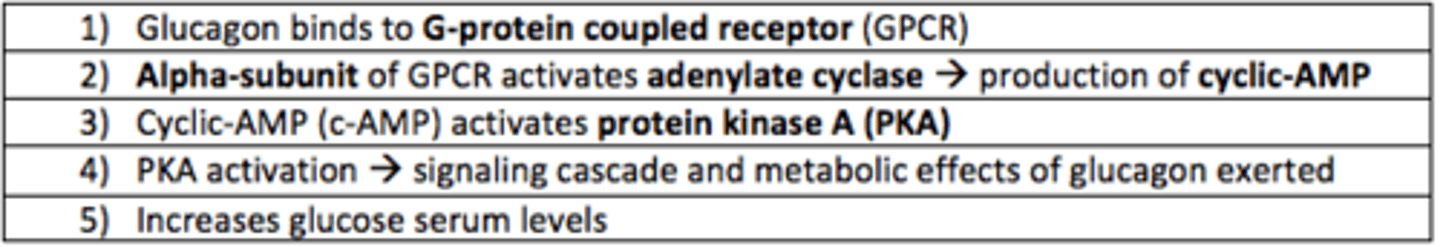
How does glucagon exert its effects on glucagon receptors?
Glucagon binds to G-coupled protein receptors
alpha subunit of GCPR activates adenylate kinase → production of cyclic AMP
cyclic AMP activates protein kinase A (PKA)
PKA activation → acts as signaling cascade and metabolic effects of glucagon exerted
increase glucose serum levels
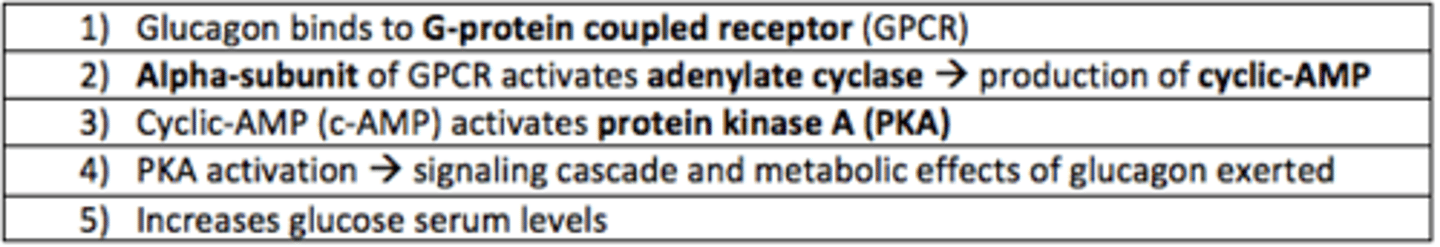
Glucagon receptors are...
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR)
The ___-subunit of GPCR (glucagon receptor) activates ___ cyclase which prompts the production of cyclic-AMP
The alpha-subunit of GPCR (glucagon receptor) activates adenylate cyclase which prompts the production of cyclic-AMP
Condition with low blood glucose
Diabetes mellitus
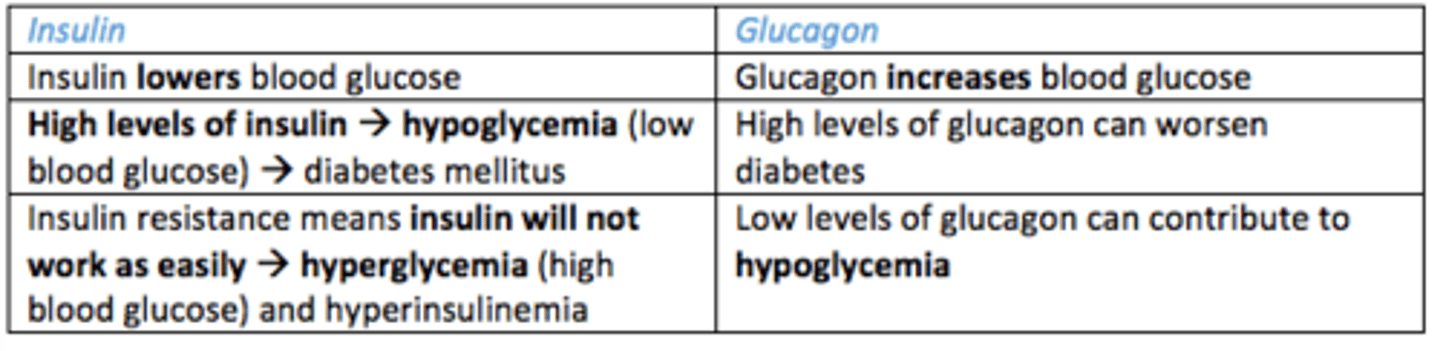
Clinical signs of abnormal insulin/glucagon levels
HIGH
INSULIN - leads to hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) → diabetes mellitus
GLUCAGON - high glucagon can WORSE DIABETES
Name hormone of which secretion is controlled by circadian rhythms
cortisol