L6 light and matter
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
watt
flow of energy per unit time; 1 Joule/second
components of white light
all rainbow colors
photon’s energy depends on
frequency
light has _ fields which oscillate in _
electric and magnetic; opposite directions
what do waves carry and not carry
energy, not matter
atmospheric transmission
some wavelengths are blocked by Earth’s atmosphere, others aren’t
what do transparent and opaque objects do
transmit vs block light
atomic number
number of protons
atomic mass number
number of protons + neutrons
different isotopes have same number of _ but different
protons, neutrons
continuous spectrum
e.g a common lightbulb spanning all visible wavelengths, white noise
emission spectrum
specific wavelength depending on composition and temperature
absorption spectrum
can absorb light of specific wavelengths, leaving dark absorption lines in the spectrum
solid sphere model
Dalton, Greek idea of an indivisible, identical elemental sphere
plum pudding model
Thomson, electrons scattered throughout a sphere of + charge
nuclear model
rutherford, atoms are mostly empty space, with most mass in nucleus and electrons orbiting
planetary model
bohr, orbits have quantized sizes and energies
quantum model
Schrödinger, electrons move in waves instead of set paths, clouds of probability instead of knowing exact location
vibrational and rotational lines
movement of molecules that complicates their spectra, many of which are the infrared range
blackbody spectrum
thermal emission’s continuous spectrum, its peak tells us object’s temperature
thermal radiation
emitted by nearly all large or dense objects, depends on temperature (poker in fireplace getting white-hot
doppler shift
light as well as sound → red and blue-shifting; tells you about the relative motion of distant objects
we measure doppler effect from
shifts in wavelengths of spectral lines; tells us an object’s speed toward or away from us, but only if there’s a component of its motion parallel to our line of sight
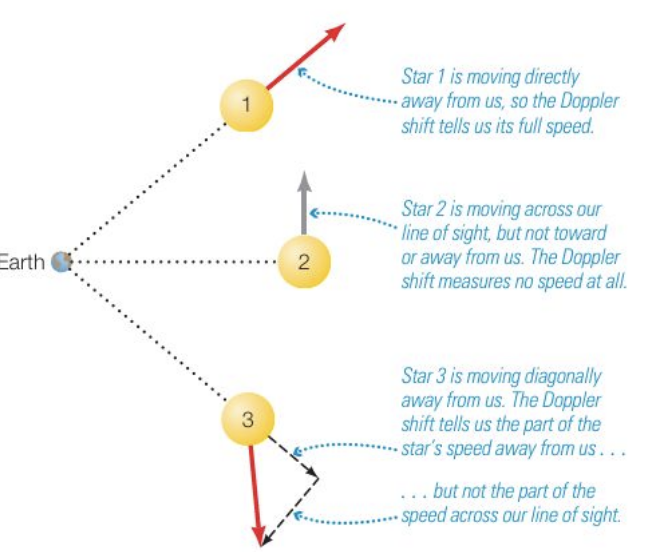
doppler shift and rotating objects
different sides of a rotating object spread out its spectral lines (brings in redshift and blueshift), wider when an object rotates faster
doppler broadening in gas
random motions in gas particles caused by a higher temperature broadens the spectral lines
cosmological redshift (not doppler)
light shifts lower in frequency due to Universe’s and the wave’s expansion
velocity of molecule and spectral lines
NO CONTRIBUTION; while it can cause doppler broadening or shifts, it doesn’t create unique spectral lines