11. causes and risk factors of amblyopia
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is amblyopia
A condition of diminished visual form sense which is not associated with any
structural abnormality of disease of the media, fundi or visual pathway and
which is not overcome by correction of the refractive error
3 risk factors for amblyopia
Refractive error
anisometropic
ametropic
meridional- astigmatism
stimulus deprivation
Strabismus-tropia
What is the critical period for developing amblyopia
eight years old and is relatively easy to correct until that age by improving the quality of visual input in the affected eye but becomes increasingly resistant to reversal with age
Whe is the most sensitive period for amblyopia
until 2-3 yrs old
what is happening in amblyopic eyes
changes in visual cortex (area V1 and some in V2) with a loss of bincoular driven cells and neurones that are driven by amblyopic eye
amblyopia can be unilateral or bilateral and caused by one or more factors:
light deprivation- not enough light on retina
form deprivation
abnormal binocular interaction
Reasons against amblyopia treatment
Binocularly good vision
May develop abnormal BV
May not restore normal BV
Risk of intractable diplopia
Psychological issues
Reason for treating amblyopia
If something happens to the good eye then the patient has another eye with at least reasonable VA
improved BV development
Which eye does Strabismic amblyopia effect?
monocular
When is strabismic amblyopia most likely?
Constant deviation
More likely to occur in esotropia
Why is strabismic amblyopia more likely for esotropia
Exotropia often remains intermittent during childhood
Why is alternating deviation amblyopia less likely
both eyes receive visual stimulus
Which eye does Stimulus deprivation amblyopia effect?
monocular or bilateral
What is Stimulus deprivation amblyopia
Lack of adequate visual stimulus (light and/or form)
What can cause stimulus deprivation amblopia
May be complete such as ptosis when no light and form enters the eye,
May be partial such as cataract when light and some form enters the eye.
bilateral stimulus deprivation may result from congenital nystagmus
What is Anisometropic amblyopia
Monocular condition
Difference in the refractive error between the two eyes which ensures that one eye receives better visual input at all distances
the refractive error may cause a spherical or astigmatic difference between both eyes
What is ametropic amblyopia?
Occurs bilaterally
High degree of uncorrected bilateral refractive error
What rx can cause ametropic amblyopia
Normally greater than 6D of hypermetropia (Cannot be compensated for with accommodation),
High myopia
When does Meridional (astigmatic) amblyopia occur
Occurs monocularly with anisometropic amblyopia
Occurs binocularly with ametropic amblyopia
what is Meridional (astigmatic) amblyopia
A relatively clear image is formed along the more emmetropic axis, A blurred image is formed along the more ametropic axis
how to diagnose on amblyopia examination
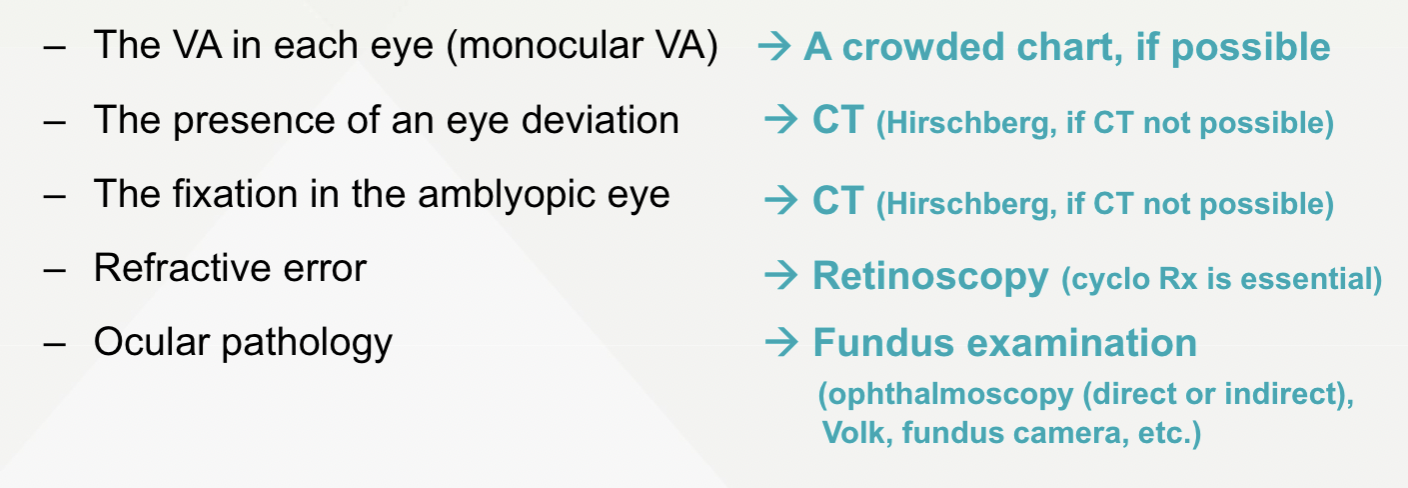
what kind of qs to ask in H&S
• What is the problem?
• Which eye?
• What age did the problem start?
• How long has it been there?
• If strabismus, constant or intermittent?
• Previous treatment in the form of glasses, occlusion therapy or others?
• If treatment, when was this given and why was it discontinued?
Why is log mar chart better than snellen when taking VAs for an amblyopic px
it takes into account the crowding phenomenon
if px has latenet nystagmus how would you adjust taking VAS
use a transculent occluder
What are Glasgow acuity cards
(marketed nowadays as Crowded Keeler logMAR) have been specifically designed to obtain accurate measurements of VA in amblyopia
what is the mean VA of 4-5 yr olds
0.087 (approx 6/7.5) +/- 0.10 for crowded,
-0.010 (approx 6/6) +/- 0.10 for uncrowded
in children with amblyopia the difference in VA crowded and uncrowded is
larger
How can eccentric fixation be grossly tested
corneal reflexes
How would you asses eccentric fixation using corneal reflexes
Cover the non-strabismic eye and ask the patient to look at a near pen torch (strabismic eye fixating)
If strabismic eye takes up central fixation i.e. the corneal light reflex is central in the pupil then there is no eccentric fixation • If the corneal reflex is not central, there could be eccentric fixation or an angle kappa is present.
To check if the lack of central fixation in the strabismic eye is due to angle kappa, cover over the strabismic eye and look at the corneal reflex in the nonstrabismic eye
If this is central then the person does not have an angle kappa so the displacement of the corneal reflex in the strabismic eye is due to eccentric fixation
If the corneal reflex in the good eye is nasally displaced then there is an angle kappa and the clinician has to determine whether the displacement of the corneal reflex in the same in both eyes
How do you interpret the results from assessing eccentric fixation from corneal reflexes
If it is the same then there is no eccentric fixation
• If it is different then there is eccentric fixation
When is the eccentric fixation test with corneal reflexes used?
young or uncooperative patients
How is stereopsis in children with amblyopia
likely to have stereopsis values bigger than 70"
How can you use ophthalmoscopy to assess eccentric fixation
Project the ophthalmoscopic target (visuscope) on the patient's retina
Start testing the non-amblyopic eye to check the patient's response
The eye that is not being assessed is occluded • Instruct the patient to look straight at the centre of the target
The target will be seen by the practitioner at the centre of the fovea (nonamblyopic eye)
The repeat the process in the amblyopic eye
If the target is seen at the centre of the fovea in the amblyopic eye no eccentric fixation
If the target is seen on any other part of the retina (when patient is instructed to look straight to the target) this is eccentric fixation
in SOT where will the eccentric fixation be
nasal
in XOT where will the eccentric fixation be
temporal
If eccentric fixation, how does the location of the eccentric point indicate of VA level
Further from the fovea the worse the VA
why would you dilate the pupil durimg opthalmoscopy
the ophthalmoscope light directed to the foveal area will cause significant pupil constriction
why would you do DO after cycloplegic refration
young patients may accommodate when asking to look at the target and this
will blur the practitioner’s view of the fundus
How can you measure size of suppression
Sbiza bar
What is a sbiza bar?
Graded bar of varying density of red filters
How do you use a Sbiza bar for measuring depth of suppression
Placed in front of non-amblyopic/non-deviating eye
Patient is requested to view light and asked what colour
As we increase the filters we compromise the vision of the non-amblyopic/nondeviating eye
Increase density of filters until patient reports two lights or a white light
if a white light is reported it means the non amblyopic eye is no longer the eye fixating, its now the amblyopic eye fixating
if two lights are seen, both eyes are fixating
what would motitly test for
to detect incomitant deviations and muscle palsies
what could Accommodation and convergence test for
Amblyopia is associated with an abnormal accommodative function, which
is clinically detected as reduced amplitude of accommodation and greater
lags of accommodation in the amblyopic eye