Nuclear Reaction
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element having different number of protons and neutrons
Mass number
The sum of an atoms protons and neutrons
Atomic number
The number of an atoms protons
can be found in the periodic table
Radioactive Isotope (Radioisotope)
This isotope is unstable and spontaneously emits energy to stabilize its nucleus
Radioactivity
Nuclear Radiation emitted by radioisotope
Artificial Isotope
This Isotope do not exist naturally and are created by scientist in laboratories.
Alpha (α) particle
This particle is a high energy particle with 2 protons and 2 neutrons
charge: +2
Mass number: 4
Beta (β) particle
This particle has high energy electron
Formed when a neutron is converted to a proton and an electron
Charge: -1
Mass: Negligible compared to proton
Positron (β+) Particle
Antiparticle of Beta Particle (opposite charge but same mass)
Formed when proton is converted into a neutron
Charge: +1
Gamma Ray γ
high energy radiation released from radioactive nucleus
Effects of Radioactivity - Damage
Nuclear radiation will damage or kill rapidly dividing cells
bone marrow
skin
reproductive system
intestinal system
Effects of Radioactivity - Cancer cells
Cancer cells divide rapidly (effect treatment for cancer)
Effects of Radioactivity - Food
Radioactivity towards food
exposed to gamma rays
Effect: kills microbes, parasites & insects
Safety: food will not become radioactive
Benefit: longer shelf life + safer to eat
Nuclear Reactions - radioactive decay
Unstable radioactive nucleus emits radiation
Nuclear reactions - nuclear equation
Original Nucleus → New Nucleus + radiation emitted
Alpha Emission
This type of emission is the decay of a nucleus by emitting an alpha particle
Mass ↓4
Atomic number ↓2
Beta Emission
This type of emission is the decay of a nucleus by emitting beta particle
1 neutron is lost and 1 proton is gained
Atomic number ↑1
Mass: stays the same
Positron Emission
This type of emission is the decay of a nucleus by emitting a positron particle
1 proton is lost and 1 neutron is gained
Atomic number: ↓1
Mass: Stays the same
Gamma Emission
This type of emission is the decay of a nucleus by emitting Gamma Radiation
γ rays are a form of energy only
γ emission accompanies alpha or beta emission
NO CHANGES
Balancing Nuclear Reactions - Step One
Write an equations with the original nucleus on the left, and the particles emitted on the right
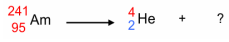
Balancing Nuclear Reactions - Step Two
Calculate the mass number and atomic number of newly formed nucleus on the right
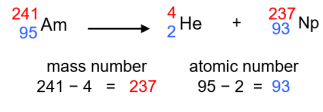
Balancing Nuclear Reactions - Step Three
Use the atomic number to identify the new nucleus and complete the equation
Half Life
Half-life (t1/2)
time it takes for one half life of a sample to decay
Independent of sample amount
Does not change with temp
Does not change with pressure