Calcium Channel Blockers
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is the role of calcium in the cardiovascular system?
electric signal conduction (AV + SA node, bundle of His)
cardiac muscle contraction
What is the role of calcium in the blood vessels?
smooth muscle contraction
vasoconstriction
increase in BP
Calcium enters through what type of channel?
L channels in the CV system
Explain the stepwise events of calcium entry into a single cell of the cardiac system?
Phase 0 = Na influx
Phase 1 = K+ efflux (hyperpolarization)
Slow Phase 2 = slow Ca2+ influx
“plateau phase”
end of phase → K+ efflux
Phase 3
Ca can either:
triggers conduction systems OR
increase contraction of cardiac muscle
Phase 4 = Na/K ATPase pump
Na and Ca efflux
K+ influx
return to resting MP
What 2 ions contribute to the electrical system completion by calcium?
Na and K
What is the resting membrane potential of a cardiac cell?
-80 mV
What are the 3 major cardiovascular conditions indicated for CCBs?
HTN (arteries)
angina (BVs in heart)
arrhythmia (cardiac muscle)
What are the 3 chemical nuclei that have properties to block CCs?
dihydropyridines (DHP)
arylalkylamines
benzothiazepines
Dihydropyridine acts exclusively on the ____ ____
blood vessels
What are the indications for dihydropyridines?
angina
HTN
What is the MOA of DHPs?
do NOT have affinity to calcium channels in the heart
indirectly causes reflex tachycardia via the baroreceptor reflex
decrease in BP = increase in HR
What are the key features of 1,4-dihydropyridines?
pyridine nucleus
1 of the 3 double bonds is hydrogenated
2 H’s are in 1,4 position
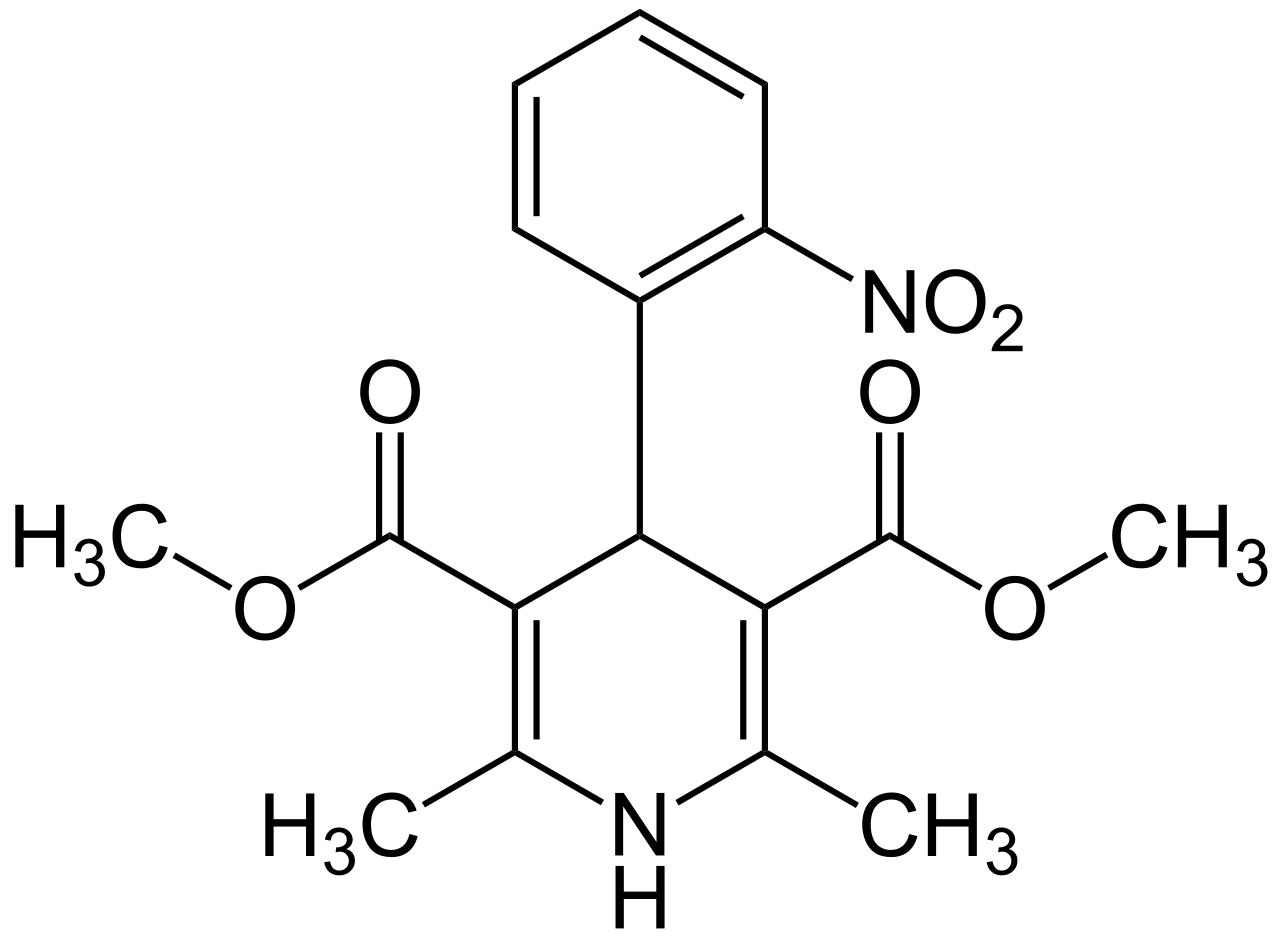

Nifedipine
1,4-dihydropyridine
2 alkyl chains at 2,6 position (methyls)
2 esters in 3,5 position
low bioavailability due to
lipophilicity (esters will be hydrolyzed easily, no polar groups)
high 1st pass metabolism
phenyl ring in position 4
e withdrawing group at 2,3 position of phenyl
N atom is completely nonbasic due to conjugation of lone pair
Nifedipine is only given orally due to what factors?
cannot form a salt for injection
suffers 1st pass metabolism
low bioavailability
metabolized by esterase enzymes in GIT, liver, and plasma
What are the different doses of nifdedipine?
5 mg
10 mg
20 mg
Nicardipine
1,4-dihydropyridine
basic N on ester alkyl at position 3
only given as injection (HCl salt) due to low bioavailability
Amlodipine
1,4-dihydropyridine
basic N in side chain at position 2
allows for formation of a salt with besylate → allows to be SLOWLY released → long acting product
Compare the besylate salt of amlodipine to the HCl salt of nicardipine.
HCl salt → hygroscopic
besylate salt → NOT hygroscopic
allows drug to be released SLOWLY as a long acting product dosed once daily
Where do benzothiazepines and arylalkylamines have highest affinity to calcium channels?
both blood vessels AND heart
Benzothiazepines and arylaklyklamines are used for what indications?
arrhythmia
HTN
angina
What is the effect of benzothiazepines and arylalkylamines?
(-) chronotropic effect
decrease in HR by directly inhibiting cardiac muscle contractions
All 3 nuclei are more selective to (veins/arteries) than (veins/arteries). They cause (arterial/venous) vasodilation and decreased (preload/afterload) in angina.
arteries
veins
arterial
afterload
What is the key feature of aryl-alkyl amines?
aliphatic tertiary Nitrogen surrounded by carbon chains attached to aromatic rings
least active class
Verapamil
aryl-alkyl amine
cyano group
aliphatic tertiary amine
N demethylation on methyl → very low bioavailability
4 ether groups
O demethylation → very low bioavailability
no polar groups = increased lipophilicity
What are the dosage forms of verapamil?
oral
injection as HCl salt
Describe what happens when you take verapamil orally.
there will be a high absorption rate due to its high lipophilic nature
will also excessively undergo 1st pass metabolism (O/N-demethylation) → very low bioavailability
only 7% of oral dose reaches circulation intact
What are the key features of benzothiazepines?
thiazepine
7-membered ring
sulfur
nitrogen
high absorption → very lipophilic
high plasma protein binding (PPB) → very lipophilic
low bioavailability due 1st pass metabolism → esters are quickly hydrolyzed
identical properties to verapamil in:
HCl salt formulation and given IV
Diltiazem
benzothiazepine
ether group
O demethylation
ester group
easily hydrolyzed by esterases = low bioavailability
amide group
hydrolyzed by amidases → NH4 + COOH
tertiary amine