Tides and Currents
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
How far away is the moon from the earth?
384 000 Km
How far away is the sun from the earth?
150 000 000 Km
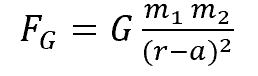
Name the components of the equation for the tidal force
FG=The tidal force from the moon
G=gravitational constant
m1=mass of the moon
m2=mass of the earth
r=distance of the centre of the earth from the centre of the moon
a=radius of the earth
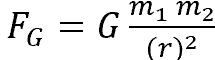
Name the components of this equation
FG=Tidal force from the moon
G=Gravitational constant
m1=Mass of the moon
m2=Mass of the earth
r=radius of earth
How heavier is the mass of the sun compared to the moon?
X 27 million times
How much further away is the sun from the earth compared to the moon?
X 400
How much effect does the sun have on tides compared to the moon?
Has ½ of the effect compared to the moon
Lunar cycle (Spring tides)
When the sun and the moon in the sky in line the same direction
-Creates strong gravitational pull
-Either very high tides or really low tides
Lunar cycle (Neap tides)
When the sun is pulling in the opposite direction to the moon
-Moon and sun cancel each other out by pulling tides into opposite directions
-Small hight tide
-High low tide
What would happen to a tidal bulge with a frequency of two cycles per day if there were no land and no seabed?
It would still continue around the earth
What happens when waves when they hit land?
They get reflected and refracted
Amphidromic points
Areas with zero tidal variation
What causes Coriolis effect?
Earths rotation
Due to the Coriolis effect how will objects be deflected from N. hemisphere and S. hemisphere?
N. hemisphere=Deflect to right
S. hemisphere=Deflect to left
What is the major drving force of surface ocean circulation?
Wind
What is the major driving force of atmospheric circulation?
Solar energy
Hadley’s model of atmospheric circulation
In the Ecuador it gets hot, so it causes air to rise and it draws air from underneath it.
Due to pulling air form the polls it creates a vacuum
Coriolis effect
Air flowing from high pressure zone to low pressure zone, where its trajectory is modified by earth rotation
What do circulations patterns further get modified by what?
-Coriolis effect
-Pressure gradient
-Presence of landmass
Ekman motion
The movement of ocean water influenced by the balance between wind forces, the Coriolis effect, and turbulent drag.
What does the combination of Coriolis effect and Ekman transport create?
Large, cylindrical currents in the north and south hemisphere
-Subtropical gyres
What is piled up in the centre of these gyres systems?
Warm, nutrient poor water