bio retake 3
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
The ABO blood group refers to antigens that can be found on red blood cells. Some people have AB blood. This is an example of
codominance
Anatomical features that serve the same function on two different groups of organisms, but are not structured similarly and did not evolve from a single structure in a common ancestor, but rather came about through convergent evolution are called
analogous
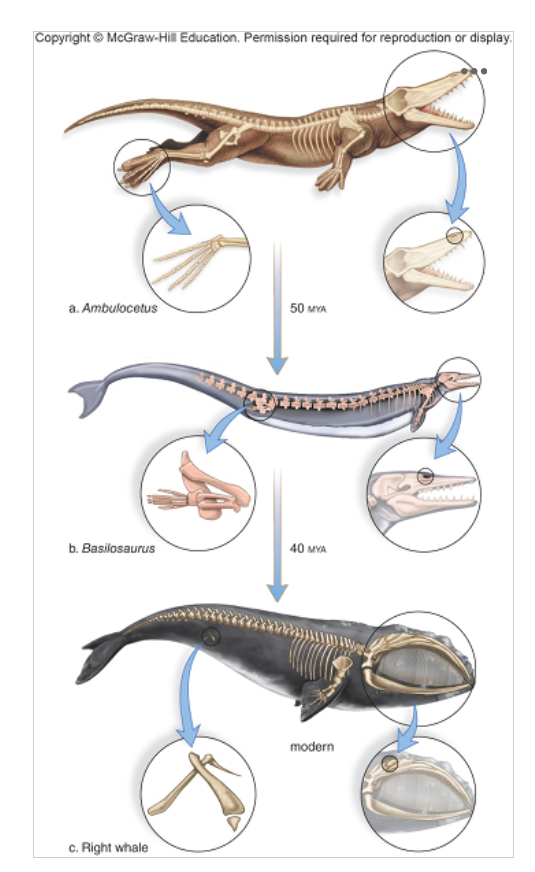
The above shows the changes in fossils as ancient land animals evolved into whales. This represents a type of evidence for evolution called
transitional forms
Which is NOT one of the preconditions in a population where natural selection is at work?
Adaptive characteristics in some individuals make them more likely to survive and reproduce.
All mating in the population is random.
There is variation that can be inherited in a population.
Many more individuals are produced by a population than can survive and reproduce.
Adaptive characteristics in some individuals make them more likely to survive and reproduce.
All mating in the population is random.
There is variation that can be inherited in a population.
Many more individuals are produced by a population than can survive and reproduce.
If an allele is dominant then
it is the allele causing the phenotype in a heterozygous individual
An individual who has an only one X chromosome is said to have _____ syndrome.
Turner
Fossils (such as Archaeopteryx) of organisms with physical traits that are intermediate between two major groups of organisms are called:
transitional fossils
During elongation of translation
the growing polypeptide is transferred to the newly arrived tRNA and amino acid.
If a parent cell has a diploid number of 36 chromosomes before mitosis, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have?
36
In which stage of mitosis do the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell?
metaphase
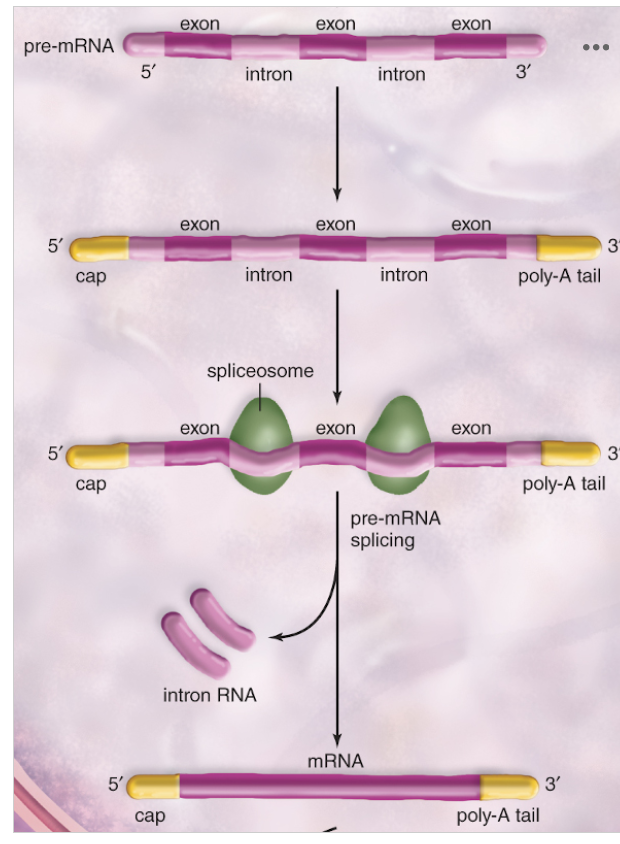
The ______ contain(s) the information for the structure of the protein. There is a hint in the image above.
A: exons
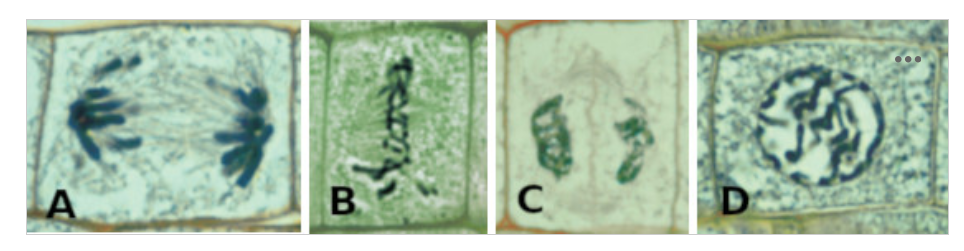
Plant Mitosis Images – The above image shows the 4 basic stages of mitosis, but not necessarily in the proper order. The stage indicated by the letter A is
anaphase
Imagine a heterozygous individual with type A blood and a heterozygous individual with type B blood have children. Match each blood type with the proportion of children expected to have that blood type.
Genotypes: IAi × IBi → kids: 1/4 IAIB (AB), 1/4 IAi (A), 1/4 IBi (B), 1/4 ii (O).
A → 25%
B → 25%
AB → 25%
O → 25%
Meiosis results in
: four haploid cells that are genetically different from one another.
Down syndrome is
usually caused by nondisjunction resulting in trisomy of chromosome 21.
Fertilization in the human life cycle results in
a zygote
The part of a transfer RNA molecule that binds to the codon is the
anticodon
A population of bats lives in a cave. Some of the bats have an allele that gives them pale fur while other bats have brown fur. When the bats are flying in the early evening the pale ones are caught by hawks and eaten at a higher frequency than the brown ones. Therefore the pale ones reproduce less often. This is an example of
Natural Selection
A royal blue painted bunting leaves its group and mates with a green painted bunting in another area. What is this an example of?
Gene Flow
DNA replication, transcription, and the binding of tRNA to the mRNA transcript all work properly in a cell due to the fact that
complementary base pairing
Consider the sentence “The dog ate the cat.” Which of the following is most like an insertion mutation of DNA?
The dog tet hec at.
Which type of natural selection increases the frequency of an intermediate phenotype? It is represented by the example of most human babies being born of an intermediate size.
A: stabilizing selection
The reason that missing an X chromosome and having an extra X chromosome do NOT cause more harm than they do is best explained by the
inactivation of any X beyond the first as a Barr body.
Which type of natural selection increases the frequency of an intermediate phenotype? It is represented by the example of most human babies being born of an intermediate size.
stabilizing
Q: Alternate versions of the same gene are called:
alleles
Q: Natural selection causes new mutations. (T/F)
False
Q: Transcription of DNA sequence ATTCGGAAG to complementary mRNA is
UAAGCCUUC
Two individuals are heterozygous for a gene on an autosomal chromosome (Aa × Aa). Genotypic ratios of offspring?
A: 1 Homozygous dominant : 2 Heterozygous : 1 Homozygous recessive
Old Order Amish have higher polydactyly because one original member carried that allele. More than one may be correct.
This is an example of genetic drift.
This is an example of gene flow.
This is an example of the bottleneck effect.
This is an example of the founder effect.
Genetic drift AND founder effect
Q: Two genes are linked if
A: they occur on the same chromosome.
Colorblindness is X-linked recessive. Man = normal (XᴺY), woman = normal carrier (XᴺXᶜ). If they have a female child, what is the chance she is colorblind?
A: 0%
Question 31 – Matching genetic disorders
Autosomal recessive, lysosome buildup in nerve cells from missing enzyme
Autosomal recessive, thick mucus, chloride channel defect
Autosomal recessive, rod-shaped hemoglobin, sickled RBCs
Autosomal dominant, neurodegenerative, faulty protein clumping
Autosomal dominant, prion protein, can’t sleep
Fatal Familial Insomnia
Huntington Disease
Sickle Cell Anemia
Cystic fibrosis
Tay-Sachs Disease
Autosomal recessive, lysosome buildup in nerve cells from missing enzyme → Tay-Sachs Disease
Autosomal recessive, thick mucus, chloride channel defect → Cystic fibrosis
Autosomal recessive, rod-shaped hemoglobin, sickled RBCs → Sickle Cell Anemia
Autosomal dominant, neurodegenerative, faulty protein clumping → Huntington Disease
Autosomal dominant, prion protein, can’t sleep → Fatal Familial Insomnia
Translation elongation picture (A–D)
In the panel labeled C, you see two tRNAs in the ribosome at the same time, and the growing peptide chain is now on the newer tRNA.
Q: Which description best matches stage C?
Two tRNA molecules are complementary base paired to their anticodons on the mRNA at the same time. The growing protein has just been transferred to the newest amino acid in the sequence.”
Pure-bred pigeons vs wild pigeons: what is likely true genetically?
A: wild pigeons are heterozygous for more alleles.
Straight-haired man (homozygous), curly-haired woman (homozygous), child has wavy hair. This is
: incomplete dominance
Q: One is most likely to find fossils in
A: sedimentary rock
Q: Prophase of mitosis vs prophase I of meiosis differ because
homologous chromosomes come in contact to allow crossing over in prophase I of meiosis but not in prophase of mitosis.
Q: Messenger RNA is produced in the
nucleus
A cell from any eukaryotic species can have its condensed chromosomes removed and stained. A picture of the chromosomes is taken through a microscope and all the homologous pairs can be matched with image software. This can be used to find chromosomal disorders. The image of the chromosomes is called a/an
karyotype
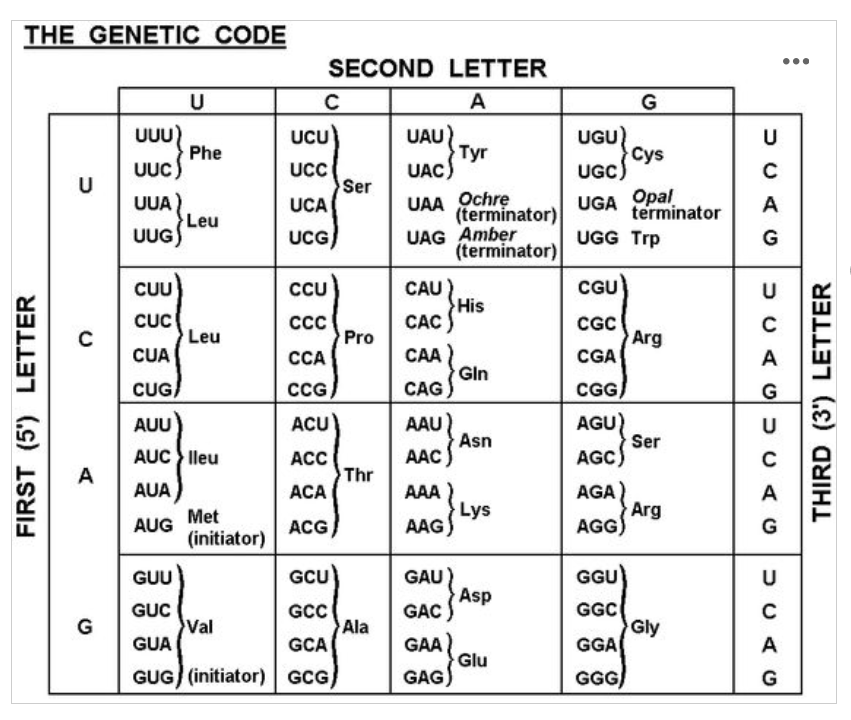
Refer to the genetic code chart above to translate the mRNA sequence CUA-UAU-AUG.
Leu-Cys-Val
Leu-Leu-Asp
Leu-Tyr-Met
Met-Cys-Val
Met-Tyr-Arg
Leu – Tyr – Met ✅
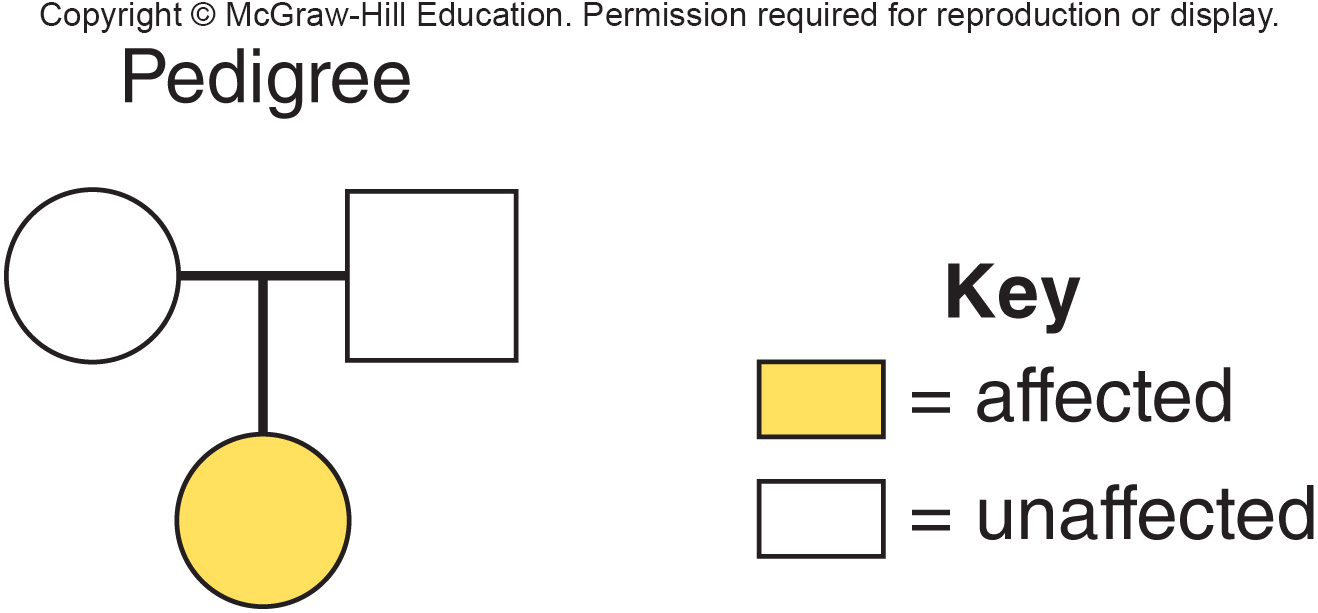
In the above pedigree the inheritance pattern is
recessive
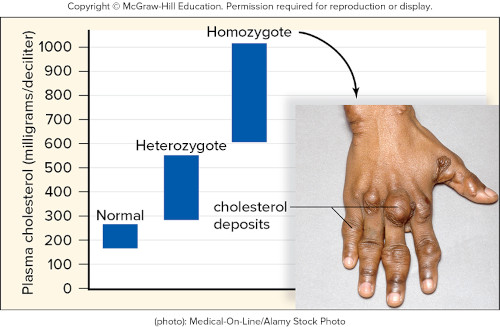
Consider the image above. The alleles for the gene for hypercholesterolemia give the above phenotypes depending on the genotypes listed. The pattern of inheritance for this disorder is
more than two alleles in the population.
incomplete dominance. ✅
codominance.
simple dominance.
occurs when chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis, leading to gametes with an unusual number of chromosomes.
Nondisjunction
Which of the classes of RNA molecules carries the genetic information from the nucleus as it is needed for the construction of a protein?
messenger RNA
When the female in a clownfish mating pair dies, the male changes sex to become a female and takes a smaller male as a mate. This is an example of:
the influence of environment on phenotype
Which of the following are genetically identical?
sister chromatids
During which stage do homologous chromosomes separate? More than one may be correct.
anaphase of meiosis 1 ✅
Which form of microevolution leads to adaptation?
natural selection
The process of transcription produces __
RNA
The p53 protein is part of a pathway that inhibits cell division. When the p53 gene mutates it fails to turn on genes that inhibit cell division. The p53 gene is a/an
tumor suppressor gene.
If the diploid chromosome number is 38, the chromosome number of each gamete will be
19
Traits that are controlled by several sets or pairs of alleles, such as skin color and height in humans, are the result of what form of inheritance?
polygenic
Which of the following statements is NOT true about oogenesis, the production of eggs, in humans?
The egg will contain 23 chromosomes.
Four equal size daughter cells will form.
It occurs in the ovary.
At least two nonfunctional polar bodies will form.
The egg will contain 23 chromosomes.
Four equal size daughter cells will form. ✅ (NOT true)
It occurs in the ovary.
At least two nonfunctional polar bodies will form.
Q: If a parent cell has a diploid number of 48 chromosomes before mitosis, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have?
48
The reason that missing an X chromosome and having an extra X chromosome do NOT cause more harm than they do is best explained by the
inactivation of any X beyond the first as a Barr body.
Which of the following are genetically identical?
sister chromatids
Colorblindness is a sex-linked recessive trait. A man has normal vision and a woman has normal vision but is a carrier for the colorblindness allele. If they have a female child, what is the chance of it being colorblind? You can find a link to a Punnet square tool in the instructions at the top of the exam.
25%
0%
100%
75%
50%
Traits that are controlled by several sets or pairs of alleles, such as skin color and height in humans, are the result of what form of inheritance?
polygenic
Disorders involving an unusual number of chromosomes are ultimately caused by:
Nondisjunction
Consider the images representing steps in elongation of translation above. Which of the following descriptions best corresponds to what is happening at the stage labeled A?
A tRNA with attached amino acid is approaching the ribosome to bind at the A binding site.
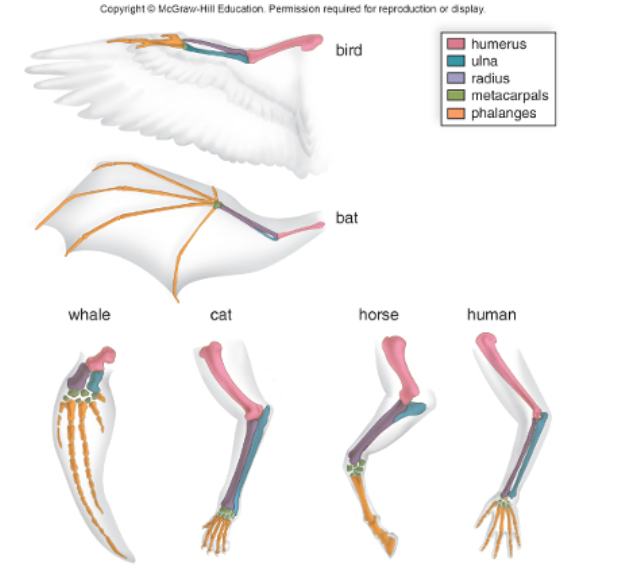
The image shows diagrams of the forelimb bones for multiple types of living animals. This represents evidence for evolution of the form called.
homologous structures.
DNA replication, transcription, and the binding of tRNA to the mRNA transcript all work properly in a cell due to
complementary base pairing.
Two genes are linked if
they occur on the same chromosome