Bio Exam 2 - DNA Replication and PCR
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Central dogma
DNA is transcribed into mRNA, DNA serves as the template for RNA, RNA is translated into proteins
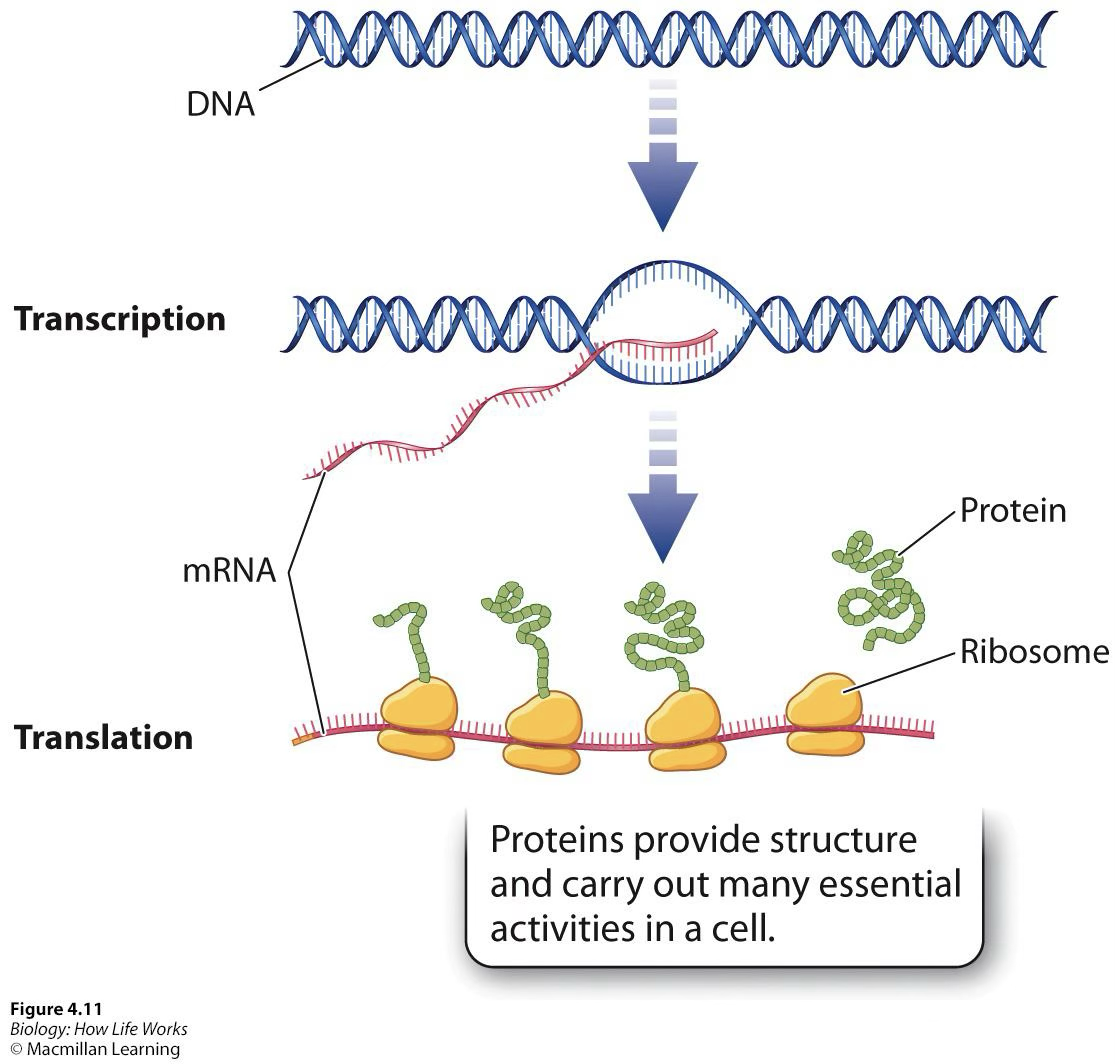
Gene expression
Production of protein from instructions on the DNA
Steps to gene expression
Transcription, translation, folding of the protein into functional 3D form
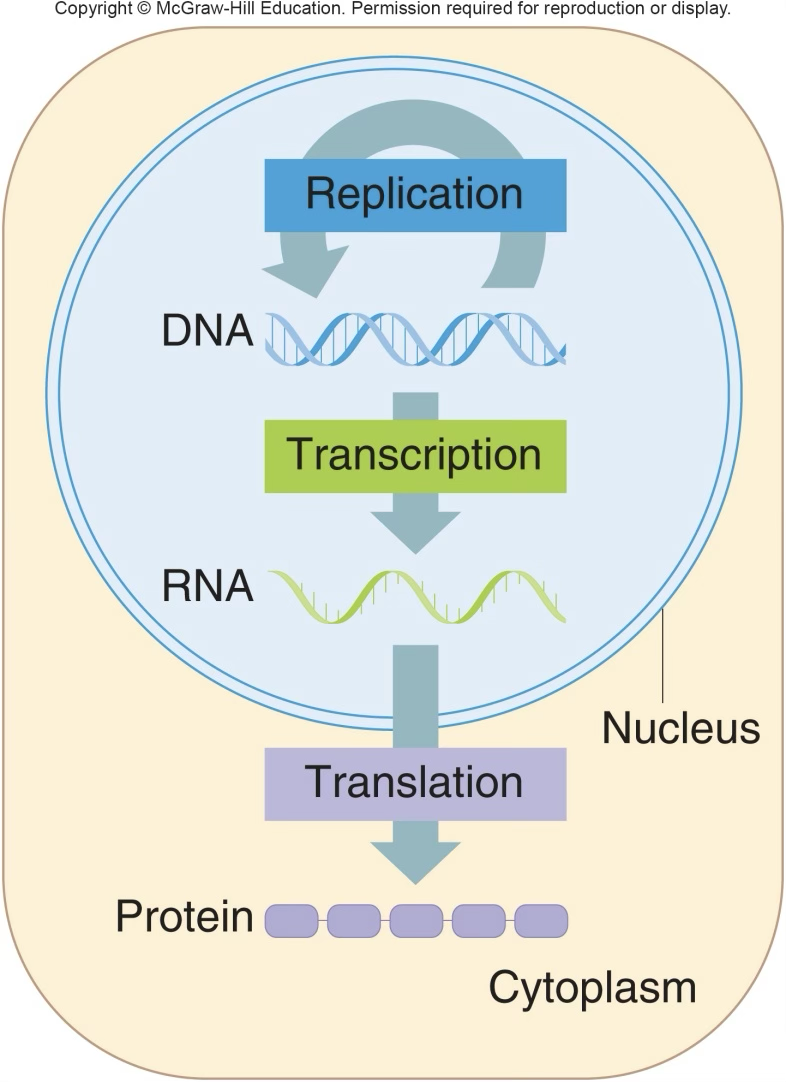
2 main functions of DNA
storing genetic information and copying itself
Structure of a nucleic acid
Pentose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
Which carbons do the phosphate, hydroxyl group, and base attach to
phosphate attaches to 5’, hydroxyl group attaches to 3’, base attaches to 1’
How many hydrogen bonds do A and T form; How many hydrogen bonds do C and G form
2; 3
Bases for DNA; Bases for RNA
ATCG; AUCG
Difference between deoxyribose and ribose
Deoxyribose has one hydroxyl group at 3’; ribose has two hydroxyl groups at 2’ and 3’
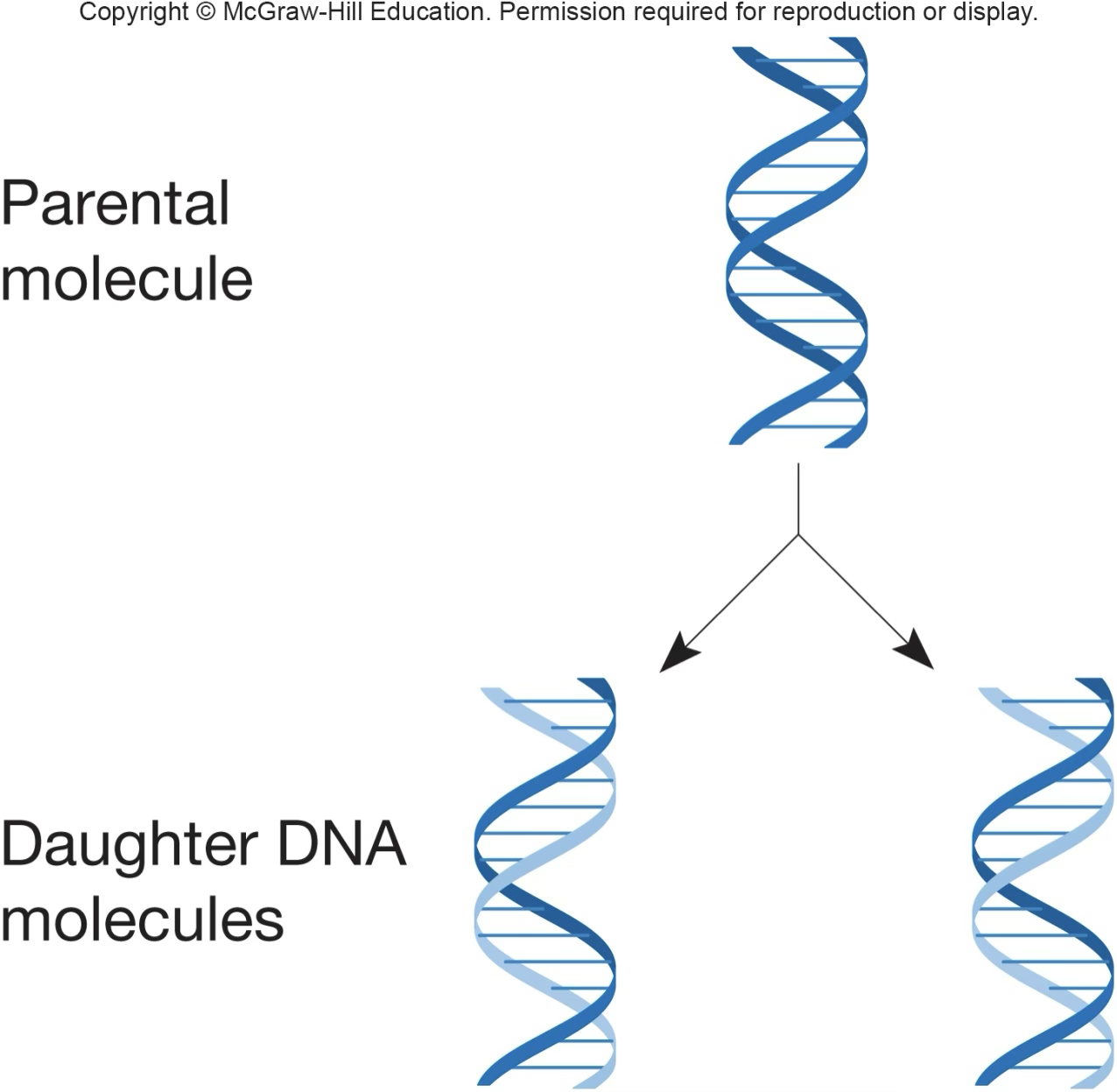
DNA replication is semiconservative
the double helix will split in 2, and each strand is used as a template for the new strand; half the DNA is from the original, and half the DNA is new
Parental strands; Daughter strands
template; new strand
Which bonds are broken when DNA is replicated
Hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together
Site where DNA is locally opened
replication fork
Enzymes in DNA replication
Helicase, DNA binding proteins, primase, DNA polymerase 3, exonuclease, ligase
Helicase
Unwinds parental double helix
DNA binding proteins
keep the strands separated, prevent them from rewinding
Primase
adds RNA primer to template strand
DNA polymerase 3
adds nucleotides to the RNA primer and proofreads
Exonuclease/DNA polymerase 1
removes RNA primers and inserts correct bases/replaces the nucleotides
Ligase
joins okazaki fragments together and seals nicks in sugar-phosphate backbone/forms bonds
Topoisomerase
Relieves tension on the double helix
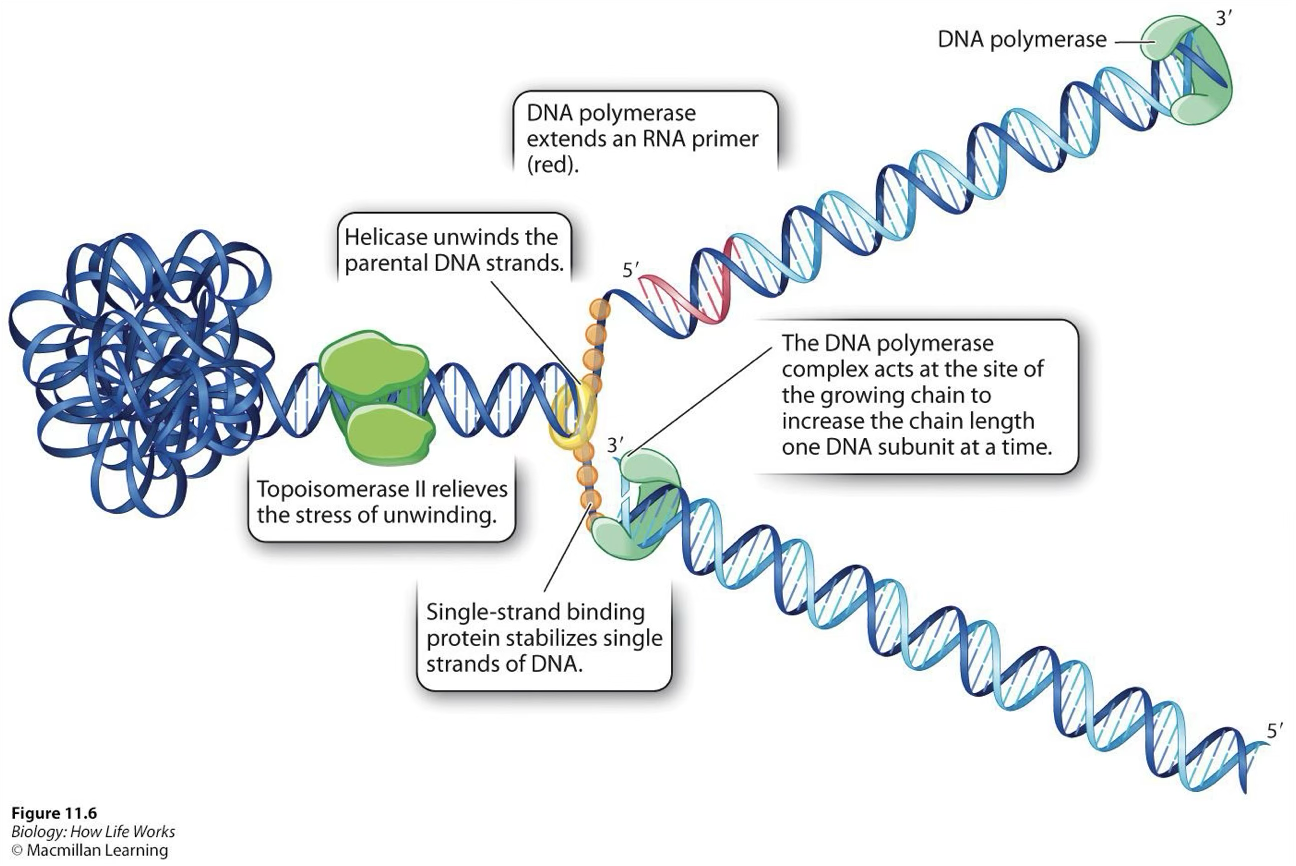
Order the enzymes work in
helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, ligase
What direction does replication occur
5’ to 3’
Leading strand vs Lagging strand
Leading - continuous, lagging - okazaki fragments
How do you know which strand will be the leading strand and which will be the lagging strand
Leading strand will be going the same direction as the fork opens, lagging will go the opposite direction
Proofreading
DNA polymerase removes and replaces incorrect nucleotides, it recognizes if the bases are paired correctly
PCR
method in which multiple repetitions of DNA replication are performed in a test tube
What do you need for PCR
DNA template, primers, nucleotides, DNA polymerase bacteria
PCR steps
Denaturation - DNA template is denatured with high heat to separate strands; annealing - DNA primers bind to the template DNA; extension - DNA polymerase creates a new strand of DNA complementary to the template DNA starting from the primer; repeated many times