Understanding the Cell Cycle and Mitosis
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Cell Cycle
Life of a cell from formation to division.
Interphase
Longest phase of the cell cycle (90%).
Mitosis
Division of the nucleus into two identical nuclei.
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm after mitosis.
Chromatin
Non-condensed form of DNA in interphase.
Chromosome
Condensed DNA structure during cell division.
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome joined together.
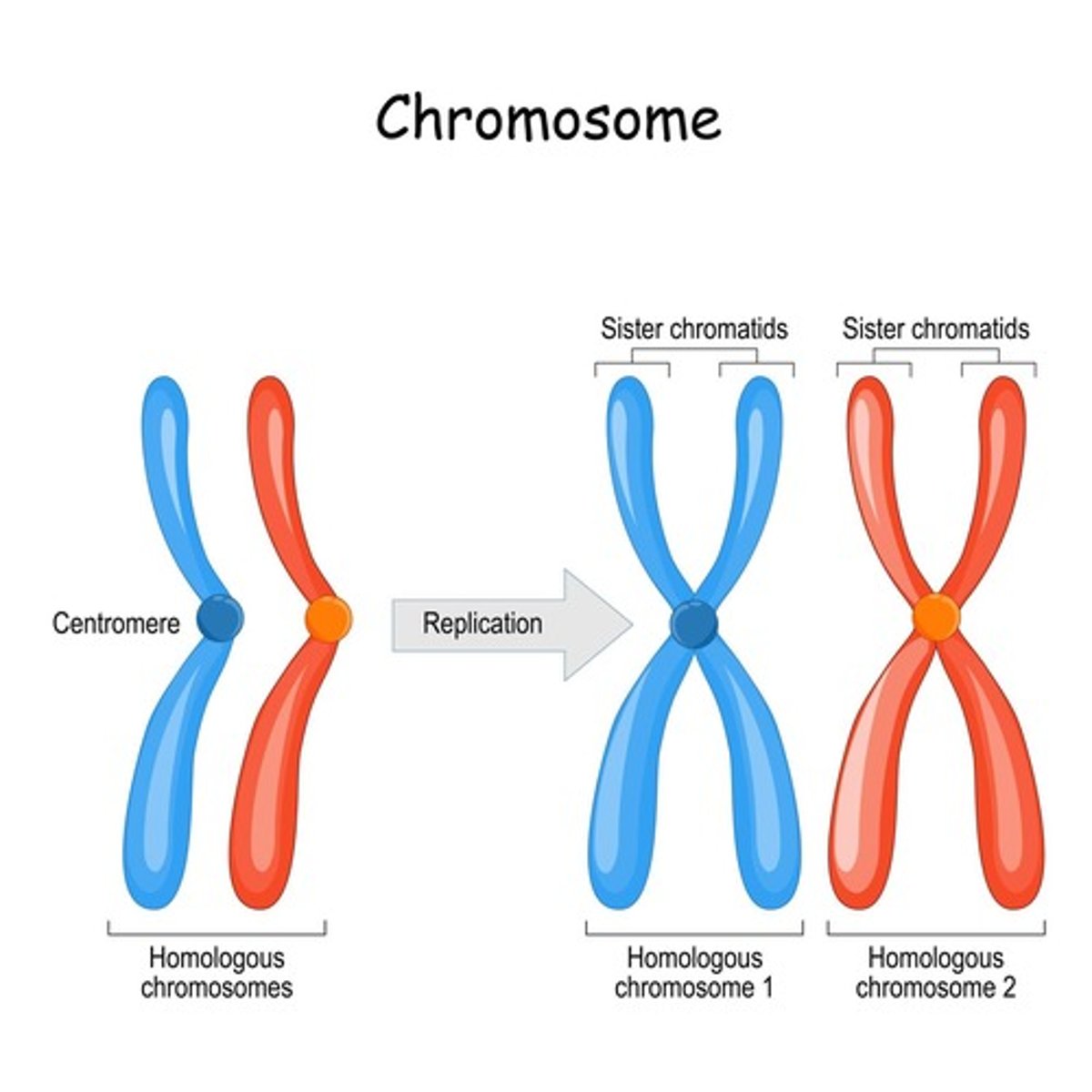
Centromere
Region where sister chromatids are attached.
Kinetochore
Protein structure linking chromatids to spindle.
Genome
Total genetic information of a cell.
Prokaryotes
Organisms with singular, circular DNA.
Eukaryotes
Organisms with linear chromosomes.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes from each parent with same genes.
Somatic Cells
Body cells that are diploid (2n).
Gametes
Reproductive cells that are haploid (n).
Diploid
Cells with two sets of chromosomes (2n).
Haploid
Cells with one set of chromosomes (n).
G1 Phase
First gap phase; cell growth occurs.
S Phase
Synthesis phase; DNA replication occurs.
G2 Phase
Second gap phase; preparation for mitosis.
Prophase
Chromatin condenses; spindle begins to form.
Prometaphase
Nuclear envelope fragments; microtubules attach to kinetochores.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate to opposite cell ends.
Telophase
Nuclear membranes reform; chromosomes de-condense.
G1 Checkpoint
Checks cell size, growth factors, and DNA damage.
G0 Phase
Non-dividing state some cells enter.
G2 Checkpoint
Checks DNA replication completion and damage.
M Checkpoint
Checks microtubule attachment to chromosomes.
Cyclins
Proteins regulating the cell cycle phases.
CDKs
Enzymes active with specific cyclins present.
Growth Factors
Hormones stimulating cell growth and division.
Contact Inhibition
Cells stop dividing upon contact with others.
Anchorage Dependence
Cells require attachment to divide.
Cancer Cells
Cells that divide uncontrollably due to mutations.
Benign Tumor
Non-cancerous mass of abnormal cells.
Malignant Tumor
Cancerous mass capable of spreading.
Metastasis
Spread of cancer cells to other body parts.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death in response to damage.
Tumor
Mass of tissue formed by abnormal cell growth.
Cancer Prevention
Strategies to minimize cancer risk.
DNA Mutations
Changes in DNA leading to cancer.
Cell Cycle Regulation
Control points ensuring proper cell cycle progression.
Chromosome Number
Humans have 46 chromosomes (2n=46).
Chromatid Count
After S phase, 4 chromatids present.