Nervous System CNS
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
CNS
brain and spinal cord
PNS (peripheral nervous system)
cranial and spinal nerves, ganglia, sensory neurons, neuromuscular junctions
brain anatomy
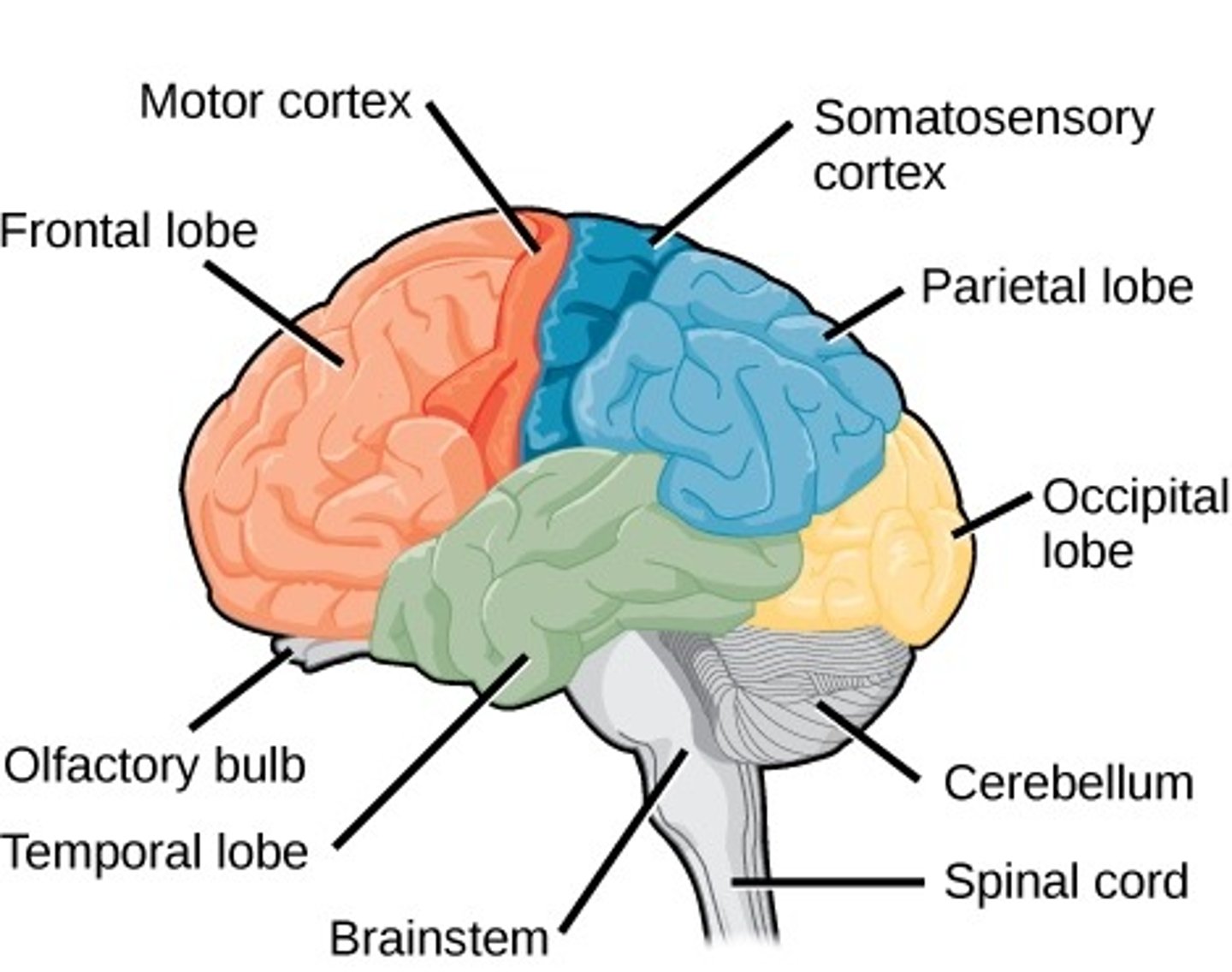
brain- frontal lobe
primary motor area and conscious thought; intellect and personality
brain- premotor cortex
The region controlling learned motor skills; skilled movement
brain- motor cortex
movement
brain- central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
brain- lateral sulcus
separates temporal and frontal lobe
brain- sensory cortex
sensations
brain- broca's speech area
Located in the left hemisphere. Responsible for the planning and production of speech. damage to this area results in the inability to form words
brain- temporal lobe
memory and auditory area
brain- wernicke's area
language comprehension
brain- occipital lobe
vision and storage of visual memories
brain- cerebellum
balance, equilibrium, and coordination
brain- brainstem (pons midbrain and medulla)
functions to survive. Breathing, digestion, heart rate, and BP and being awake.
spinal cord anatomy
C-spine: 1-7
T-spine: 1-12
L-spine- 1-5
Sacrum: 1-5
hemianopia
blindness over half the field of vision(; ex. damage to R eye or optic nerve= blind in R eye; damage to optic chiasm= blind in both eyes; damage to R occipital lobe or R optic track= loss of left visual field (just left side of both eyes))
expressive aphasia
The inability to produce language (despite being able to understand language); damage to Broca's area
receptive aphasia
inability to understand spoken or written words; damage to Wernickle's area; random words said with no meaning
global aphasia
When both production and understanding of language is damaged; combination of speech and comprehension is off
dysphagia
partial impairment; more common that total impairment
seizures
Sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain; precipitated by inflammation, hypoxia, or bleeding in the brain
increased ICP (intracranial pressure)
any changes in the composition of the brain can cause high ICP; normally 80% brain tissue, 10% blood, and 10% CSF; infection, trauma, etc. could cause this
early signs of ICP
body compensates by shifting more CSF from the brain due to...
-side effects: severe headache, vomiting, decreased responsiveness, papilledema
TIA (transient ischemic attack)
temporary reduced blood flow to the brain; 24 hr recovery; single or in a series; warning sign to a stroke
signs of TIA
FAST
F-face drooping
A-arm weakness
S-speech difficulty
T-time to call 911
symptoms are directly related to location of ischemia in brain
stroke
Damage to the brain from interruption of its blood supply
stroke risk factors
-high BP, high cholesterol, obesity, lack of exercise, sleep apnea, heavy alc use, smoking/drugs, diabetes, cardiovascular disease
cerebral aneurysms
weakened cerebral artery bulges and can rupture, leads to subarachnoid hemorrhage and increased ICP; initially small and asymptomatic
cerebral aneurysms signs and symptoms
- Loss of visual field or visual disturbances
- Headache
- sensitivity to light
-slurred speech
meningitis
inflammation of the meninges -> increased ICP -> edema in Pia and arachnoid layers; this can be viral, fungal, or bacterial (most serious)*; could be due to meningococcal or strep B
meningitis signs and symptoms
fever, stiff neck, headache, confusion, increased sensitivity to light, nausea/vomiting, and even rash; diagnosed with lumbar puncture
meninges in neonates
rash, baby won't eat, and high pitch cry; needs a prompt diagnosis and treatment; usually from undetected strep B via vaginal birth
brain abscess
localized infection usually in the frontal or temporal lobe; pockets of infection, edema, from spread of organisms, sinus infection, etc.
encephalitis
inflammation of the brain; mostly viral and can be caused by rabies
brain injuries
skull fracture, hemorrhage, edema, direct injury to brain tissue; may be mild or severe
concussion
mild blow; reversible; no bruising to brain tissue
contusion
blunt blow; bruising to the brain; blood vessels ruptured b/c of hit on skill; need CT/MRI
closed head injury
skull not fractured but injured brain; no visible injury/bleeding
hydrocephalus
accumulation of fluid/ CSF in the spaces of the brain; need shunt to drain fluid
spina bifida
a congenital neural tube defect that occurs during early pregnancy when the spinal canal fails to close completely around the spinal cord to protect it; not enough folic acid/ or maybe gestational diabetes
cerebral palsy
motor impairment that occurs before, during, or shortly after birth
causes: genetic mutation, abnormal fetal formation, infection, fetal brain damage
multiple sclerosis
progressive demyelination of brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Parkinson's disease
Progressive Degenerative disorder affecting motor function through loss of extrapyramidal activity
ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis)
fatal degenerative disease of the motor neurons marked by muscle weakness and atrophy
myasthenia gravis
a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the neuromuscular junction and produces serious weakness of voluntary muscles; idiopathic disease
myasthenia gravis symptoms
fatigue, breathing difficulty, difficulty to climb stairs/lift objects, drooping of eyelids, weakness of eye muscles, and blurred/double vision
huntington's disease
a hereditary disease marked by degeneration of the brain cells and causing chorea and progressive dementia.
dementia
an umbrella term to describe a range of symptoms associated with cognitive impairment
alzheimers
60% of all dementias, chronic, progressive degenerative cognitive disorder; cortical atrophy; personality changes, confusion; genetics can play a role
vascular dementia
form of dementia caused by a stroke or other restriction of the flow of blood to the brain
creutzfeldt-jakob disease
Rapidly progressive dementia with startle myoclonus
Prions (PrP) change from alpha to beta pleated sheet (resistant to proteases); rare, fatal, degenerative brain disorder
AIDS dementia
a broad cognitive impairment caused by HIV infection; later stages of AIDS
mental disorders
Conditions affecting mood, thinking, and behavior
schizophrenia
a psychological disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, and/or diminished, inappropriate emotional expression
major depression
endogenous: genetic; developmental
bipolar disorder
depression/mania
depression
exogenous: relative to an episode/event
signs of depression
Sadness
Inactivity
Problems sleeping
Withdrawn
post partum depression
depression following childbirth after 2 weeks; due to great hormonal changes
panic disorders
frequent prolonged panic attacks
spinal cord disorder
dermatome map; where it is vs where it causes pain