Anatomy and Physiology of the Human Eye and Ear
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
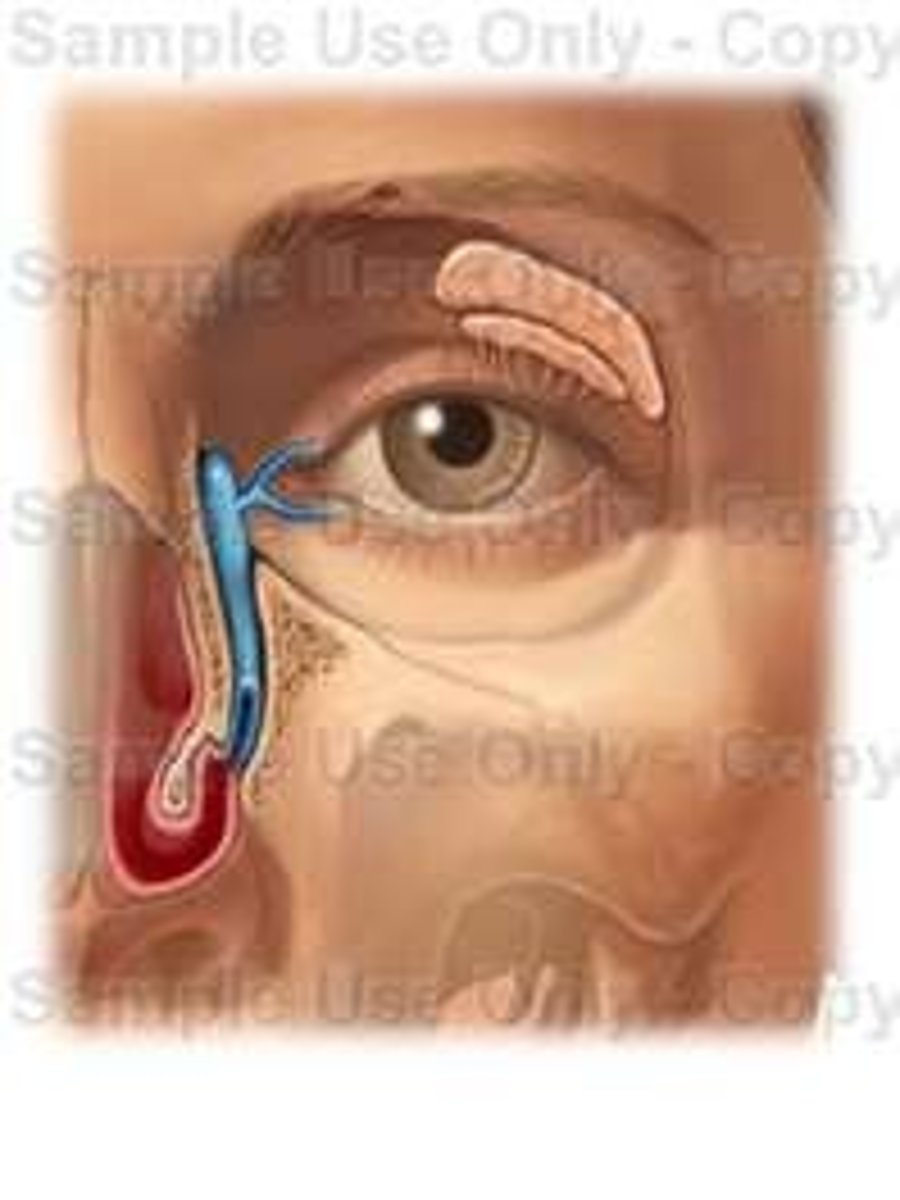
lacrimal apparatus
system of glands and ducts that produces, stores, and drains tears to keep the eye's surface lubricated, clean, and protected; maintains the health and functions of the ocular surface through the production of a tear film
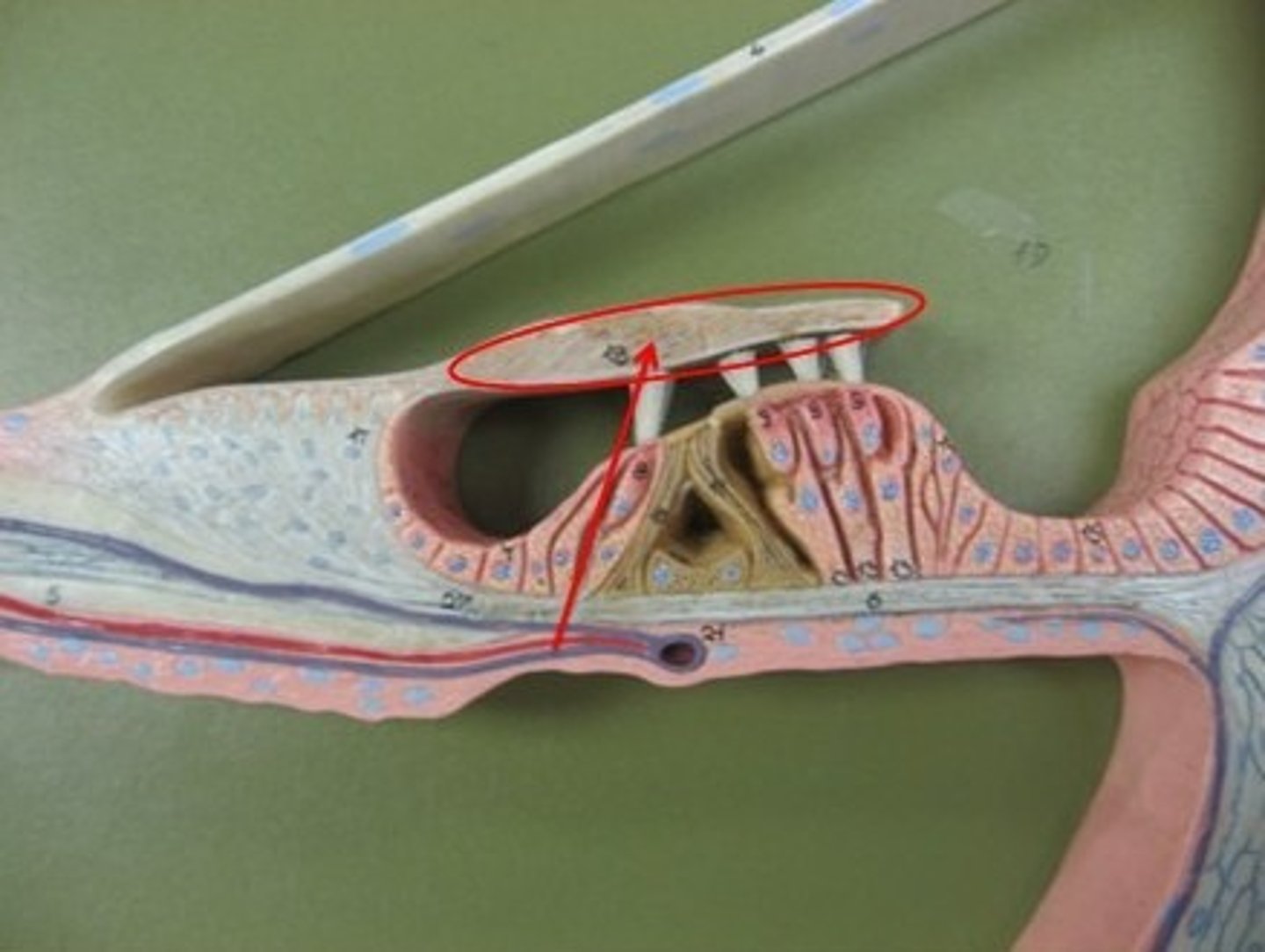
lacrimal gland
an exocrine gland located in the upper outer corner of each eye socket that produces the watery component of tears; keeps the surface of the eye moist, clean, and nourished
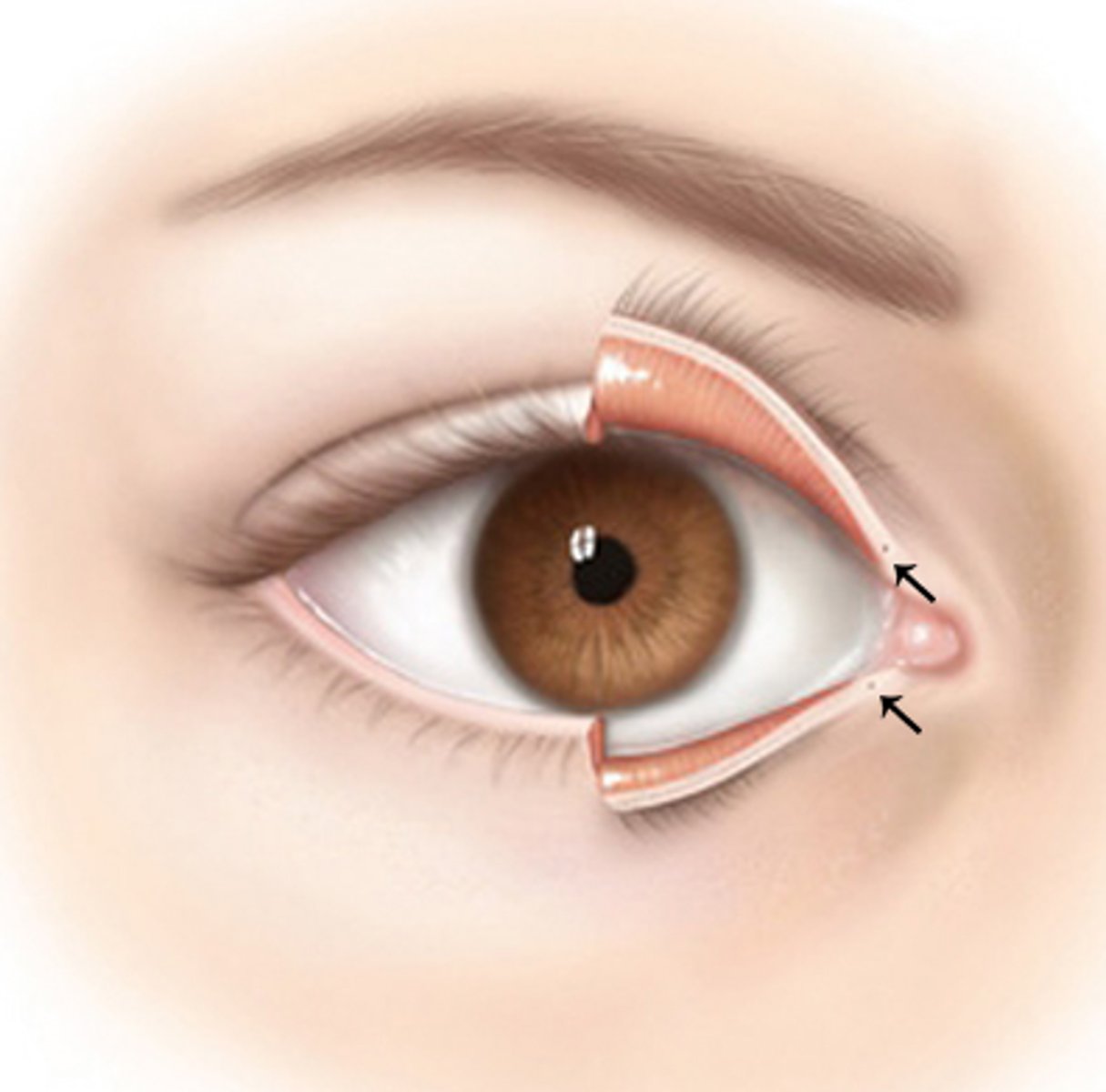
puncta
two small openings, on the upper and lower eyelid's inner margin, that functions as the entry points for draining tears from the eye into nasal cavity
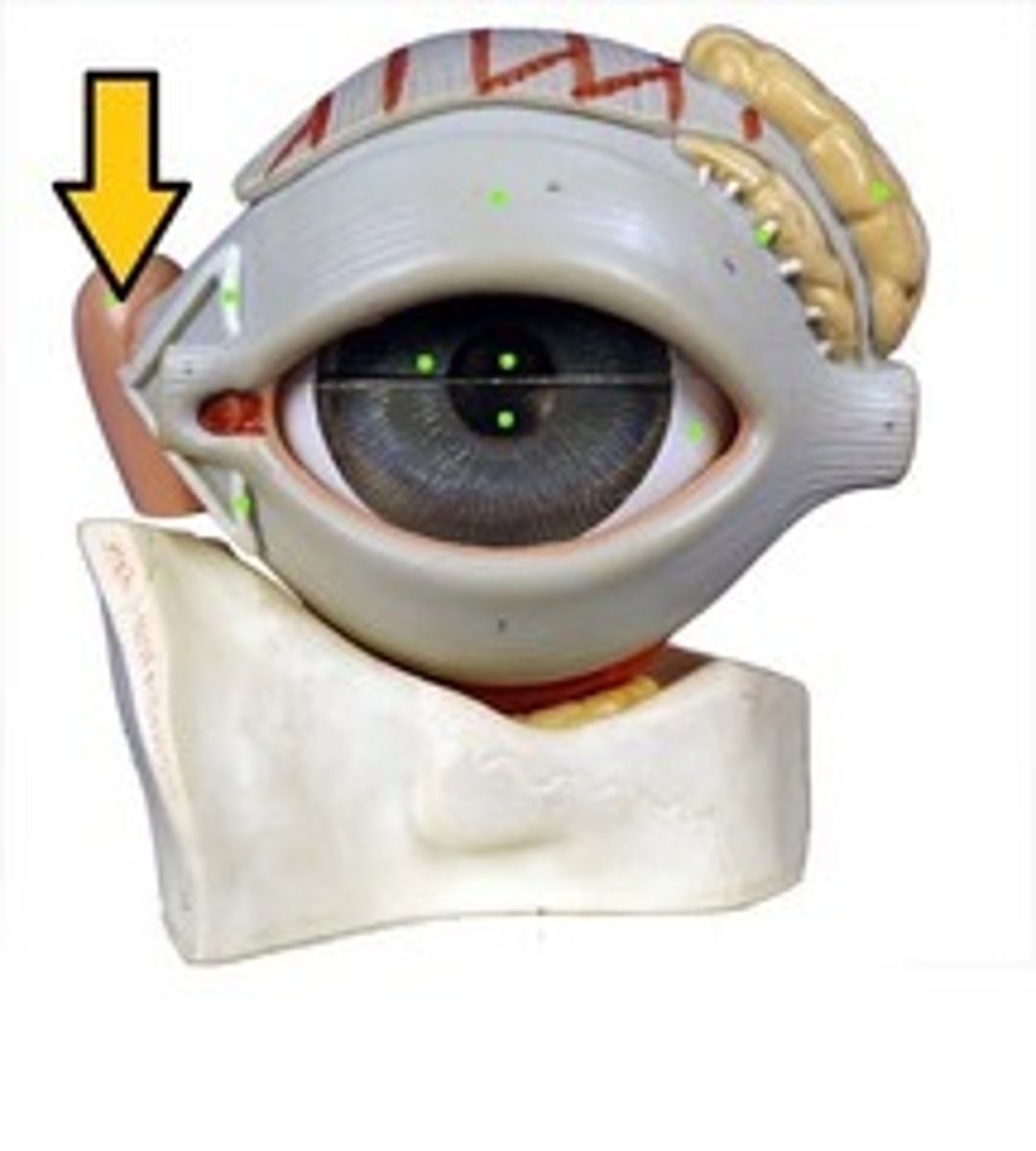
lacrimal sac
an anatomical structure located in the inner corner of the eye that serves to collect tears before they are drained into the nose; acts as a temporary reservoir for tears, which then flows through the nasolacrimal duct into the nasal cavity
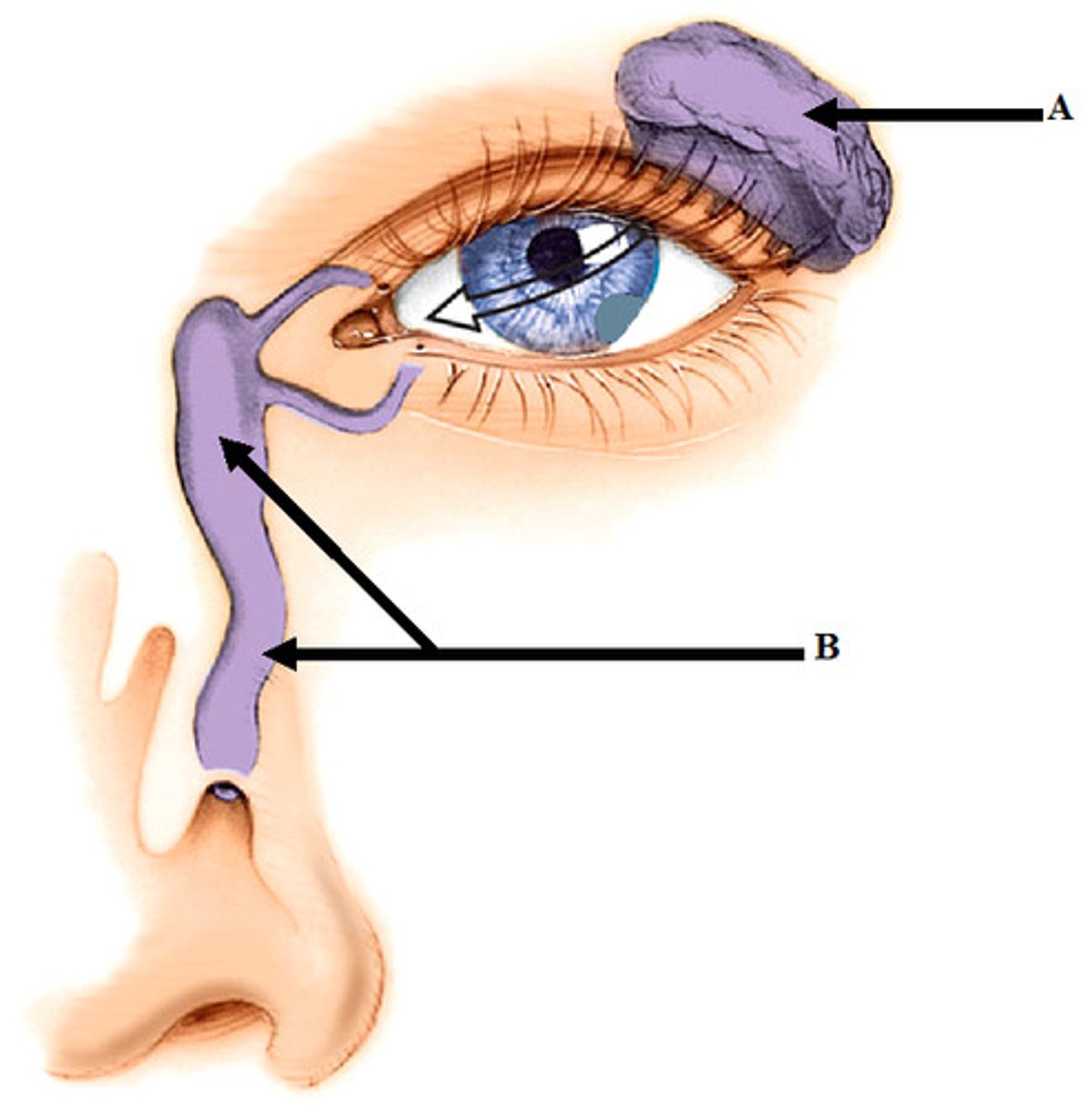
nasolacrimal duct
tube that drains tears from the eye's surface into the nasal cavity; moves lacrimal fluid from the eye to the nose, where it can be reabsorbed or drained
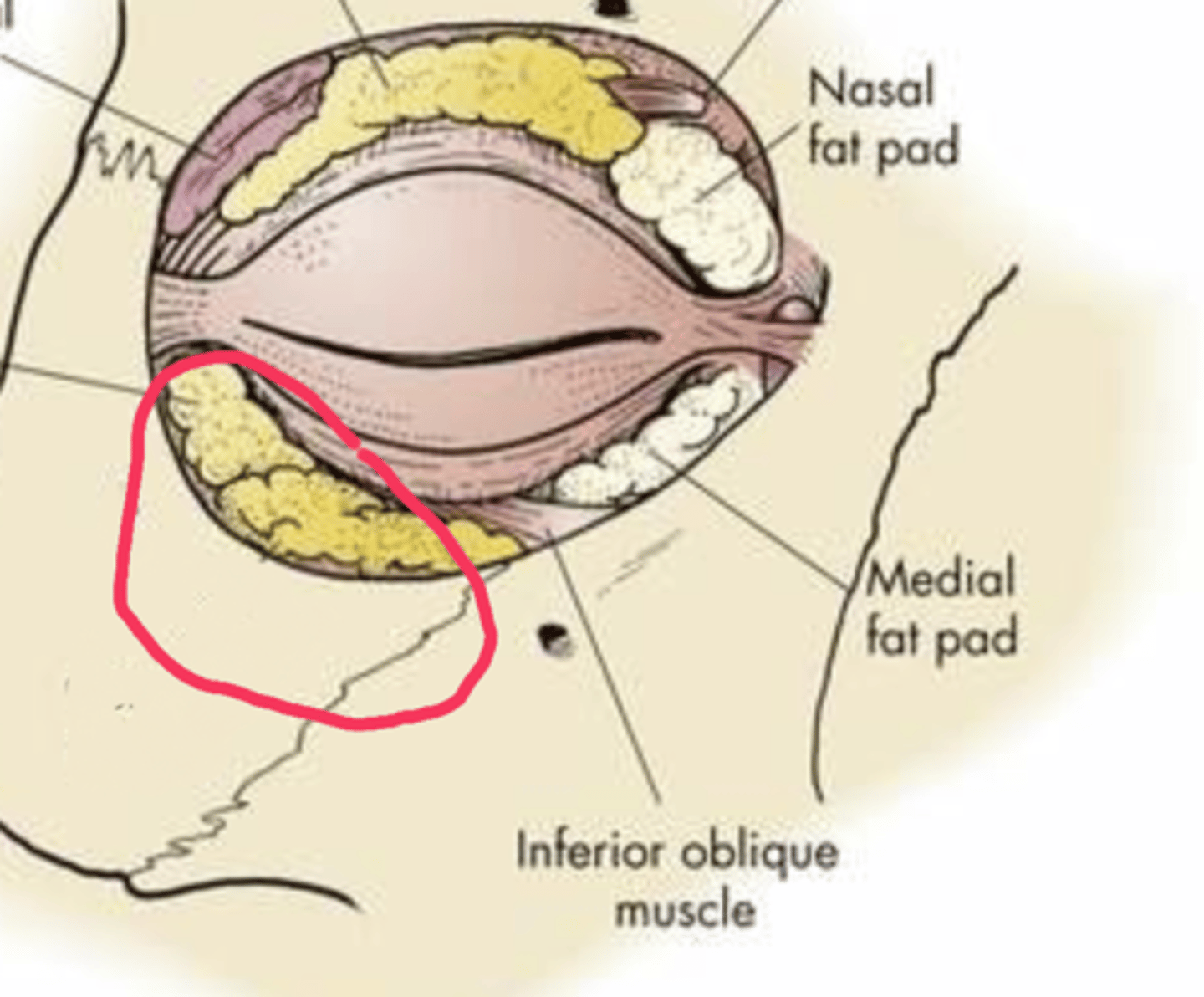
orbital fat
specialized adipose tissue that fills the space within the eye socket, surrounding the eyeball extraocular muscles, nerves, and blood vessels; acts as a protective cushion for the eye, supporting and stabilizing the globe while allowing for movement and protecting delicate neural and vascular structures
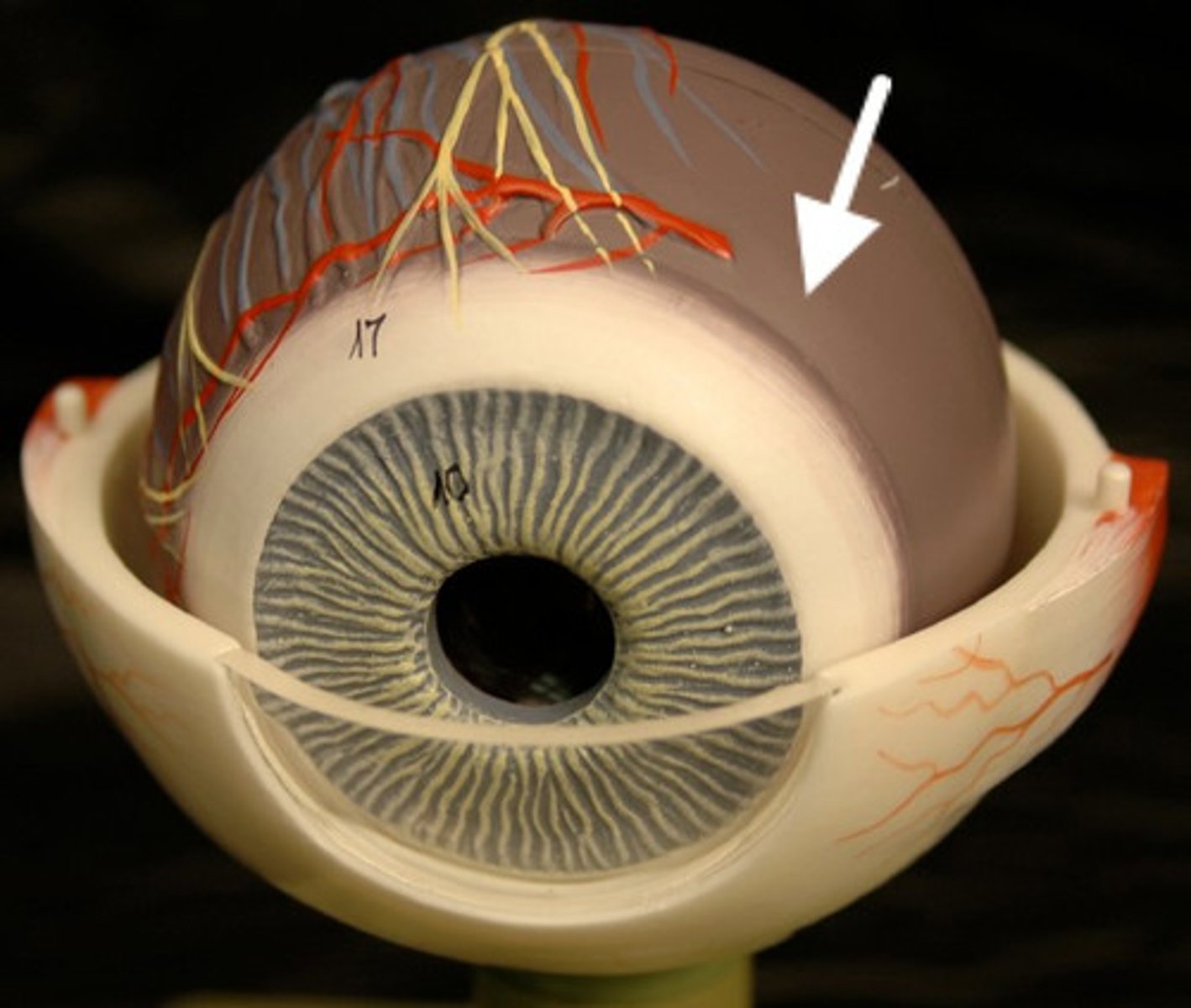
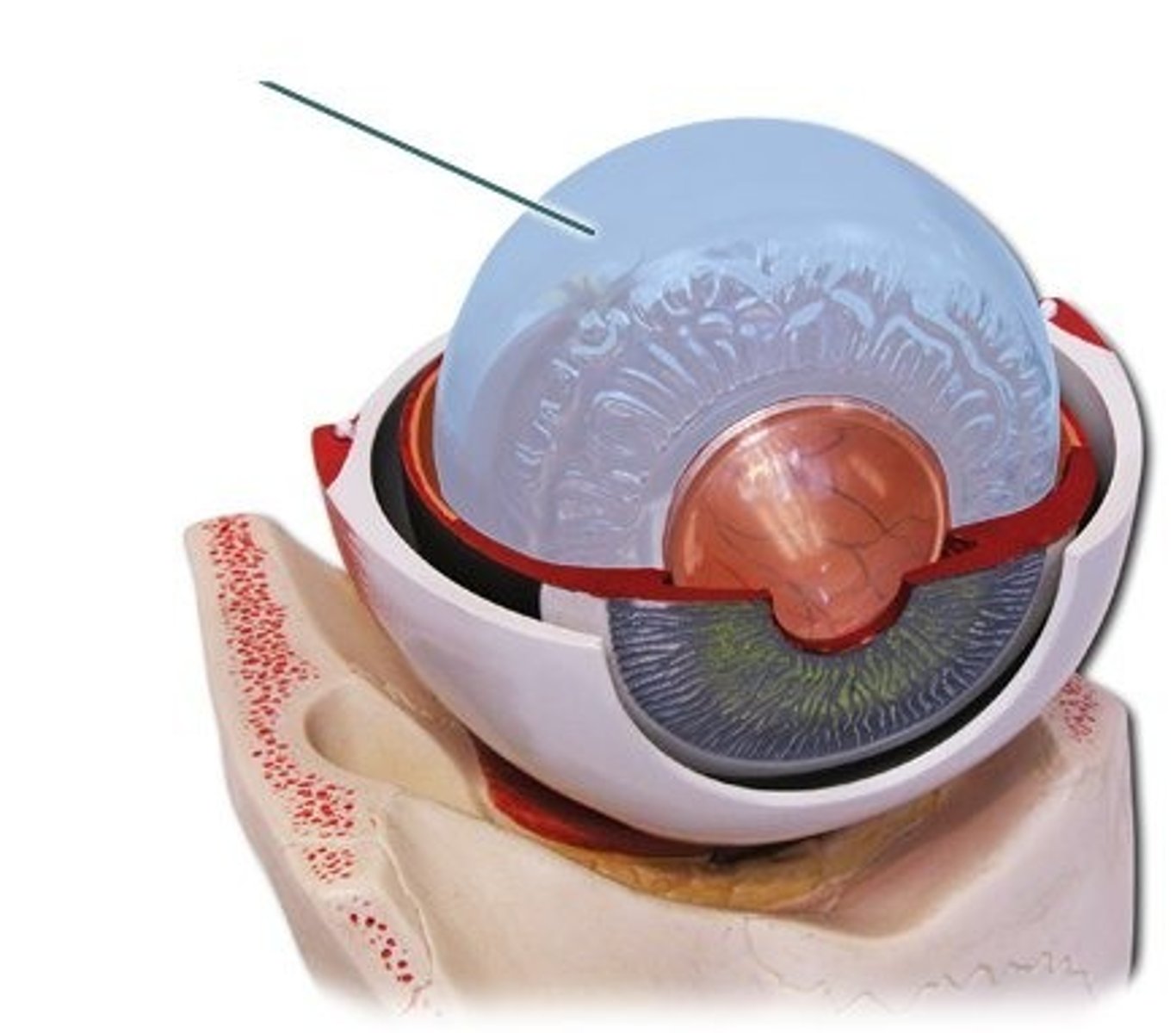
choroid layer
vascular layer of the eye between the sclera and the retina that provides oxygen and nutrients to the outer retina; nourishes the retina, and regulates the eye temperature and intraocular pressure
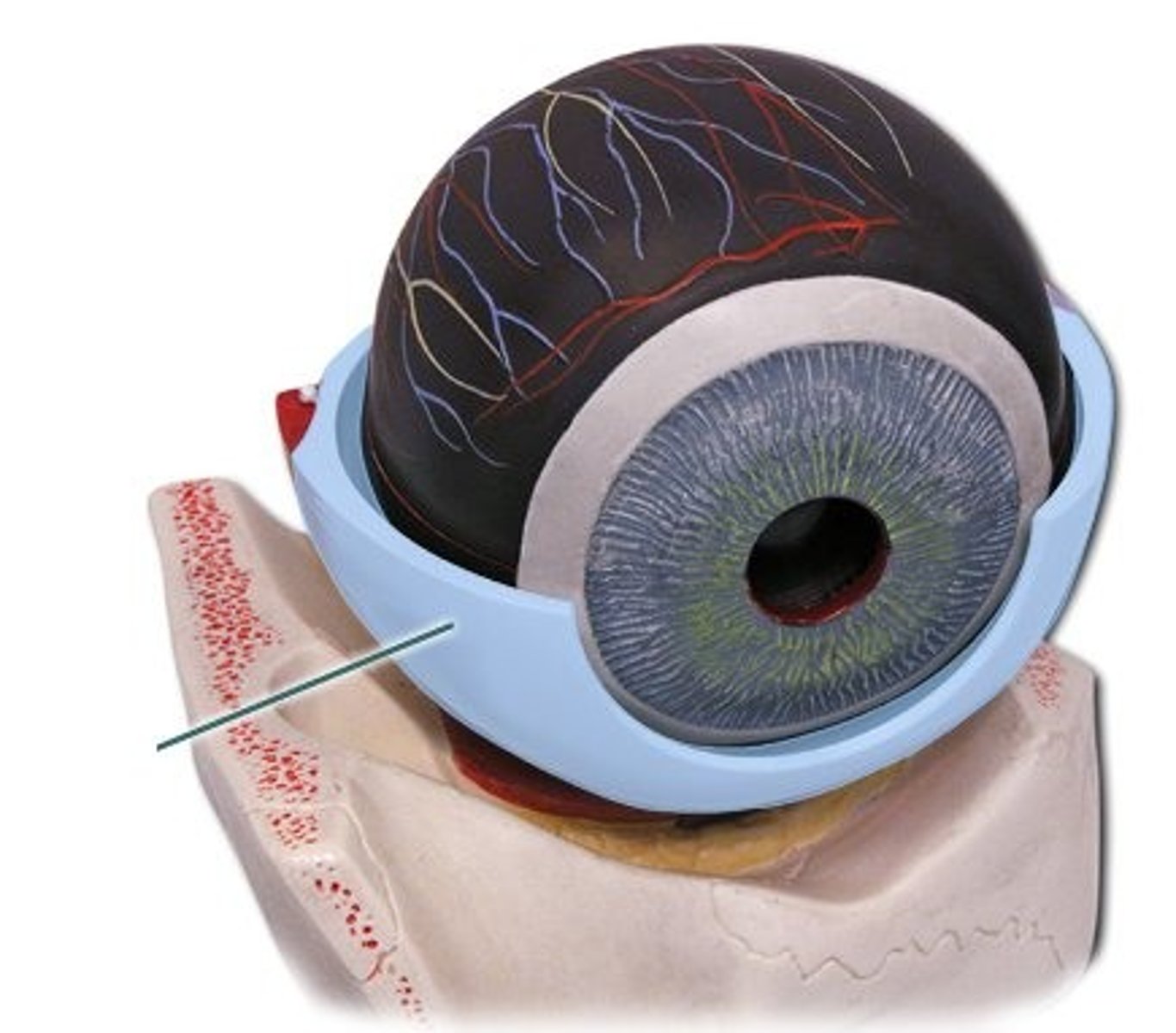
sclera
tough, fibrous, white outer layer of the eyeball that protects the eye and maintains its shape; provides structural support for the eyeball, protects the delicate inner components from injury, and serves as an attachment stie for the extraocular muscles that control eye movement
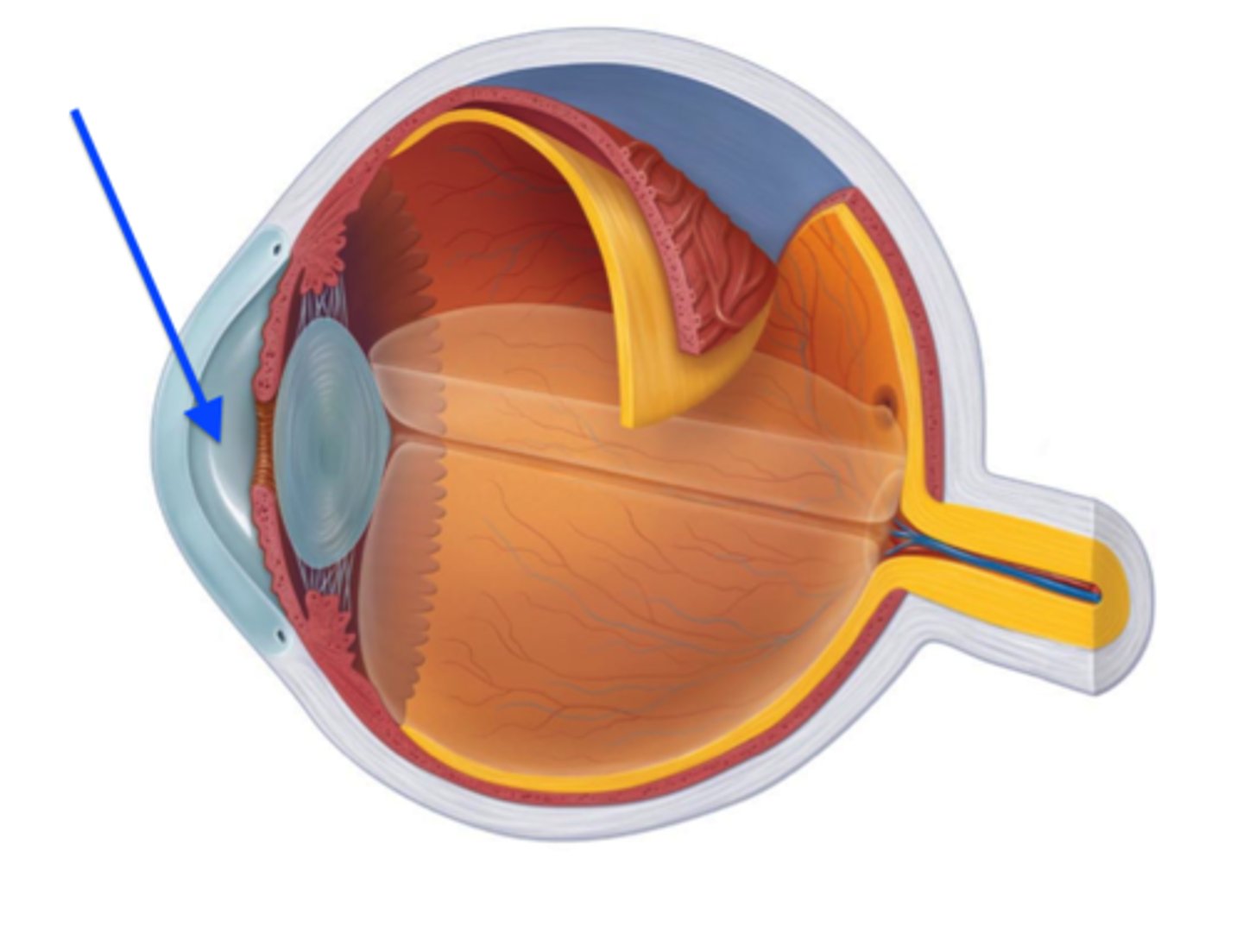
cornea
transparent, dome-shaped outer layer at the front of the eye that serves two main purposes: protect the eye from germs and debris while acting as the eye's outermost lens, focusing light onto the retina for clear vision
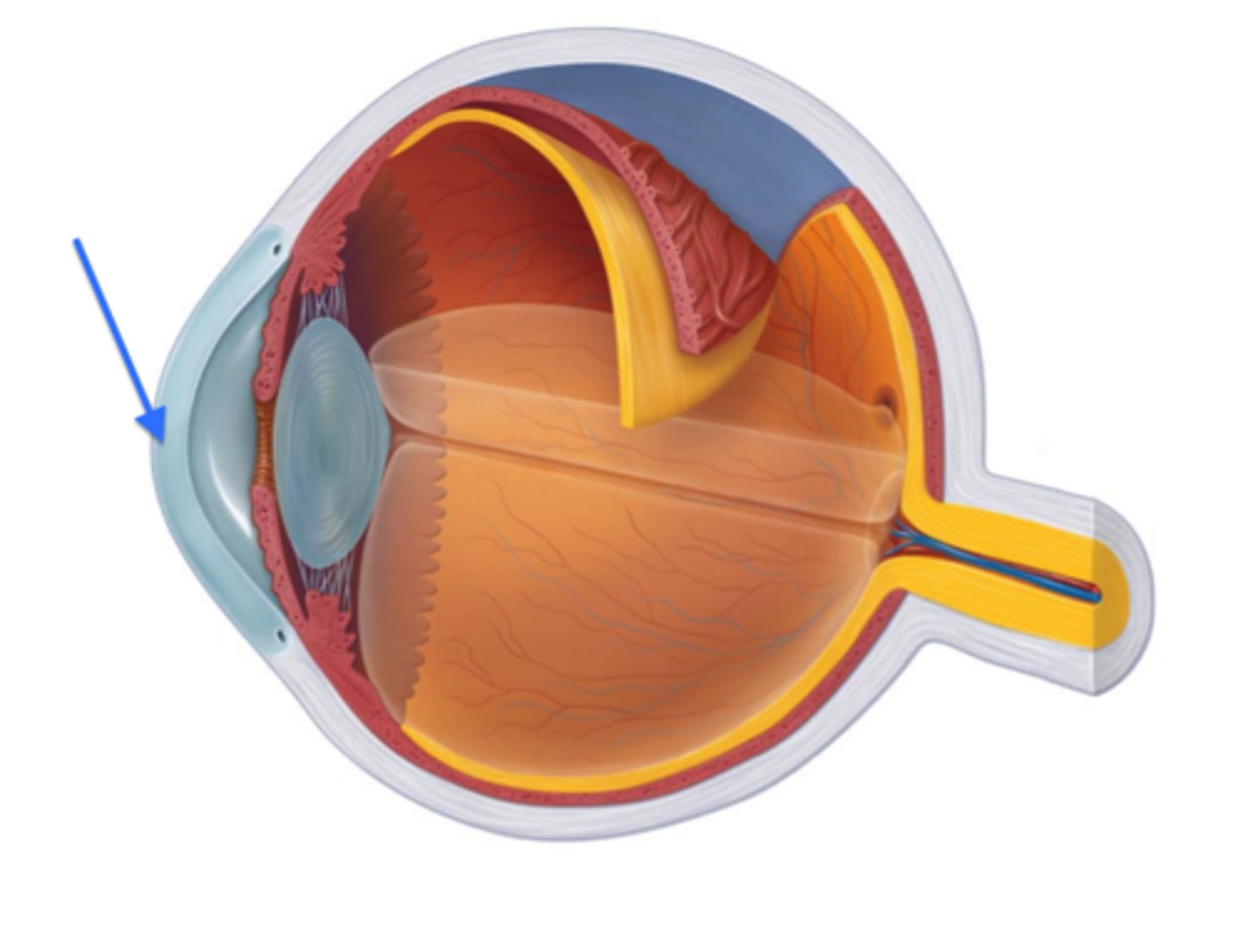
suspensory ligaments
group of connective tissues that supports and holds organs in place; suspends a structure like ovary, eye lens, breasts and maintains its positions
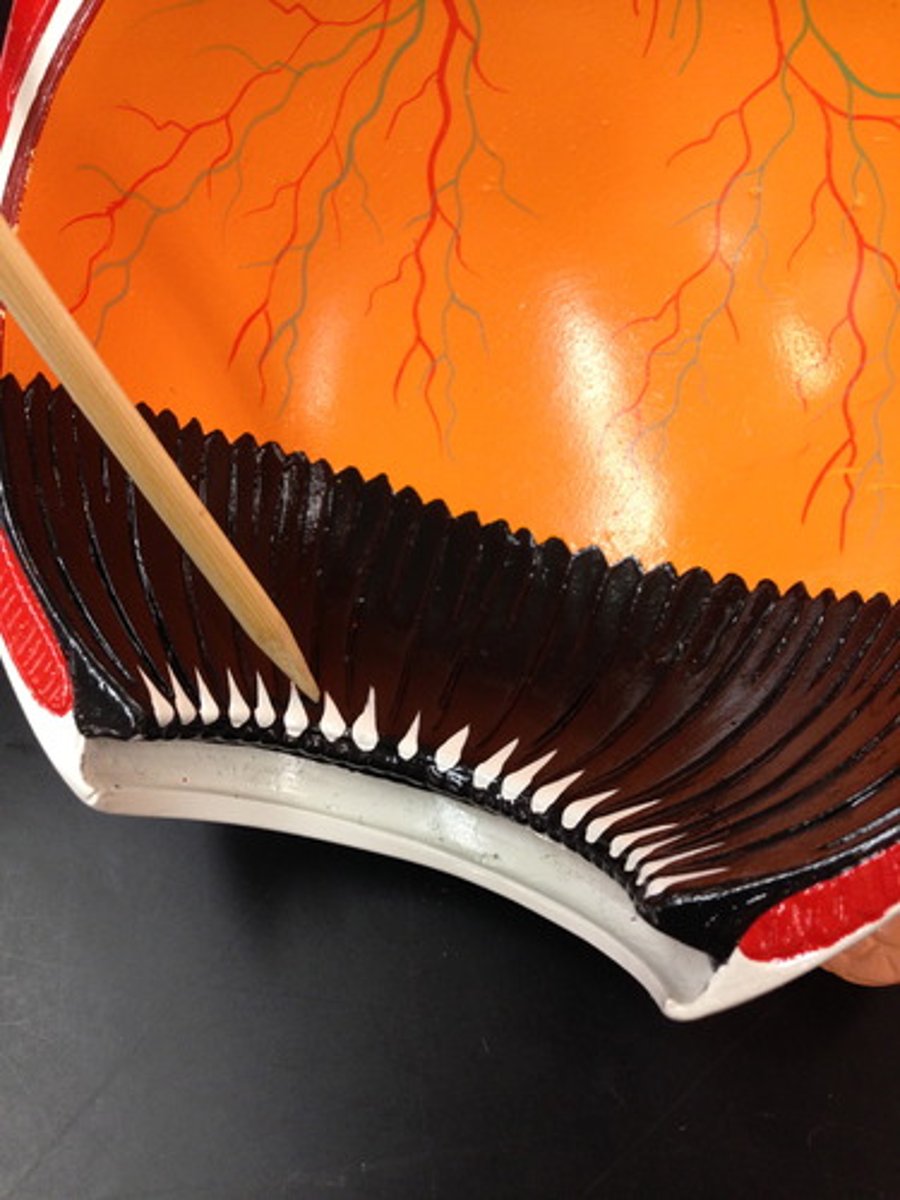

ciliary body
ring-shaped structure in the eye that serves two main purposes: changing the shape of the lens to focus on objects at different distances, and produces the aqueous humor (fluid that nourishes the eye)
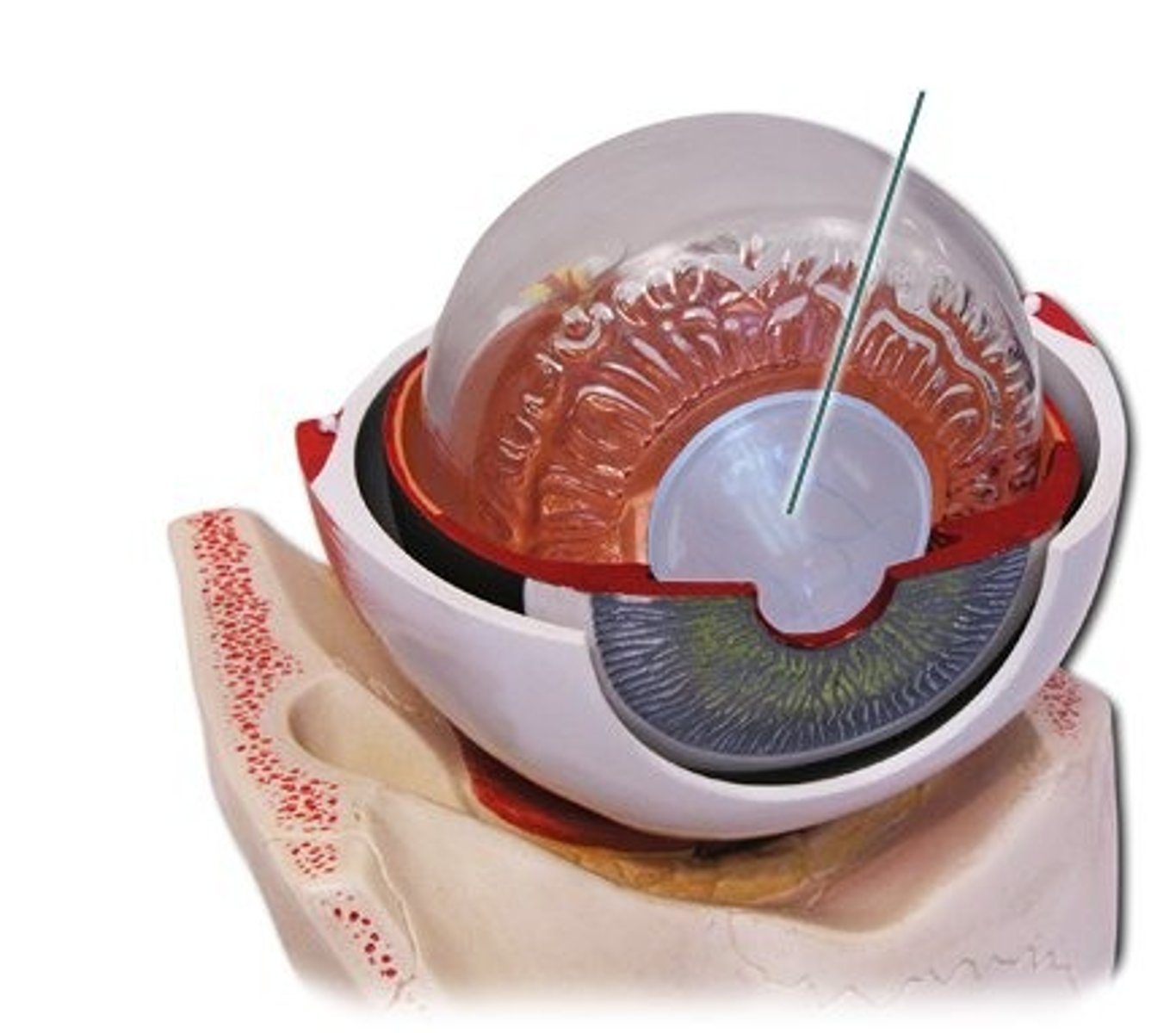
iris
the colored, muscular part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil to regulate the amount of light entering the eye; acts like a diaphragm in a camera, adjusting the amount of light that reaches the retina to allow for clear vision in both bright and dim conditions
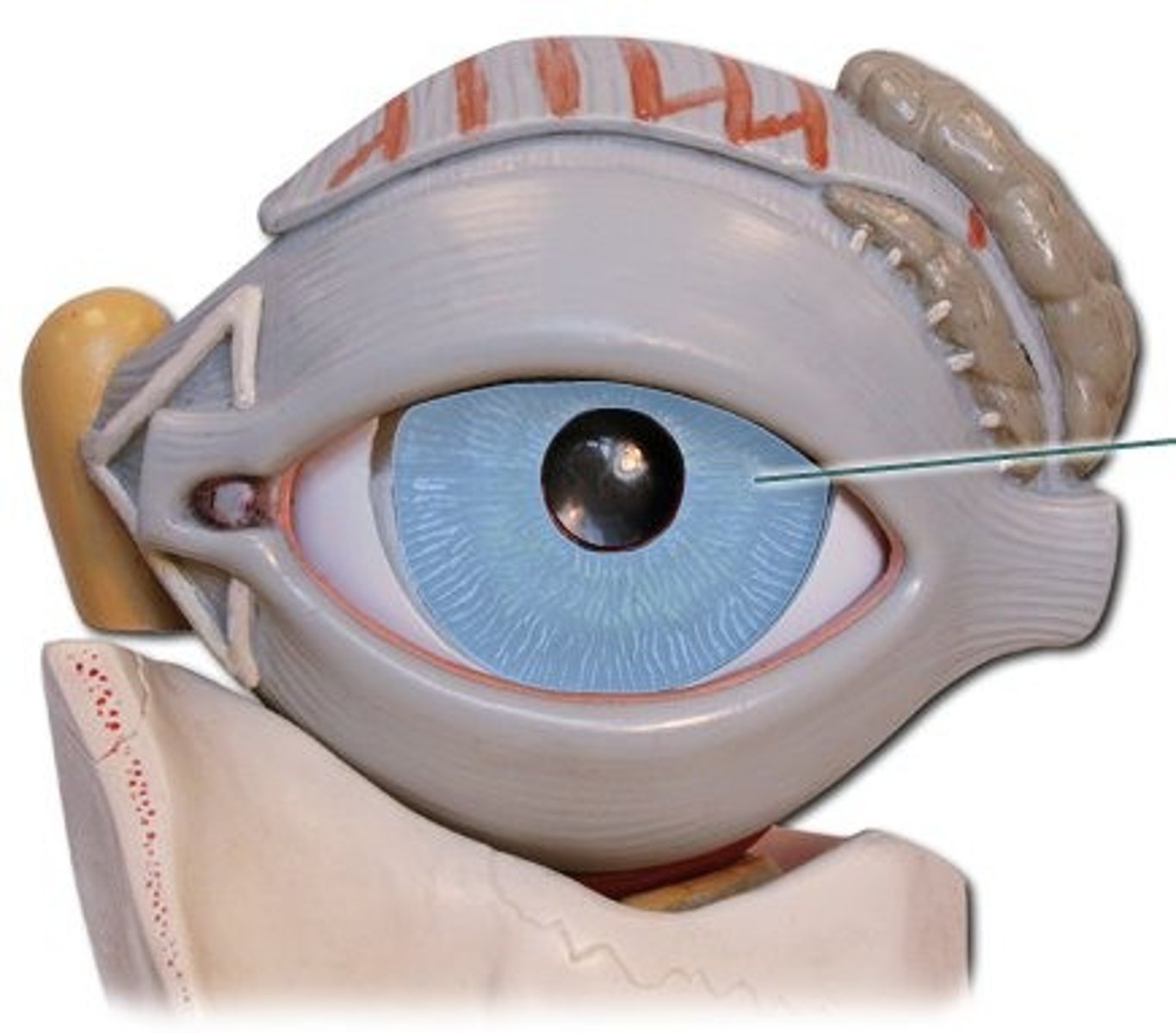
pupillary constrictor
circular muscle in the iris that constricts or shrinks the pupil; controls the amount of light that enters the eye by reducing the pupil's diameter
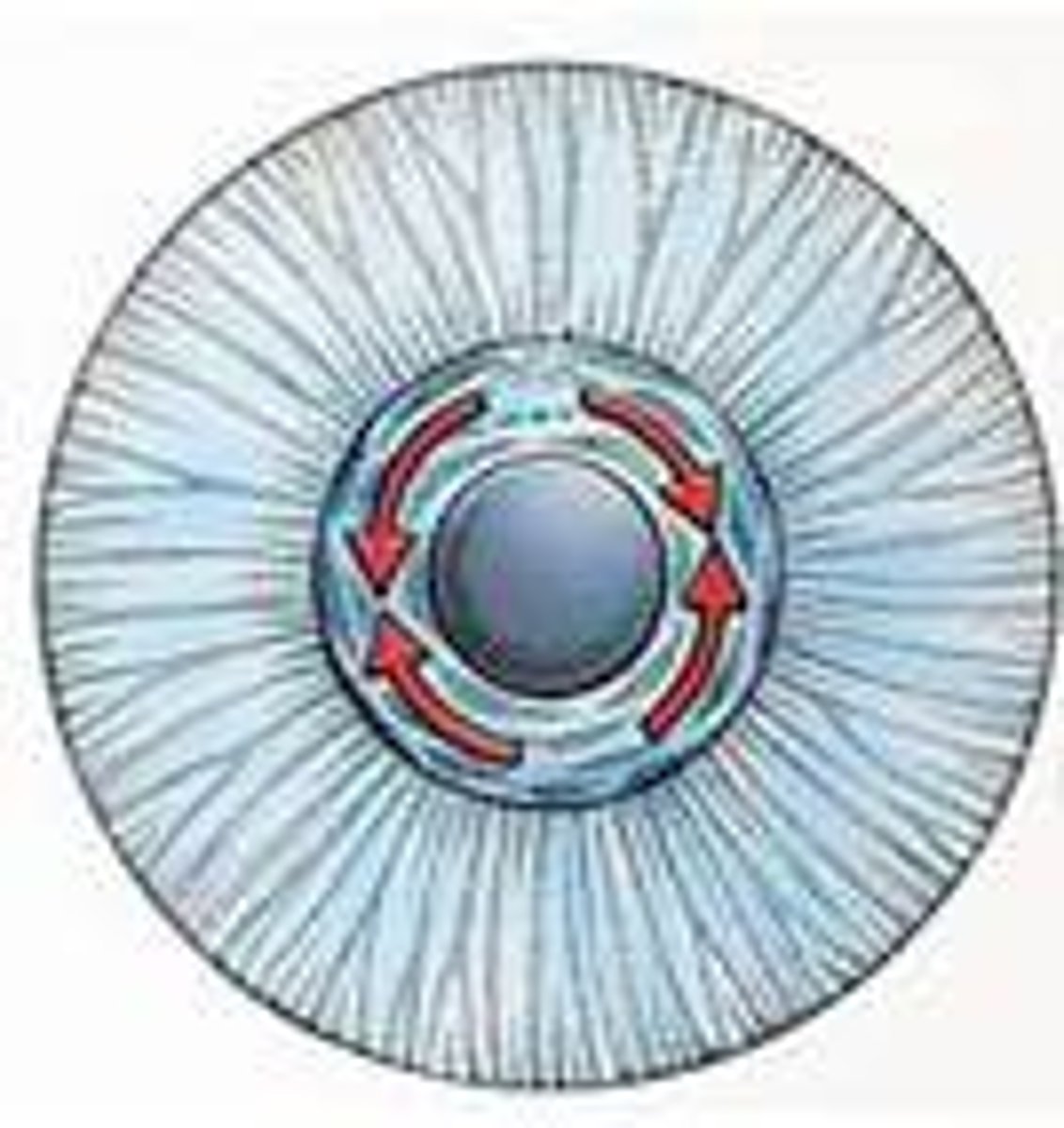
pupillary dilator
smooth muscle within the iris of the eye that functions to widen the pupil; allows more light to enter the eye, which is essential for vision in dim environments
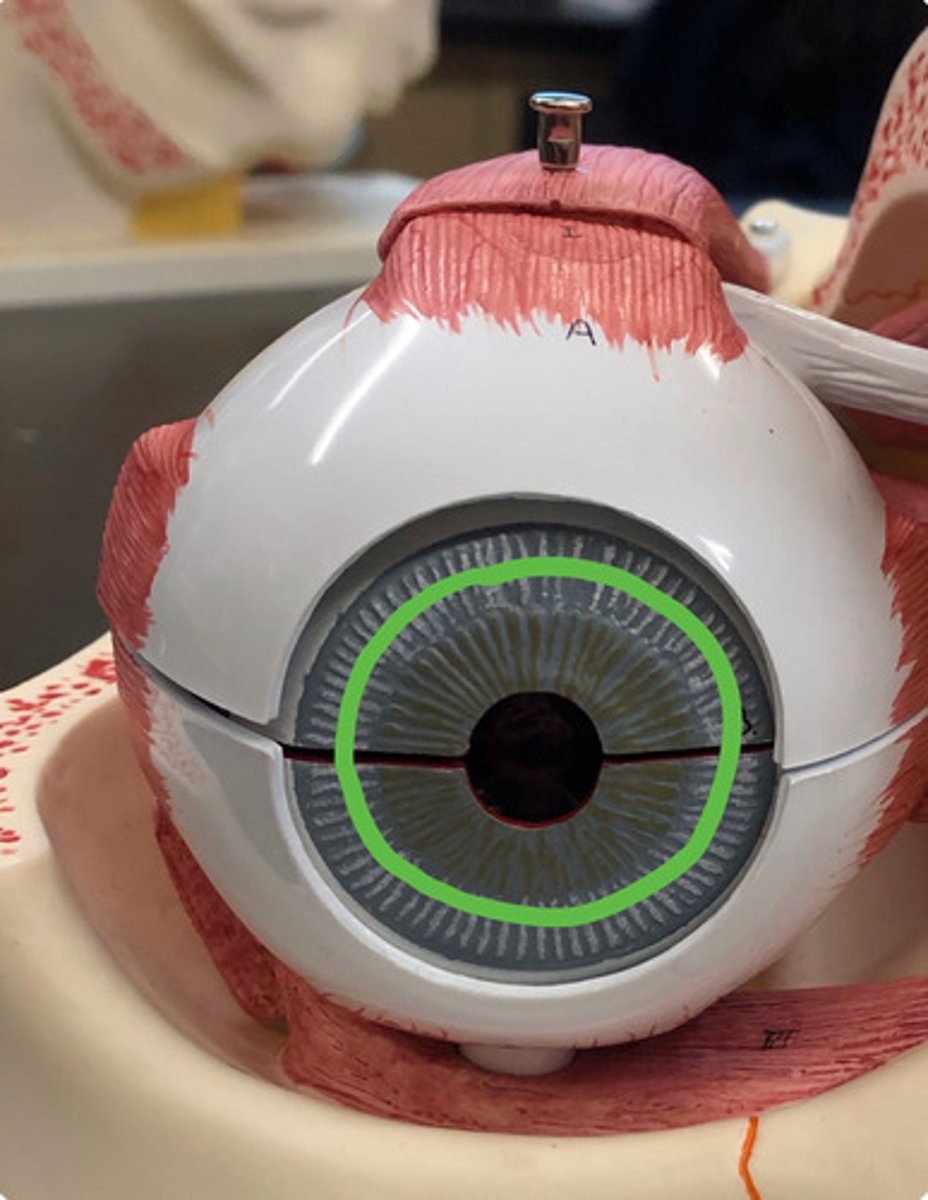

pupil
black opening in the center of the iris that controls the amount of light entering the eye; regulates light intake to ensure clear vision, dilating in dim conditions and constricting in bright light
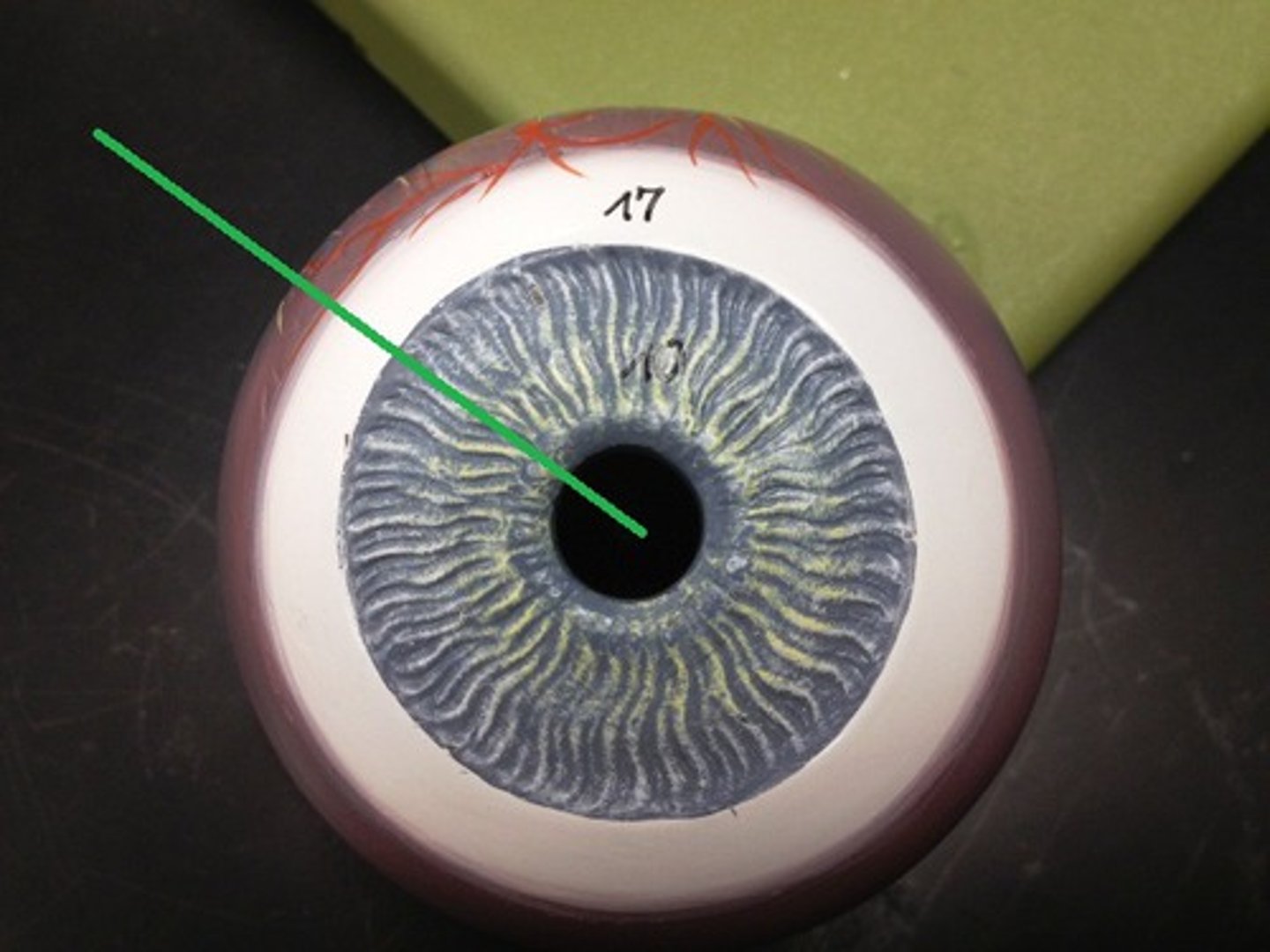
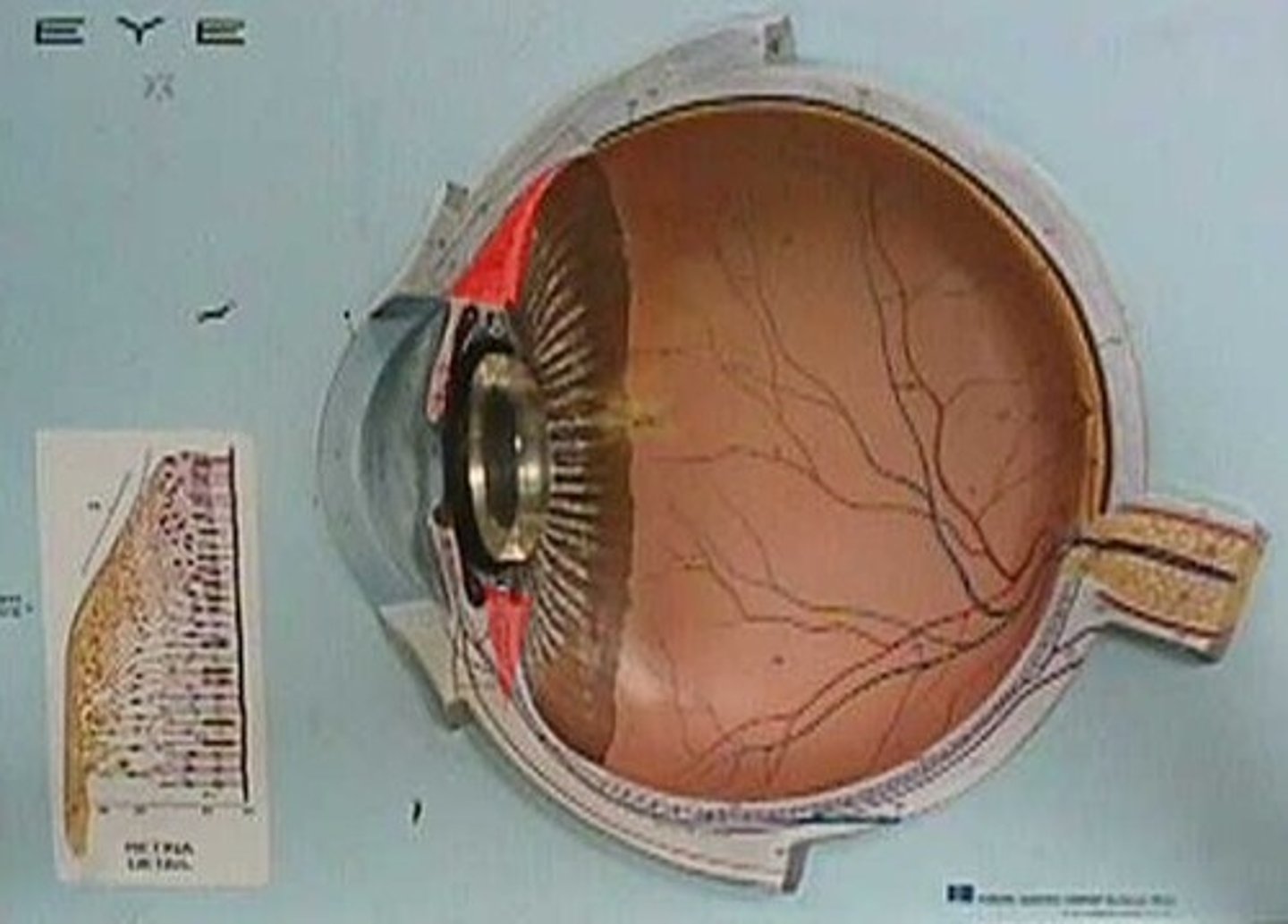
retina
light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye that converts light into neural signals, which are then sent to the brain via the optic nerve for processing into vision; captures and translates incoming light, enabling sight by creating visual image, which includes processing color and details
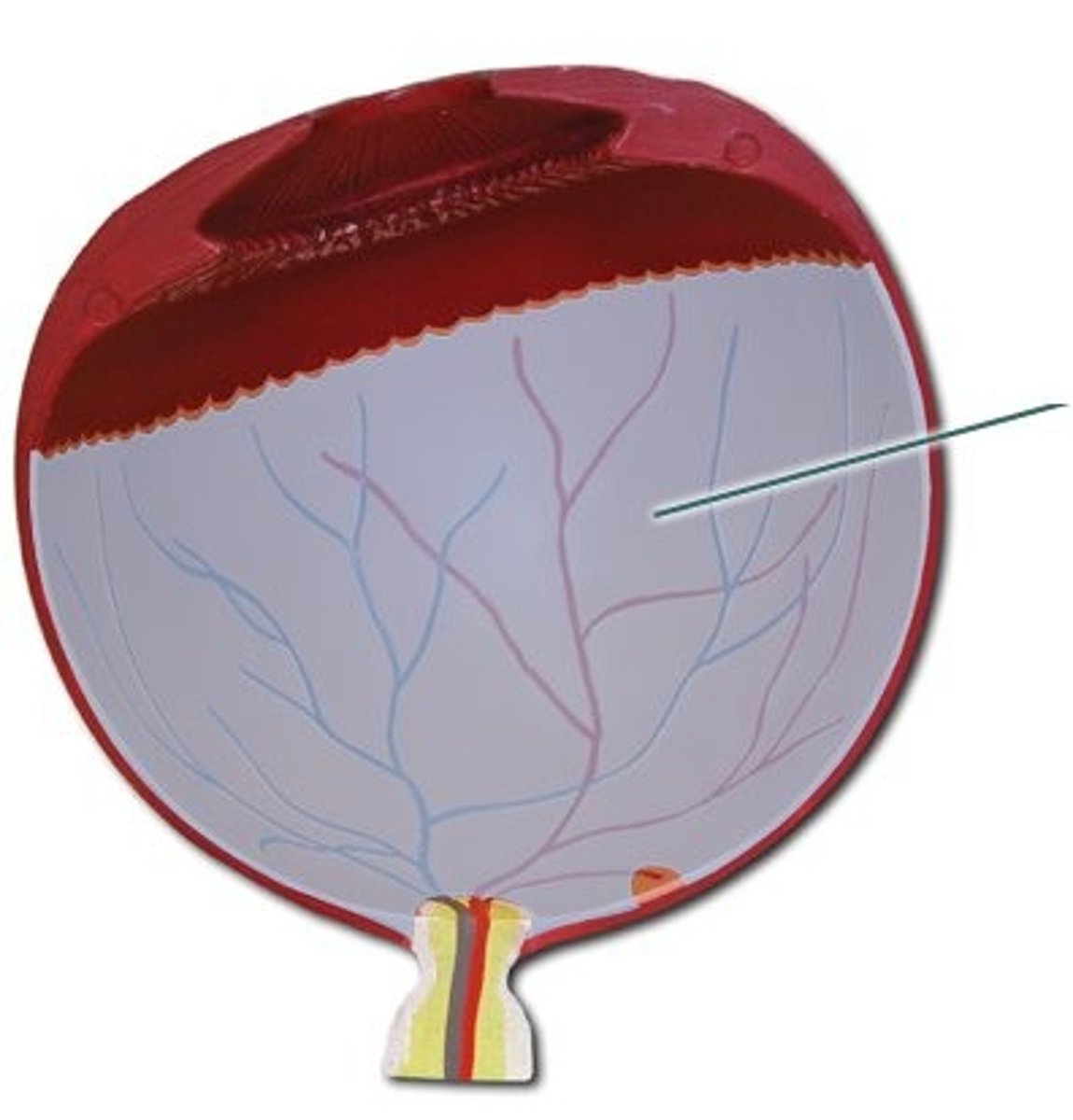
optic disc
circular area at the back of the eye where the optic nerve exits to connect to the brain; serves as the connection for all the retinal nerve fibers, forming the optic nerve and transmitting visual information as electrical signals to the brain
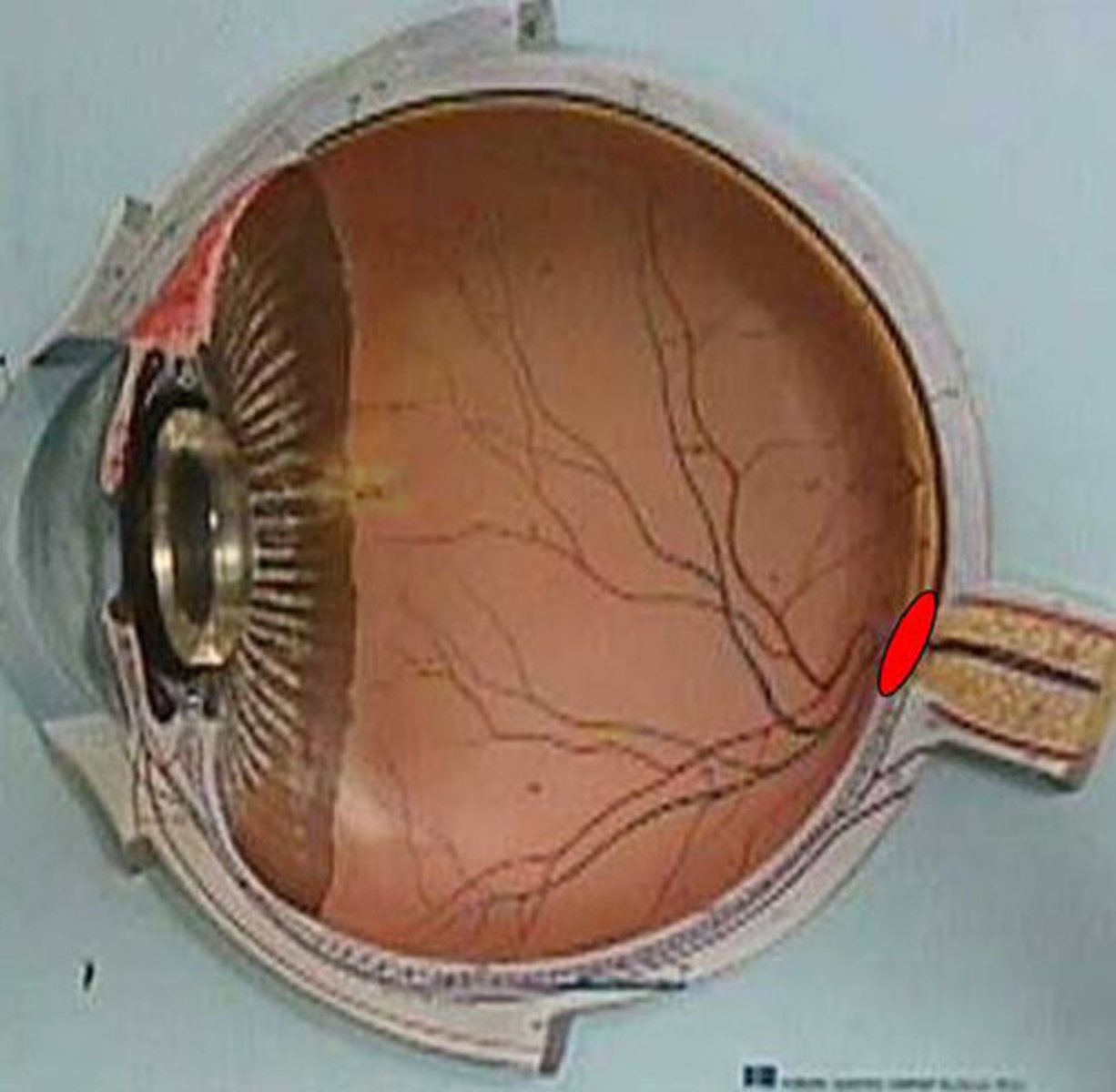
aqueous humor
clear, watery fluid located in the front part of the eye, filling the anterior and posterior chambers; nourishes the surrounding tissues, maintains eye's shape and internal pressure, and removes waste
anterior chamber
fluid-filled space in the front of the eye, between the cornea and the iris; maintains internal eye pressure, nourishes avascular cornea and lens by providing nutrients and removing waste, and contributing to eye's overall shape and optical clarity
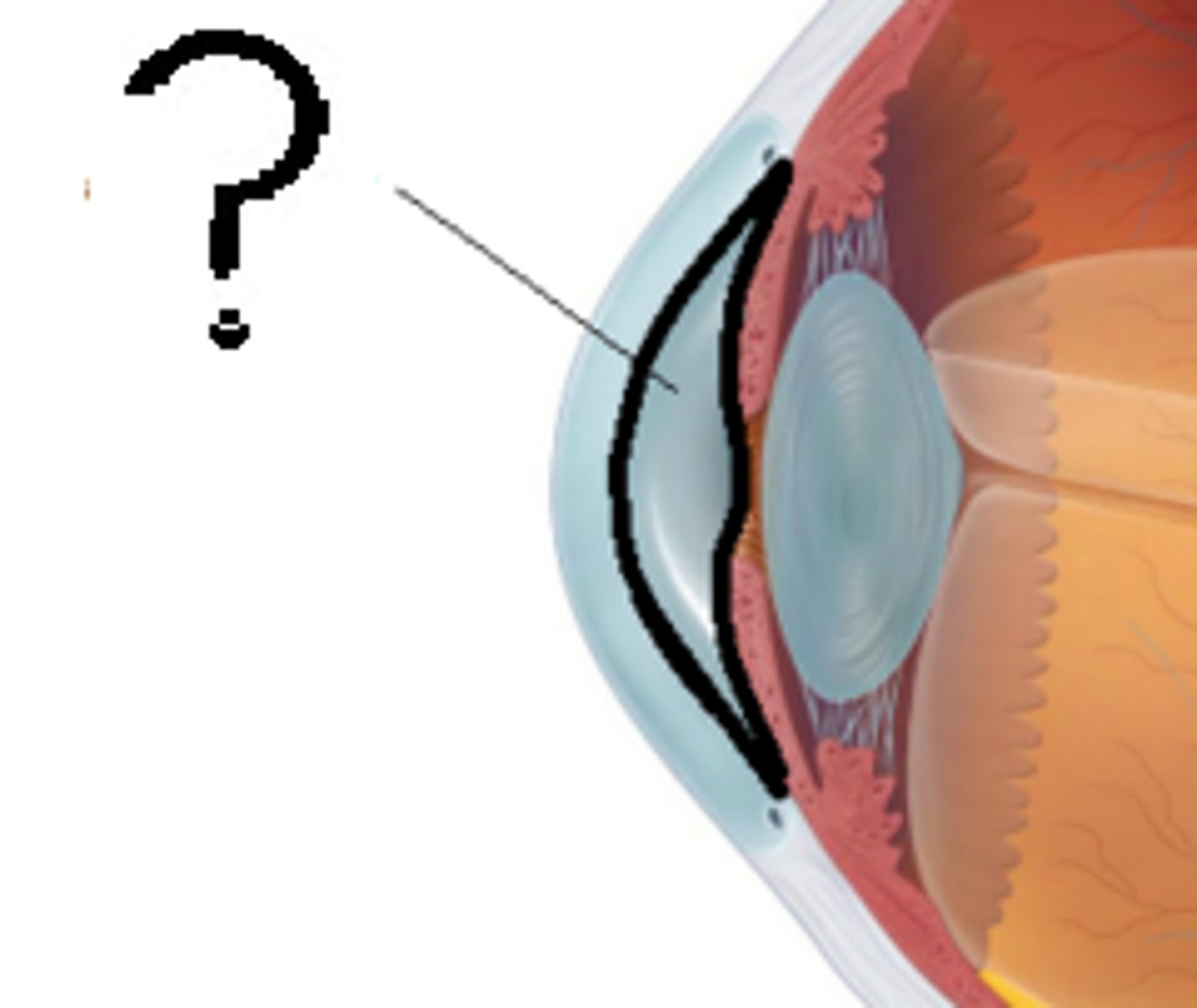
posterior chamber
narrow, fluid-filled space in the eye located behind the iris and in front of lens; it's the first part of the eye to receive aqueous humor which ten flows through the pupil to the anterior chamber
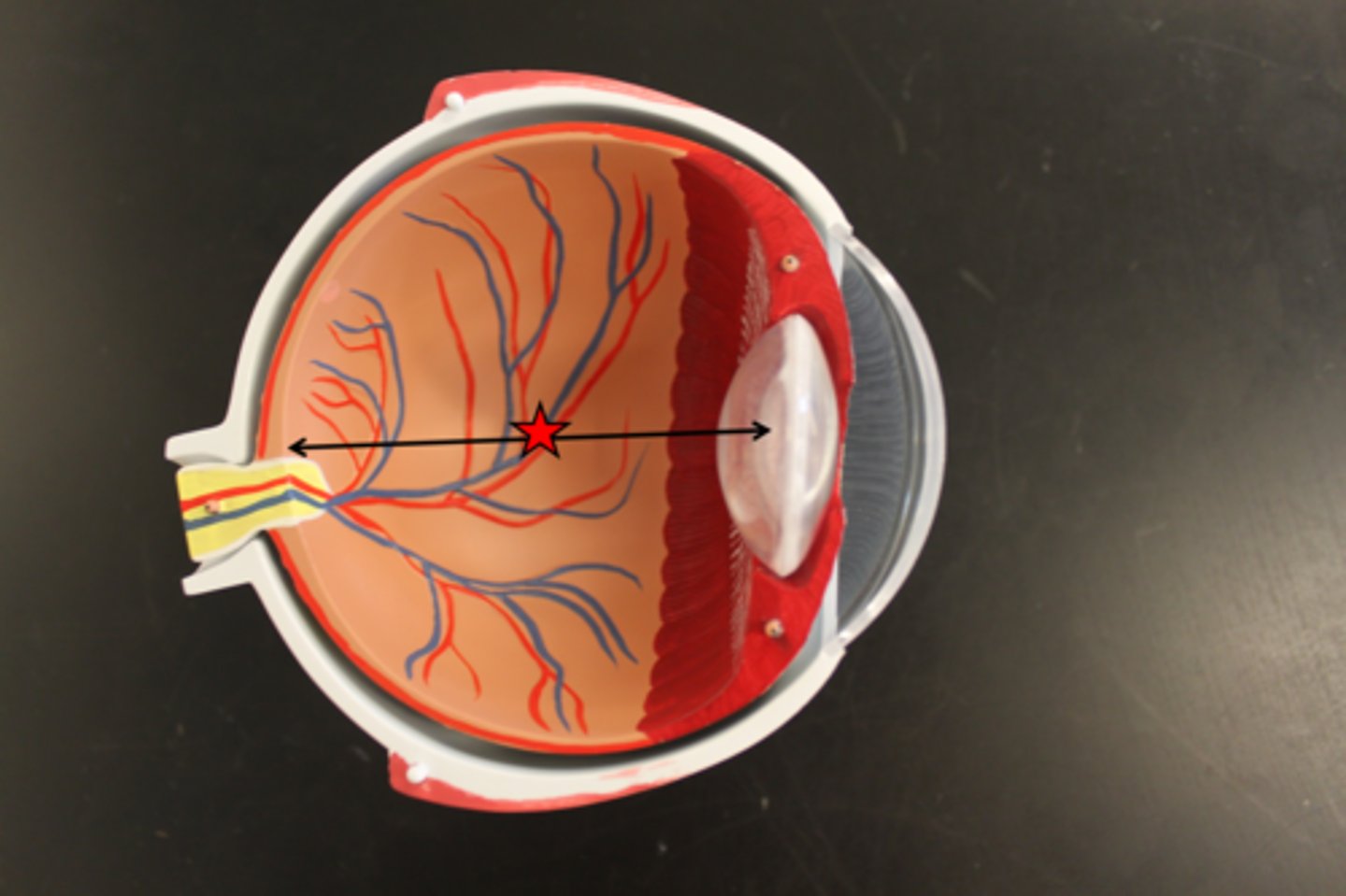
vitreous body
gel-like substance that fills the large space between the lens and retina in the eye; keeps the eye's shape, holds the retina in place, allows light to pass through the retina, and provides nutrients to avascular parts of the eye
lens
transparent, biconvex structure located behind the iris that focuses light onto the retina; bends and focuses incoming light to create a sharp image
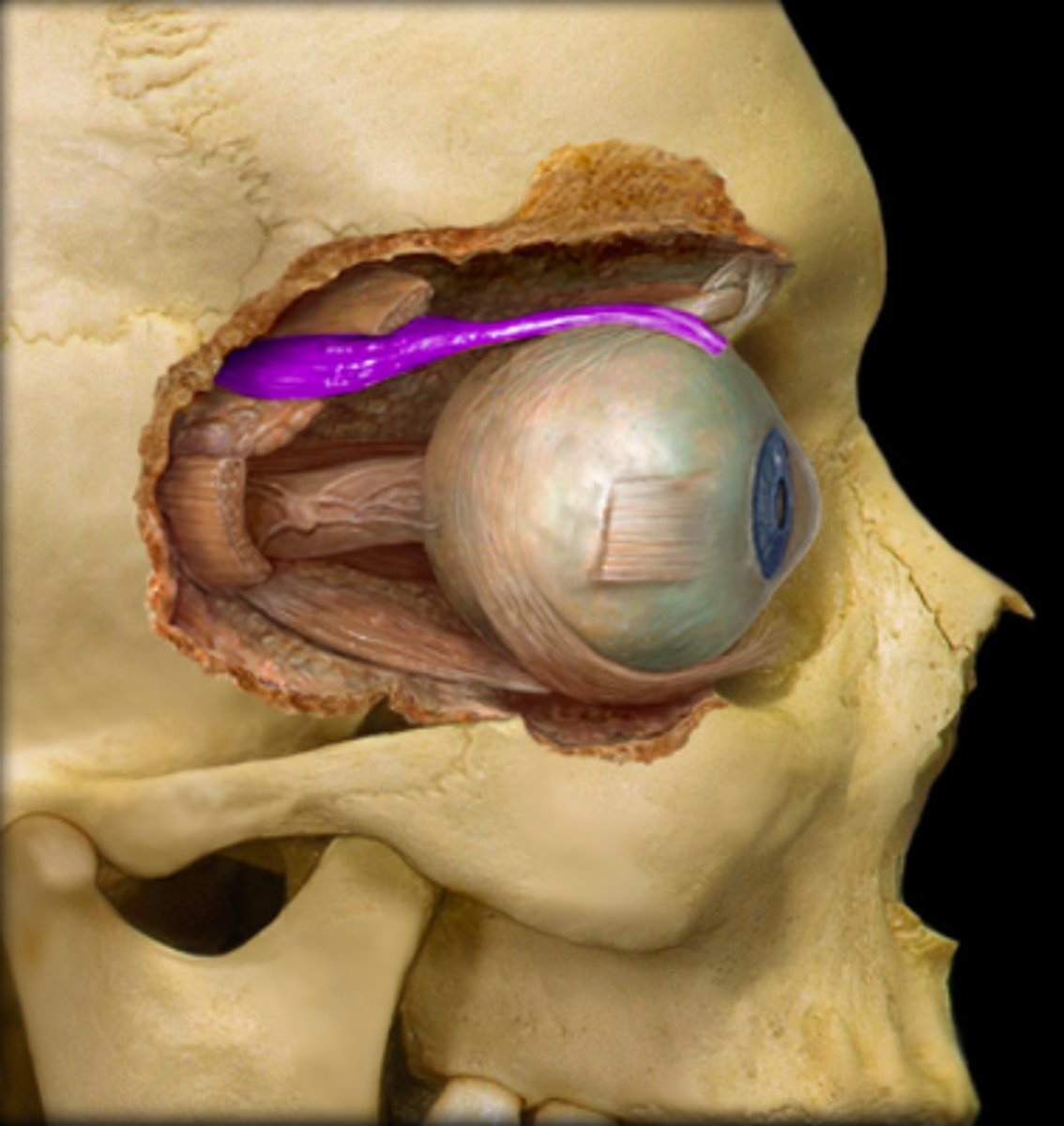
superior rectus m
extraocular muscle in the eye; elevates the eye, moves the eye toward the nose, rotates the eye inward
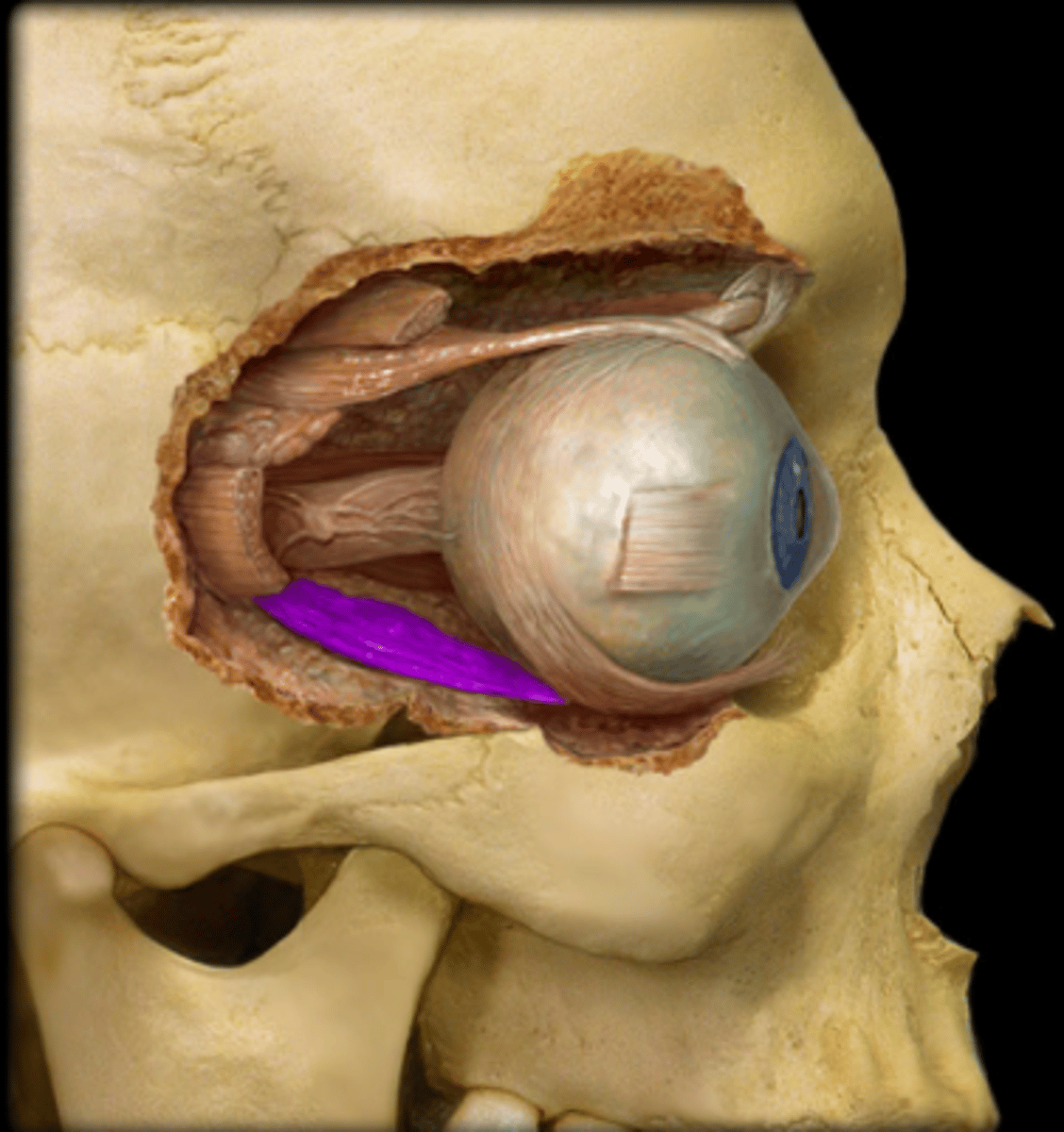
inferior rectus m
muscle in the orbit that controls eye movement; depresses the eye, and helps move the eye toward the nose and external rotation
medial rectus m
muscle in the orbit that moves eye toward the nose; facilitates horizontal eye movement and convergence
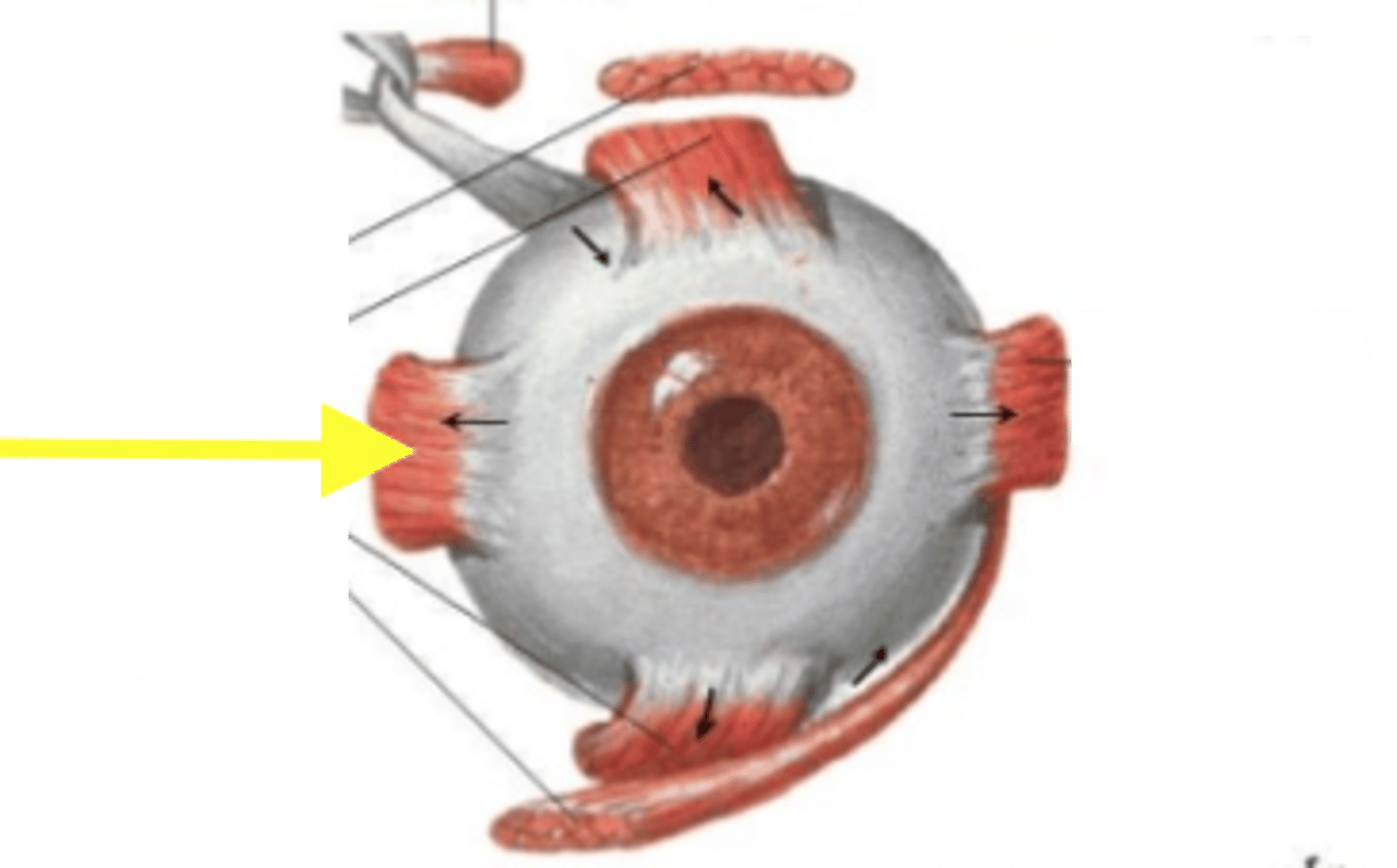
lateral rectus m
muscle of the eye responsible for moving eye outward; allows for the movement of the pupil toward the ear
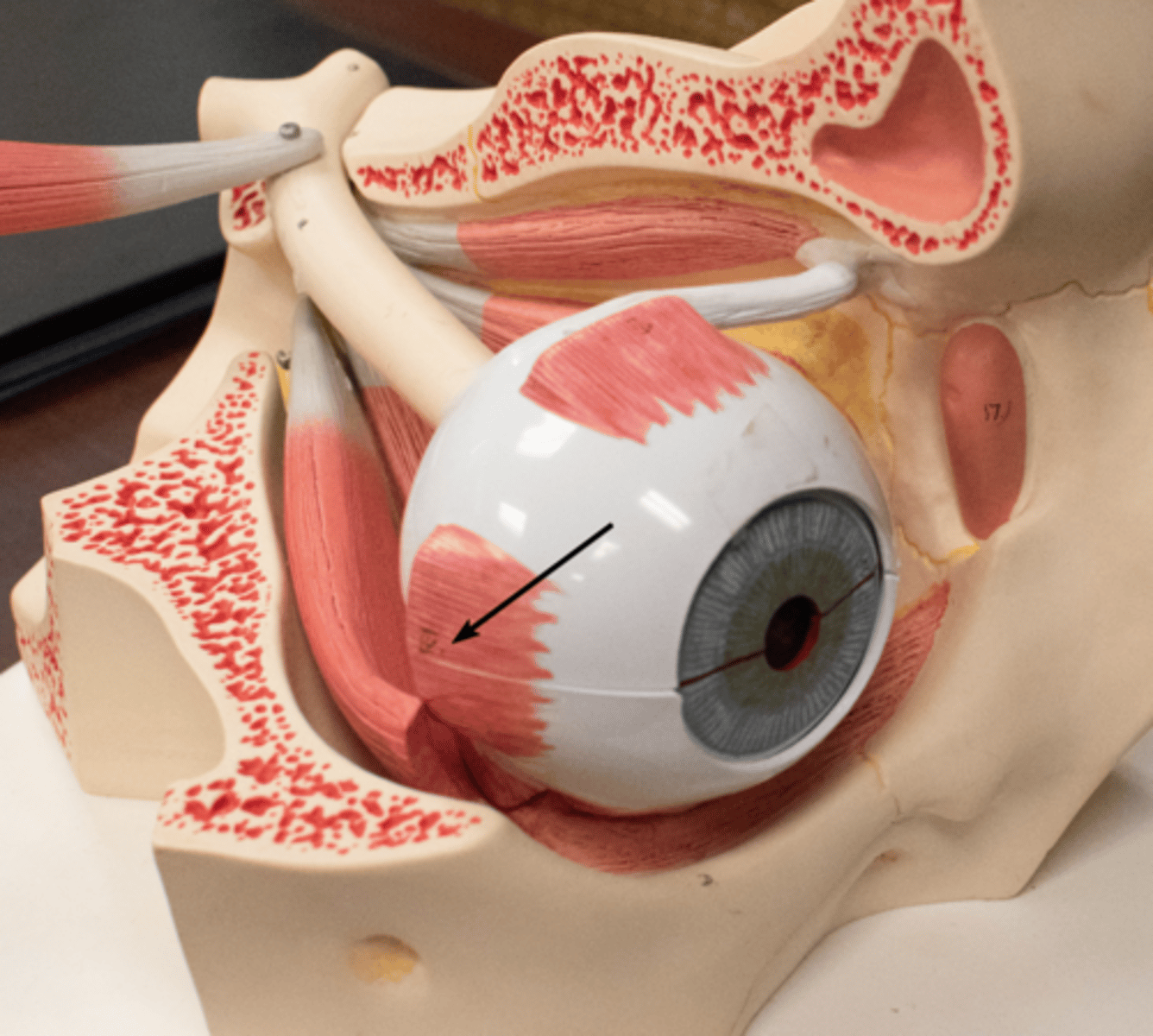
superior oblique m
extraocular muscle that controls eye movement; moves eye downward and outward, while also rotating the top of the eye inward
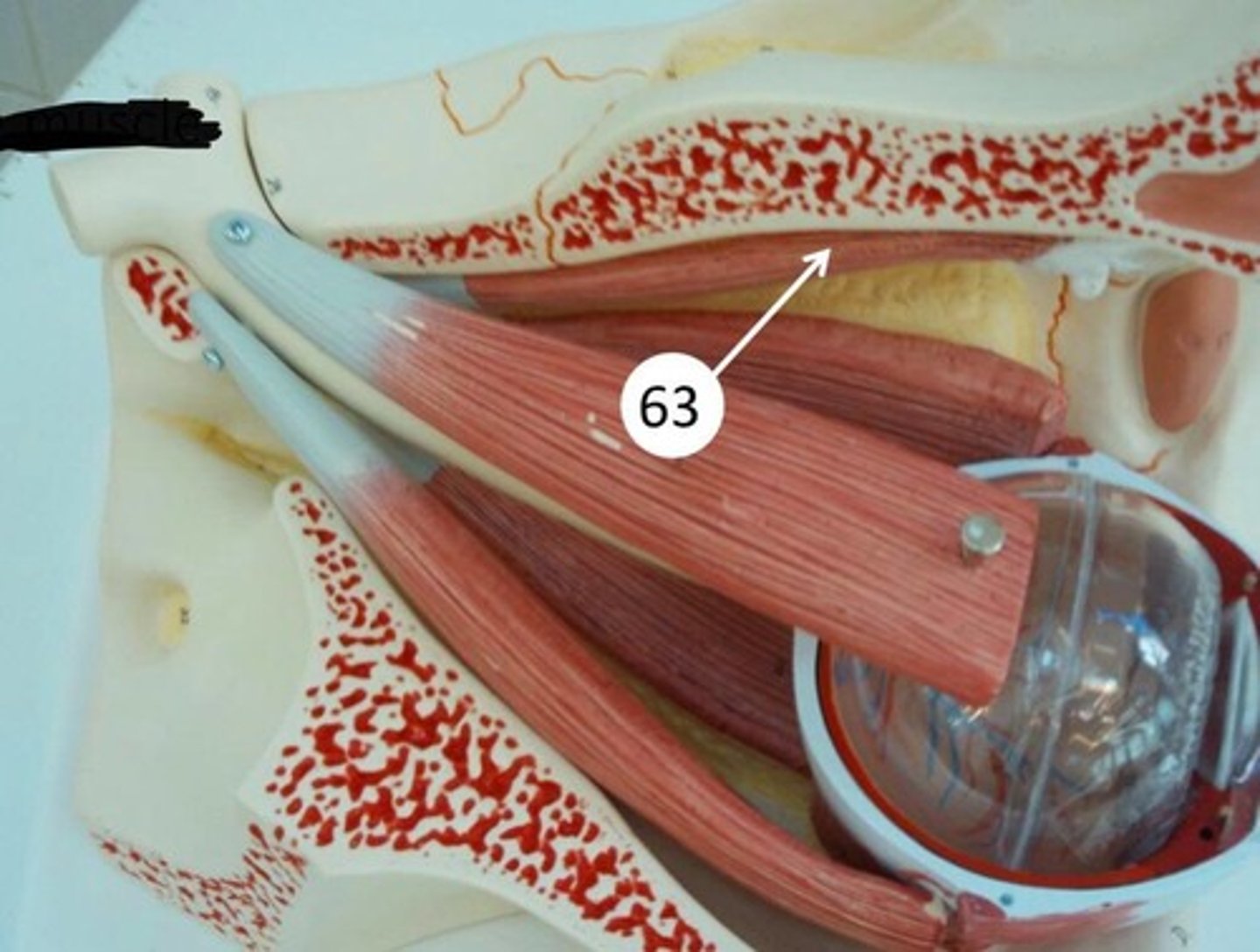
trochlea
pulley-like structure in upper-inner corner of the eye socket that redirects the tendon of the superior oblique muscle; changes the direction of the muscle's pull, enabling it to depress the eye, abduct it, and intort it (rotate it so the top moves toward the nose)
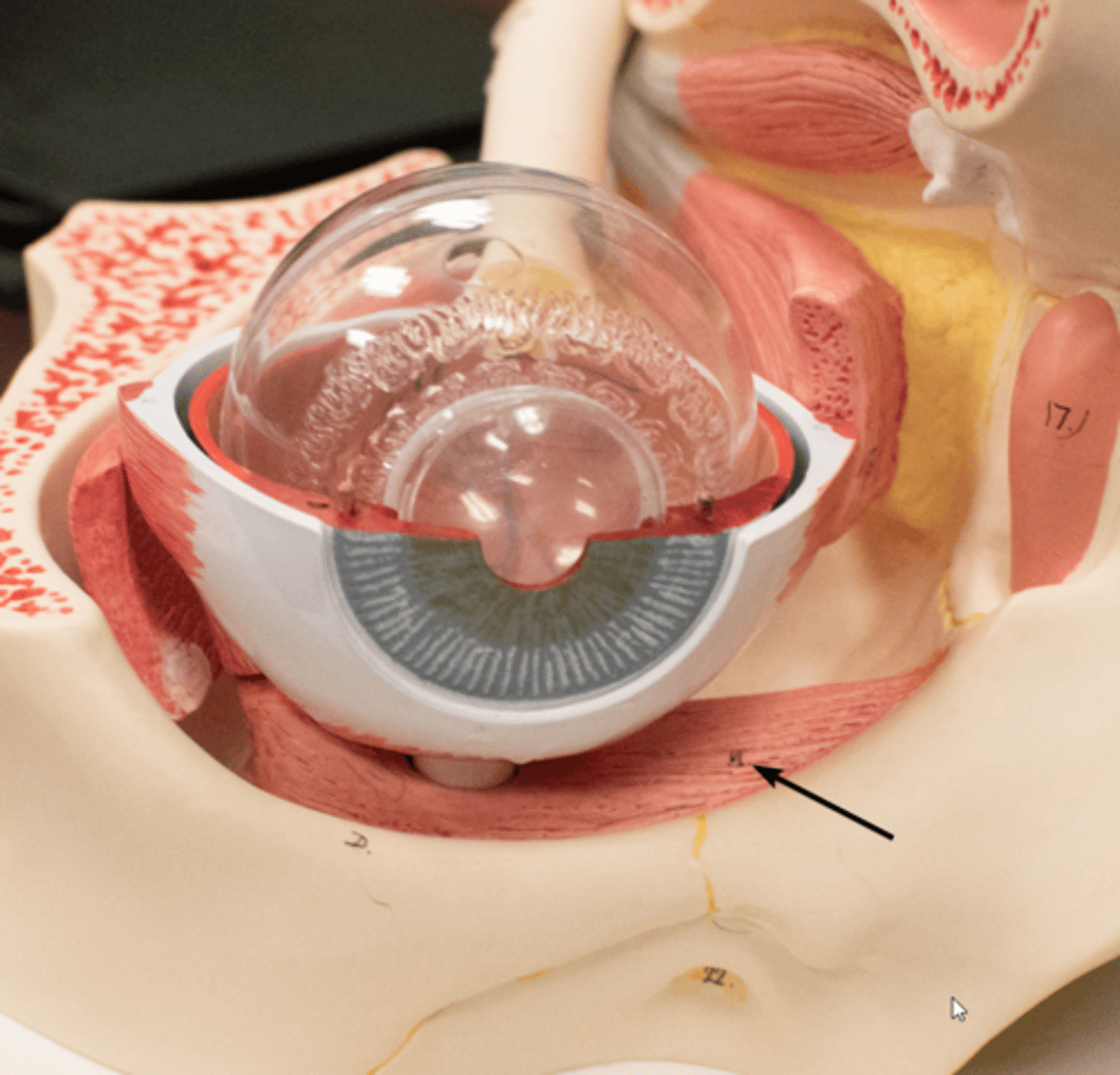
inferior oblique m
muscle in the eye that originates on the floor of the orbit and inserts on back of the eyeball; helps move the eye by extorsion (outward rotation), elevation (upward movement), and abduction (lateral movement away from nose)
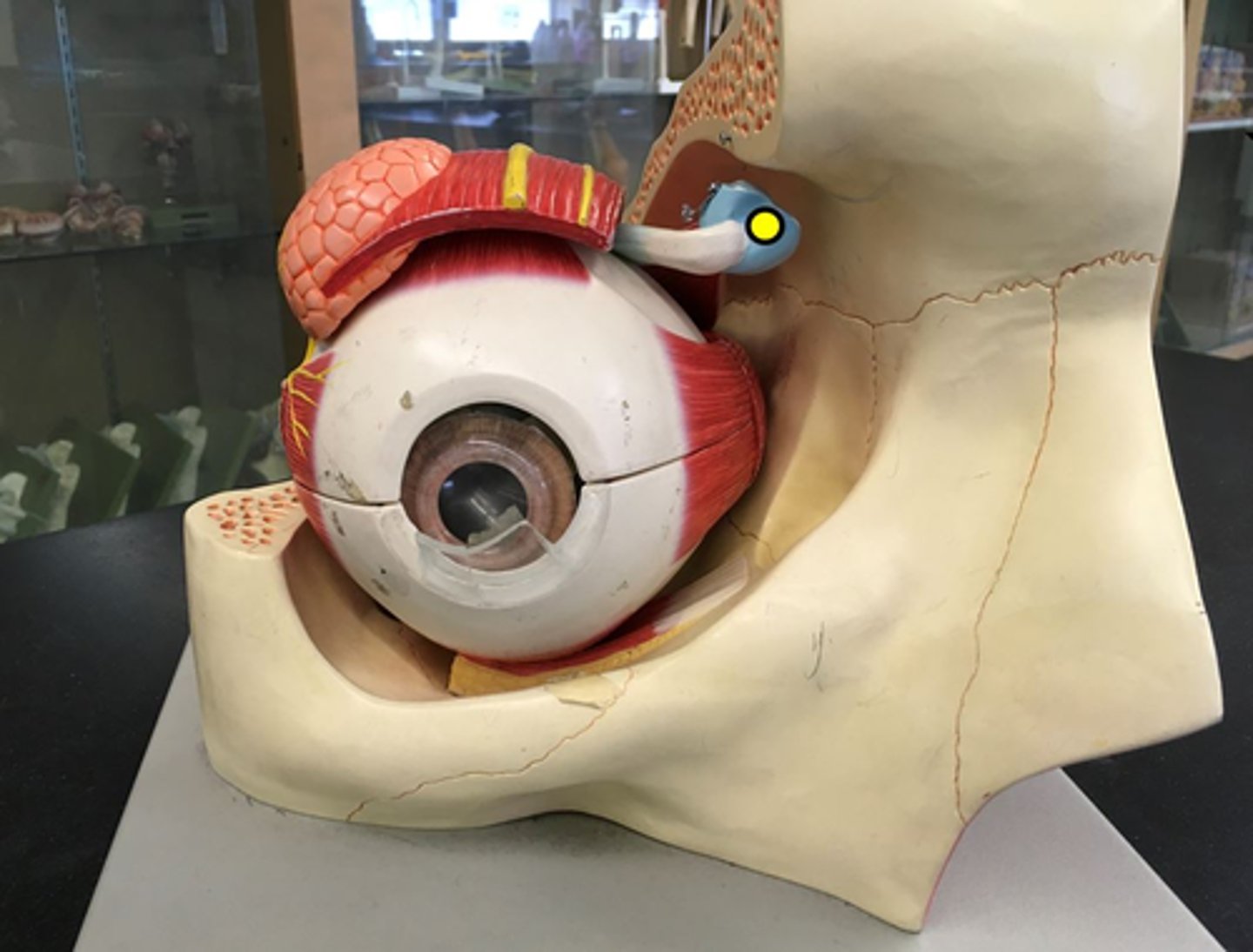
trochlear nerve
fourth cranial nerve, a purely motor nerve that controls superior oblique muscle in the eye; enables the eye to look down and rotate inwards
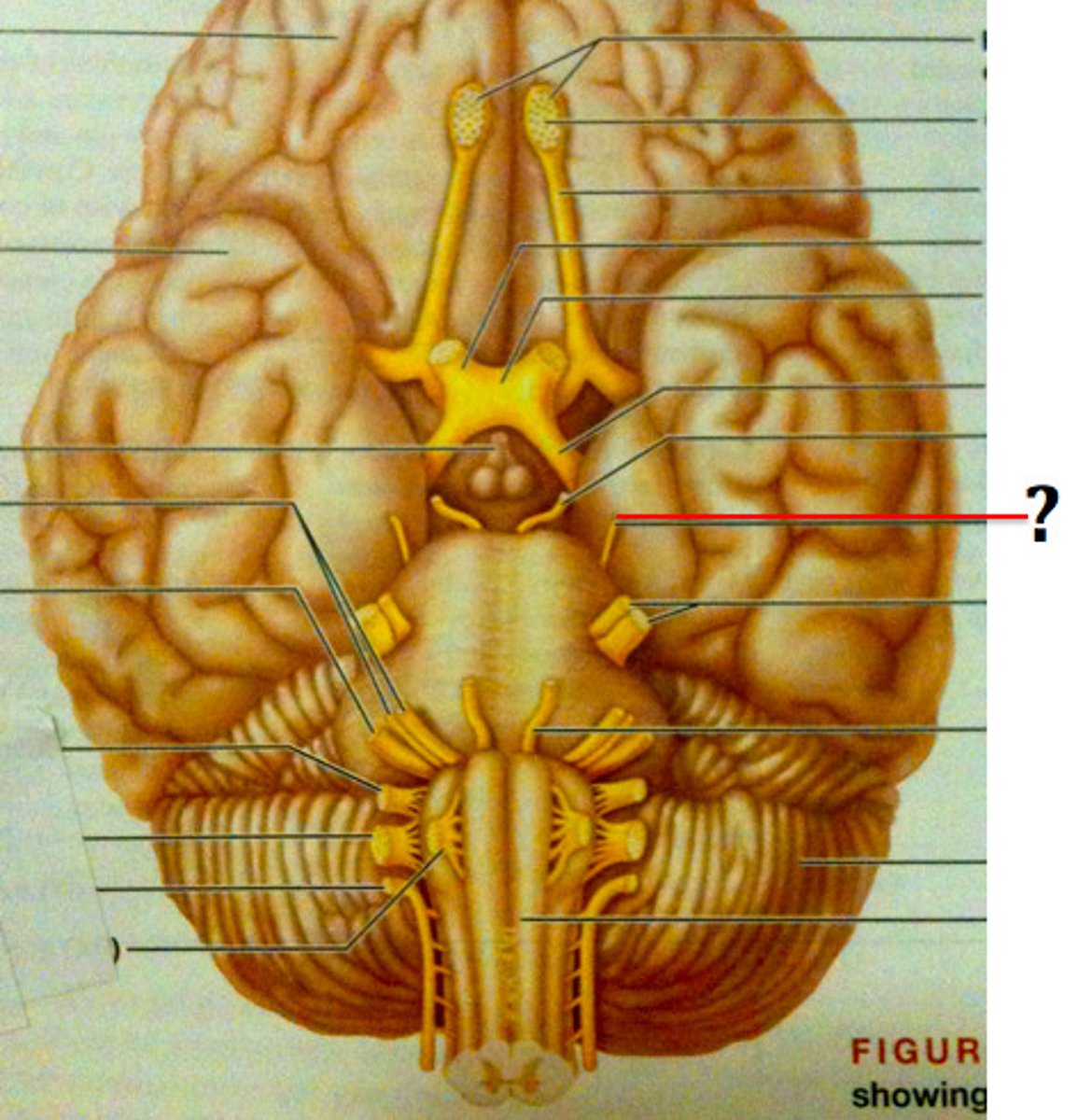
abducens nerve
sixth cranial nerve, purely motor nerve responsible for eye movement, primarily by innervating the lateral rectus muscle; allows the eye to move laterally or abduct
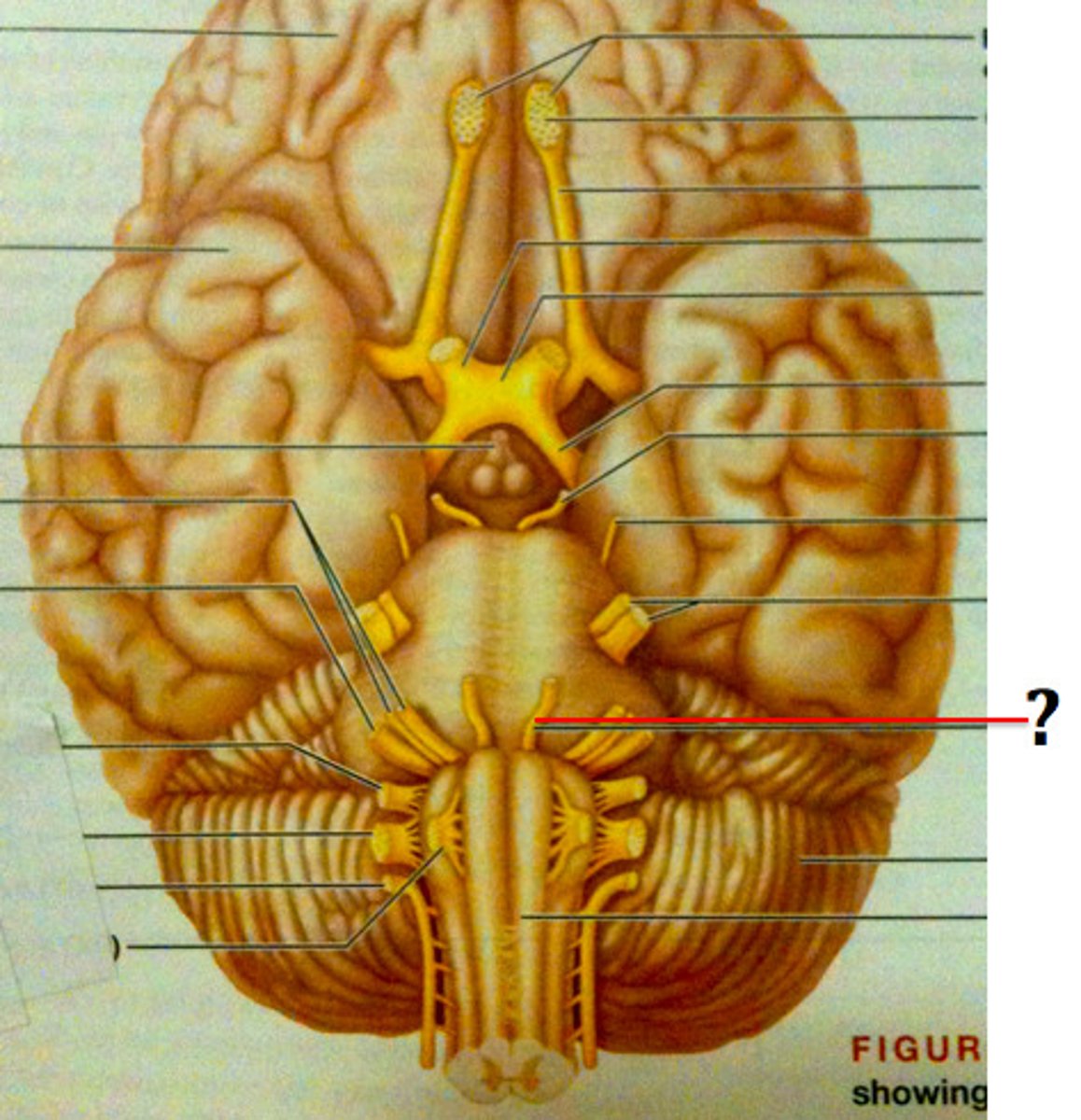
oculomotor nerve
cranial nerve three, a motor nerve that controls most eye movement, eyelid elevation, and pupil constriction; enables a wide range of visual functions, including moving the eye to follow a moving object, constricting the pupil to adjust to light, and focusing the lens for near vision
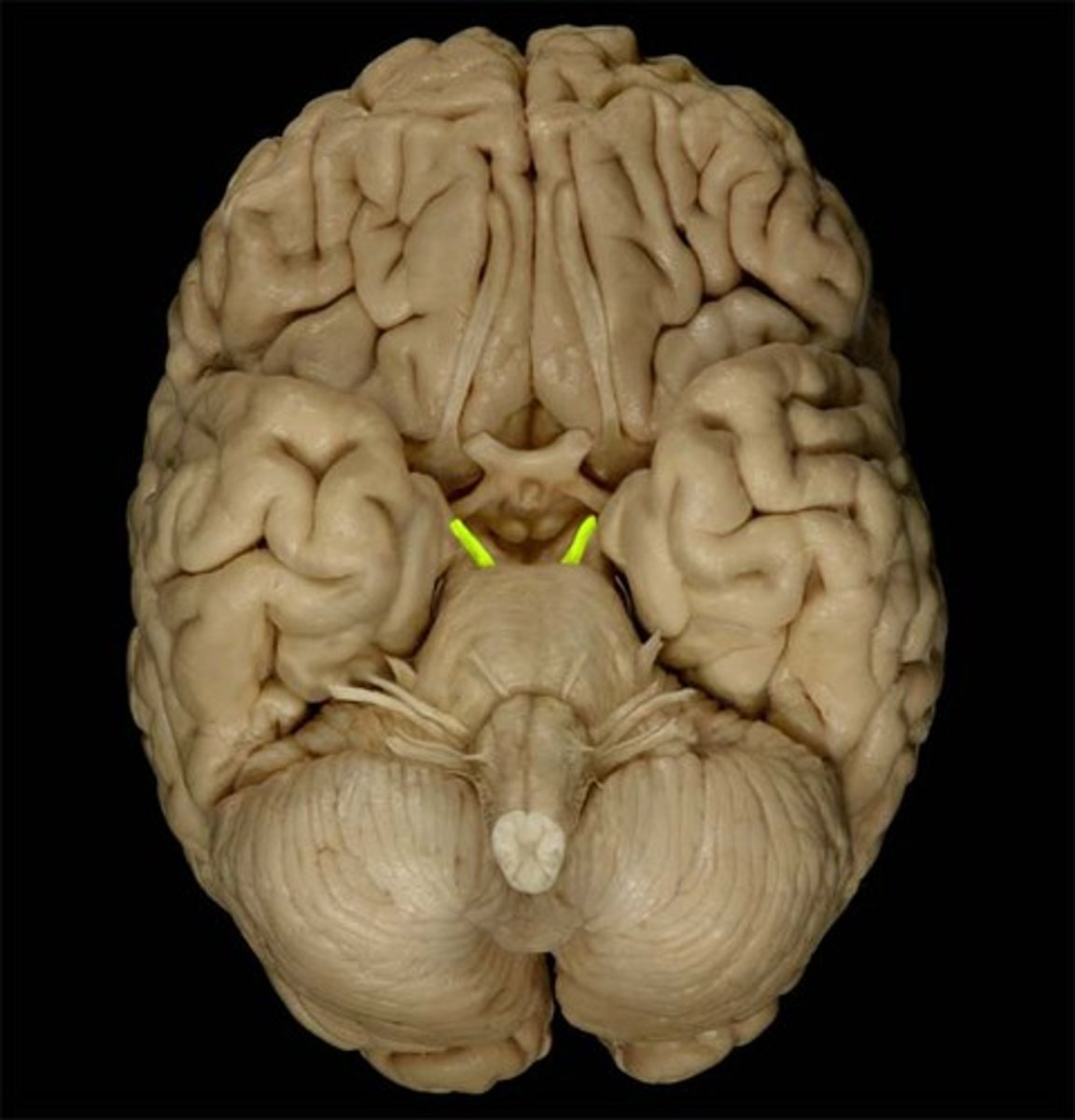
optic nerve
second cranial nerve, connecting the retina to the brain to transmit visual signals for sight; relays sensory information from the eye to the brain, which processes the electrical impulses into images
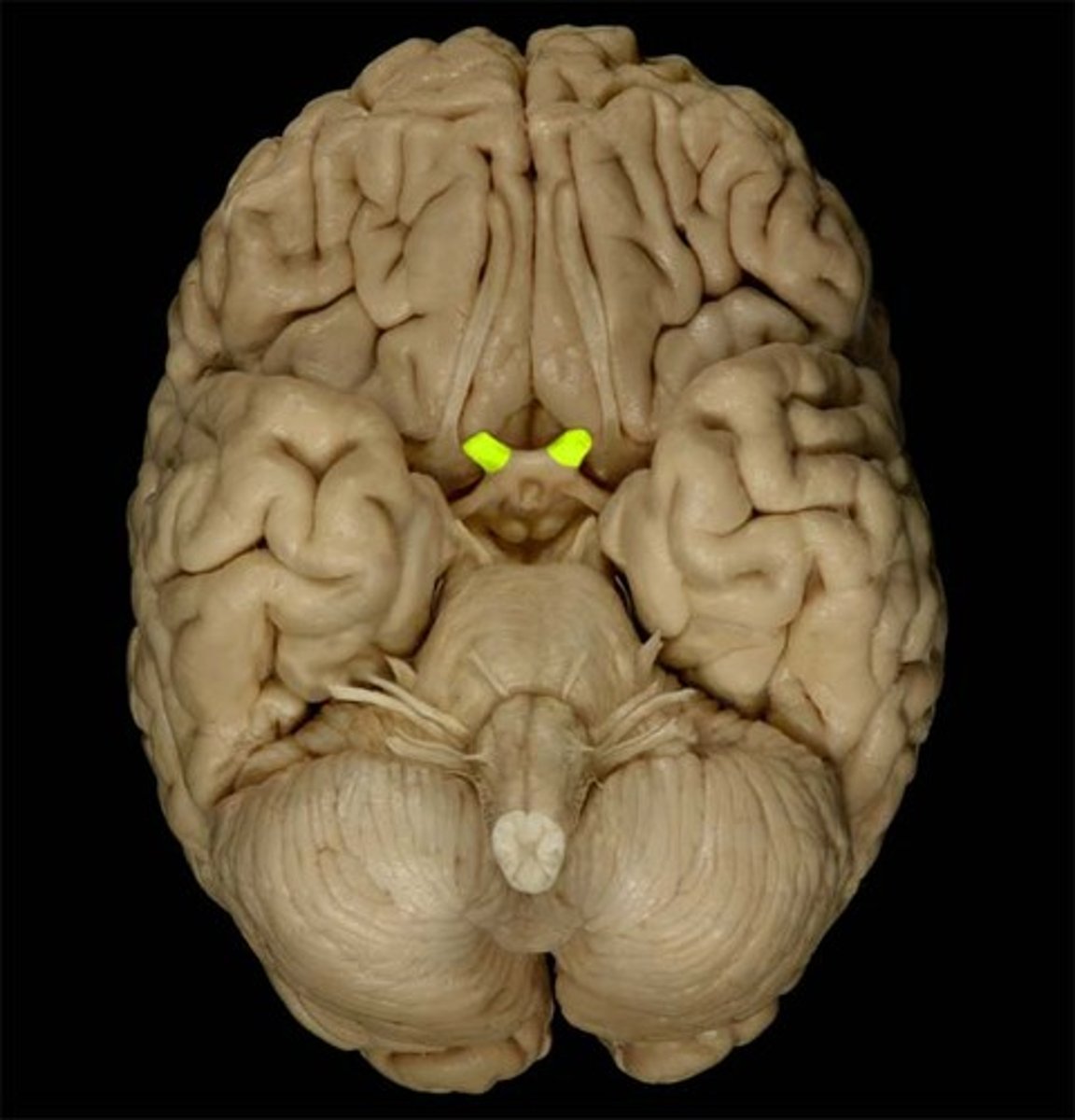
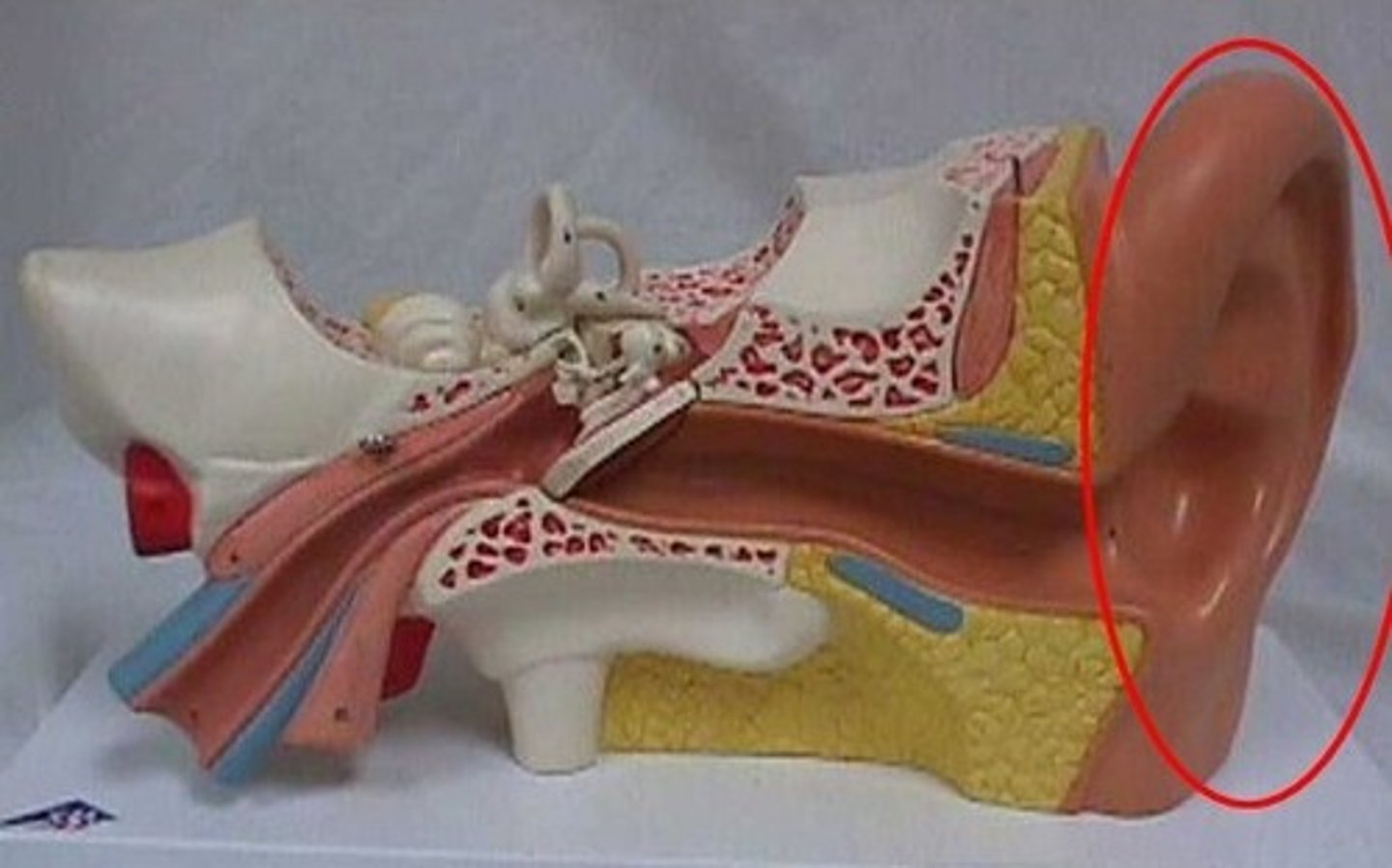
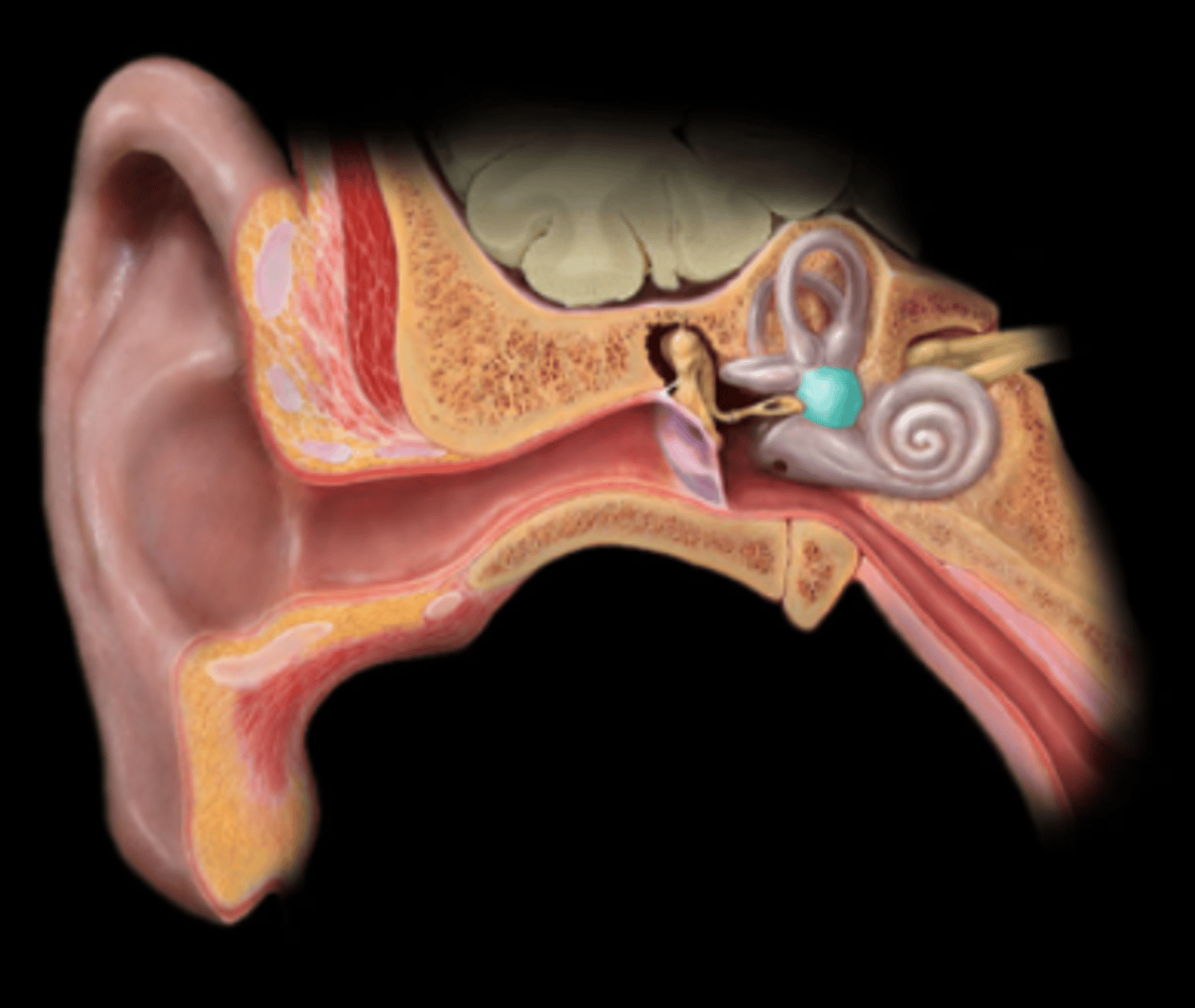
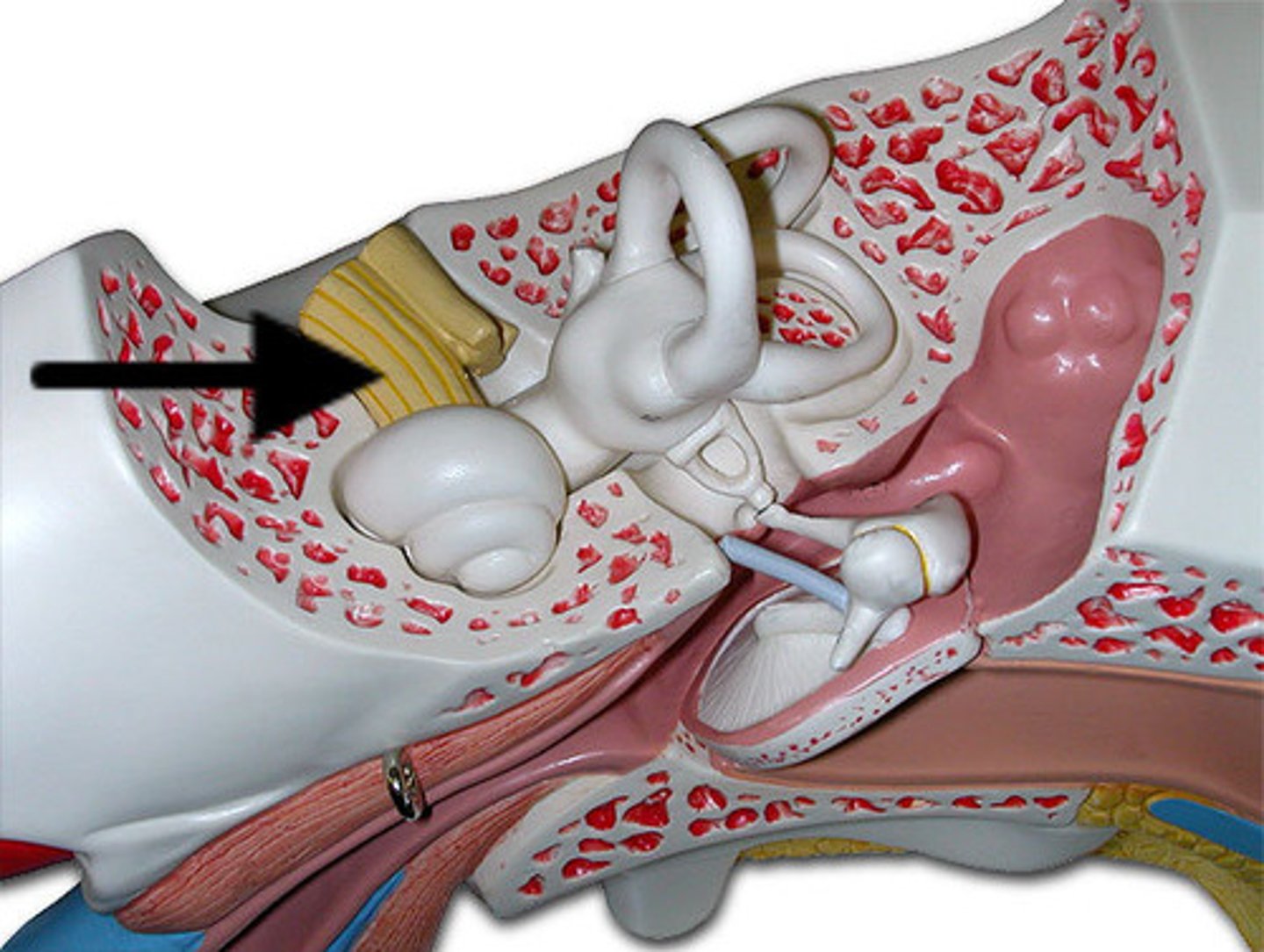
auricle
visible, external part of the ear; collects, funnels, and directs sound waves into the ear canal, where they are then converted into signals the brain can interpret
auditory canal
tube that connects the outer ear to the eardrum; channels sound waves from the environment to the eardrum and protects the inner ear
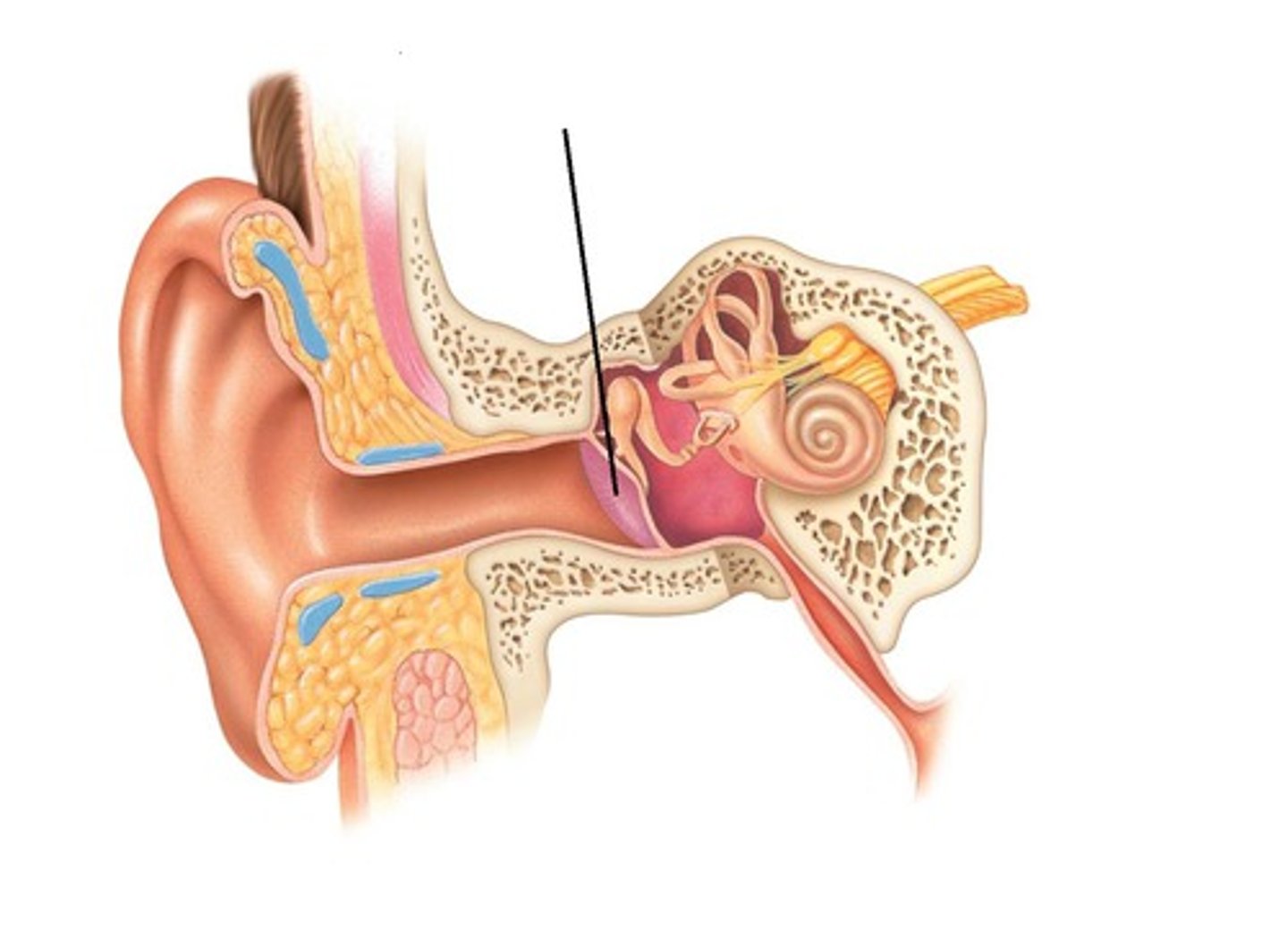
tympanic membrane
thin membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear; protects the middle ear from debris and germs and transmits sound vibrations from the outer ear to the tiny bones in the middle ear
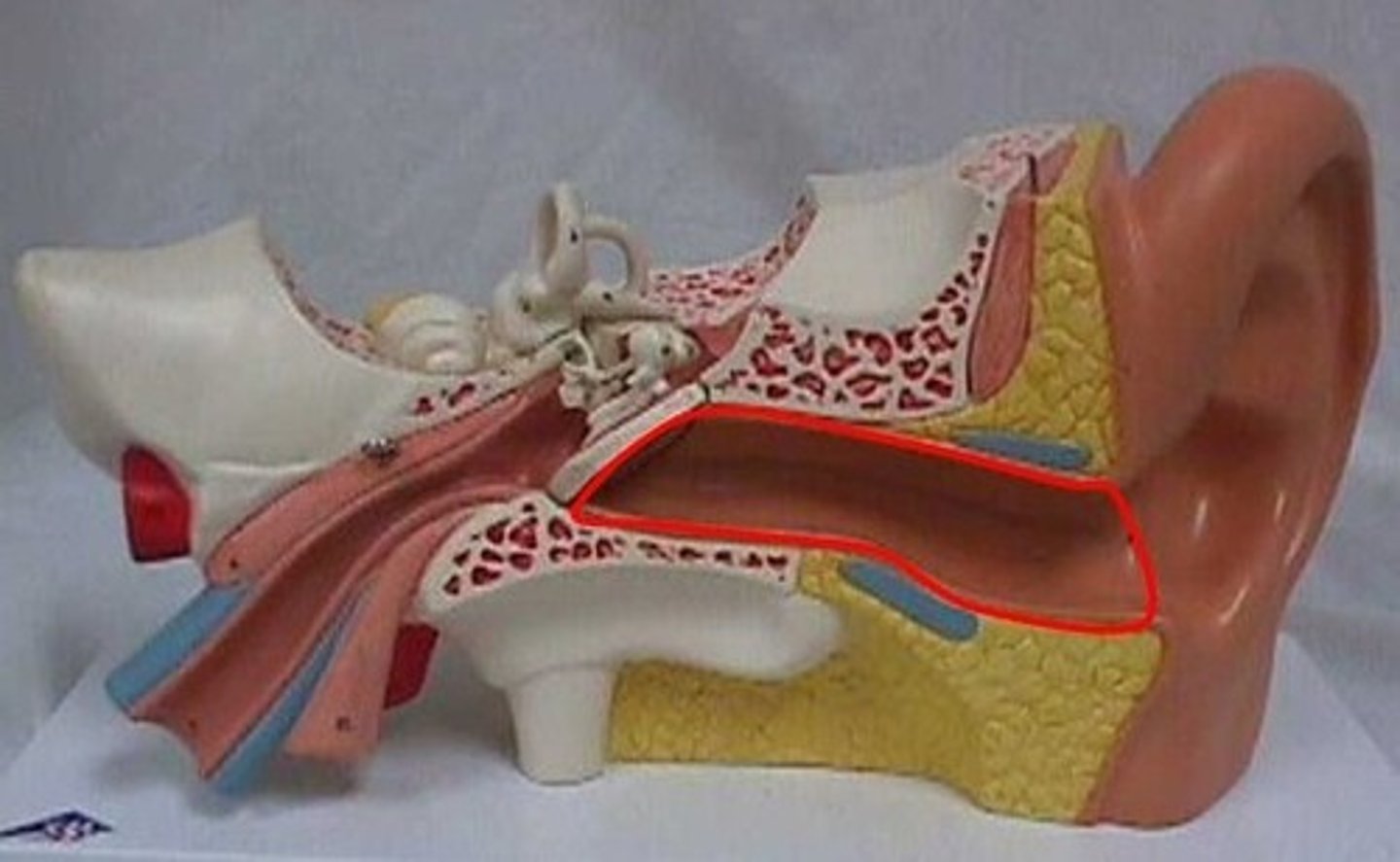
tympanic cavity
air-filled space of the middle ear, located behind the eardrum, that serves to transmit and amplify sound vibrations; houses the malleus, incus, and stapes
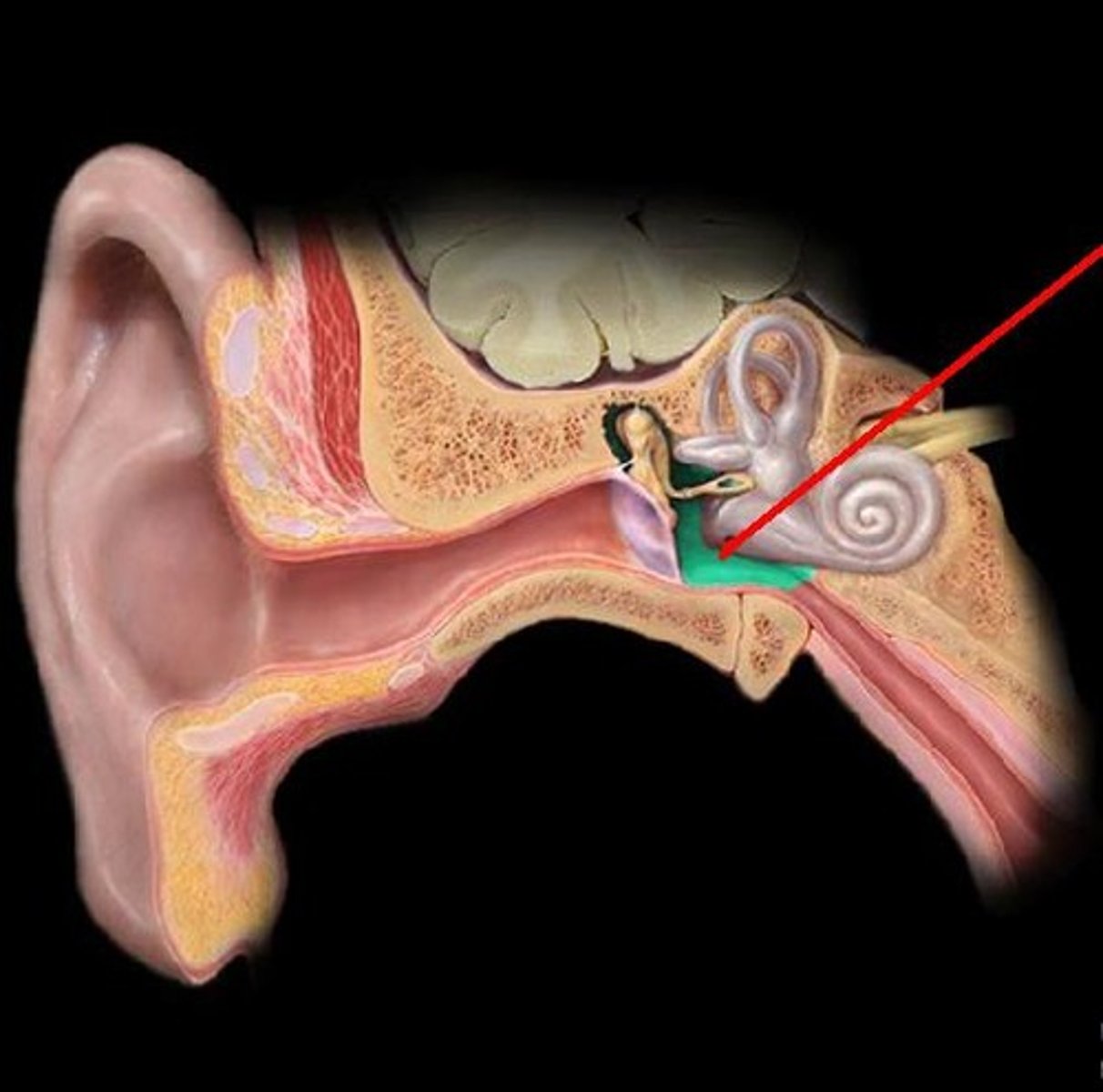
malleus
largest, most lateral of the three tiny bones in the middle ear; transmits sound vibrations from the eardrum to the incus
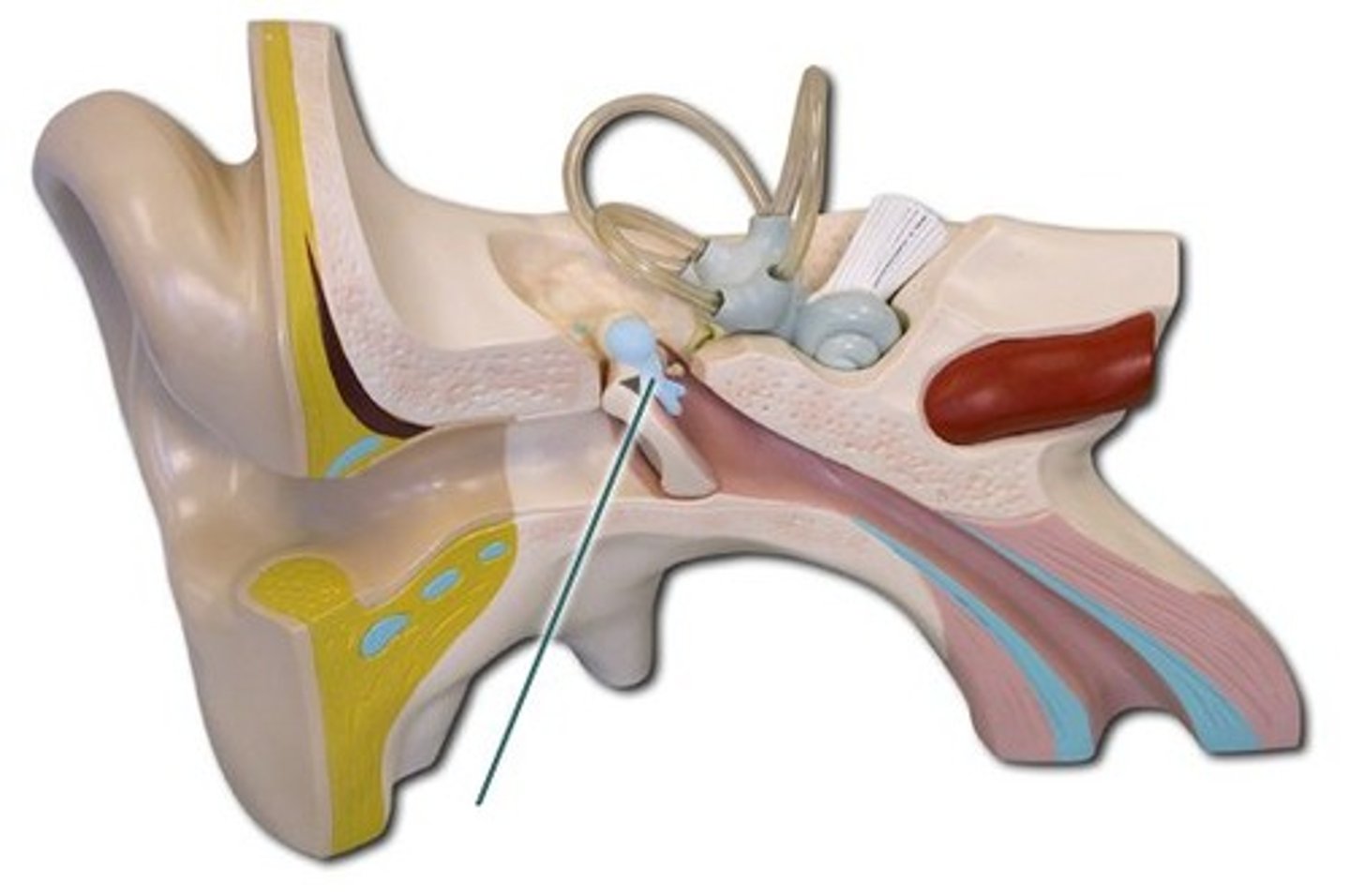
incus
anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear located between the malleus and the stapes; transmits and amplifies sound vibrations from the malleus to the stapes
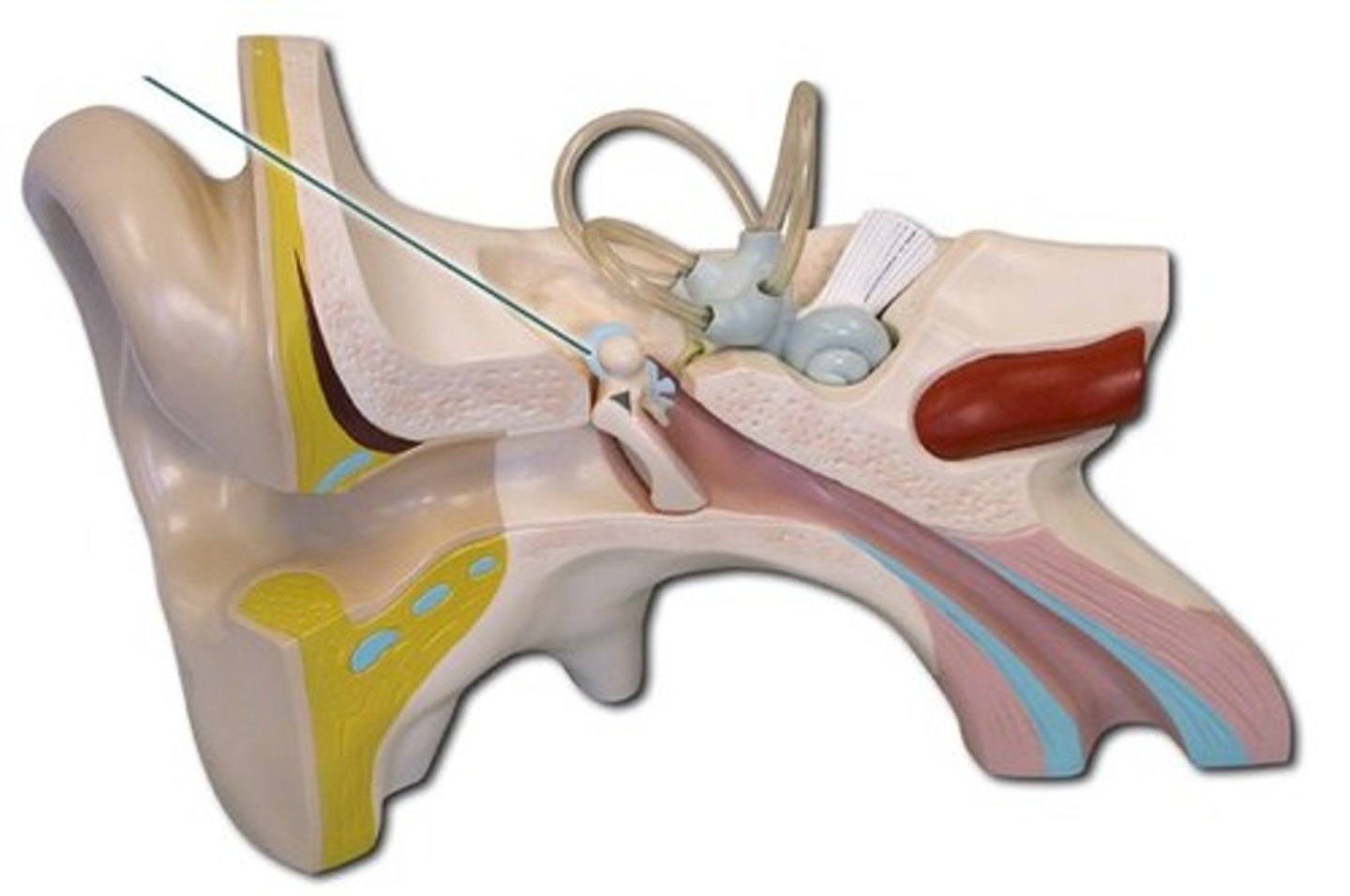
stapes
smallest, lightest bone in body, in the middle ear; transmits and amplifies sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear
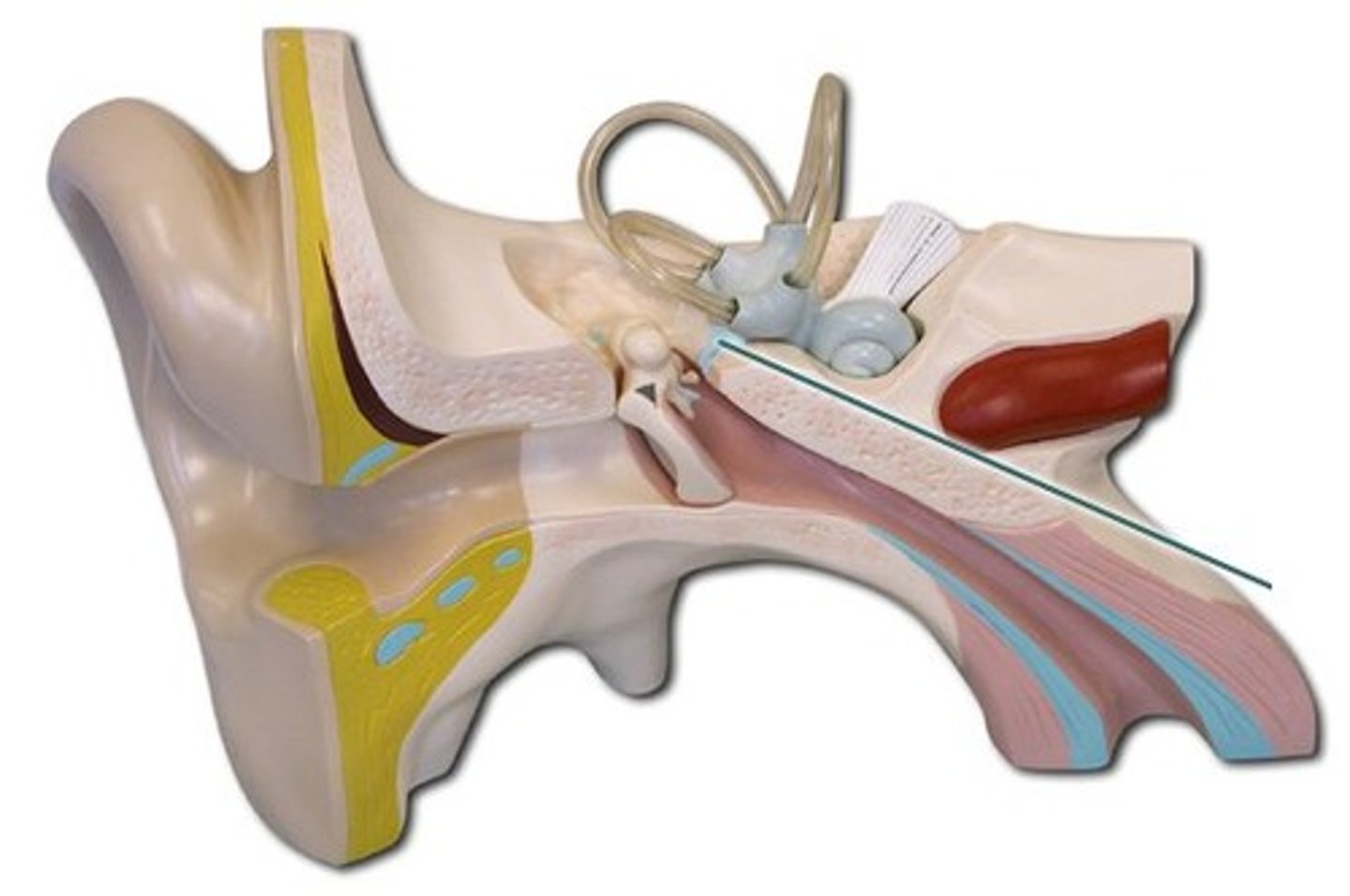
auditory tube
channel connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx; equalizes pressure across the eardrum, drains fluids, and protects the middle ear from infection
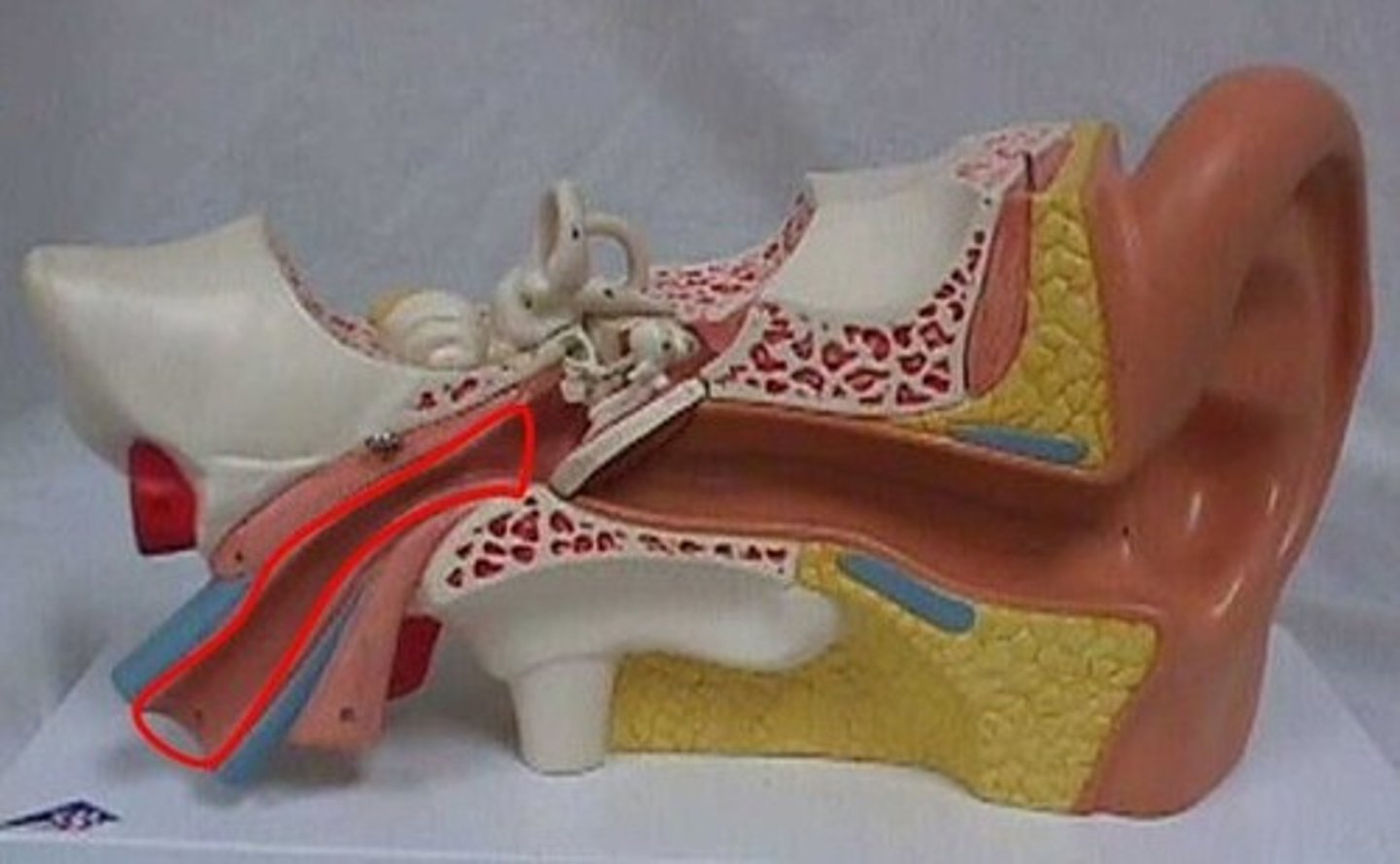
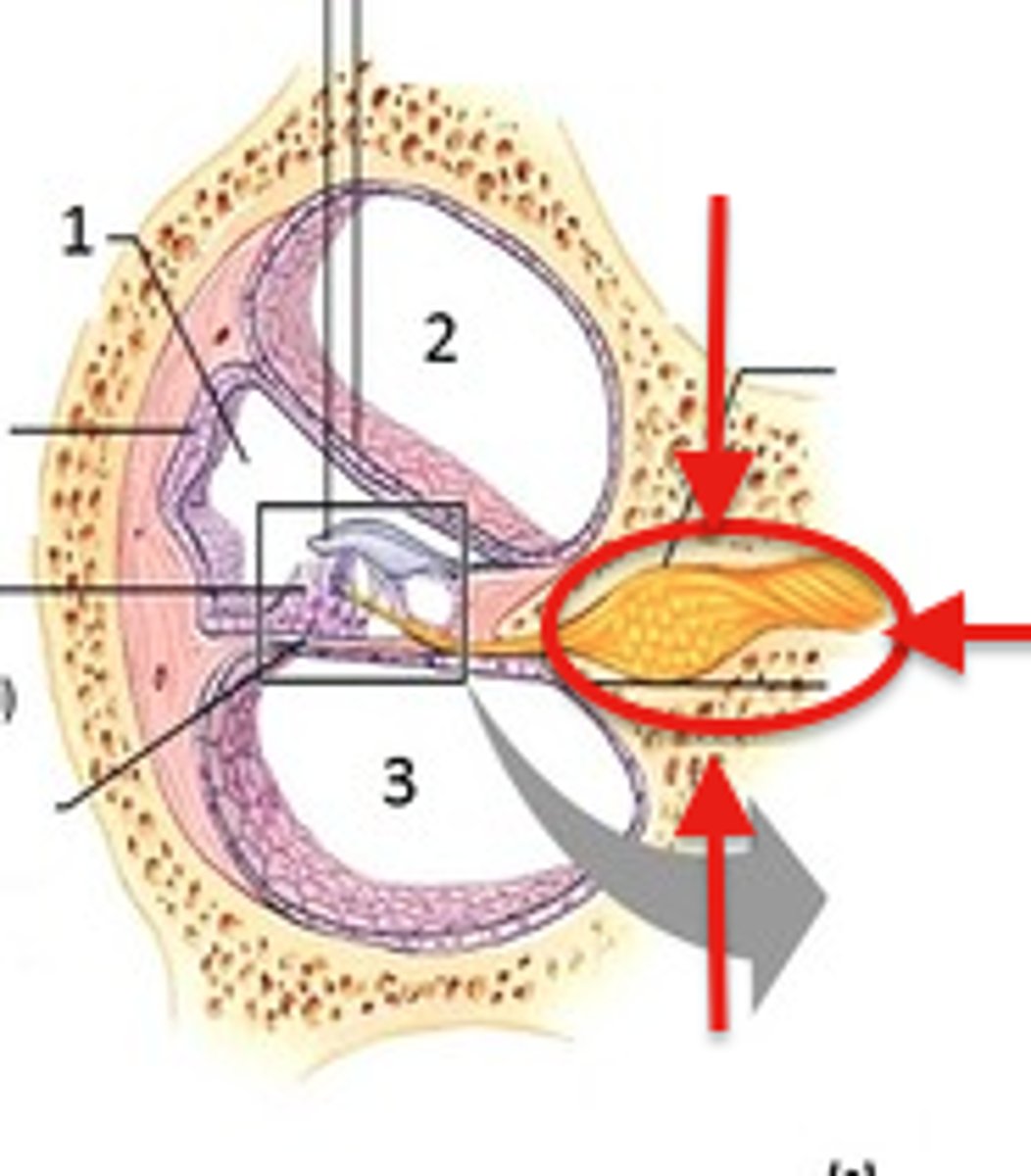
tensor tympani muscle
small muscle in middle ear that attaches to malleus bone; tenses the eardrum, which dampens loud sounds and protects the inner ear from damage
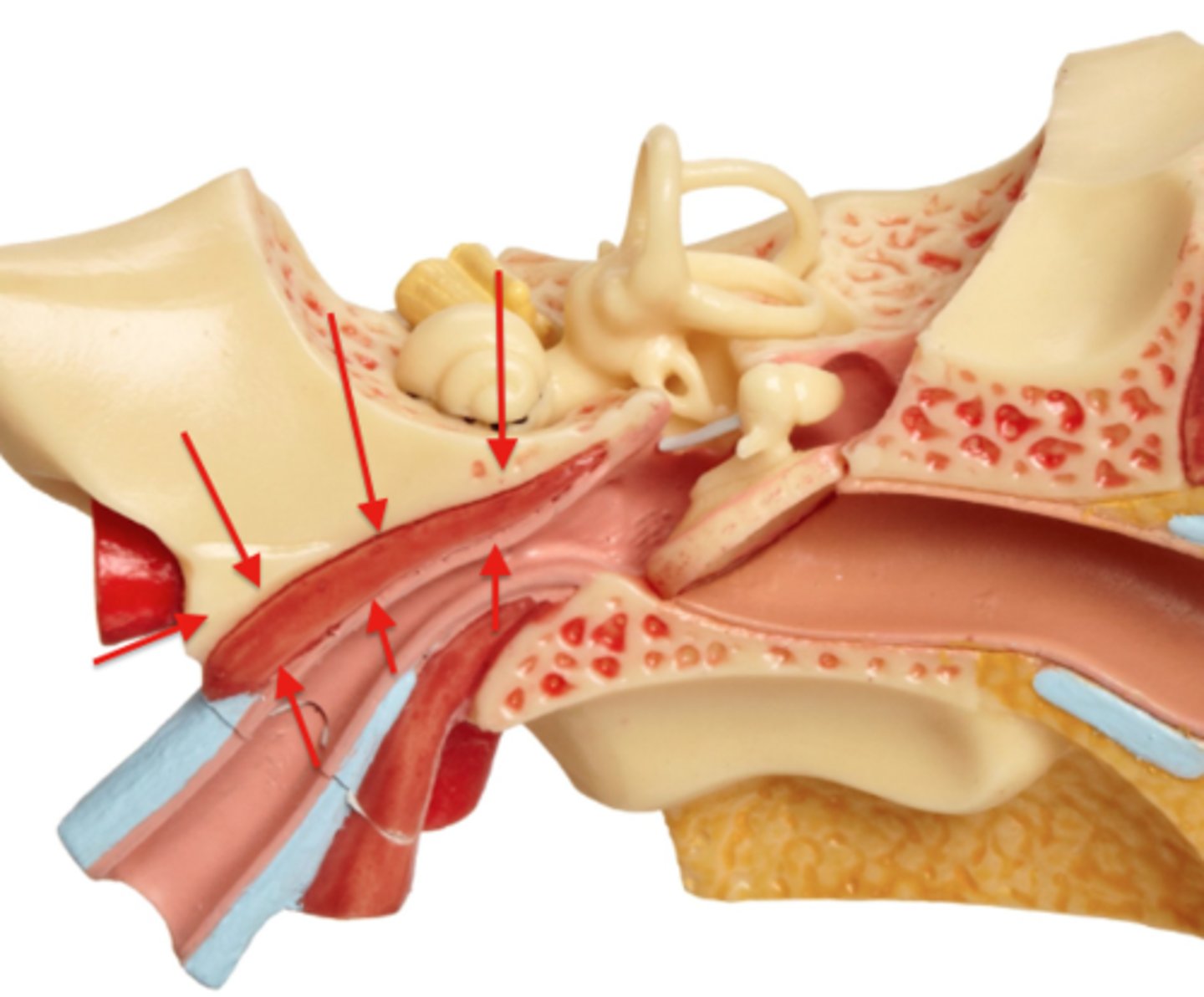
bony labyrinth
series of interconnected cavities within the temporal bone of inner ear that houses the organs for hearing and balance; protects the delicate inner ear structures, forming a rigid shell for the membranous labyrinth
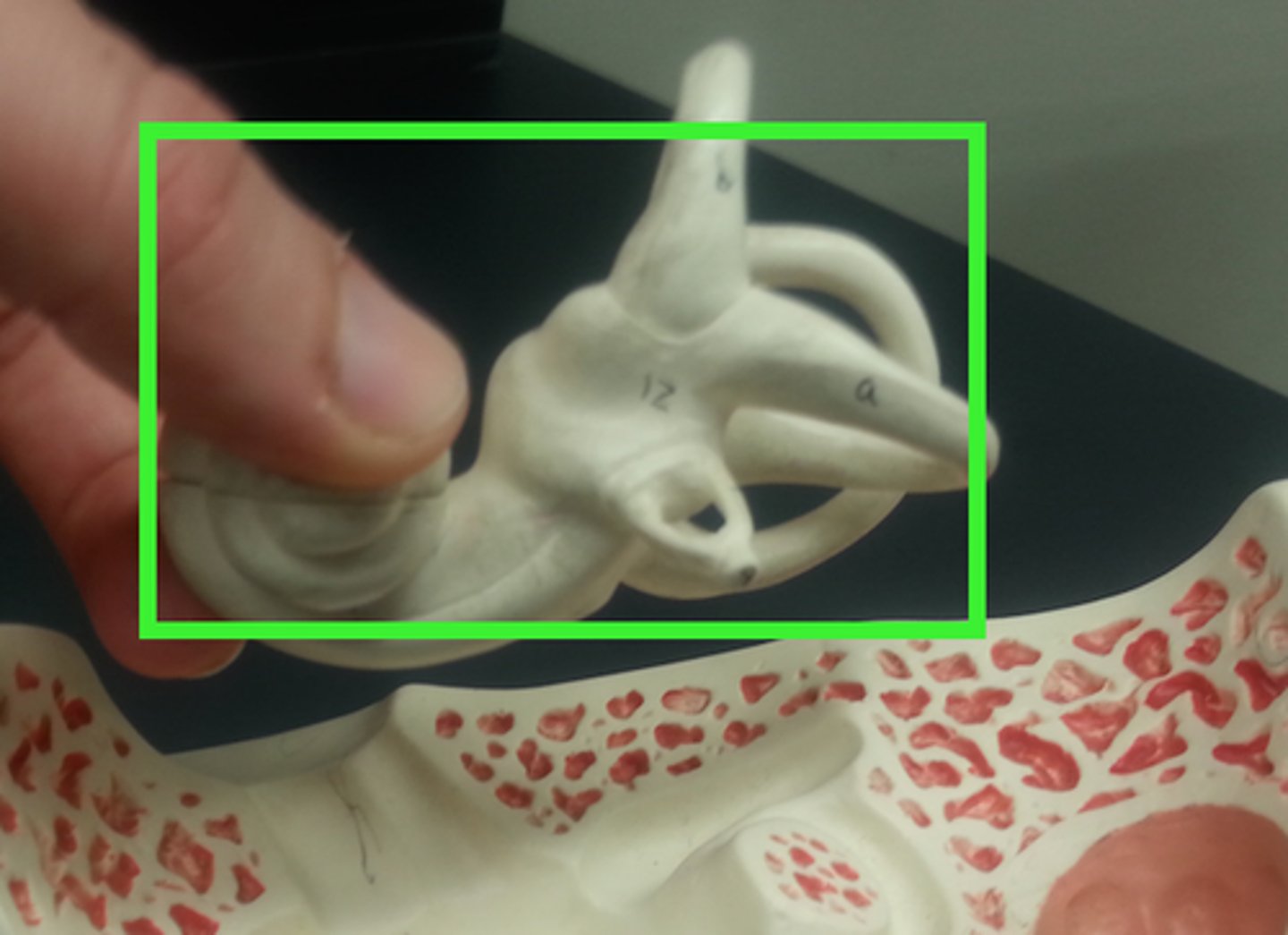

membranous labyrinth
delicate, fluid-filled system within the inner ear that is responsible for the senses of hearing and balance; converts mechanical stimuli like sound vibrations and head movements into the electrical nerve signals that the brain interprets
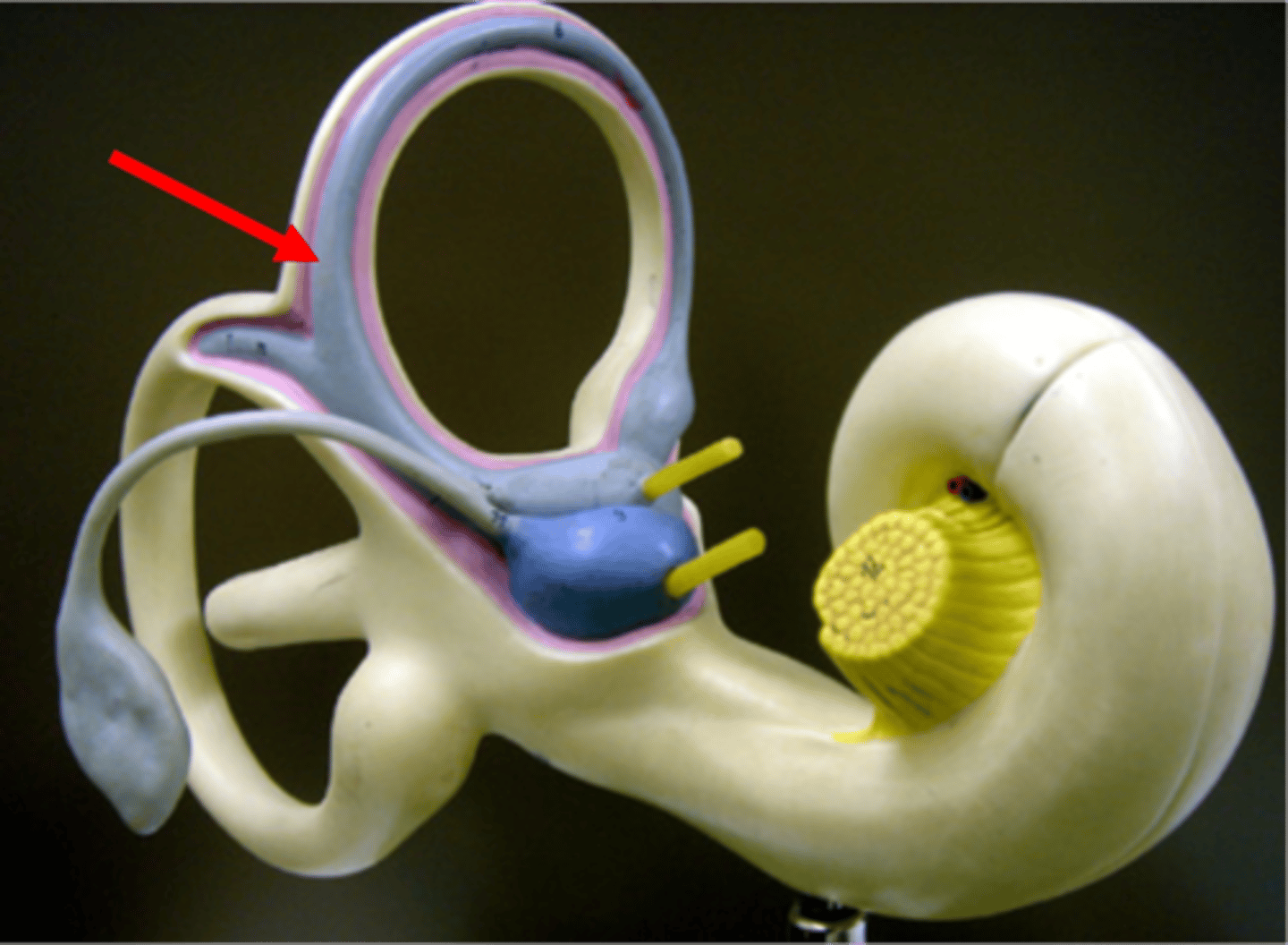
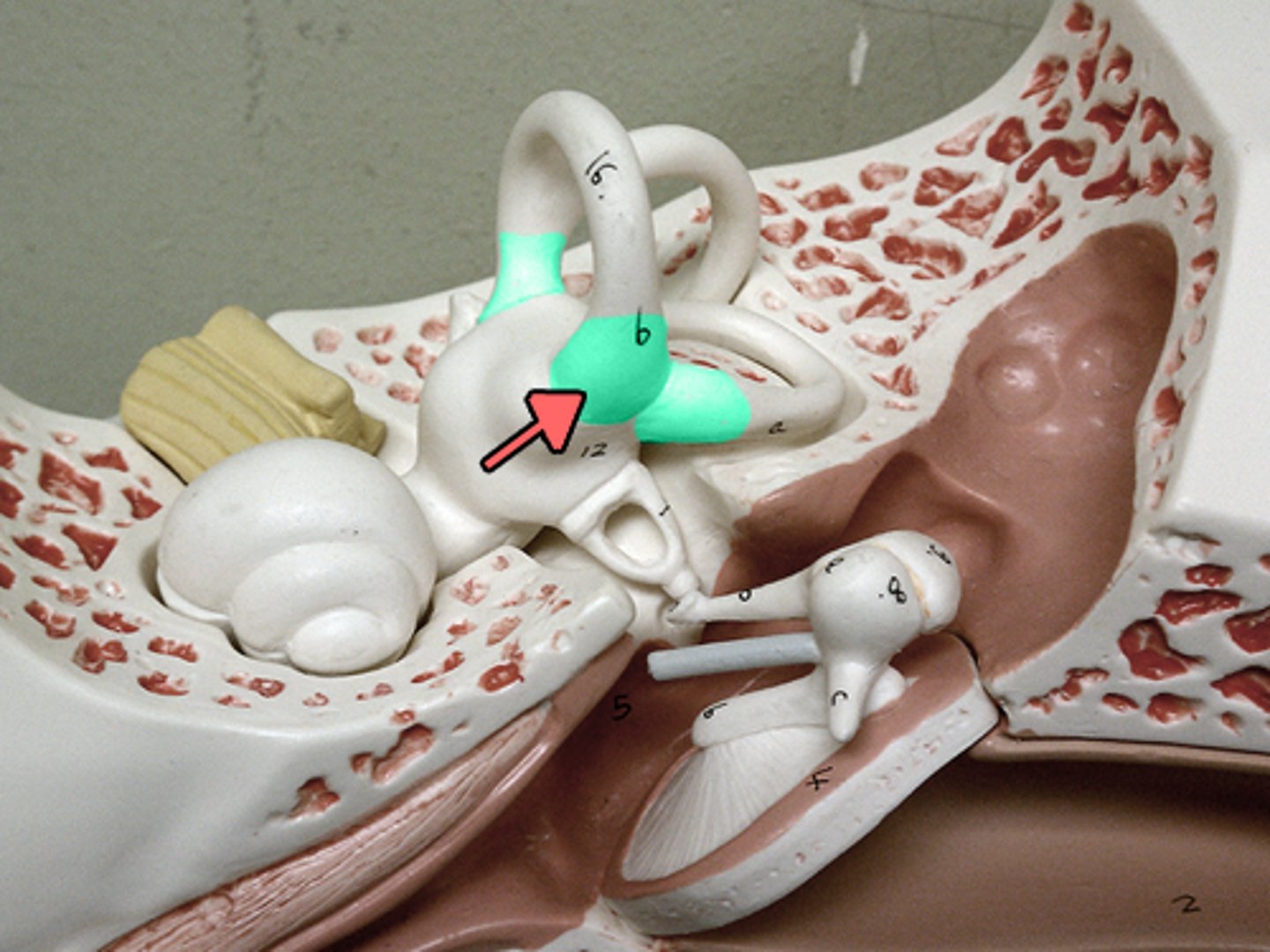
vestibule
central chamber in the inner ear that contains the utricle and saccule, which are crucial for balance and equilibrium; senses head position relative to gravity, and linear acceleration
saccule
small, fluid-filled sac in the inner ear that is part of the vestibular system, responsible for balance; detects vertical acceleration and head position changes in the vertical plane
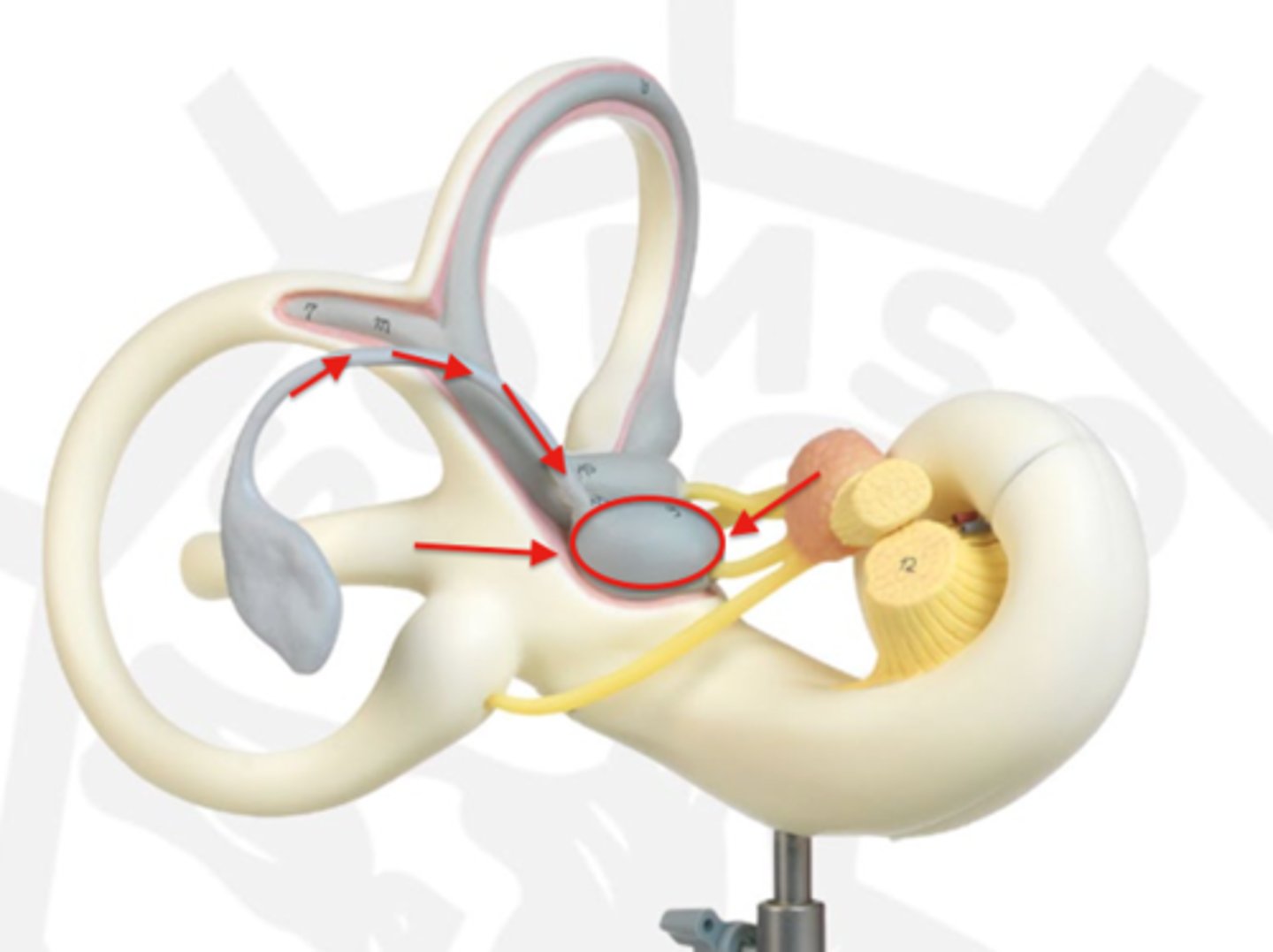
utricle
fluid-filled sac in the inner ear that is part of the vestibular system, playing a key role in balance and spatial orientation; senses gravity and linear acceleration like forward and backward movement
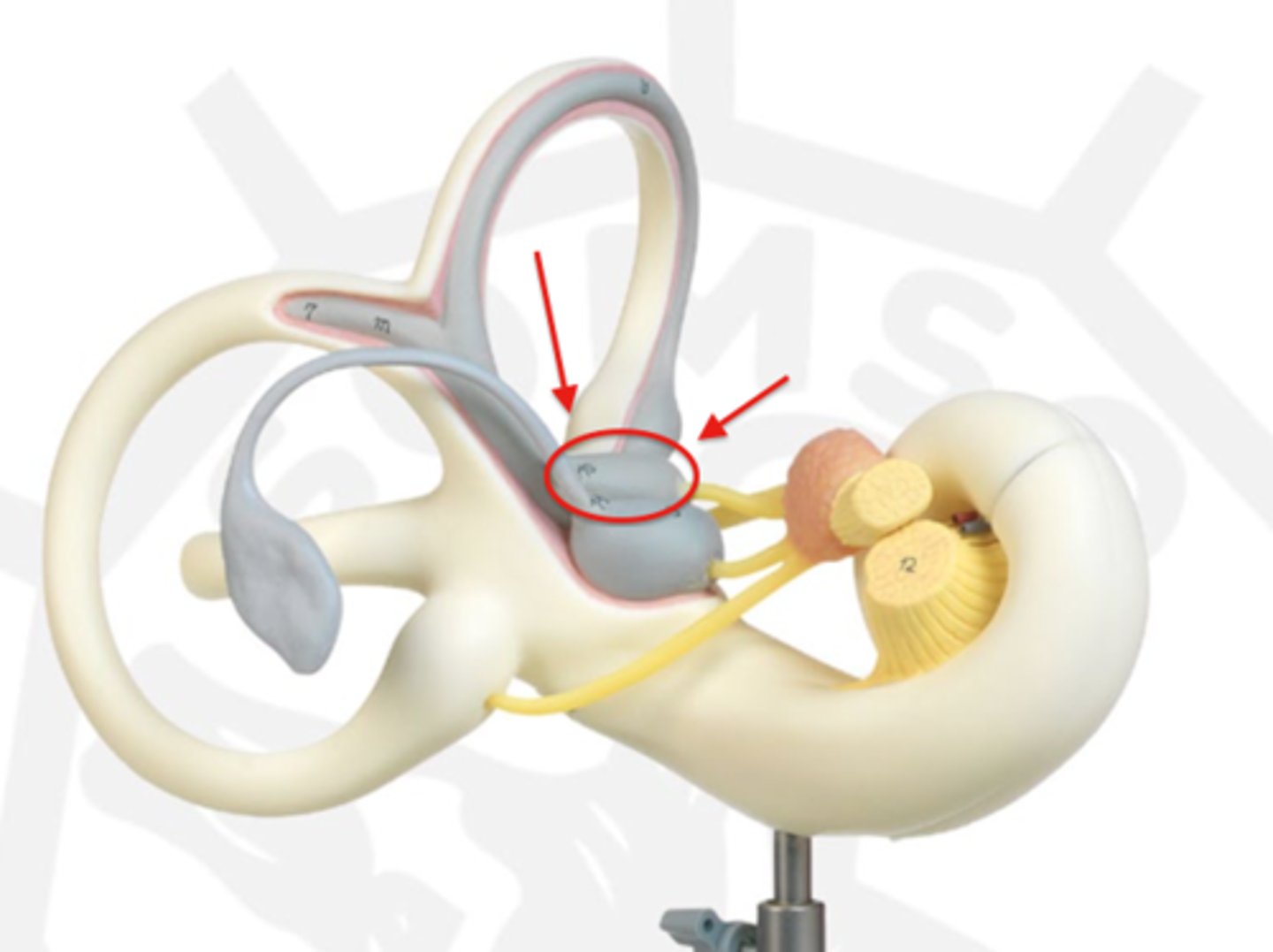
oval window
membrane-covered opening between the middle ear and the inner ear that transmits sound vibrations from the stapes bone to the fluid-filled cochlea; transfers mechanical sound energy from the air-filled middle ear into the liquid-filled inner ear
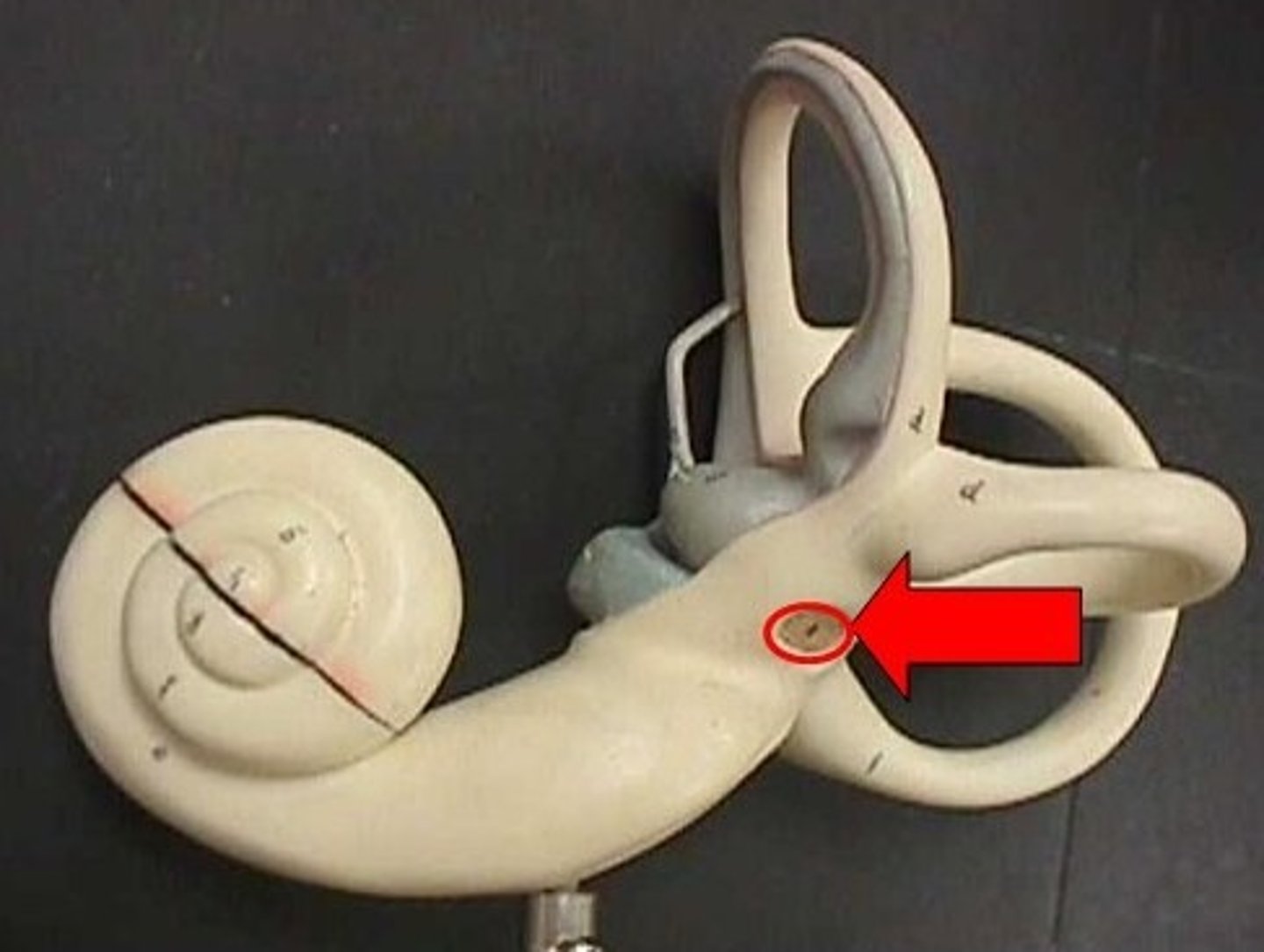
round window
small opening in the cochlea of the inner ear, covered by the membrane, that functions as a pressure-relief valve to allow for hearing
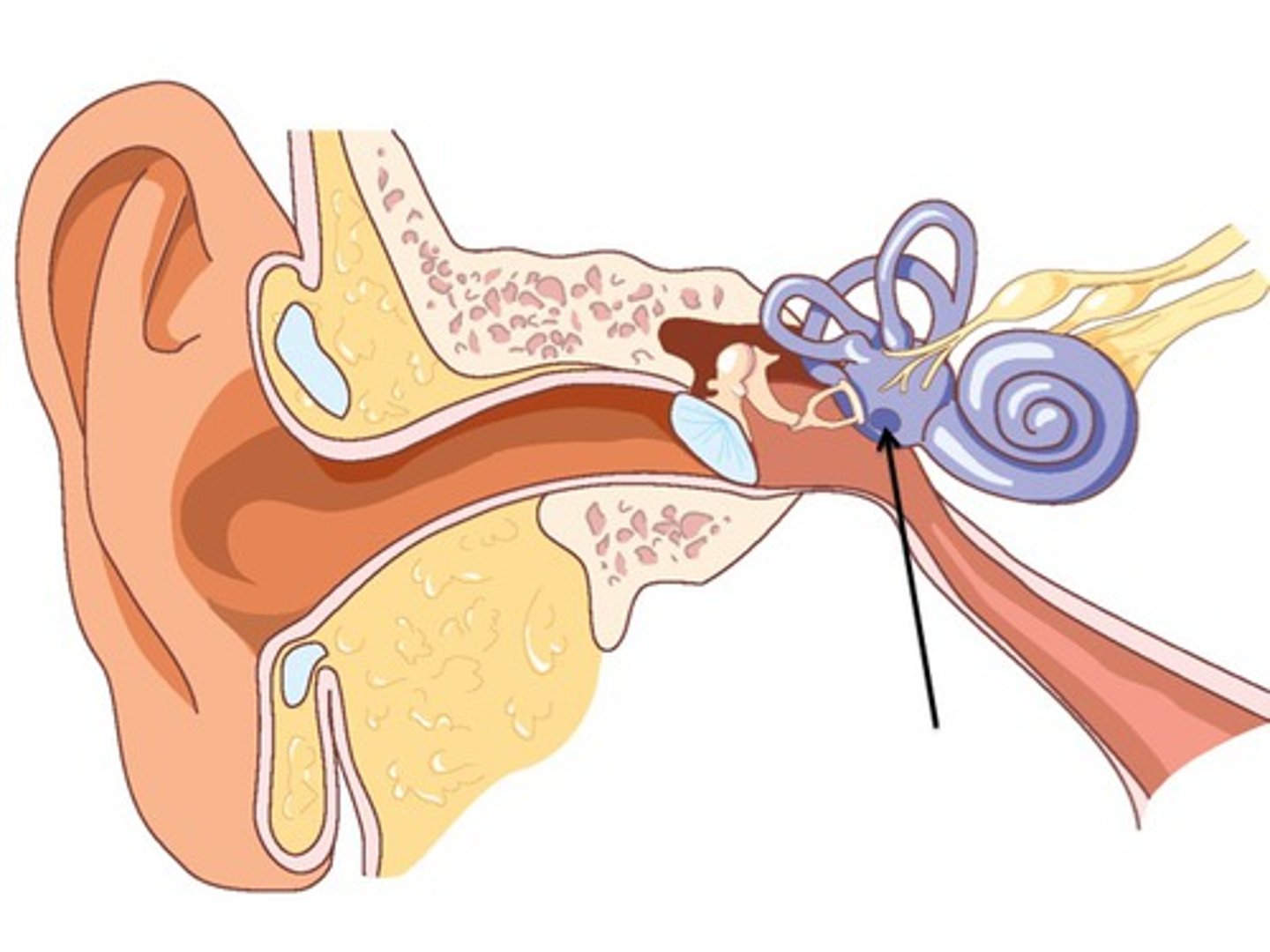
cochlea
spiral-shaped, fluid-filled cavity in the inner ear that is crucial for hearing; converts vibrations into electrical signals that the brain can interpret as sound
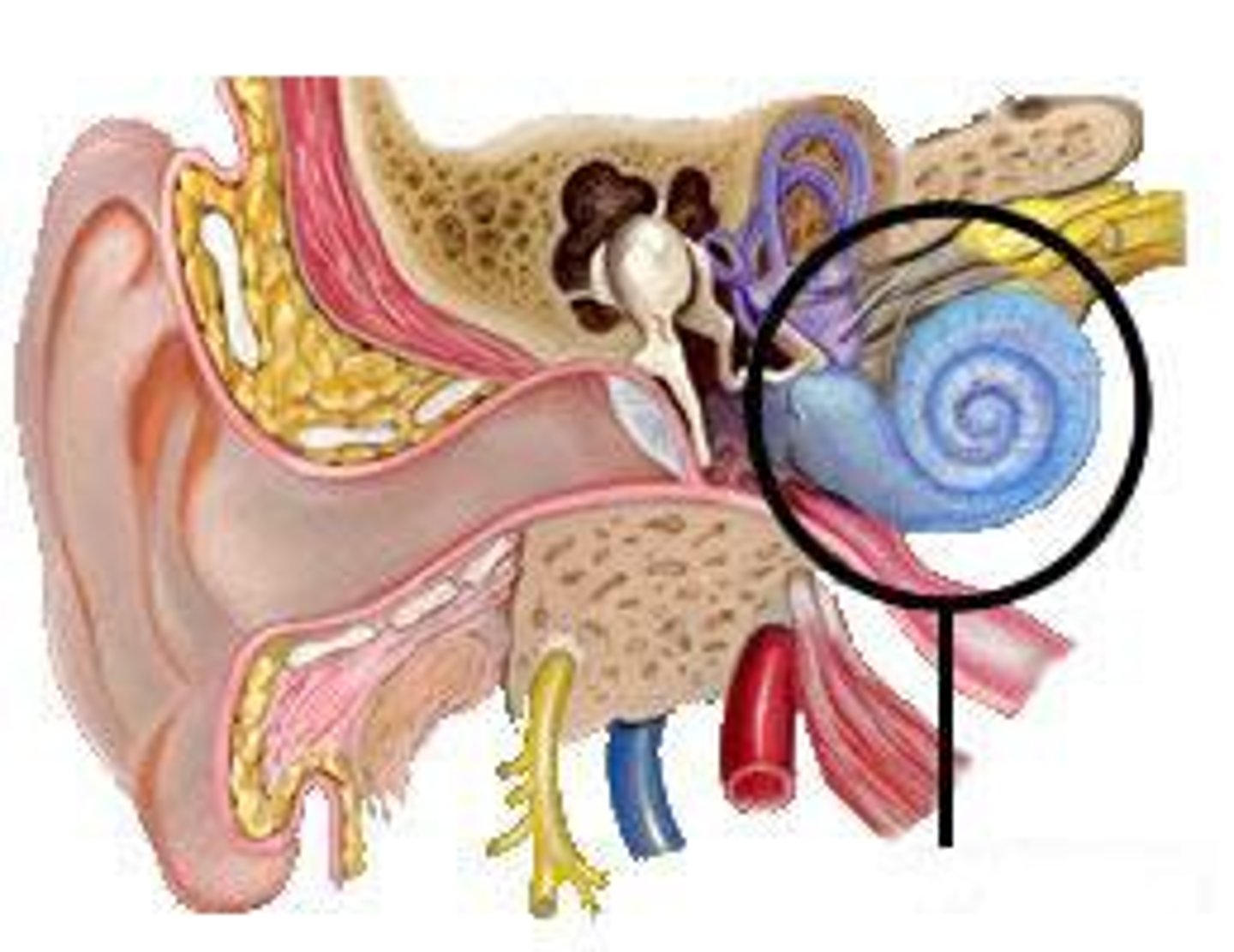
semicircular ducts
three fluid-filled tubes in the inner ear that are part of the vestibular system and are responsible for detecting rotational head movements; helps maintain balance, enables stable vision by coordinating eye movement with head motion, and control posture
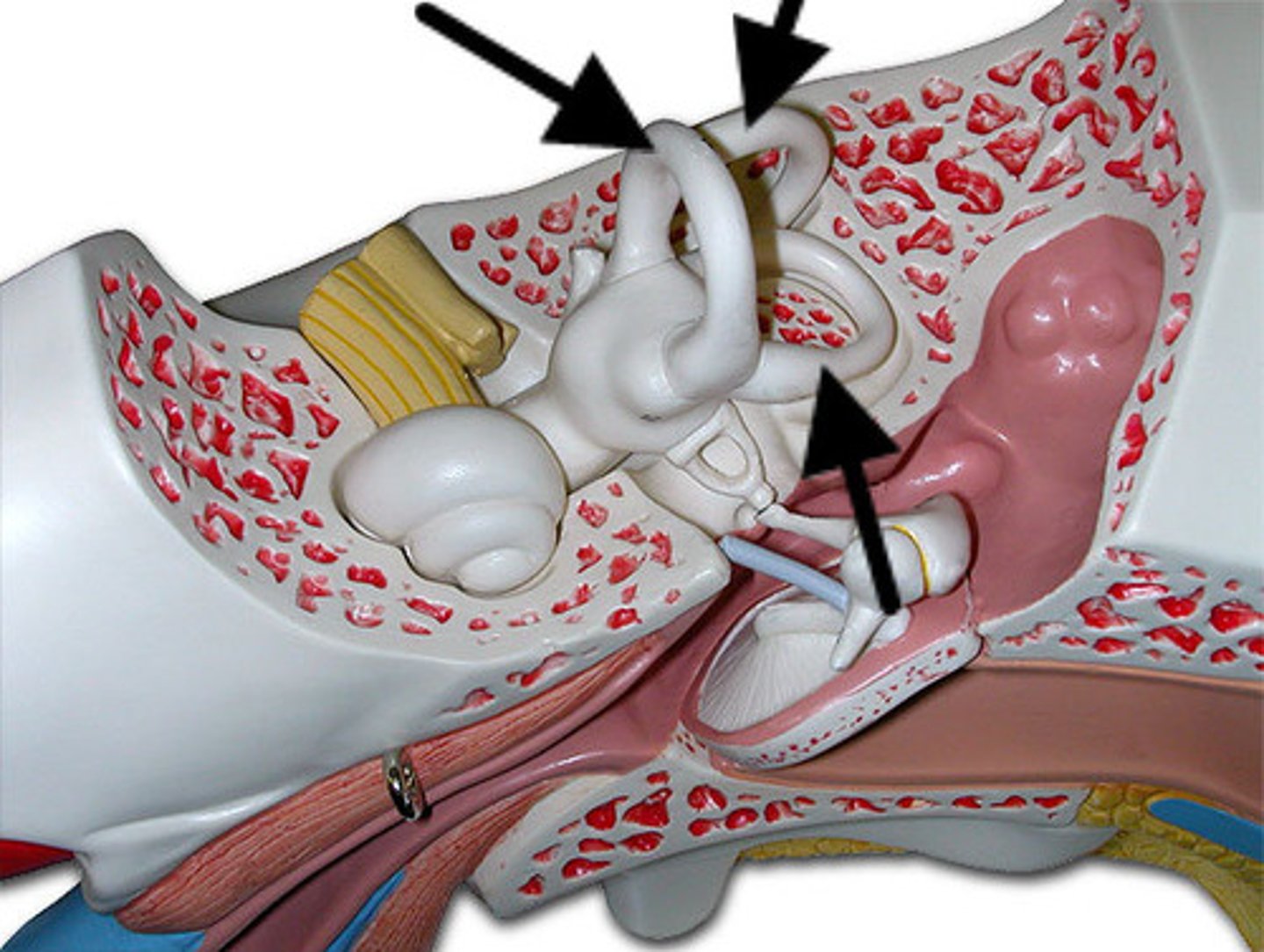
ampullae
expanded ends of the inner ear's semicircular canals, which contain the crista ampullaris; detects rotational head movements by sensing the movement of endolymph (fluid) within the canals
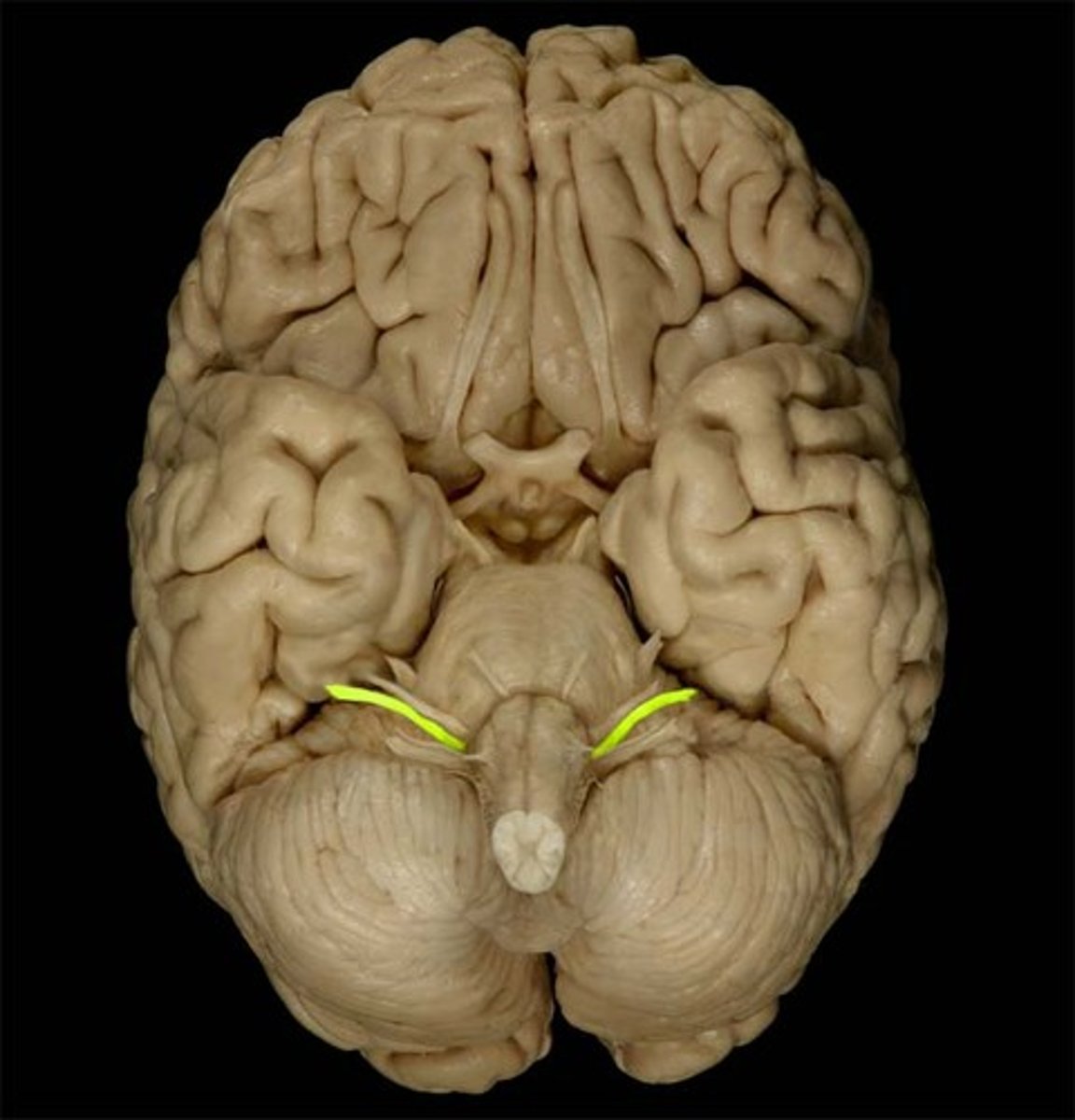
vestibulocochlear nerve
sensory nerve that transmits information for hearing and balance from the inner ear to the brain; the cochlear nerve division processes auditory signals for hearing, while the vestibular nerve division transmits information about head position and movement to maintain balance
spiral ganglion
cluster of nerve cell bodies in the inner ear that transmits auditory information from the cochlea to the brain; converts mechanical sound vibrations into electrical signals and relay them via the auditory nerve to the brainstem and beyond
cochlear nerve
the sensory part of the eighth cranial nerve that transmits auditory information from the cochlea of the inner ear to the brainstem, enabling hearing; converts mechanical sound vibrations into electrical signals for the brain to interpret as sound
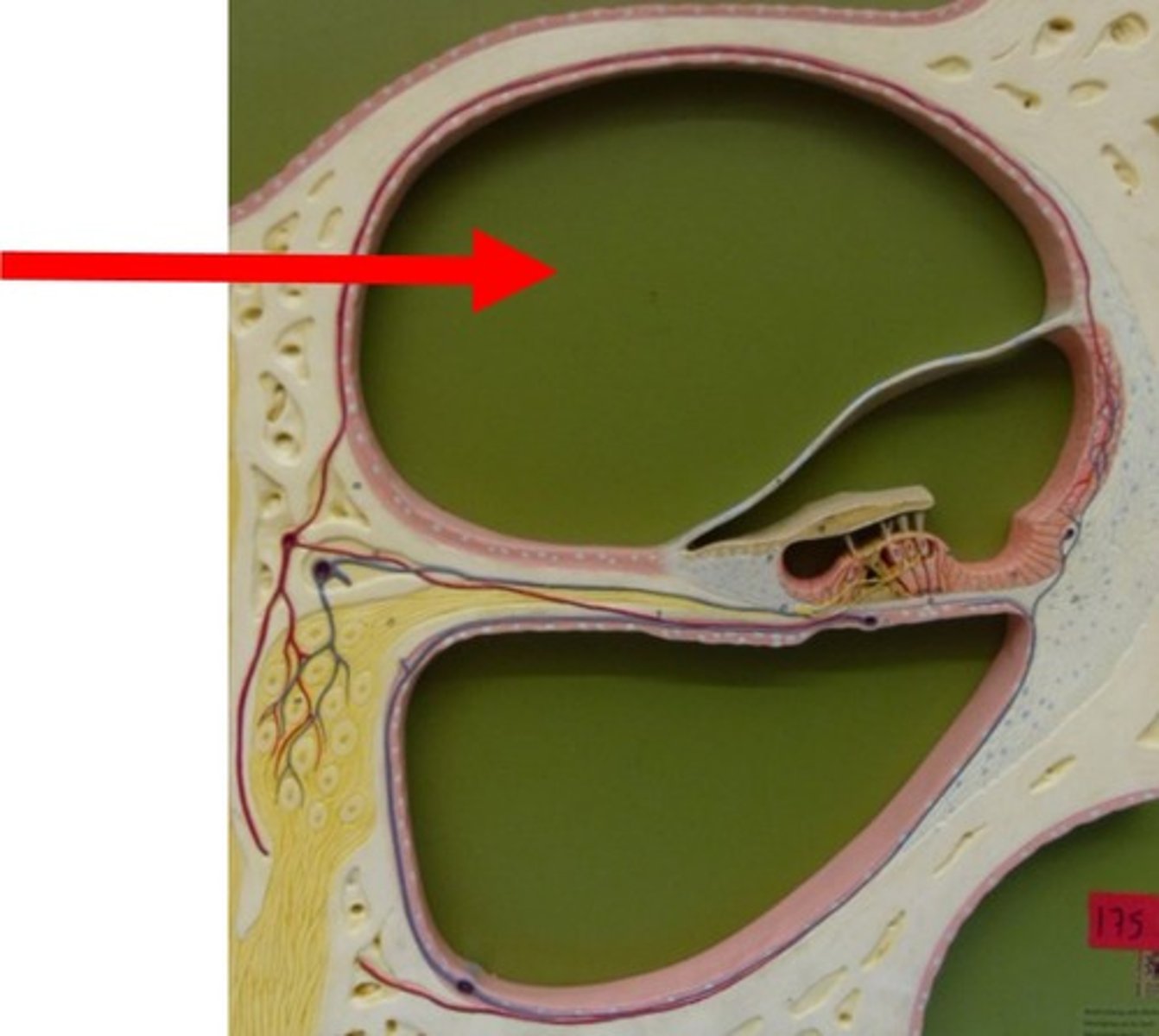
scala vestibuli
upper fluid-filled chamber of the cochlea, an inner ear structure responsible for hearing; transmits sound vibrations from the oval window to the cochlear duct
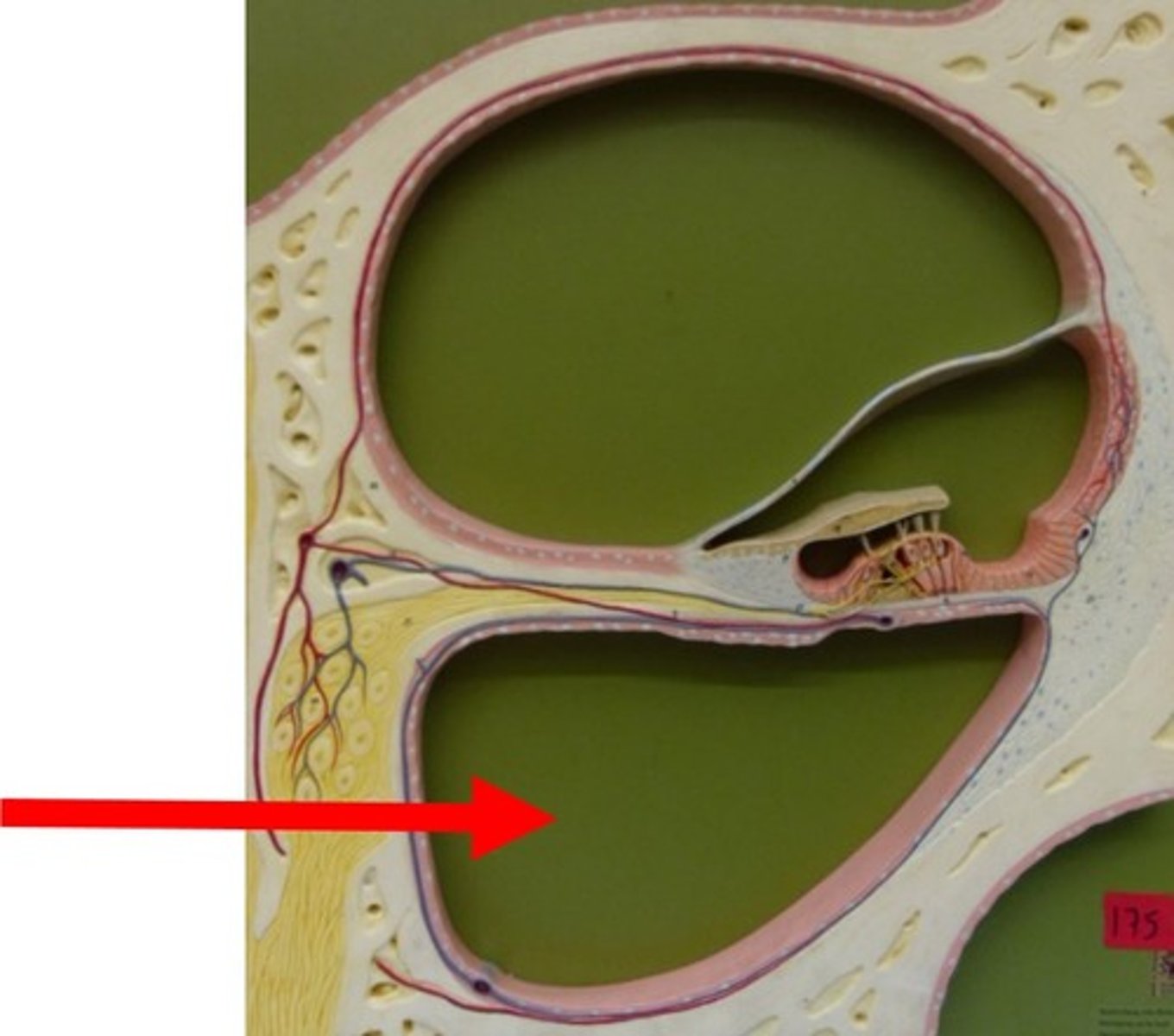
scala tympani
fluid-filled chamber in the inner ear's cochlea that plays a crucial role in hearing by transmitting sound vibrations; conducts sound vibrations from the oval window to the basilar membrane via the perilymph fluid
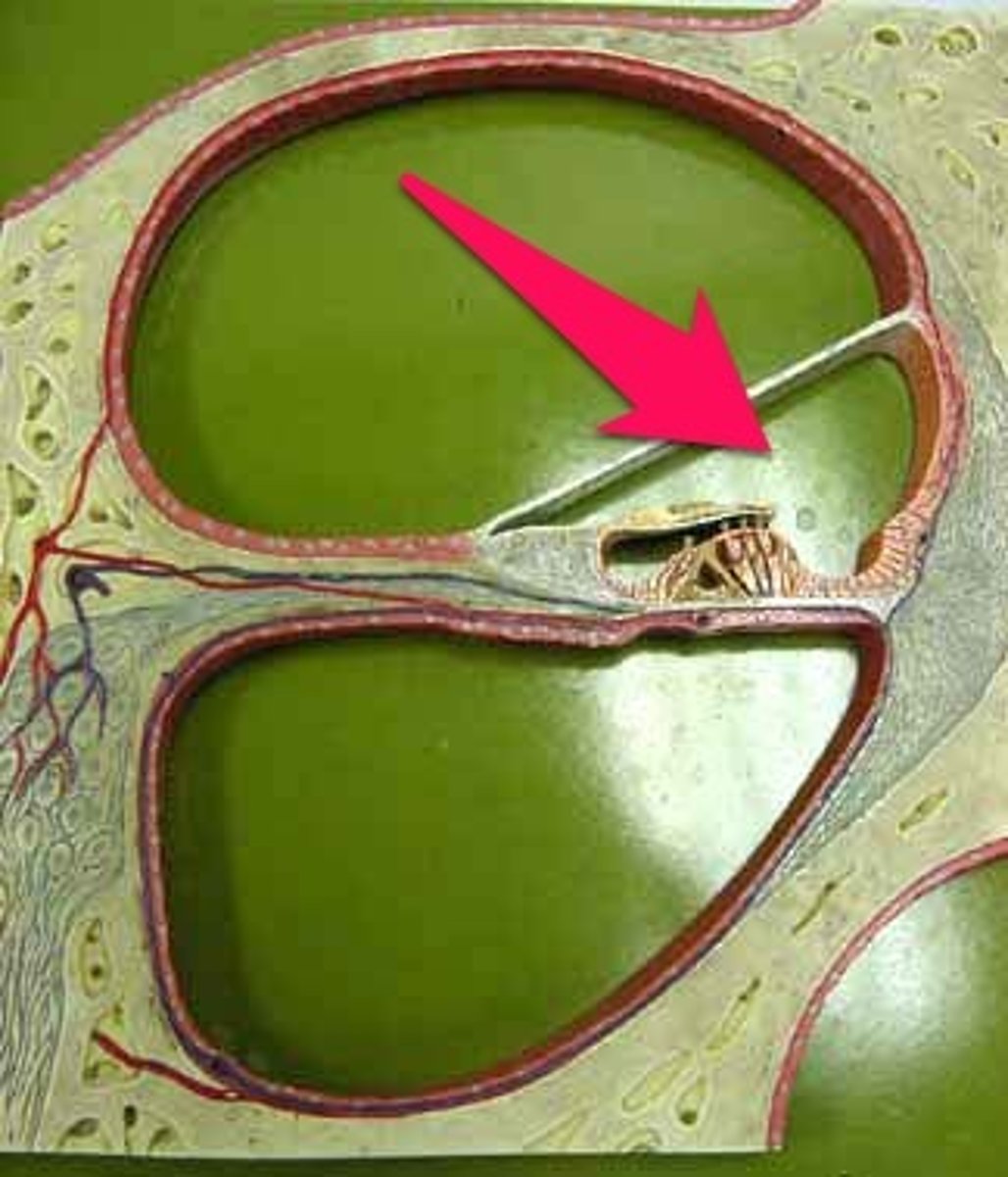
cochlear duct
spiral, fluid-filled tube within the cochlea of the inner ear that contains the organ of Corti; converts sound vibrations into electrical signals for the brain to interpret as hearing
vestibular membrane
delicate membrane in the inner ear that separates the cochlear duct from the scala vestibuli; acts as a partition between the two fluids that have different ion concentrations, preventing them from mixing and maintaining the proper fluid balance needed for hearing and balance
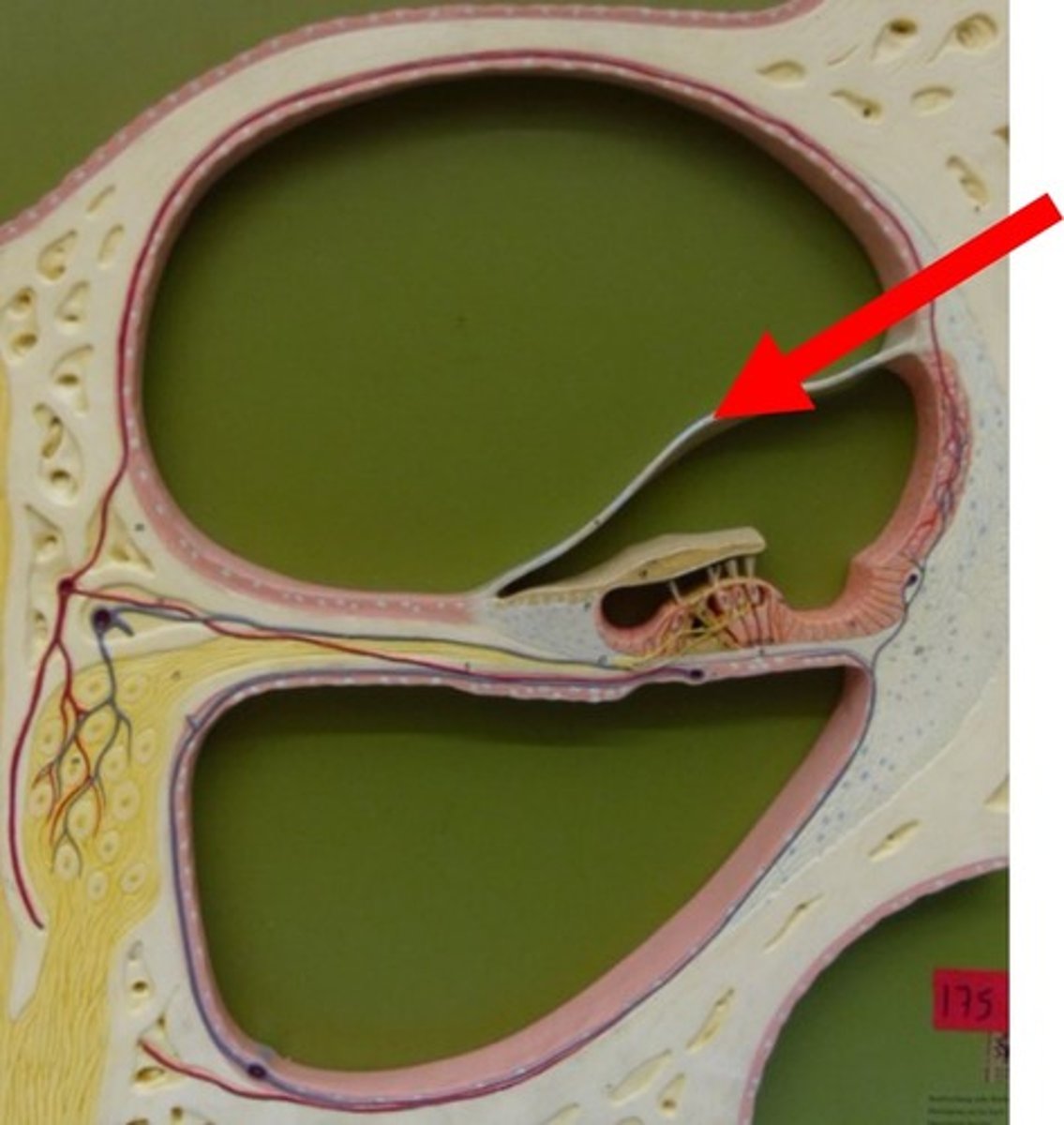
basilar membrane
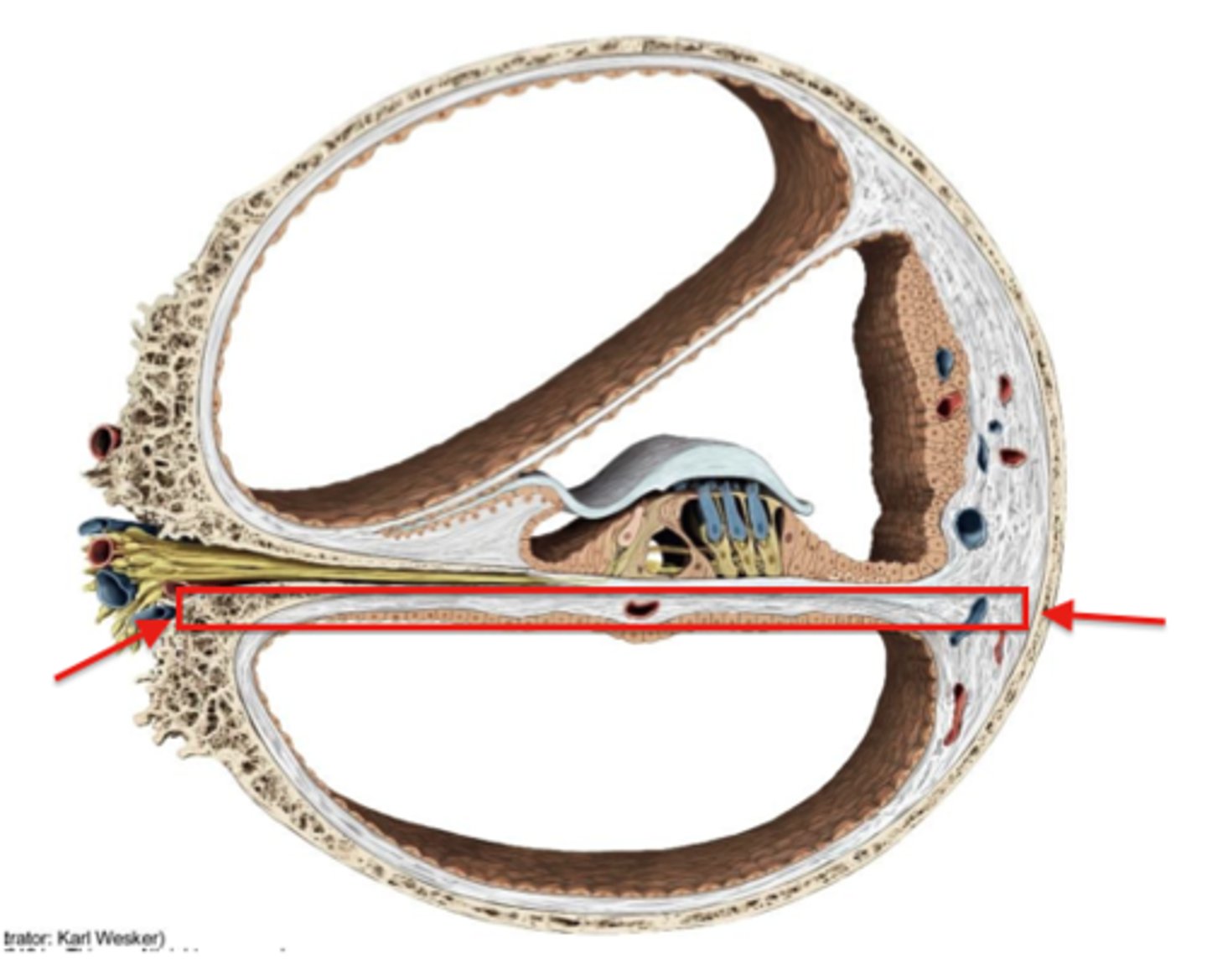
stiff structural element within the cochlea of the inner ear that separates two fluid-filled tubes and serves to frequency-analyze sounds; vibrates in response to sound waves, with different parts of the membrane vibrating at different frequencies
hair cells
sensory cells in the inner ear that converts sound waves into electrical signals sent to the brain for hearing
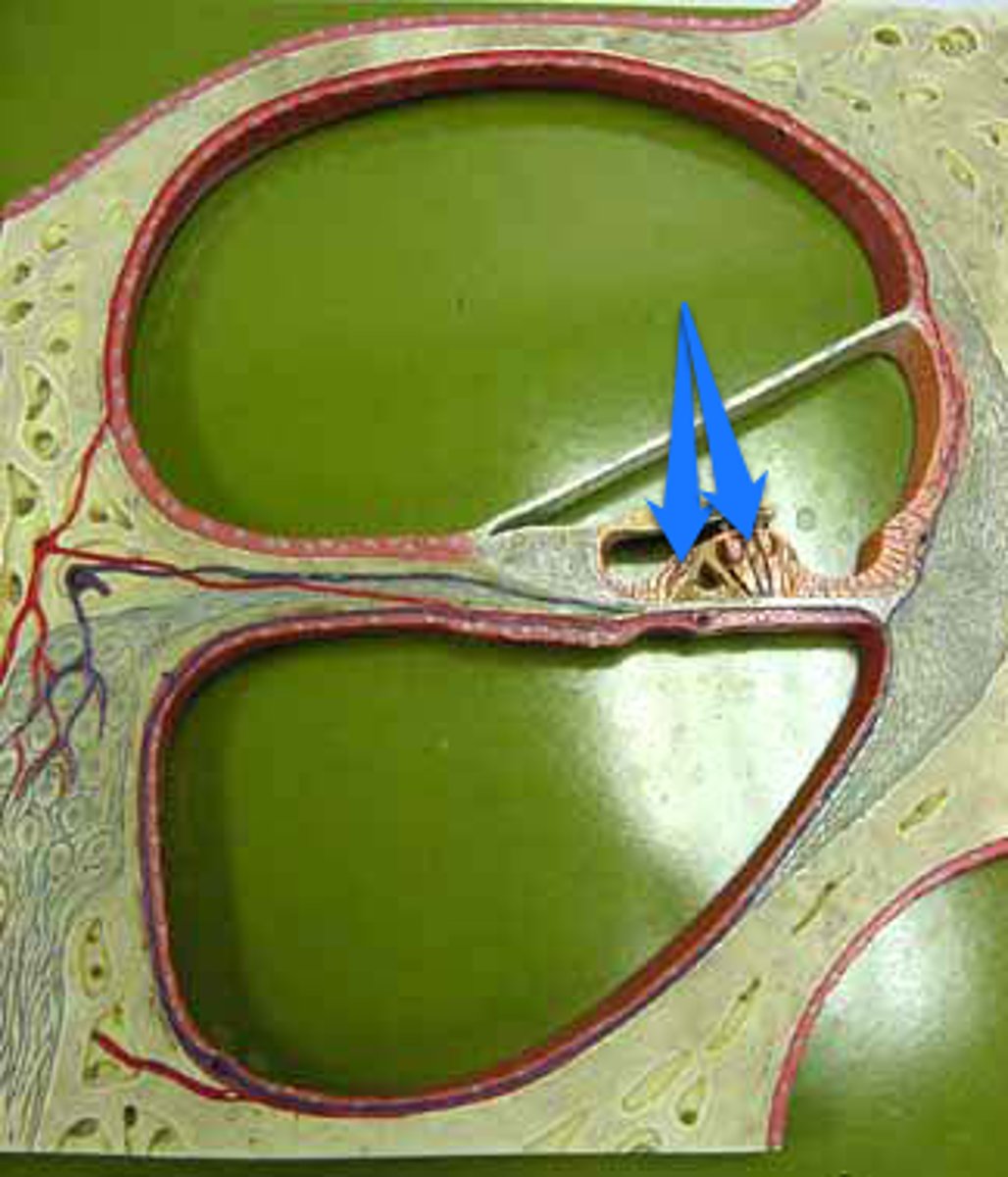
supporting cells
the pillar cells, Deiter's cells, Hensen's cells, inner border cells, and inner phalangeal cells; provides structural support and maintain the environment necessary for the hair cells to function and transmit sound signals to the brain
tectorial membrane
gel-like, extracellular matrix in the cochlea of the inner ear that plays a crucial role in hearing; stimulates the hair cells in the organ of Corti by bending their stereocilia