3 - Measuring stress
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What are the 4 used approaches to measure stress?
physiological arousal
life events
daily hassles
exposures to stress
Physiological measures of arousal
Heart rate, perspiration, breathing rate, temperature, blood pressure
Biochemical markers of arousal
Blood, sweat, tears, hair, urine
Used to assess the level of hormones the adrenal glands secrete during stress.
Using this approach, researchers can test for 2 classes of hormones
corticosteroids
catecholamines
Pros and cons of physiological measures?
Direct, objective, quite reliable, and easily quantified.
expensive
Can be confounded or influenced by many things.
life events measures?
Social Readjustment Rating Scale (Holmes & Rahe, 1967)
student stress scale
Social readjustment rating scale
Given a list of events that force people to make changes in their lives.
Participants are asked to check off which ones have happened to them recently.
Higher score = greater likeliness of getting some sort of disease in the future.
Problems with measuring life events?
The correlation between score and illness is only .3 (not very strong)
People get sick for reasons other than stress.
Individual differences in responses not accounted for.
Some of the items are vague.
Treats (+) and (-) events the same (ex. divorce or breakup)
Combines single events and ongoing chronic stressors (ex. after the breakup)
Self-report problems (recall bias, negative response bias)
Daily hassles measure
Some people experience more daily hassles than others
This scale measures people experiences with day-to-day unpleasant or potentially harmful events.
Ex. “Think about how much of a hassle or strain each item was for you today”
Death by a thousand cuts
Many stressors, microaggressions, etc can add up over time and lead to chronic stress.
General/perceived stress measure
Does not ask about specific events
Asks about general perceived level of stress, because people can vary in what they consider stressful
More stress is linearally associated with illness
Selye’s experiments were used to demonstrate a __________
"Non-specific physiological response to a demand put on our body"
After exposure to stress for long periods, what did Seyle noticed in the rats?
When stressors become chronic, we try to resist for so long and our reserves become depleted.
(i.e. initially adaptive, until our body gives up.)
Ex. rats were stressed out for so long that they eventually died from exhaustion.
Selye called this series of physiological reactions in the rats the________________
general adaptation syndrome (GAS)
general adaptation syndrome (GAS)
The sequence of physiological reactions to prolonged and intense stress. The sequence consists of the alarm reaction, the stage of resistance, and the stage of exhaustion.
3 stages of GAS?
Alarm Reaction: mobilize resources (epinephrine, and norepinephrine)
Resistance period: cope with stressor (arousal remains high)
Exhaustion: reserves depleted
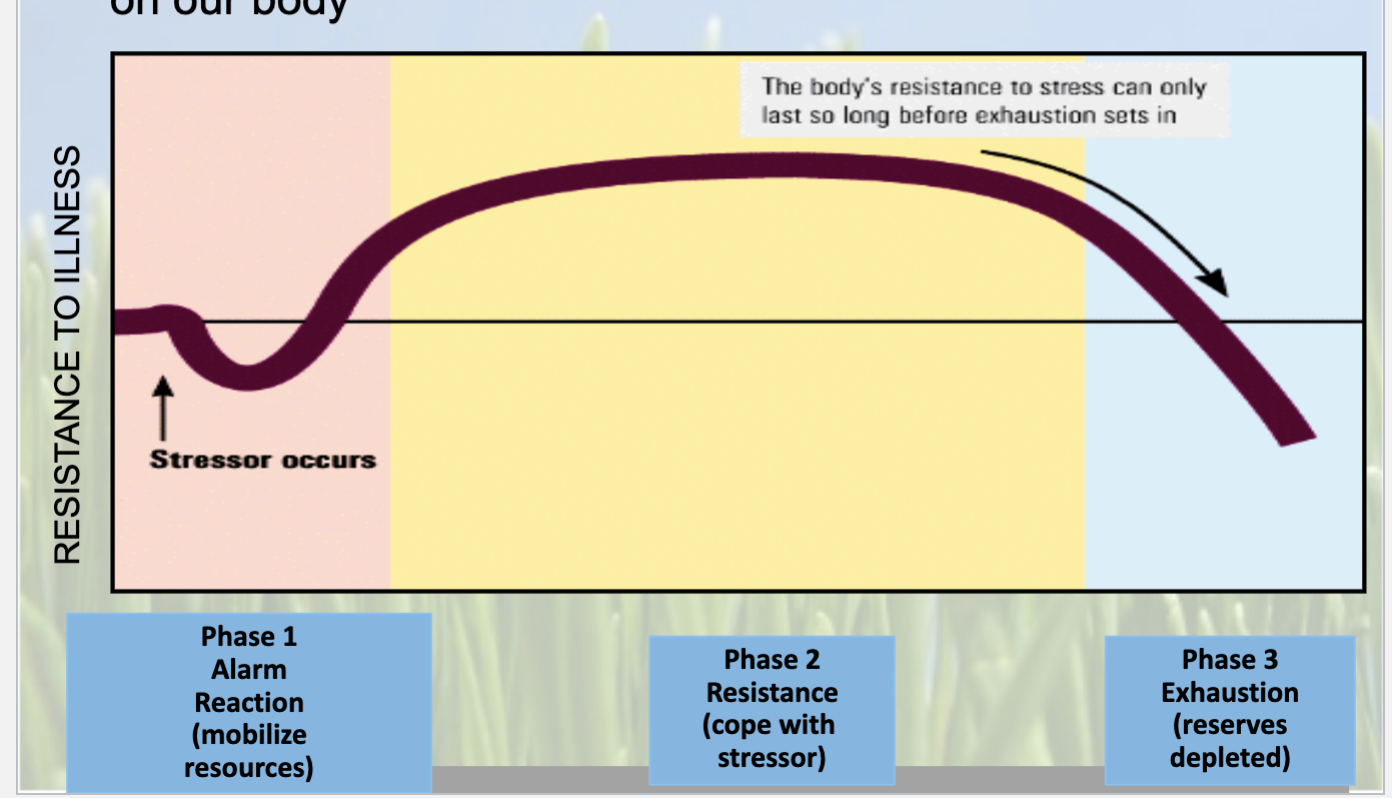
Continuous arousal in the resistance period may impair the ability to resist new stressors.
This impairment may lead to
diseases of adaptation
Prolonged arousal from severe, long-term, or repeated stress can weaken the immune system, and deplete energy until resistance is very limited --> leading to _______.
exhaustion
allostatic load
The accumulated effects of one’s body adapting repeatedly to stressors over time—as with fluctuations in levels of hormones like cortisol and epinephrine, blood pressure, and immune function
High levels of ________ are related to poor health in children and elderly.
allostatic load
The ____________ has a greater influence than the degree of activation in response to any one stressor.
cumulative amount of strain
4 factors are important in the overall amount of bodily activation or physiological stress:
Amount of exposure --> more frequent/intense/prolonged = greater activation
Magnitude of reactivity --> changes in BP or hormones.
Rate of recovery --> how long it takes to return to normal.
Resource restoration --> replenishment of resources (i.e., sleep).
Critics of GAS?
GAS is nonspecific with regard to the type of stressor (i.e., does not take into account psychosocial processes).
Amount and type of stress hormones released appear to vary. (ex. sometimes stronger)
Physiological variability may depend on the kind of stress
Does not consider cognitive appraisal/individual differences. (Ex. some more reactive to stress)
What are the 2 kinds of stress?
effort (eustress)
distress
Effort (eustress)
involves a person's interest, striving, and determination; good for you.
Effort with distress --> increase in catecholamine and cortisol (ex. daily hassles)
Effort without distress --> increase in catecholamine (ex. joy)
Distress
involves anxiety, anger, boredom, etc.; bad for you.
Distress without effort --> increase cortisol and catecholamine (ex. helpful)
How does stress affect cognition?
Stress can impair cognitive functioning by interfering with memory and attention.
Ex. noise can be a stressor.
Evidence suggests that children who try to tune out chronic noise may develop_____________because they have difficulty knowing which sounds to attend to and which to tune out
generalized cognitive deficits
higher levels of stress in older adults are associated with increased _____________ in their daily lives
cognitive decline and memory problems
How does stress affect emotions?
Cognitive appraisal processes can influence both the stress and the emotional experience.
Ex. Fear --> Phobias and anxiety
the _________ of stress can result in a physiological stress response that includes increased cortisol output
anticipation
How can stress affect social behaviour?
Stress changes people’s behaviour toward one another.
Ex. seek comfort from others vs more hostile/less sociable.
anger in response to stress often leads to aggressive behaviour, and these negative effects ______ after the stressful event is over.
continue
Women generally report experiencing ____________ than men do, especially interpersonal strains and home-based stressors.
more major and minor stressors
men show more ________ than women when psychologically stressed, and also ________
reactivity
seem to take longer for their physiological arousal to return to baseline levels after the stressor has ended.
Psychoneuroimmunology
An area of health psychology focused on the interaction between psychological factors (like stress) and the nervous and immune systems.
(i.e., takes into account cognitive appraisal)
Systems form a feedback loop (nervous/endocrine --> increase/decrease immune function)
While positive emotions increase immune function, Stress can evoke increases in __________, as can chronic levels of negative affect.
inflammatory substances in the blood,
Consequences of long-term excess of catecholamines (EP and NE)?
Suppress immune system
Elevated lipid levels (e.g., cholesterol)
Damage to blood vessels and arteries, elevated blood pressure
DNA Damage
A study found DNA damage in rats after long term exposure, this was likely a consequence of long-term excess of _______
catecholamines (ep and ne)
When things go right, cortisol levels __________
When things go wrong, chronic or recurring stress can __________
differ during the day
alter daily cortisol patterns
The altering of daily cortisol patterns is known as ___________
HPA axis dysregulation
Consequences of long-term excess of cortisol:
Impaired immune functioning
Depression (ex. prednisone mimicks cortisol)
Fat storage in central visceral area
Damage to hippocampus
one study found that people who showed larger increases in cortisol in response to difficult mental tasks were more likely to develop _______ over the next three years.
hypertension
Diathesis-stress model
people's vulnerability to a physical or psychological disorder depends on the interplay of their pre-dispositions to the disorder (the diathesis) and the amount of stress they experience.
In the study looking at stress and the common cold, they found that ..
47% of those with high stress and 27% of those with low stress developed colds
Not everybody got sick, and not to the same degree.
Positive correlation between stress and getting cold
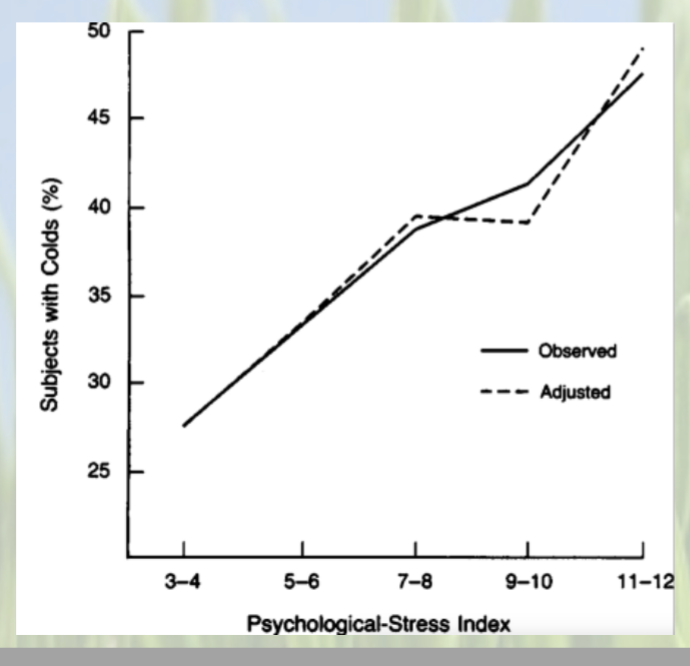
people under ___________ are more vulnerable to catching cold when exposed to the virus than people under less stress
chronic, severe stress
people who experience a lot of ____________, are less likely to catch a cold or the flu when exposed to the viruses than are people with less of these emotions
positive emotions, such as feeling energetic or happy
people who have ____________ prior to exposure to the virus are more likely to develop colds than those with the oppsite.
sleep problems
What are the two route of stress to illness?
A direct route --> resulting from physiological changes produced by stress
An indirect route --> affecting health through the person’s behaviour
Direct route to illness from stress
Stress produces many physiological changes in the body that can affect health, especially when stress is chronic and severe
High allostatic load --> higher mortality rates
High levels of stress in childhood (+pregnancy) can become biologically embedded and lead to increased stress responses, slower recovery, and greater risk of illness.
Cardiovascular issues --> high levels of job stress are associated with high blood pressure and abnormally enlarged hearts.
Immune system --> chronic stressor supress nonspecific and specific immune functions, and increase inflammation (disrupts immune function).
A direct route to illness from stress includes increases in…
Allostatic load
BP
Unfavourable lipids in blood
Activated platelets in blood
Clotting factors in blood
Stress hormones (catecholamines, corticosteroids)
Increase inflammation
An indirect route from stress to illness
Stress can affect behaviour, which, in turn, can lead to illness or worsen an existing condition.
Ex. adverse childhood experiences can lead to the eventual adoption of unhealthful or risky behaviours.
People who experience high levels of stress tend to behave in ways that increase their chances of becoming ill or injured.
An indirect route from stress to illness includes increases and decreases in …
Increase:
Dietary fat
Tabacco, alcohol use
Accidents
Decrease:
Dietary fruits and vegetables
Exercise
sleep
In a study looking at the healing rate of mouth wounds in dental students, what was the finding?
The wound gets smaller over time
But there was faster wound healing time over the summer.
i.e. everybody healed slower during exams.
Challenges in health psychology research?
Variables either cannot be manipulated, or it would be unethical to do so.
Participant recruitment
Logistical limitations
Chronic disease often has gradual onset, typically onsets later in life
Development of chronic disease influenced by myriad of biological, psychological, and societal factors
In a study looking at stress disorders and autoimmune diseases, they found that
Those with a stress-related disorder were at a significantly greater risk of developing …
autoimmune disease (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis)
In a study looking at gut microbiota-driven pathways linking chronic stress to tumour progression, they found that
Chronic stress influences the health of the __________ and
Leads to
microbiome in our gut.
Gut dysbiosis (imbalance in the guts microbial community; good microbes decrease and harmful ones increase; reducing the overall diversity of bacteria)