units 1.1-1.3 terms
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bro im cooked
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
what is a neuron and what kind of process is it?
the ways in which your brain communicates with the rest of your body; electrochemical
what is the nucleus? (neuron)
control center of the neuron
what is the function of dendrites? (neuron)
recieve the message
what is the function of the axon? (neuron)
pathway in which the message is going to travel
what does it mean that a cell body (soma) “keeps the cell alive"? (neuron)
get rid of waste, takes in food, protects the nucleus
what are myelin sheaths and their function?
a fatty tissue that surrounds the axon that protects and speeds up the message
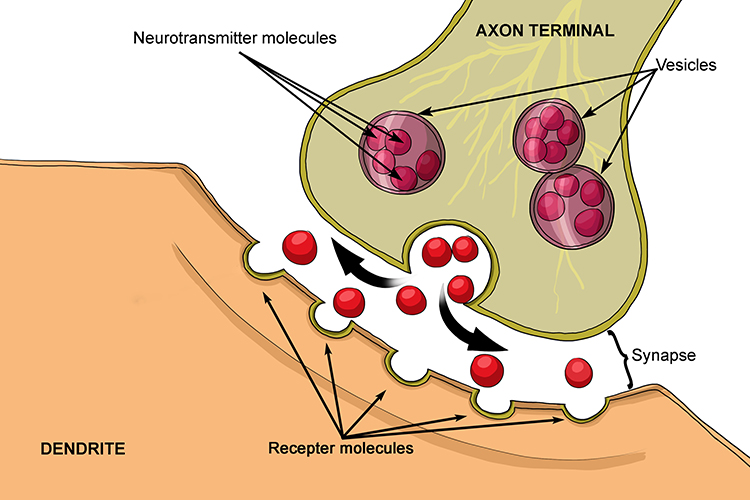
what are synapses?
space between 2 neurons so they never really contact each other
what do axon terminals/terminal button do?
pass on the message to the rest of the body
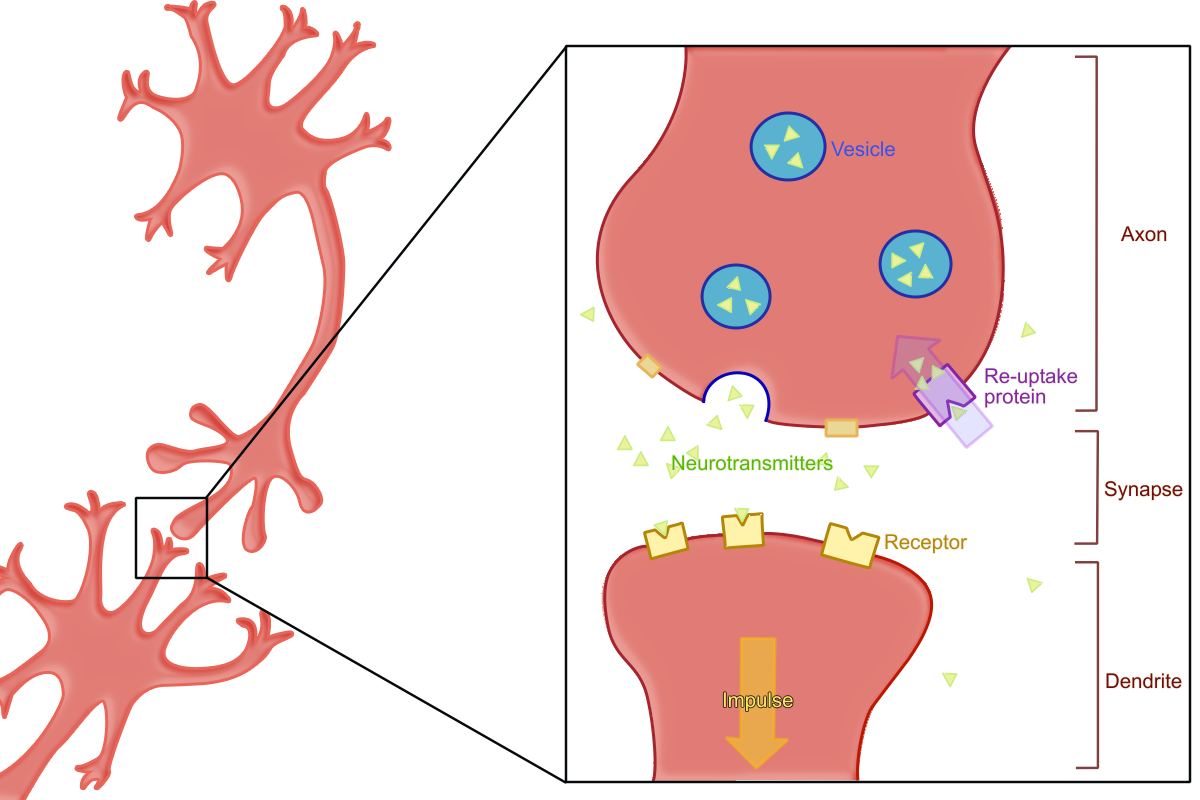
what is reuptake?
recycling of neurotransmitters
what do vesicles do (in the synaptic cleft)?
carry 4 neurotransmitters and releases them
what is myasthenia gravis (MG)?
chronic autoimmune disorder that destroys neurons ability to communicate by disrupting the message from the axon terminal to the dendrite
what do glial cells do?
help protect the neuron and play a role in thinking, memory, and learning
what does the multiple sclerosis (MS) do?
causes the myelin sheath to slowly degenerate
what does the endocrine system do?
send signals throughout the body by sending hormones through the bloodstream
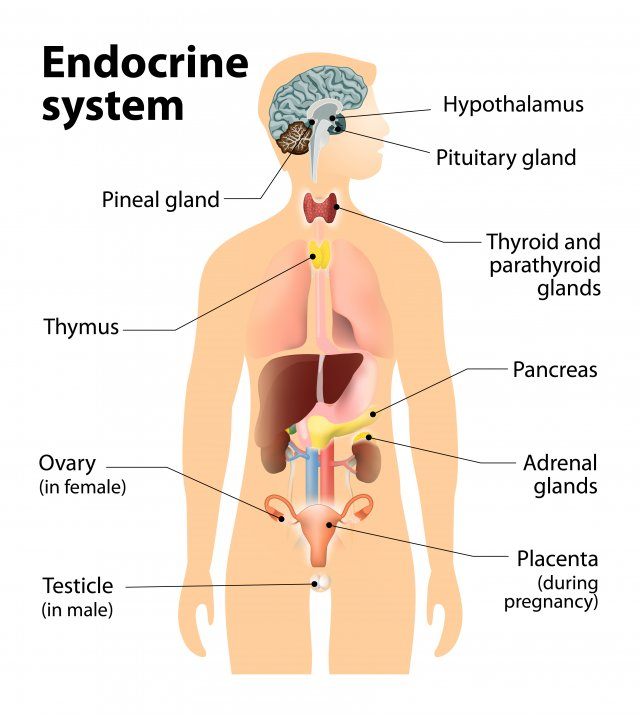
describe the hormones for the endocrine system
produced and secreted from various glands in the body
even though the endocrine system is slower to operate than the nervous system…
its effects last longer
describe the pituitary gland (master gland)
plays an important role in regulating other glands in the body; regulating stress, growth, and reproduction (+ parts of pregnancy, childbirth, lactation)
what is the pituitary gland controlled by?
the hypothalamus in the brain
the pituitary gland includes 2 hormones, what is the human growth hormone?
regulates growth
the pituitary gland includes 2 hormones, what is the oxytocin?
helps increase trust, bonding, and feelings of attachment between people
what happens when you have too much of the growth hormone?
lead to Acromegaly or gigantism
what happens when you have too little of the growth hormone?
(in early development) it can lead to dwarfism
describe the pituitary gland and its location
small, pea-sized gland, found at the base of your brain and is in line with the top of your nose
what is adrenaline’s function?
stimulate the nervous system to prepare the body for a quick response when facing a stressor/threat
where is adrenaline produced?
in the adrenal gland and is then released into bloodstream
what does too much adrenaline cause?
negative effects on the heart, difficulty sleeping, can make you anxious
what does too little adrenaline cause?
rarely happens btw
limit the body’s ability to respond properly in stressful situations
what are some oxytocin functions?
plays an important role in pregnancy, reproduction, childbirth, and breastfeeding; human bonding as well (maternal and romantic relationship)
where is oxytocin produced?
naturally produced by the body in the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland
what happens where there is too much of oxytocin?
healthy young adults can be oversensitive to the emotions of others
what happens where there is too little of oxytocin?
mental health disorders (depression, anxiety, and eating disorder)
what is melatonin’s function?
makes us tired at night and less tired during the day, it’s responsible for timing your sleep-wake cycle
where is melatonin produced?
brain’s pineal gland
what happens when there is too much of melatonin?
seasonal affective disorder (SAD) can overproduce melatonin, causing them to feel sleepy during the day
what happens when there is too little of melatonin?
insomnia (difficulty falling and staying asleep)
what is ghrelin’s function?
affect your energy regulation when you’re hungry (burn calories, fat, and storing fat for energy); triggers hunger (brain reminds that you need to eat)
where is ghrelin produced?
when your stomach is empty, it produces ghrelin which causes hormone levels to rise in the bloodstream
what happens when there is too much of ghrelin?
increase in hunger/appetite which can lead to overeating, weight gain, and reduce energy expenditure and hinder weight loss efforts
what happens when there is too little of ghrelin?
decrease in hunger/appetite which can lead to a decrease in food intake, weight loss, and difficultly in maintaining nutritional intake
what is leptin’s function?
help maintain normal weight on a long-term basis, regulate hunger which provide sensation of being full
where is leptin produced?
mainly acts on the brainstem and hypothalamus to regulate hunger and energy balance
what happens when there is too much of leptin?
OBESITY

what happens when there is too little of leptin?
starvation, increase of hunger and decrease in energy expenditure
what is the function of inhibitory neurotransmitters?
reduce the chance for a receiving neuron to fire and action potential
which drugs contain inhibitory neurotransmitters?
heroin, marijuana, alcohol
which drugs contain dopamine neurotransmitters?
cocaine, meth
which drugs contain serotonin neurotransmitters?
LSD, ecstasy
in heroin and marijuana, the inhibitory neurotransmitters…
restrain/prevent dopamine from being released
you have natural opiates in your body that shuts down inhibitory neurotransmitters when activating opiate receptors. what does heroin do when it enters your body?
mimics the natural opiate and also binds to opiate receptors in order to release dopamine
similarly to heroin, your body has its own native cannabinoid called Anandamide which connects to cannabinoid receptors in order to turn off the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters. what happens when THC (active chemical in marijuana) enters the body?
mimics anandamide and binds to cannabinoid receptors
ecstasy mimics serotonin and is taken up to serotonin transporters without hesitation. what does this interaction do to serotonin transporters?
alters the transporter, making it temporarily confused and doing its job in reverse (transporting neurotransmitters OUT of the cell). this causes the excess serotonin to rebind to the receptors and also overstimulate the cell
what is the function of dopamine transports?
responsible for removing dopamine neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft after they’re done doing their job
meth mimics dopamine, taken into the cell by the dopamine receptors. once inside the cell, meth enters the dopamine vesicles forcing the dopamine molecules out. what happens when there is excessive dopamine?
causes transporters to work in reverse, actively pumping dopamine out of the cell and can also be trapped in the synaptic cleft, resulting in the excessive dopamine to bind over and over again to receptors which can overstimulate cell
what is another neurotransmitter other than GABA for alcohol?
Glutamate, it acts as the brain’s general purpose excitatory neurotransmitter
alcohol delivers a double sedative punch when it enters the brain. what are the 2 interactions that occur?
first interacts with GABA receptors to make them more inhibitory and then it binds to glutamate receptors preventing the glutamate from exciting the cell.
where does alcohol affect the brain?
areas of the brain involved with memory formation, decision making, and impulse control
what does cocaine do?
blocks the dopamine transporters causing dopamine to be trapped in the synaptic cleft. this results in dopamine binding over and over again, overstimulating the cell.
what does LSD do?
acts almost only as serotonin neurons since it chemically resembles and elicits its effects by binding it to serotonin receptors (either exciting or inhibiting)
what is Acetocholine’s (Ach) function?
excitatory: released by motor neurons. stimulates muscle contraction; involved in attention memory, learning and general intellectual functioning
what is Acetocholine’s (Ach) effect on deficit?
Alzheimer’s disease; cognitive impairments, memory loss, etc.
what is Acetocholine’s (Ach) effect of surplus?
severe muscle spasms; salvation, lacrimation, diarrhea, slow heart rate
what would happen if we didn’t have Acetocholine’s (Ach)?
voluntary muscle movements are impossible
is Acetocholine (Ach), dopamine (DA), and serotonin excitatory or inhibitory?
depends on which type of receptor it binds to
what is dopamine (DA)’s function?
inhibitory: regulates movement, motivation, reward, and mood regulation
what is dopamine’s (DA) effect of deficit?
Parkinson’s disease; less motivation, can’t feel pleasure, fatigue, motor control issues, depression
what is dopamine’s (DA) effect of surplus?
heightened pleasure, increase of risky behaviors, psychotic symptoms, schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
what type of symptoms does dopamine (DA) mainly contain?
mainly motor symptoms, less dopamine = less regulation
what is serotonin’s function?
inhibitory: regulates mood, appetite, digestion, sleep, and cognitive
what is serotonin’s effect of deficit?
psychological issues such as depression (MDD), anxiety disorders, sleep problems, digestive issues
what is serotonin’s effect of surplus?
autism, serotonin syndrome (agitation restless, fast heart rate, high blood pressure, tremors, hyperthermia, etc.)
how can serotonin be surplus through?
too much medicine
since SSRIs boosts serotonin, what does it help treat?
depression
what is norepinephrine’s (NE) function?
mainly excitatory: used for arousal in the flight/fight response, modulation of mood, plays a role in learning and memory retrieval, and cardiovascular functions
what is norepinephrine’s (NE) effect of deficit?
depression (lack of energy, decrease in focus and attention span), ADHD, MDD
what is norepinephrine’s (NE) effect of surplus?
anxiety, panic attacks, high blood pressure, excessive sweating, pheochromocytoma, hypertension and palpitations
what is gamma aminobutyric acid’s (GABA) function?
inhibitory: inhibits neural activity regulates neuronal excitability and balance between excitation and inhibition, regulation of muscle tone
what is gamma aminobutyric acid’s (GABA) effect of deficit?
anxiety, restlessness, seizures (epilepsy, anxiety disorders, insomnia)
what is gamma aminobutyric acid’s (GABA) effect of surplus?
sleep and eating disorders, sedation, drowsiness, impaired cognitive and motor emotions
which nervous system is gamma aminobutyric acid’s (GABA) in?
central nervous system
what are endorphins’ functions?
inhibitory: reduce pain signals and provide calming effects
what are endorphins’ effect of deficit?
reduced pleasure, increased mood disturbances and pain sensitivity
what are endorphins’ effect of surplus?
lack of pain sensitivity, overconfidence, reduced stress hormone
what does endorphins’ function as
neurotransmitters
what is glutamate’s function?
excitatory: used in memory learning, movement, helps message cross the synapse more efficiently
does glutamate have any effect on deficit?
no
when there is a little too much glutamate and too little GABA is often associated with what from the effect of surplus?
epileptic seizures
is glutamate critical for long-term or short-term memory
long-term memory