23
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Manager
people in charge of organizations and their resources.
Characteristics of managers
-Hold formal position of authority and power
-Communicate effectively
-Make reasoned decision based on relevant information and to live with the consequences
-Judge when they should be in charge and when they should delegate and allow others to be in charge
-Make decisions about organization function, including resources, budget, hiring, and firing
Styles of Managers
Autocratic~
Participative~
Free-rein~
~Autocratic management
Managers that CENTRALIZE power and tell employees what to do; authoritarian.
Negative use:
- employees feel uninformed, insecure and afraid
Positive use:
- rewards for compliance

~Participative management
Managers who DECENTRALIZE power and share it with employees. Work together to achieve goals. Keep employees informed and encourage sharing of ideas

~Free-rein management
occurs when no one particular person is the authority figure in the practice. Employees are left to self-motivate themselves.
Can be messy and advised only to use on a group that is self-motivated and self-disciplined.

Influences of Cultural Differences
Participation in making Decisions~
Hiring Preferences~
Permanence of employment~
Labor-Management Relationship~
~Participation in making Decisions
Some cultural groups (US) want subordinates to be actively involved in decision making v. others (Venezuela) prefer to be told what to do.
~Hiring Preferences
Different cultural groups value different selection criteria for hiring employees: job-qualificaiton v. family/friendship relations
~Permanence of employment
Attitudes about the permanence of employment vary among members of different cultural groups.
Less employment security (US) v. lifetime employment (Japan)
~Labor-Management Relationship
U.S. workers tend to have confrontional attitudes to bring more equitable work and satisfying relationship v. European/Asians more discreet and respectful to superiors
What are the four major components of managing?
planning and decision making~
organizing, staffing and communicating~
motivating and leading~
controlling~
~planning and decision making
Setting the organization's goals and deciding how best to achieve them: involve budgeting and profit planning, cash flow management, and other decisions related to operations.
~organizing, staffing and communicating
Structuring business operations in logical and meaningful ways: how business activities are put together
Acquiring employees w/necessary knowledge, skills, and attitudes to fill the position.
Networking/Interacting with employees: give/receive/share information effectively.
~Motivating and leading
Creating the desire to achieve: internal or w/in the employee and external like salary raises. And getting employees to voluntarily pursue goals of the organization.
~controlling
Regulating the business operations: monitoring performance, comparing it with goals, and taking corrective action as needed.
What are three common business organizational structures?
By Function, By Product, By Geography
Organization by function
Organizational structure is divided into departments based on the different business functions (finance, HR, operations, marketing).
Organization by product
Related products are grouped together to form departments (Large manufacturing corp. is divided into aviation parts and consumer appliance divisions)
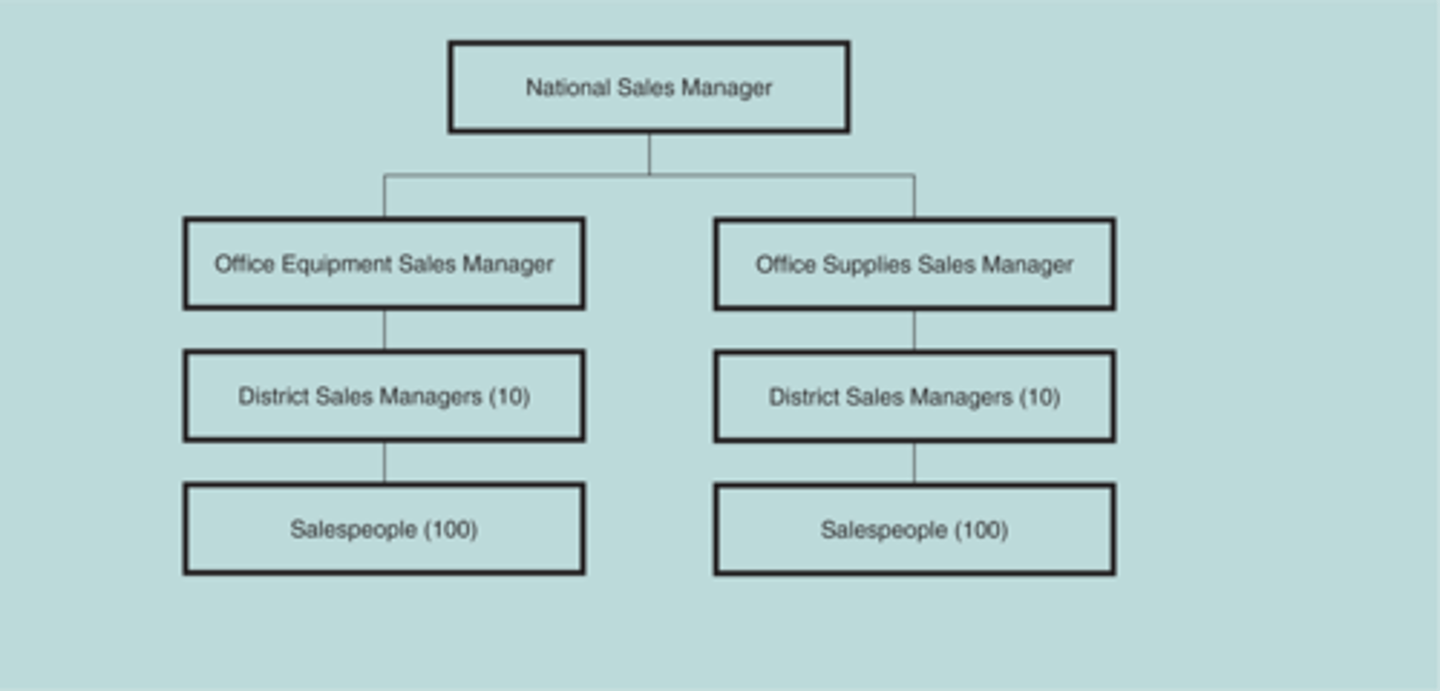
Organization by geography
Organizes on geographic basis: city, county, state, region, country, or continent. Used by those that operate beyond the borders of one country.
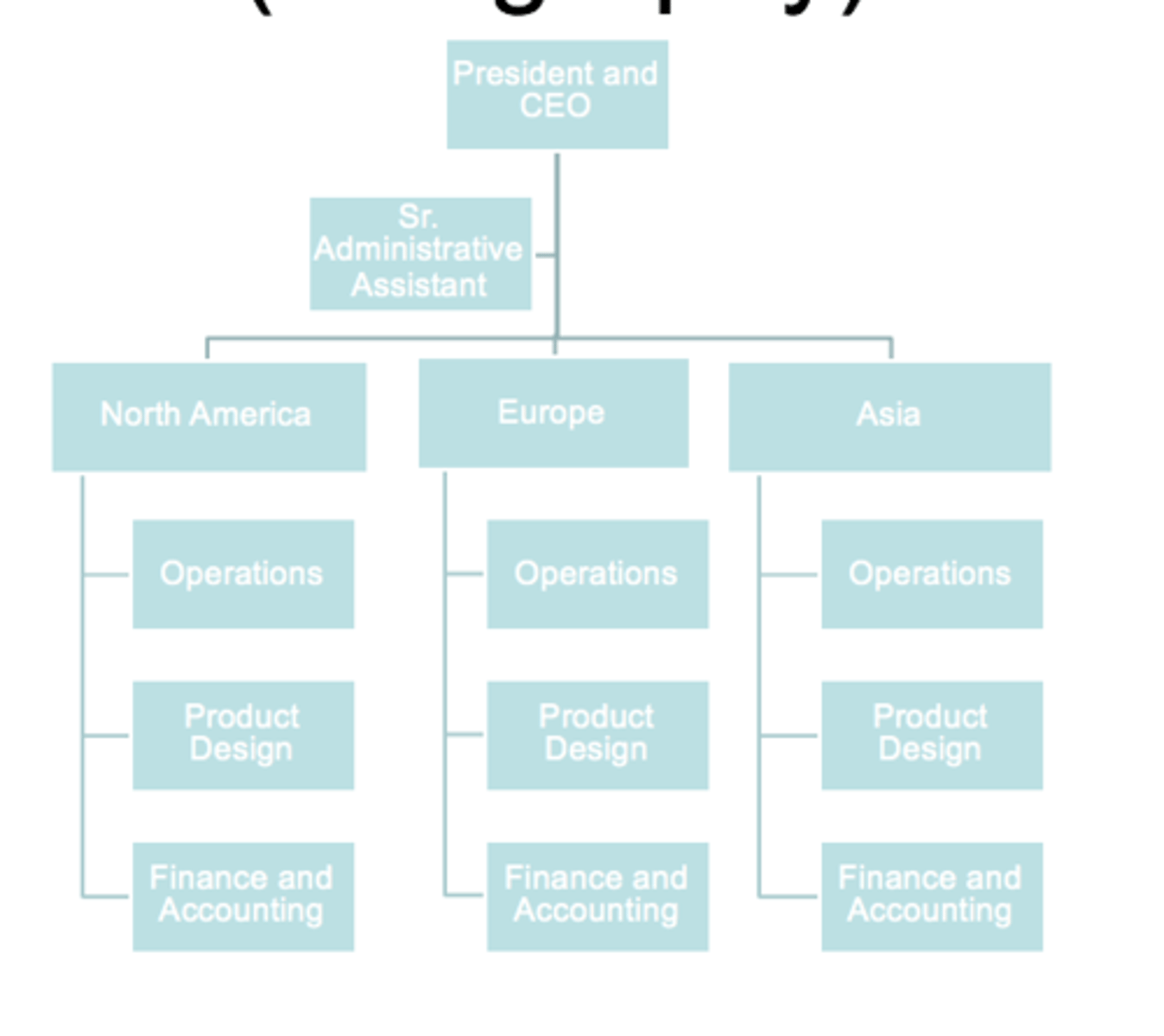
Organizational chart
a visual display of the organizational structure, lines of authority (chain of command), staff relationships, permanent committee arrangements, and lines of communication
Line positions
(Managerial) positions that have direct responsibility for the basic objectives of an organization
Staff positions
(Nonmanagerial) positions that support or advise those in line positions.
Levels of Management
the differentiation of managers into three basic categories-senior, middle, and first-line.
Span of control~
Lines of Authority~
Delegations of authority and responsibility~
~Lines of Authority
indicate who is responsible to whom and for what.
Clear lines of authority allow an organization to run smoothly and efficiently.
Delegations of authority and responsibility
How much authority and responsibility they delegate or transfer to others.
Too much authority and responsibility : autocratic
Too little authority and responsibility : no productivity
Degree of centralization
the amount of authority and responsibility that is delegated to small group people or to organizational units.
Distributed power between employees and manager : DECENTRALIZED; participative
Focused in one or small group : CENTRALIZED; autocratic
~span of control
the optimal number of subordinates a manager supervises or should supervise:
Front line manager~
Middle manager~
Senior manager~
~front line manager
make short-term operating decisions, directing the DAILY tasks of non managerial personnel in specific departments.
~middle manager
a manager who oversee the first-line managers and implements the strategy and major policies developed by senior management.
~senior manager
an upper-level executive who guides and controls the overall fortunes of an organization: oversee the work and departments of middle managers
chief executive office (CEO)
highest manager within a company;
vmadisenxx michell.e60 mishkahh_ _gayakurwadkar
What are the stages through which a business might pass to attain global status?
1. Domestic Company
2. Exporting Company
3. International Corporation
4. Global Corporation
~Domestic Company
A company that conducts business in only one country, which is known as the home country.
- Sell and create its products and services in the HOME COUNTRY
- easiest to manage
~Exporting Company
A company that sells in other countries. Relies on its home marketplace advantages as it expands. Focus on selling familiar products in foreign markets.
Rely on agents or distributors.
- saves money and time
- allows to take adv. while not having to accept full responsibility
~International Corporation
Also known as multinational corporation (local, national and regional levels) that uses its existing capabilities to move into overseas markets: subsidiaries or subdivisions of the international corporation.
How will management tomorrow be different from management today?
Managers of tomorrow will:
- strive to facilitate the visionary development of others
- need the trust of owners, customers, employees, suppliers, and governmental officials.
- be multilingual and multicultural
- develop and use global strategic skills
- have outstanding communication skills
- work as a team
Entrepreneur
A risk taker who operates a business.
Small business
An independently owned and operated business that does not dominate an industry. (major creators of new products, major source of jobs, often provide personal service)
Telecommuting
This involves using a computer and other technology to work at home instead of in a company office or factory.
Business Plan
A guide used to start and operate a business. This includes business descriptions, organizational structures, and marketing activities.
Marketing
Includes the business activities necessary to get goods and services from the producer to the consumer.
Marketing plan
A document that details the marketing activities of an organization. Includes information about customer needs, social factors, competition, target markets, economic trends, political environment, and the marketing mix.
Budget
A financial tool that estimates a company's funds and its plan for spending those funds.
Start-up costs
The expenses that occur when a company is new. Costs include equipment purchase, remodeling costs, legal fees, utility company deposits, and beginning inventory expenses.
Continuing expenses
Business operating costs that occur on an on-going basis. Costs include rent, utilities, insurance, salaries, advertising costs, employee training costs, taxes, and interest on loans.
Variable costs
Business expenses that change in proportion to the level of production.
Fixed costs
Expenses that do not change as the level of production changes.
Breakeven point
The number of units a business must sell to make a profit of zero.
Gross profit
Difference between the cost of an item for a business and the price for which the business can sell that item.
Equity funds
Business funds obtained from the owners of the business. The money the owners of a business have invested from their personal accounts.
Debt funds
Business funds obtained by borrowing. Loans from financial institutions also help to finance companies and are ____ ____.
Balance sheet
The document that reports a company's assets, liabilities and owner's equity.
Income statement
A document that summarizes a company's revenue from sales and its expenses over a period of time, usually per fiscal year.
Fixed cost
Are salaries fixed or variable costs.
Human Resources Management
Part of the business plan that deals with hiring, training, and obtaining employees.
Cash flow statement
Reports the current sources and amounts of cash inflows and outflows
Management information system
Organized method of processing and reporting data for business decisions (Part of the business plan).
Financial Planning
Most important part of the business plan.
Extracting
Type of business that removes raw materials from the earth.
Manufacturing
Type of business that turns raw materials into usable products.
Retailer
Type of business that sells directly to consumers.
Wholesaler
Type of business that buys in mass quantities and resells to other businesses in smaller quantities.
Marketing plan
The second most important part of the business plan.
Service-based business
lawn care is an example of this type of business.