Movement Disorders - Clin Med
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What does this refer to
A 65-year-old man present with a tremor in his right hand.
His tremor is most apparent at rest and improves with movement.
His movements are noticeably slower and he has difficulty initiating movement.
Physical exam, the patient appears apathetic and has rigidity with passive arm movement.
Gait testing is notable for shuffling with a stooped posture.
Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Neurodegenerative disease
Progressive disorder of the nervous system
Idiopathic dopamine depletion
Characterized by
Bradykinesia
Rigidity
Postural instability
Resting tremor
Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
60,000 cases dx every year in the US
M > F
Family hx
Genetic link
Epidemiology Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Late(MC) and early onset
Family hx/genetic link
Autosomal recessive
Autosomal dominant (MC)
Hx TBI
Drug induced
Toxins
Etiology Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Mutations in the LRRK2or SNCA (autosomal dominant) or PARK7, PINK1, or PRKN gene (autosomal recessive)
Loss of dopaminergic neurons failure of Ach inhibition in the basal ganglia
Most cases of Parkinson’s —> protein deposits called Lewy bodies
Seen in dead or dying dopamine-producing neurons
Absence of Lewy bodies —> Parkinsonism
Pathogenesis Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Resting tremor
Worse at rest and stress
Relieved with voluntary activity, intentional movement and sleep
Usually starts on 1 side of the body
Clinical History Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to

Physical exam Parkinson’s Disease
What do

es this refer to
Physical exam Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Postural instability and classic gait
Gait assessment Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to

Considerations Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Hypomimia (masked facial expression)
Decreased spontaneous eye blink rate
Speech impairment, including hypokinetic dysarthria, hypophonia, and palilalia (repetition of a phrase or word with increasing rapidity)
Dysphagia
Sialorrhea
Craniofacial motor features Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Blurred vision
Impaired contrast sensitivity
Hypometric saccades
Impaired vestibuloocular reflex
Impaired upward gaze and convergence
Eyelid opening apraxia
Visual abnormalities Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to

Musculoskeletal Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Gait
Shuffling, short-stepped gait
Freezing
Festination
Gait assessment Parkinson’s Disease
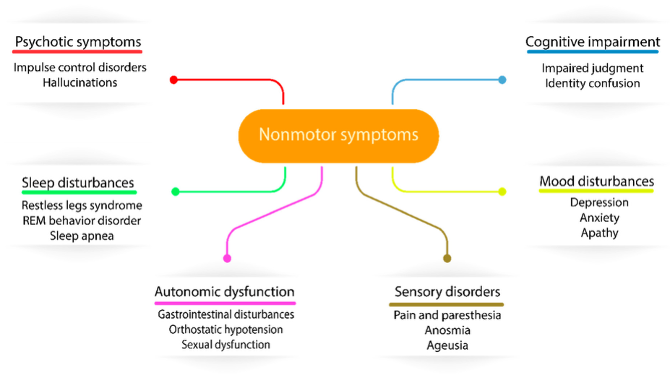
What does this refer to

Non-motor symptoms Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Alzheimer’s Disease
Cardioembolic stroke
Chorea
Huntington ds
Lewy body dementia
Essential tremor
Differential diagnosis Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to

Workup Parkinson’s Disease
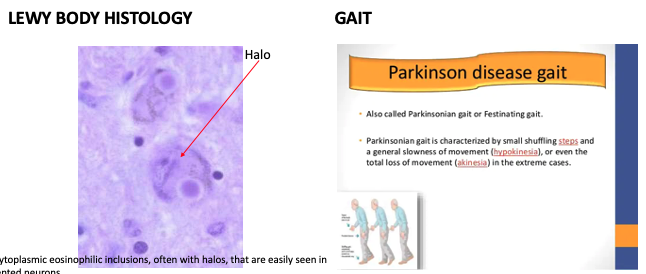
What does this refer to
Characteristics Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Consult/referral Neurology
Physical/Occupational Therapy
Deep brain stimulation for rigidity and tremors in some patients
Clinical intervention Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to

Complementary & alternative therapy Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Levodopa-carbidopa (Sinemet) 1st line
Dopamine agonists may be used as initial treatment
Bromocriptine (Cycloset or Parlodel)
Pramipexole (Mirapex)
Ropinirole (Requip)
Anticholinergics
Antiviral
Amantadine (Gocovri) (treats influenza but increases dopamine)
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
Severe disability or death
25% of patients within 5 yrs onset sx
89% within 15yrs onset
Older age at onset and initial rigidity/hypokinesia can be used to predict (1) a more rapid rate of motor progression in those with newly diagnosed Parkinson disease and (2) earlier development of cognitive decline and dementia; however, initially presenting with tremor may predict a more benign disease course and longer therapeutic benefit from levodopa
Older age at onset, dementia, and decreased responsiveness to dopaminergic therapy may predict earlier nursing home placement and decreased survival
Prognosis Parkinson’s Disease
What does this refer to
A 30-year-old woman presents with a two-year history of anxiety, gait instability, and progressively worsening tics.
She has no family history of neurologic disease, but her father committed suicide at age 32.
MRI scan of the brain shows atrophy of the cerebral cortex and caudate nucleus.
Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
Incurable, adult-onset inherited disorder characterized by the triad
Extrapyramidal movement d/o
Progressive cognitive decline (dementia)
Behavioral disturbances
Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
Autosomal dominant —> Neurodegenerative diseases
M = F
Any age
Dx < 20yo → juvenile variant
MC 30-50yo
Death within 10-20yrs after onset
Greatest frequency in European ancestry
Less common in Japanese, Chinese, and African descent
Epidemiology Huntington’s Disease
What does this ref

er to
Etiology Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
Presents before age 20
Akinetic-rigid phenotype
Chorea is typically absent
Paternal inheritance
juvenile onset Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
Characterized by
Involuntary movements
Chorea
Early chorea —> fidgetiness
Cognitive deterioration
Psychiatric dysfunction
Less Common sx
Weight loss
Difficulty swallowing
Aspiration
Clinical history Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to

Physical exam Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
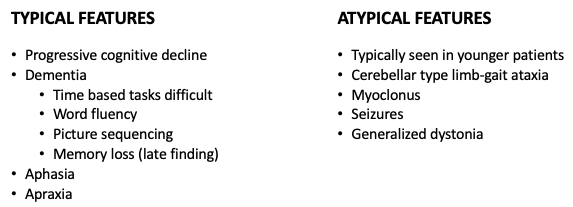
Features of Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
Movement, cognitive & behavioral sx
Early chorea → fidgetiness
Physical exam Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to

Stages of disease progression Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
Tardive Dyskinesia
Parkinson Disease
Tourette’s syndrome
Chorea gravidarum
Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE)
Multiple Sclerosis
Schizophrenia
Differential diagnosis Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to

Workup Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
Consult/referral Neurology
Referral for genetic counseling
Support groups
Severe chorea
Assistive equipment
Helmets
Padded reclining chairs
Low beds
Protective padding of the environment
Clinical intervention Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to

Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
Progressive
Inevitably fatal
MC 10-20 yrs after onset of sx
Prognosis Huntington’s Disease
What does this refer to
A 62-year-old man reports involuntary shaking of both his hands, arms, and head.
The hand shaking appears to worsen with writing, eating, or drinking from a cup.
During periods of stress, his shakes worsens.
He has noticed that drinking wine improves his symptoms.
Family history is significant for his father also having similar symptoms.
On physical examination, there is a 4-10 Hz tremor elicited when both of his arms are outstretched forward.
There is no tremor at rest.
Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Rhythmic, oscillatory movement
Characterized by a slowly progressive postural and/or kinetic tremor
Usually affects bilateral UE
Postural tremor occurs when a person maintains a position against gravity, such as holding the arms outstretched.
Kinetic tremor is associated with any voluntary movement, such as moving the wrists up and down or closing and opening the eyes.
Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
MC cause of action tremor
Incidence increases with age
Familial component
No prevalence with race/ethnicity
M = F
MC 35-45yo
Risk Factors
Family hx
Aging
Epidemiology Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Result of an abnormally functioning central oscillator,
Genetic
Etiology Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Action tremor of hands & arms
Onset w/ voluntary movement
May also affect voice, head, face, lips
Sx may improve with small amounts of alcohol, but worsen with large amounts
Clinical history Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
TCAs
Depakote
Dopamine
Lithium
Metoclopramide (Reglan)
Neuroleptics
Theophylline
Thyroid hormone
Drugs associated with Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Visible tremor
Worsens with intentional movement (“stress”)
Tremor may improve with small amount of alcohol ingestion and rest
Both upper extremities are typically affected
Mild asymmetry is not uncommon
Muscle tone and reflexes are normal
Physical exam Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Parkinson disease
Cerebellar tremor
Movement disorders
Psychogenic tremor
Drug induced tremor
CML
Wilson disease
Differential diagnosis Essential Tremor
What does this refer to

Workup Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Consult/referral Neurology/Neurosurgery
Surgical intervention for refractory cases
Thalamotomy
Clinical intervention Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Typically no treatment is needed
Propranolol (1st line)
Primidone (2nd line)
Alprazolam (3rd line)
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Korean herbal medicine
Acupuncture/chiropractic care
Guided imagery
Meditation
Yoga
Complementary & alternative therapy Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
Disability is common
Decreased quality of life
Increased mortality in patients >65yo
Prognosis Essential Tremor
What does this refer to
A 6-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his mother due to noticing him "acting strange."
She reports that the patient would jerk his head rapidly and sniff a considerable amount of times per day for over a year.
The jerking and sniffing episodes would begin and end abruptly, and the frequency would increase during periods of increased stress.
She notices the patient trying to suppress these sniffing episodes and jerking movements, and appears relieved after they occur.
Neurologic exam is normal besides the neck jerking and sniffing.
Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to
Neurological disorder manifested by sudden, brief, intermittent motor and phonic tics
Included in DSM-V
Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to
M > F (4 : 1)
Age 2-15yrs
Similar among ethnicities EXCEPT
Uncommon AA
Epidemiology Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to

Etiology Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to
Tics are the clinical hallmark findings
Motor
Verbal/phonetic
Self-mutilating
Clinical history Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to

Tourette syndrome
What does this refer to

Diagnostic criteria – DSM-5 Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to
Chorea
Complex Partial Seizures
Frontal lobe syndromes
Hemifacial spasm
Huntington’s disease
Dystonia
Myoclonus
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Differential diagnosis Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to

Workup Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to
Habit reversal therapy
Psychotherapy
Clinical intervention Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to
Most patients do not require medical management
Dopamine blocking agents
Tetrabenazine (Xenazine)
Risperidone (Risperdal)
Haloperidol (Haldol)
Alpha-2 adrenergics
Clonidine (Catapres)
Guanfacine (Intuniv)
Clonazepam as adjunct
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to

Complementary & alternative therapy Tourette’s Syndrome
What does this refer to
Persists throughout life
Improvements in sx in adolescence and adulthood
Sx can be so severe they are disabling
Most common disability is social
Tics interrupt behavior and thought
Prognosis Tourette’s Syndrome