Week 2 M/S
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
what is CPR
achieves adequate cerebral and coronary perfusion, compromising a patient’s chances for neurologically intact survival
roles in a code blue
lead (dr or nurse)
recording/documentation
airway
medications
compressions/cpr
energy
crash cart
runner
CAB
circulation, airway, breathing
neurological re-check
LOC
orientation
motor function
pupillary response
abnormal neuro check
lethargic: drowsy, appropriate but thinking is slow, inattentive
obtunded: difficult to arouse, confused with aroused
stupor or semi-coma: only responds to physical stimulation, responds to pain
coma: completely unconscious, no response to pain
light coma: some reflex activity
deep coma: no motor response
glasgow coma scale
15 = fully alert and oriented
8 or less: endotracheal intubation to protect airway
potential causes of unresponsiveness
neuro: stroke, seizure, trauma
resp: pulmonary embolism, resp arrest
cardio: MI, cardiac arrhythmia, cardiac arrest
endo: hypoglycaemia
what to do if pt is not responding
establish unresponsiveness
shout
trapezius squeeze or pinch
press on supraorbital nerve (medial aspect of supraorbital ridge)
angle of the jaw
*these have a higher yield than the traditional sternal rub & nail bed squeeze
definite pulse and normal breathing
vital signs
assess responsiveness
glasgow coma scale
bloodwork/imaging test
definite pulse and no breathing
check pulse
open airway, bag valve mask
1 breath every 5 sec
pulse check every 2 min
definite pulse + no breathing
Obstruction
Inadequate respiratory effort
Medications
what is SBAR
non critical: communication related to identified problems
critical: communication of changes in pt condition
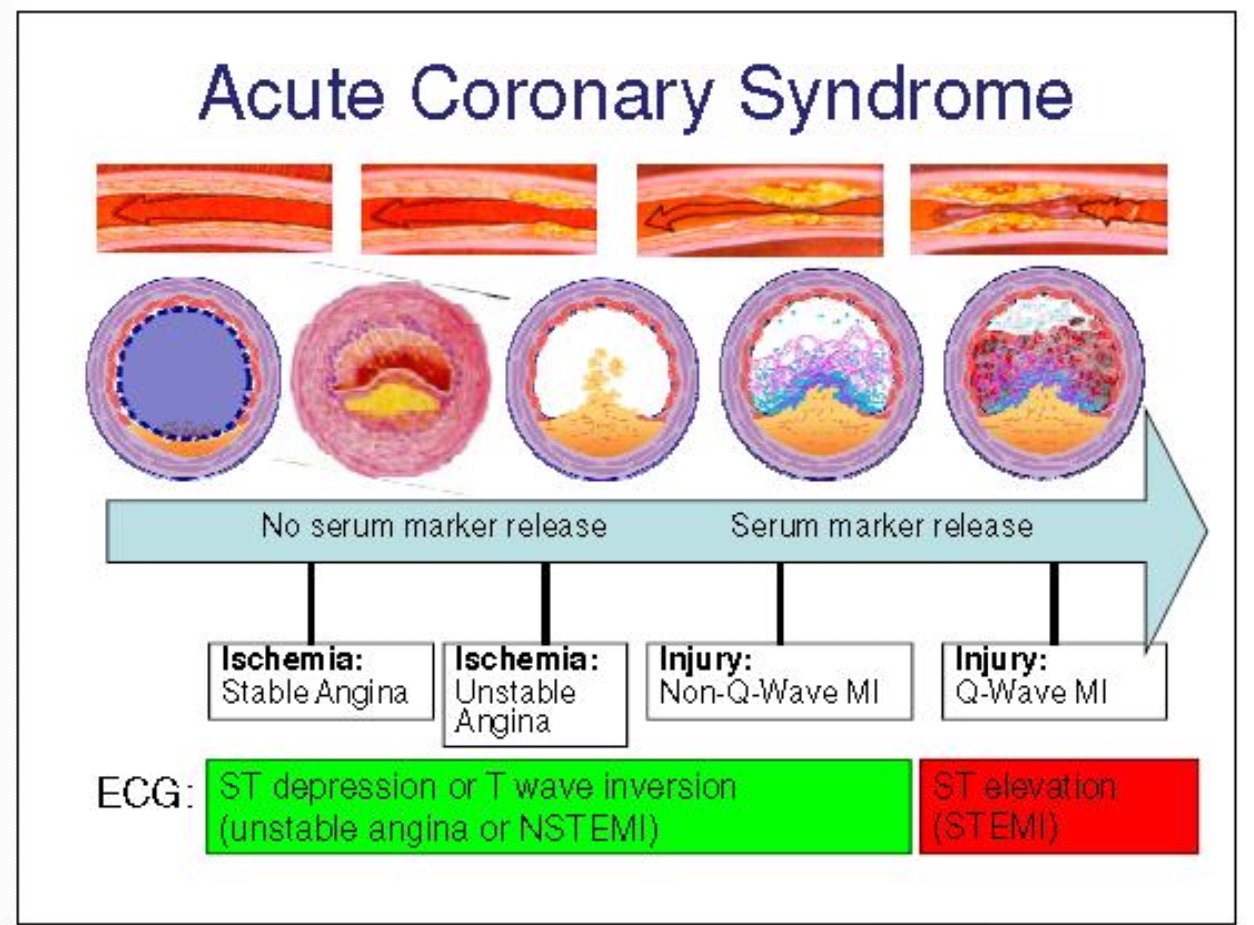
coronary artery disease
progressive atherosclerotic disorder of the coronary arteries that results in narrowing or complete occlusion of 1+ arteries
affects medium-sized arteries that perfuse the heart and major organs
progressive buildup of plaque in arteries
types of coronary artery disease
asymptomatic
stable angina: at rest there is enough oxygen in blood; when exercise: not enough oxygen in blood → chest pain
acute coronary syndrome:
unstable angina: unable to get enough O2
myocardial infarction: begins having damage to heart
sudden coronary death
what causes decreased O2 supply
anemia
CAD
hypoxia
COPD, asthma, pneumonia
arrhythmias
CHF
coronary spasm
thrombosis
valve disorders
increased O2 demand/consumption
anxiety
cocaine use
hyperthermia
hyperthyroidism
physical exertion
aortic stenosis
arrhythmias
cardiomyopathy
hypertension
stages of development in atherosclerosis
fatty streak
fibrous plaque
complicated lesion
what does the endothelium regulate
dilation and constriction of vessels
thrombosis - formation of blood clots
transport of substances to and from the vascular space
growth and apoptosis of vascular wall
endothelial dysfunction
inadequate vasodilation
prothrombotic
altered permeability
increased secretions growth factors
increased oxidation of LDL
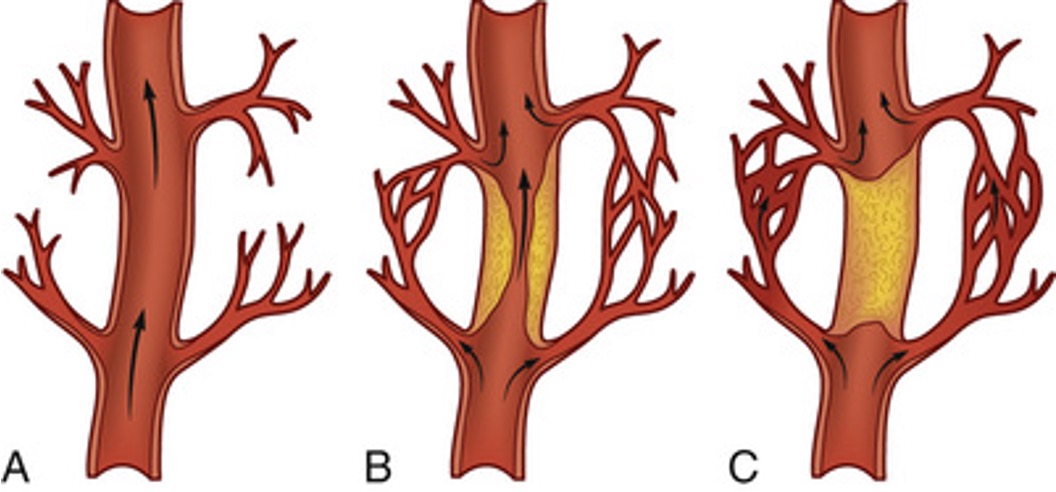
collateral circulation
ways to bypass clot and get to other side → still able to perfuse
can happen when fatty plaque happens over time
woman in menopause can have plaque build up quickly → this doesn’t happen
women and heart disease
#1 killer of Canadian women
10 times more than breast cancer
manifest 10-20 years later in life than men
why does CAD affect more women than men
estrogen helps counterbalance plaque buildup in arteries
menopause = less estrogen
less likely to build-up collateral circulation
gender differences in symptoms CAD
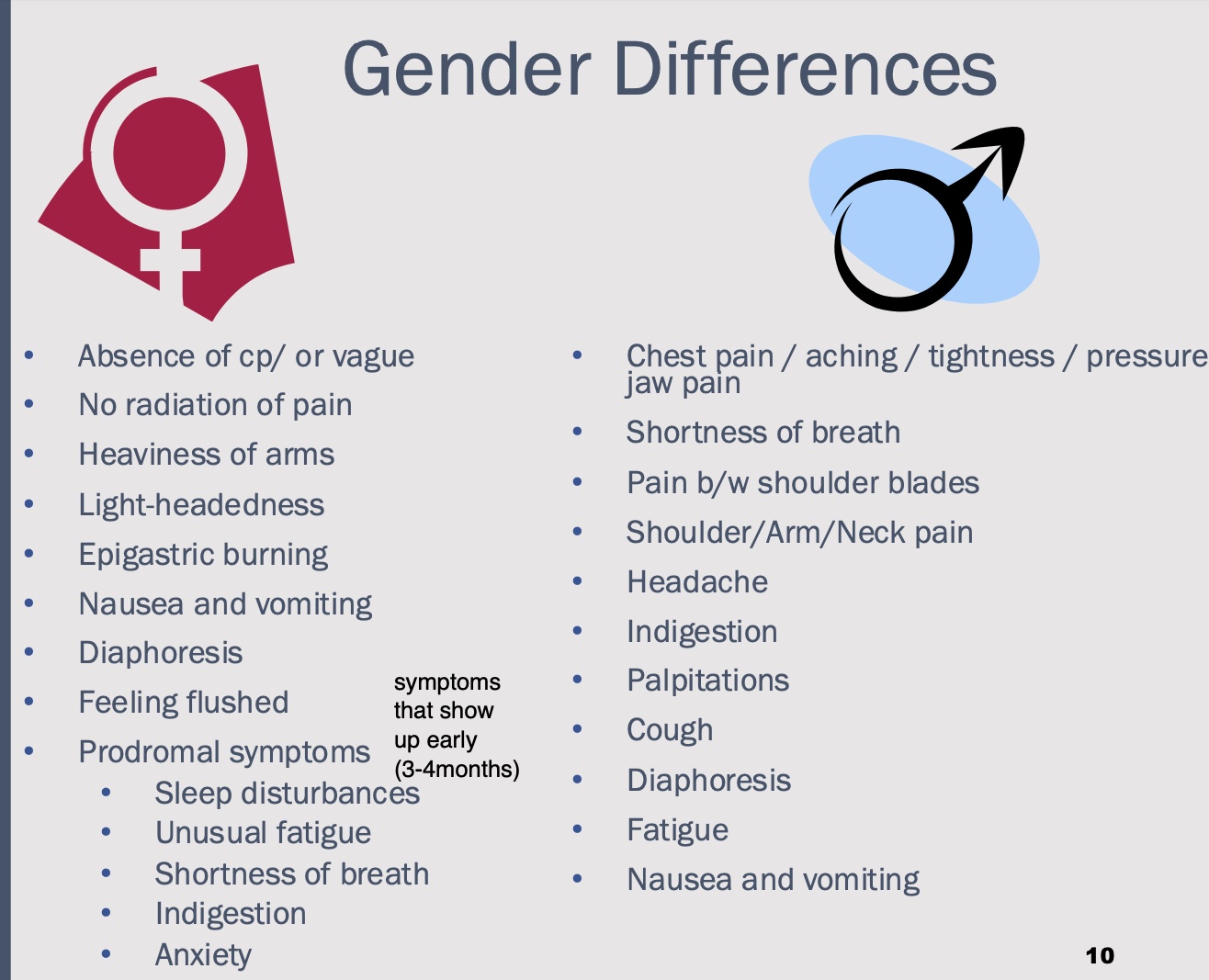
challenges of care for woman dealing with CAD
failure to recognize and difficulty interpreting symptoms
failure of HCP to recognize prodromal symptoms
ECG and stress test less sensitive
plaque tend to be distributed diffusely
less likely to be evaluated for risk factors or treated aggressively
atypical presentation in the elderly of CAD
symptoms: SOB, fatigue and weakness, abdominal or epigastric discomfort
often have preexisting conditions making this an already vulnerable population: hyperension, CHF, previous AMI
likely to delay seeking treatment
atypical presentation in the pt with diabetes
atypical presentation due to autonomic dysfunction
neuropathy could cause lack of feeling in chest = lack of chest pain
common symptoms: generalized weakness, generalized feeling of not being well, syncope, lightheadedness, change in mental status
non-modifiable risk factors CAD
age
male > female until 65
genetics
ethnicity
modifiable risk factors major for CAD
tabacco use
abdominal obesity
hypertension >140/90 mmHg
hyperlipidemia
physical inactivity
contributing factors for CAD
phychological risk factors
elevated homocysteine levels
diabetes mellitus
metabolic syndrome
who is at low-risk among non-smokers without diabetes
total cholesterol 4.7 mmol/L
untreated blood pressure <120/<80
should be assessed every 3-5 years
who is at moderate-risk among non-smokers without diabetes
total cholesterol 4.8-5.1 mmol/L
untreated systolic pressure 120-139 mmHg or diastolic pressure 80-89mmHg
ho is at high-risk among non-smokers without diabetes
total cholesterol 5.2 to 6.1 mmol/L
untreated systolic blood pressure 140 - 159 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure 90-99 mmHg
should be assessed every year
major risk factors of CAD
treated hyperlipidemia or total cholesterol 6.2 mmol/L
treated hypertension or untreated systolic pressure >160 or diastolic pressure >100 mmHg
current smoker
diabetes
who should screen for CAD
Men ≥ 40 years of age; women ≥ 50 years of age or post-menopausal)
■ Anyone with the following conditions regardless of age
Smoker
Hypertension
Elevated cholesterol
Diabetic
Family history
Erectile dysfunction
Obesity
Inflammatory disease
COPD
HIV
initial assessment for CAD
want to do it before medications
baseline VS and 12 lead ECG → within 10 min
assessment of chest pain
associated symptoms
physical assessment
medications
secondary assessment for CAD
personal and family history
environment factors
psychosocial history
pt’s attitudes and beliefs about health and illness
ECG findings
goal: complete within 10 min of presentation to ER
primary diagnostic tool
changes in QRS complex, ST segment, T wave → leave ECG leads on to continue to see changes and get worse/better
dynamic process and evolves over time
repeat ever 15-30 min to 2-4 hr
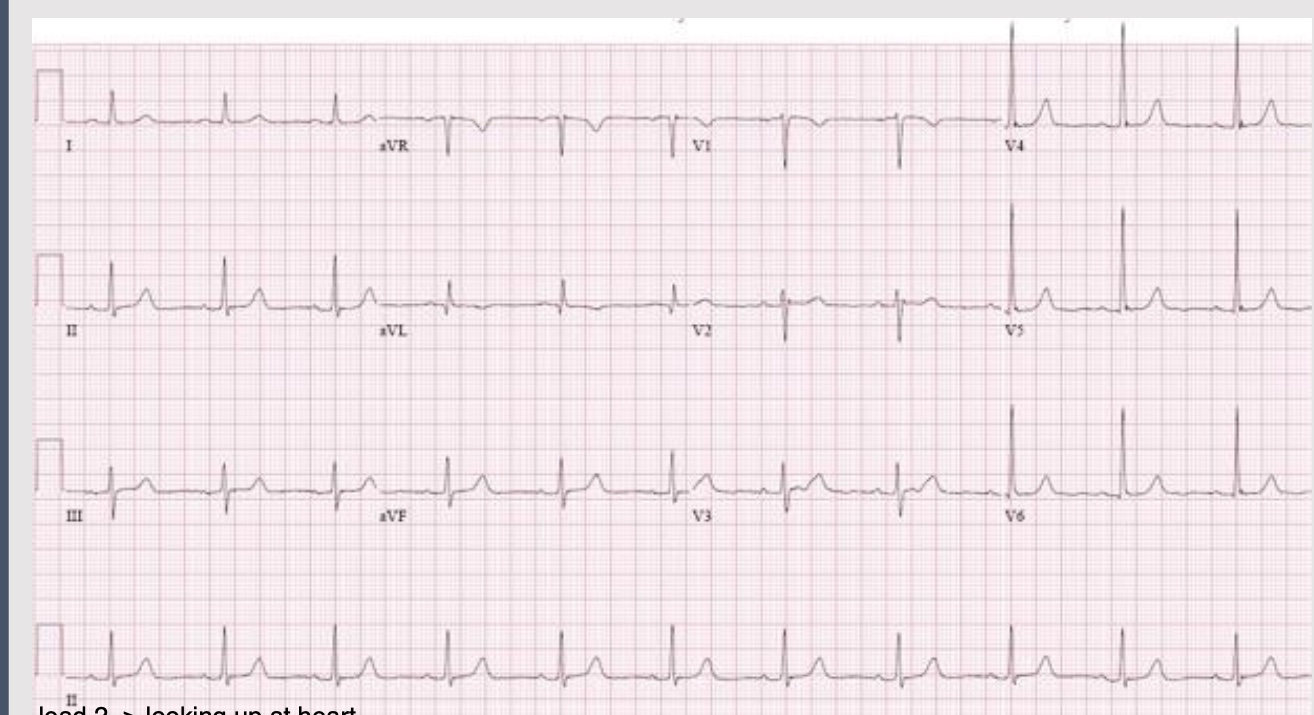
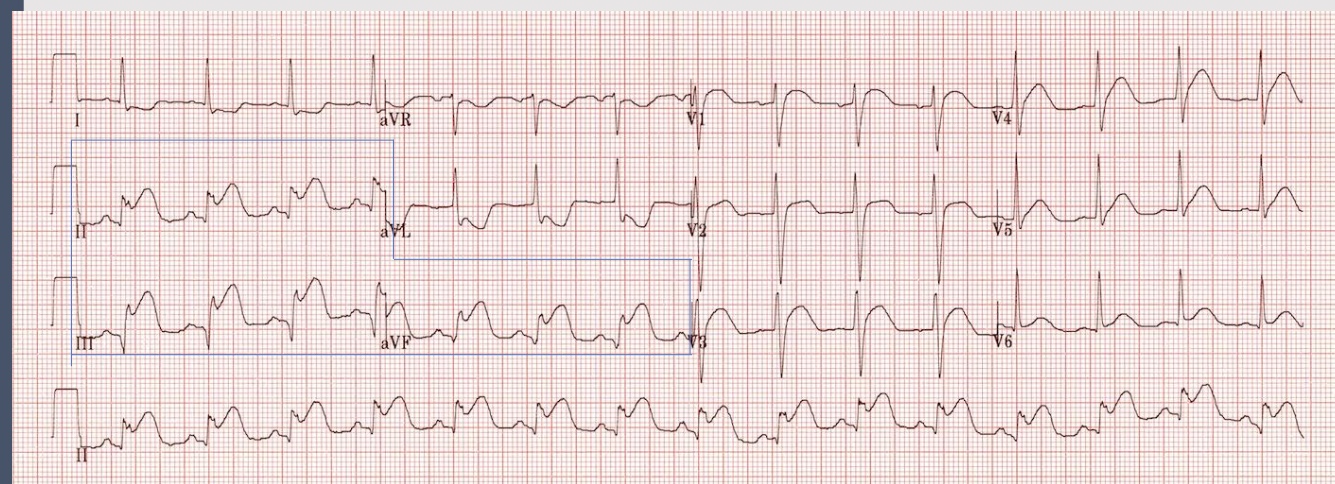
ECG interpretation
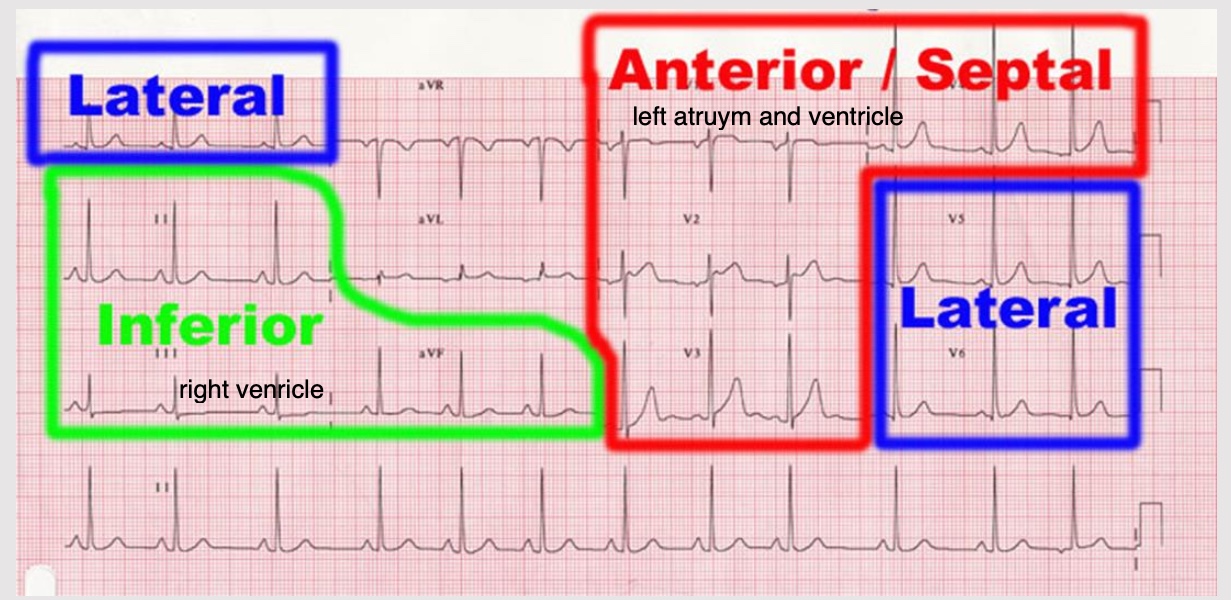
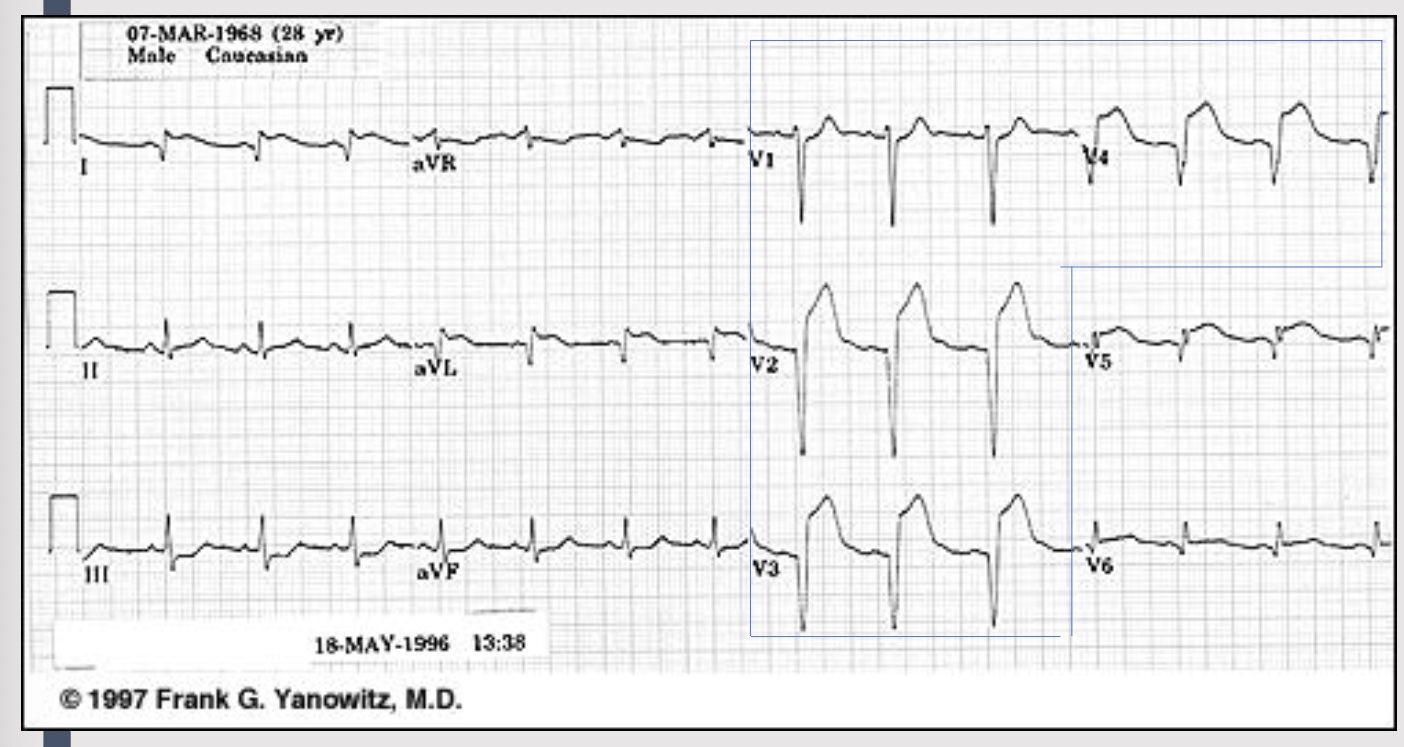
anterior site of the heart
indicitive: V1, V2, V3, V4
affected coronary: L anterior descending
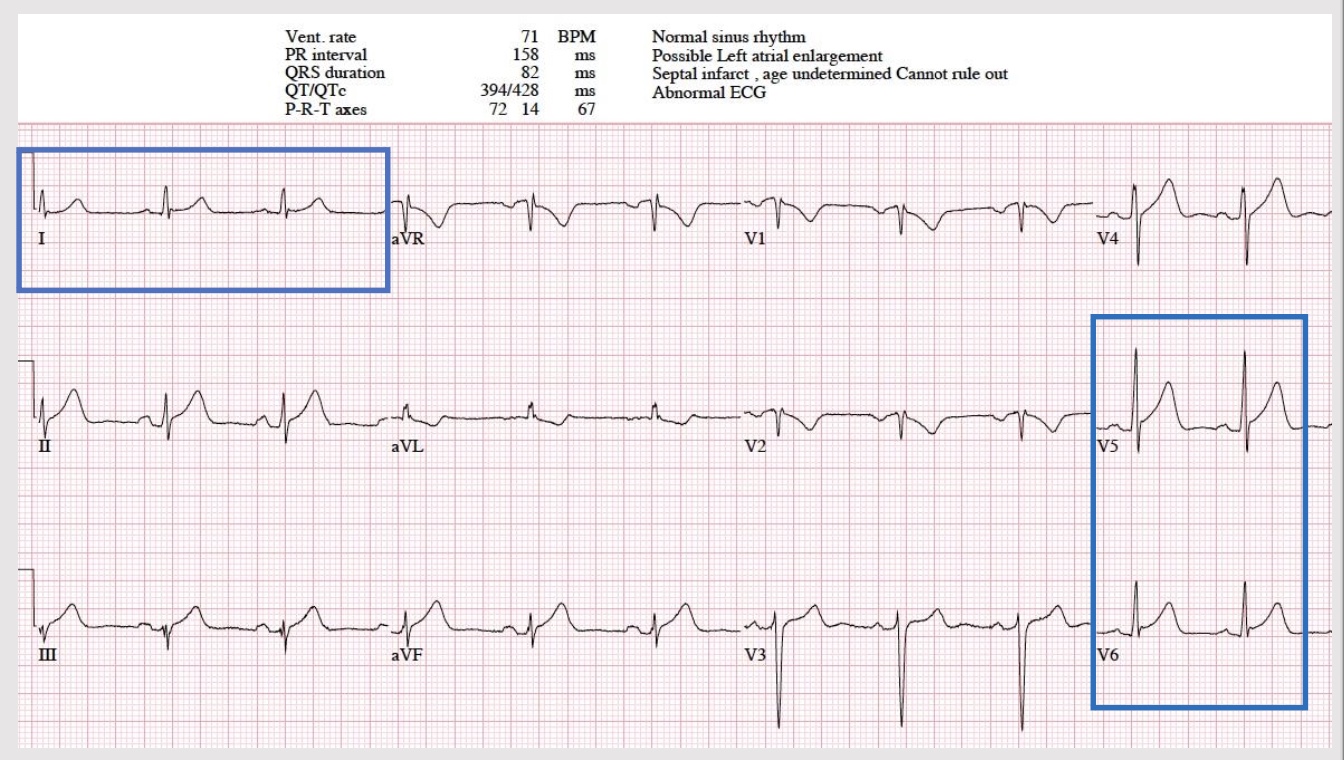
lateral site of heart
indicative: 1, aVL, V5-6
affected coronary: circumflex or LAD
inferior site of heart
indicative: II, III, AVF
affected coronary: R posterior descending
posterior site of heart
indicative: reciprocal changes leads V1, V2, V3
affected coronary: R posterior descending &/or circumflex
ST depression
when the ST does not come back to baseline
heart is not getting enough oxygen
damage is not permanent and there are things that can be done
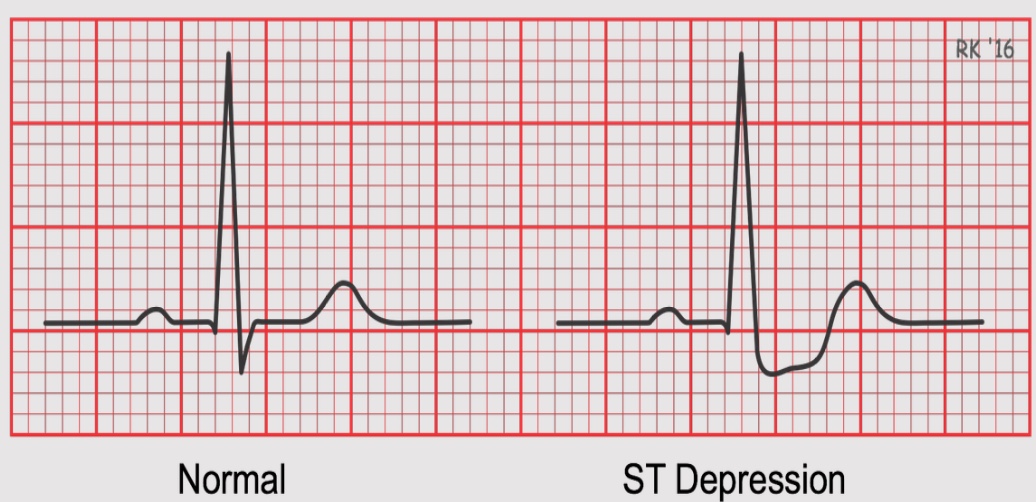
ST elevation
caused by more significant lack of oxygen
can cause an MI
if not quickly fixed, can cause permainte cell death
additional patient complaints or presentations
difficulty breathing
excessive sweating
unexplained nausea or vomiting
generalized weakness
dizziness
syncope or near-syncope
palpitations
isolated arm/jaw pain
fatigue
dysrhythmias
assessment of CAD
12 lead EKG (within 10 min and repeat q15-30 min)
cardiac monitor
chest x-ray
coronary angiography: imaging that see’s blood through coronary artery
exercise stress test: increase O2 demand = see changes in rhythm
echocardiogram: tells dr motion of heart + how well it is contracting
laboratory studies
cardiac angiography
used to assess:
coronary arteries
pressures in cardiac chambers
valve function
ventricular function
stress test
ischemia, ST segment changes, Arrhythmia
tests functional capacity
efficacy of medical or surgical intervention
can also be used as a follow up measure to see improvement
echocardiography
used to assess:
myocardial structures
ventricular function: ejection fraction and heart motion abnormalities
effusions
thrombus
ischemia
what lab studies to complete CAD assessment
serum cardiac markers: troponin (gold standard + specific to heart), Serum creatinine kinase, and myoglobin
c-reactive protein: not specific to heart
lipid profile: elevated cholesterol = higher chance CAD
electrolytes: important part of how depolarization happens
kidney function: can impact other organs, decreased perfusion to kidneys = decreased perfusion to heart
serum cardiac markers
Serum creatinine kinase
fractionated into bands - CK-MB
rises 3-12hr, peaks in 24h
returns to normal 2-3 days
troponin:
2 subsets cTnT and Ctn1
greater specificity than CK-MB
levels rise within 3-12 hr, peak 24-48, return to normal 5-14 days
assessment for chronic stable angina
pain lasts 3-5 min → responds well to nitroglycerin
chest pain that occurs intermittently over long period with same pattern of onset, duration, and intensity of symptoms
subsides when precipitating factor is relieved (physical exertion, temp, smoking, strong emotions, sex)
pain at rest is unusual
ECG shows ST segment depression
can be controlled with meds + can be timed to provide peak effects during time of day when angina is likely to occur
variants of stable angina
silent ischemia: asymptomatic, associated with diabetes
nocturnal angina: occurs only at night
angina decubitus: chest pain only occurs while lying down
prinzmetal’s angina: occurs at rest in response to a spasm of a major coronery artery
seen in ppl with migraine headaches and Raynaud’s phenomenon
may be relieved by moderate exercise
assessment of unstable angina
chest pain that is new in onset, occurs at rest or has worsening pain
chronic: increases in frequency, duration or severity
unpredictable and not received by rest → refractory to nitroglycerin
associated with deterioration of once stable atherosclerotic plaque
unstable lesion can progress to MI or return to stable lesion
myocardial infarction
servere prolonged low O2 supply (ischemia) resulting in necrosis
90% associated with acute coronary thrombosis
presence of Q wave - area of necrosis, permanent
transmural verus subendocardial
Inferior MI
anterior MI
lateral MI
ST: Stemi
full muscle is deprived of oxygen, no blood flow
full thickness
non ST: non stemi
partial amount of muscle is deprived of oxygen
partial thickness
symptoms of a MI
severe, immobilizing chest pain not relieved by rest, position change, or nitrate admin (diabetic pt may not experience pain)
epigastric pain → indigestion
SOB, diaphoresis, N&V
SNS stimulation: increase glucose, vasoconstriction, increase BP and HR
CO falls: lower BP, crackles, JVD, peripheral edema, hepatic engorgment
pulmonary edema
dizziness
extra heart sounds
fever
diagnosis of an MI
2/3 criteria required
chest pain >30 min
ECG - Q waves / ST segment elevation / T wave inversion
serum cardiac markers: Troponin T, Creatine Kinase (CK)
the overall goals for a pt with ACS include
relief of ischemic pain
‘prevention of myocardium → decrease O2 demand or increase O2 supply
immediate and appropriate treatment of ischemia → drug therapy + interventions
effective coping with illness-associated anxiety
participation in rehab plan
reduction of risk factors
collaborative care + acute interventions
prompt recognition of S&S → assessment of ABC, hemodynamic stability, preliminary history
12 lead and continuous ECG monitoring
bloodwork
oxygenation
IV access
initial meds
immediate repercussion therapy
initial medications for those with coronary artery disease
ASA (160-325 mg)/Plavix (600mg) → prevent additional platelet activation and interferes with platelet adhesion
oxygen
Nitro → S/L (x3) followed by IV for persistent pain, hypertension or heart failure
morphine: if nitro is ineffective → decrease myocardial O2 consumption, decrease BP/HR, decrease contractility
additional medications for those with coronary artery disease
B-adrenergic blockers: initiated within 24 h/no contraindications
LMWH or IV heparin: minimally 48 hr after MI → to prevent re-thrombosis or acute stent thrombosis
ACE inhibitors
P2Y12 inhibitors
antidysrhthmic medications
cholesterol lowering meds
stool softeners
repercussion therapy
mechanical repercussion: primary percutaneous coronary intervention
pharmacologic reperfusion: fibrinolytic therapy
streptokinase, alteplase, reteplase, tenecteplase
STEMI only
percutaneous coronary intervention
indications for angioplasty
electively for chronic stable angina
urgently for unstable angina
emergently for myocardial infarction
1-2 vessel disease
should be performed within 120 min of first medical contact → ideally 90 min
medications accepted for PCI: delayed >120 min
ASA 160mg po chew STAT
■ Fibrinolytic IV (STEMI only) – in consultation with cardiologist
■ Plavix 300mg po STAT
■ Unfractionated Heparin bolus 60 units/kg (maximum 5000 units) is given intravenously, followed by a continuous heparin drip at 12 units/kg/hr (maximum 1000 units/hr)
medications accepted for PCI: immediate ASA 160mg po chew STAT
ASA 160mg po chew STAT
■ Plavix 300mg po STAT
■ Unfractionated Heparin bolus 70units/kk (maximum 4000 units)
■ Standing by for transfer to Cath Lab
nursing management for PCI
angina: may be caused by transient coronary vasospasm
vascular site care: assessing for bleeding and swelling at sheath site
peripheral ischemia: secondary to cannulation of vessel, assess for adequate circulation
renal protection: hydration, fluids, D/C of some meds
pharmacological reperfusion: fibrinolytic therapy
target is within first 30 min
ideally within 1st hour after onset of symptoms → less than 6 hr has improved result
dysrhythmias are self-limited → no treatment
major complication is bleeding: surface bleeding to major bleed (stop infusion)
eligibility criteria for fibrinolytic therapy
Patients with recent onset (less than 12 hours) of chest pain and persistent ST elevation
Patients who present with bundle branch blocks (BBBs) that may obscure
ST segment analysis and a history suggesting an acute MI
Chest pain unresponsive to sublingual nitroglycerin
No conditions that might cause a predisposition to hemorrhage
absolute contradictions to fibrinolytic therapy
• Active internal bleeding or bleeding diathesis (except for menstruation)
• Known history of cerebral aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation
• Known intracranial neoplasm (primary or metastatic)
• Previous cerebral hemorrhage
• Ischemic stroke within past 3 mo
• Significant closed head or facial trauma within past 3 mo
• Suspected aortic dissection
relative contradictions to fibrinolytic therapy
Active peptic ulcer disease
Current use of anticoagulants
Pregnancy
Prior ischemic stroke not within past 3 mo; dementia; or known intracranial disease not covered under absolute contraindications
• Surgery (including laser eye surgery) or puncture of noncompressible vessel within past 3 wk
• Internal bleeding within past 2–4 wk
• Serious systemic disease (e.g., advanced or terminal cancer, severe liver or kidney disease)
• Severe uncontrolled hypertension (BP >180/110 mm Hg)
• Traumatic or prolonged (>10 min) cardiopulmonary resuscitation
coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
goal: resestablish blood flow distal to blockage
isnt an emergent procedure
who is considered for a CABG
left main disease
multivessel disease
satisfactory improvement is not reached with medical management
pt is not a candidate for PCI
lifestyle limting angina unresponsive to medical therapy or PCI
post MI ongoing assessment and care
pain: if cardiac muscle is still not getting enough O2, causes more pain
bleeding/surgical site care, chest tubes, pacer wire care
catherter site, assessment of extremties
monitoring: cardiac, resp, VS, O2
rest/sleep, activity is gradually increasing
anxiety → due to lack of understanding
effectiveness of interventions
emtotional and behaioural reactions
evaluation of left ventricular function
driving → after 1 week post-op
pt education