Surgical Nursing Skills Exam 1
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
leading questions
What kind of questions should you not ask when taking a history
temperament, attitude, BCS, possible anxiety
What things should you make note of during taking a physical
age, sex, repro status, breed
What should signalment always include
previous conditions
During a follow up history, what will be in the chart that you should ask about
consent form
Identifies the patient and the specific procedure that is to be performed, potential risks, vets name, estimate, signature of owner of patient, owner contact info
can not legally be in the hospital or receive treatment
What can not happen without a signed consent form
above the age of 18
how old do you need to be to sign a consent form
the owner of the animal
Who must the consent form be signed by
OR environment, operating team, surgical instruments, supplies, patient's endogenous flora
What are some sources of surgical infection to remember
the patient's endogenous flora
What is the most common source of surgical contamination
before surgery
Eating, Showering, Making fingernails short and clean, not putting on overpowering fragrances, put on clean scrubs, turn lights on, turn on heating devices, unwrap sterile instruments: should all be done ___
clean scrubs, surgical cap, surgical mask, shoe covers, no cellphone
Surgical Attire:
after the animal has been clipped, prepped, moved to surgery room, and is positioned
When should your scrub start
decrease the microbial load on hands during the surgical procedure
What is the Surgical Hand Scrub designed to do
open, closed, assisted
What are the 3 methods of gloving
surgical gloving
Open gloving should net be used routinely for
when the hands need to be sterile
When is open gloving most commonly used
minor procedures, bone marrow biopsy, catheterizations
When is open gloving used
closed gloving
preferred method of gloving for surgical procedures that provides assurance against contamination because bare skin is not exposed
assisted gloving
This method of gloving requires 2 people
a glove is contaminated during surgery
When do you use assisted gloving
maintaining a sterile environment, monitoring a patient, managing instrument table, passing proper instruments, maintaining tissues, maintain hemostasis
Responsibilities of a tech during surgery
continual monitoring of sterile field, handling sterile instruments, passing sterile instruments, sterile light covers
How does a tech maintain a sterile environment
loading needles properly, instrument count, sponge
How does a tech manage an instrument table
orderly arrangement, ring handles closest to surgeon, knowing what surgeon needs beforehand, knowing what each instrument does, proper passing of instruments
What is part of a tech handling instruments properly
needle holders to place on handle, never point toward any one when removing, cutting edge away from surgeon when passing, handed in a way that is ready to use
What are proper handling tips for a scalpel blade
place rings in palm of hand and ready to use, place very firmly
What are proper handling tips for ring instruments
laparotomy sponges, 4x4s, cautery, suction
How does a tech maintain hemostasis
6 mls of blood
How much blood does a 3x3 hold
10 mls of blood
how much blood does a 4x4 hold
100 mls of blood
how much blood does a laparotomy sponge hold
when counting the sponges and knowing how much blood each sponge holds, you will be able to effectively estimate how much blood the patient lost
why is a sponge count and knowing how much blood a sponge will hold important to know
alcohol
Never use ___ when doing cautery
monopolar cautery
need a grounding plate because the current passes through the patient toward the ground plate
bipolar cautery
No grounding plate is needed because the current passes from one tip to another
yankauer
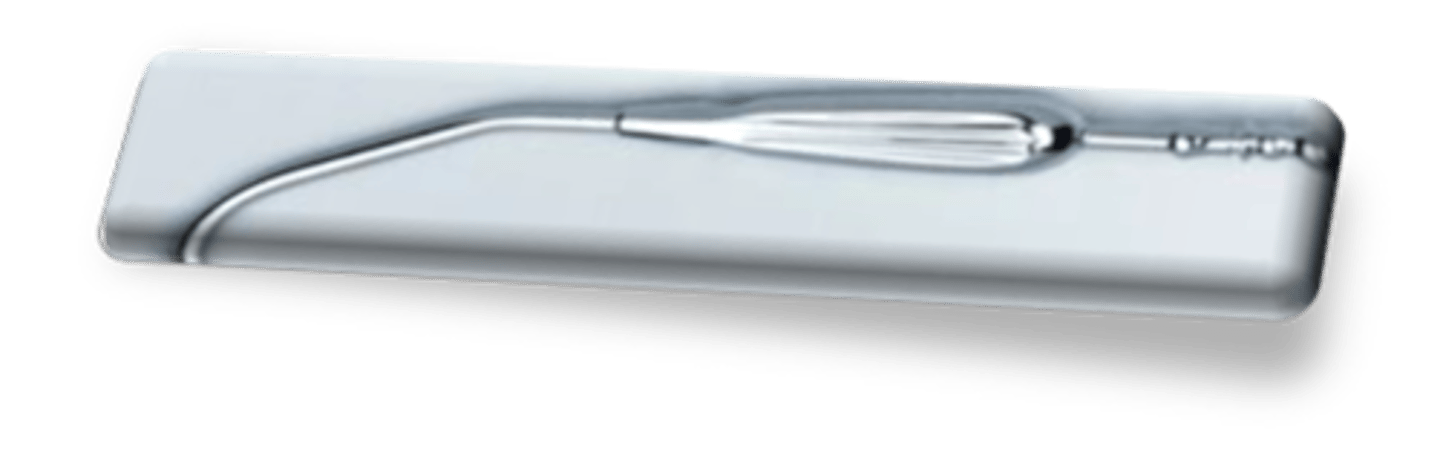
poole
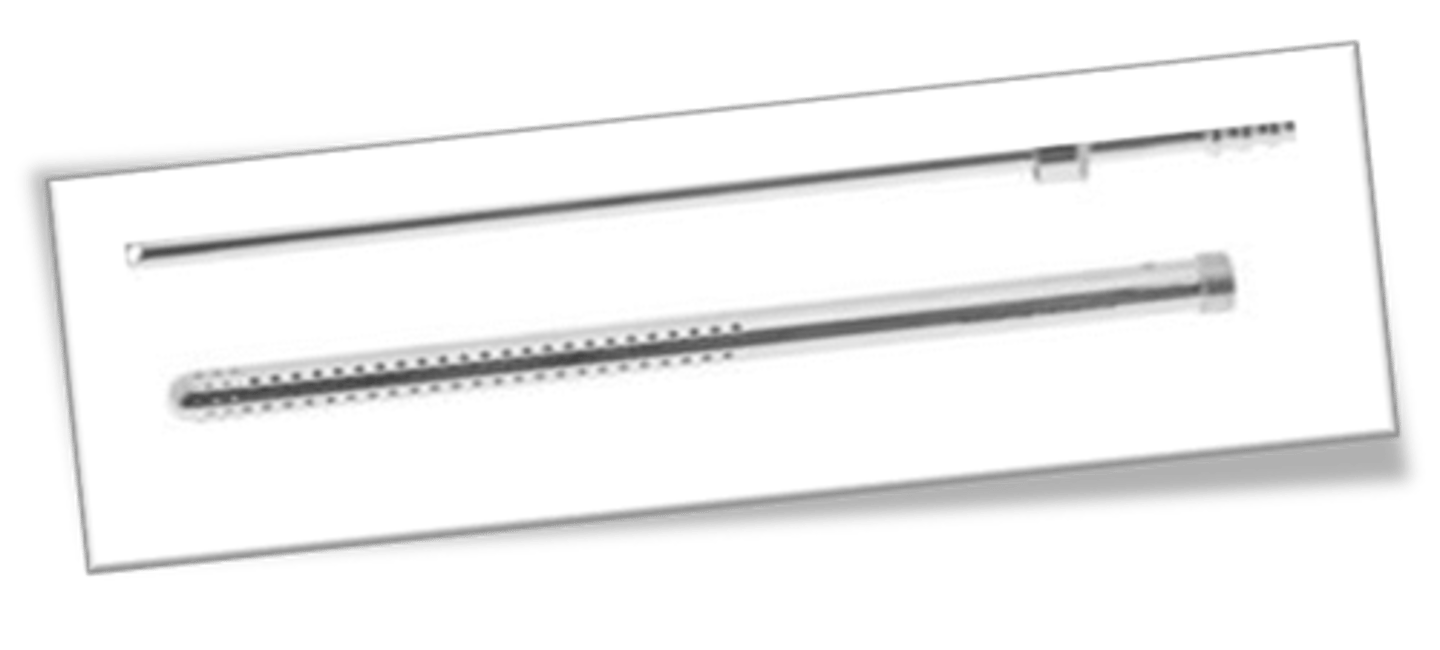
frasier

minimal reactivity with tissue, inhibits bacterial growth, holds securely, resists shrinking, absorbed with minimal reaction, non-capillary, non-allergenic, non-carcinogenic, non-ferromagnetic, inexpensive
Ideal suture properties
12-0
What is the smallest suture size
7
What is the largest suture size
memory
Flexibility often refers to ___
memory
inherent capability of suture to return to, or maintain, its original gross shape
torsional stiffness, diameter
____ and ___ also play a part in flexibility of the material
steel
Least flexible suture material
silk
most flexible suture material
tissue drag
When considering surface characteristics and coating, it is important to decrease ___
drag
the amount of friction created as suture is pulled through the tissue
more micro-trauma to the tissue
Greater drag creates ____
braided suture
____ drags more in general than monofilament
Capillarity
braided suture often is coated to reduce ____ but it also promotes a smoother surface
capillarity
The degree to which absorbed fluid is transferred along a suture. It is the process by which fluid (and potentially bacteria) are carried into the interstices of multifilament fibers
braided sutures, monofilament
____ have a degree of capillarity, whereas ___ are considered non-capillary
water soluble, insoluble
Coatings may be ____ or ____
triclosan, vicryl plus, PDS plus
Name some antibacterial coatings
a zone of inhibition around the suture
What does antibacterial coating create
tensile strength
a measurement of the ability of a material (or tissue) to resist deformation and breakage
over time as suture is absorbed, stretches, has constant load applied to it
When does tensile strength diminish
from the suture to the tissue
As tissue heals, its tensile strength returns and the load is transferred
relative knot security
holding capacity of a suture
braided material
What suture material generally has better knot security
instruments
Suture tensile strength is micro-damaged by ____ causing the suture to weaken. NEVER grasp suture with ____
elasticity
the degree to which suture will deform under stress or load and return to its original form when the load is removed
plasticity
the degree to which suture will deform without breaking and will maintain its shape after removal of the deforming force
pliability
the ease of handling and the ability of the suture to change shape
creep
tendency of a suture to slowly and permanently deform under constant stress
taperpoint
used for very soft tissue and does not cause much damage
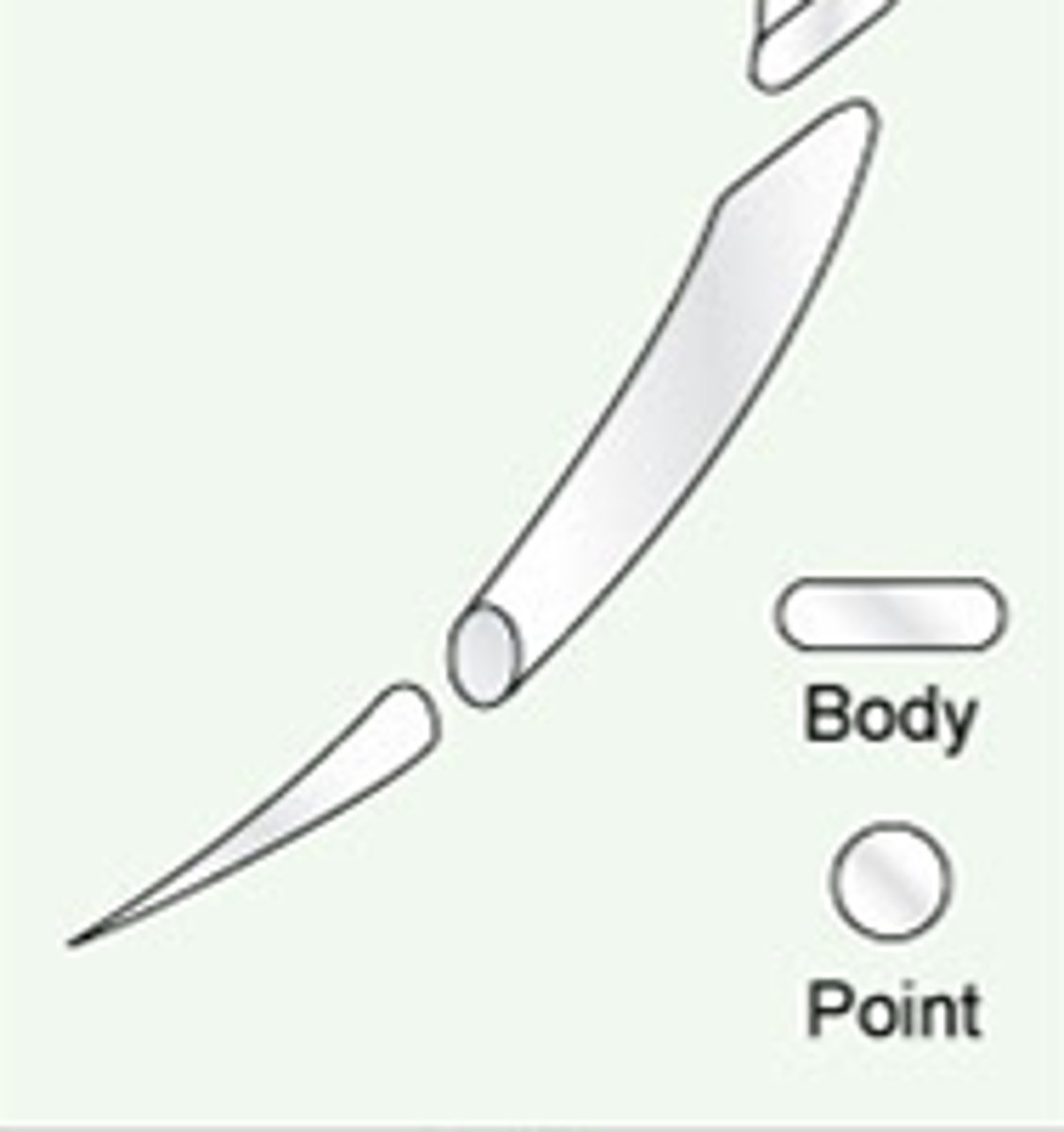
tapercut
has to cut its own way through the skin
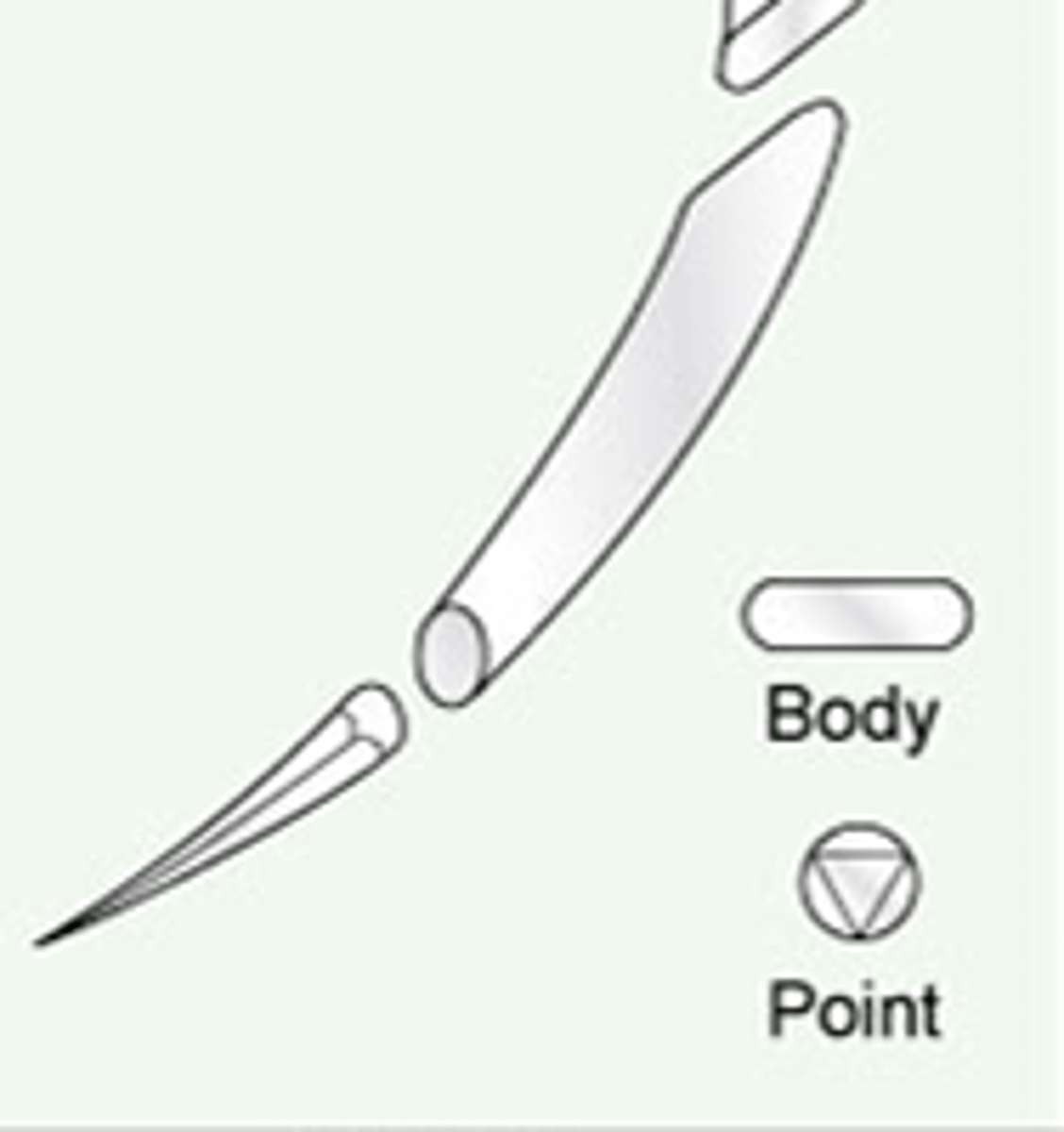
swage
Where the suture is attached to the needle
regular cutting
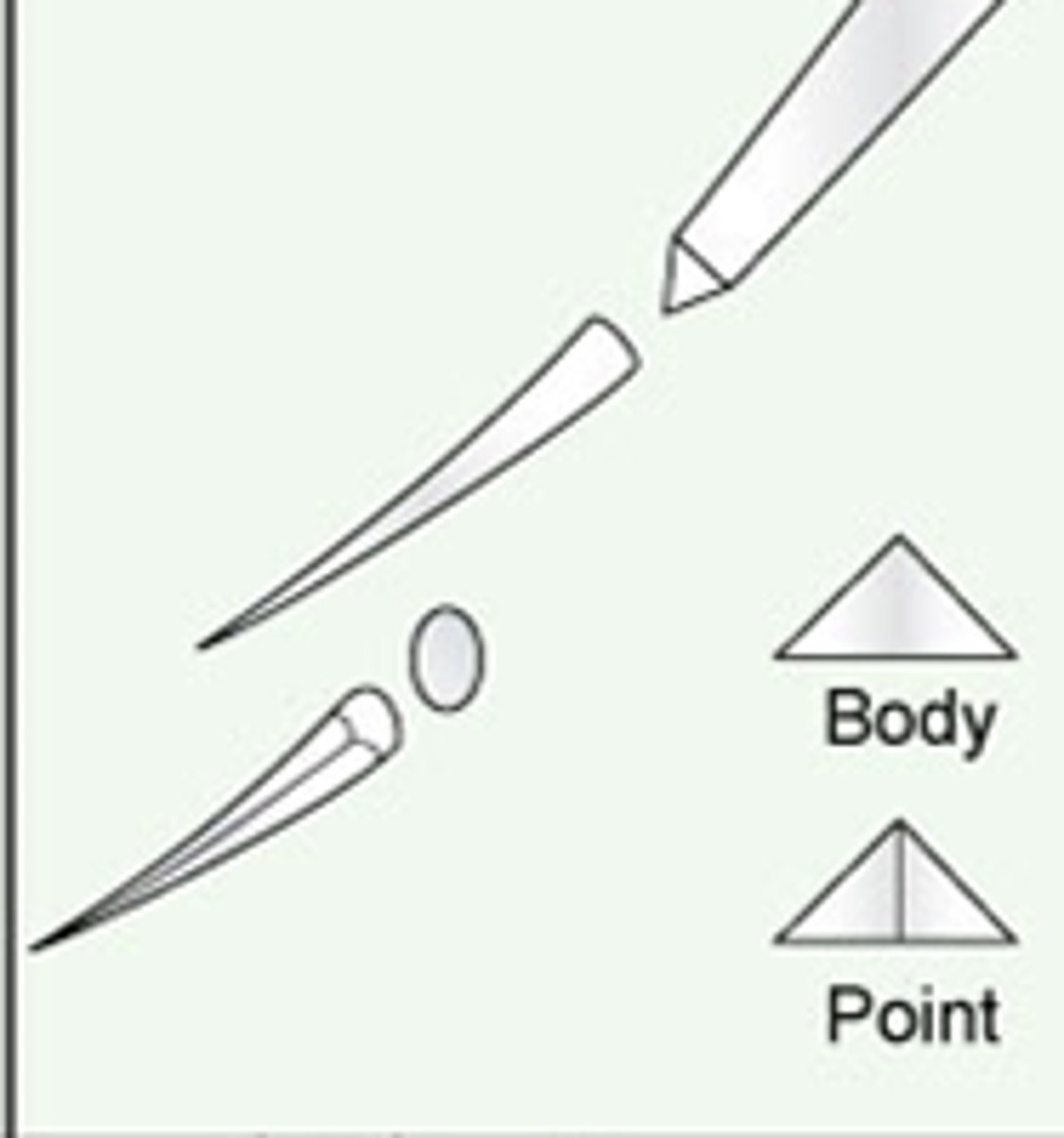
absorbable suture
a suture that loses most of its tensile strength within 60-90 days in living mammalian tissue
inflammatory reaction in tissue
Both absorbable and non-absorbable sutures promote ___
silk, catgut
What are the natural fiber sutures
cardiac surgery
Silk sutures are most commonly used on ___ surgeries
catgut
type of suture that is manufactured from the small intestine submucosa of sheep

chromic catgut
What is the recommended catgut because it decreases the inflammatory response
dexon, vicryl, monocryl, PDS, maxon
Name some absorbable sutures
nylon, prolene, stainless steel
Name some non-absorbable sutures
hydrolysis
Most sutures degrade by
cleavage of chemical bonds by the addition of water
What is hydrolysis
proteolysis
Catgut degrades by
breakdown of proteins into peptides and amino acids
what is proteolysis
absorbable
What kind of suture should you use for buried sutures
non-absorbable
What kind of sutures should you use to repair skin trauma
smallest
You should use the ____ suture necessary to do the job
knot failure
Suture failure is usually due to
gain in tissue strength
Tensile strength reduction corresponds to ___
tissue holding the suture, not the suture holding the tissue
What does strength come from
augment surgical repair of slow healing tissue
What are surgical meshes used to do
ingrowth of capillaries and fibroblasts
Small pore size of surgical mesh inhibits ___
it encounters anion in the moisture around a wound edge
Liquid monomer form of tissue adhesive polymerizes when
it will create a foreign body reaction and inflammation results secondary
Why should you not drop glue into the tissue incision
pinch skin edges together and apply to the surface on top of the skin
What is the correct way to apply tissue adhesive
simple interrupted pattern, simple continuous pattern, cruciate pattern, horizontal mattress pattern, buried interrupted and continuous patterns
Basic suture patterns:
simple interrupted pattern
easiest pattern to learn, appositional, provides secure closure, avoid excessive tension on tissue
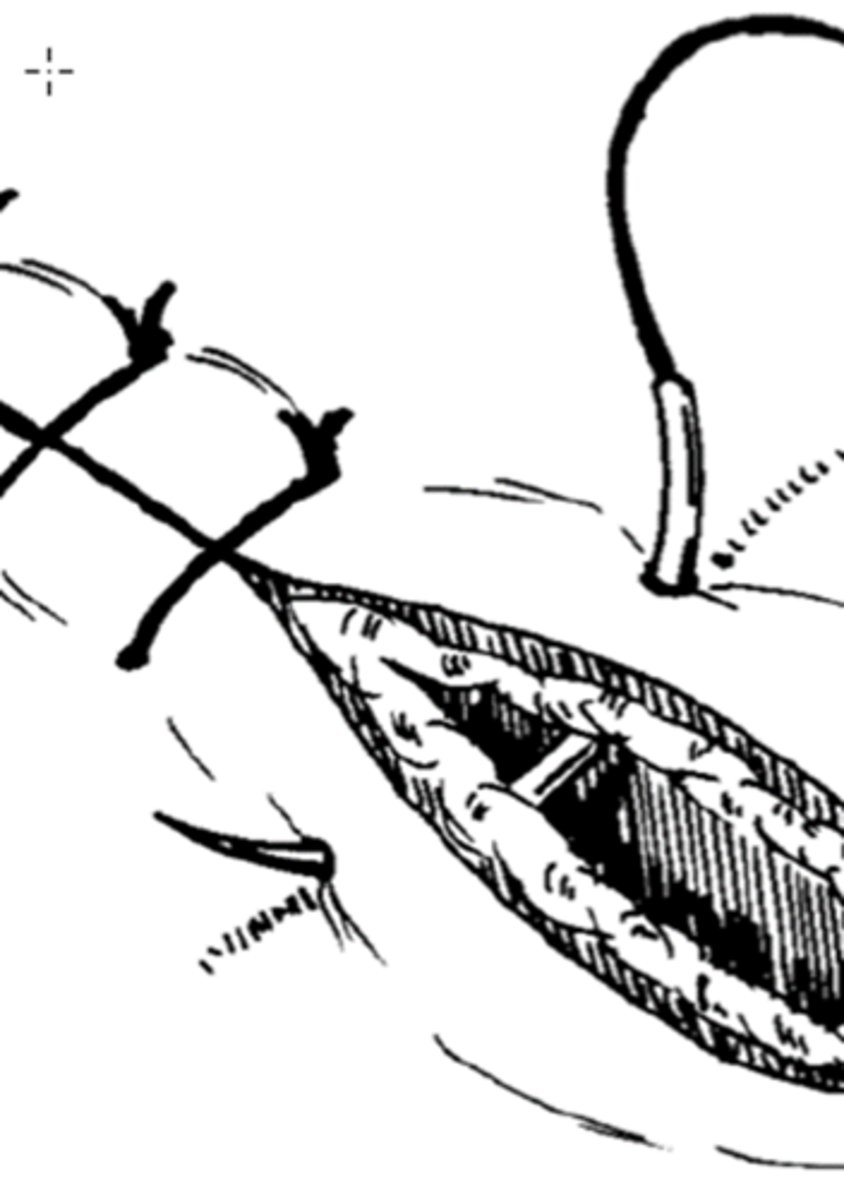
simple continuous pattern
appositional, tied off only at ends, saves time and suture material, not generally used for skin, avoid over-tightening, provides secure closure
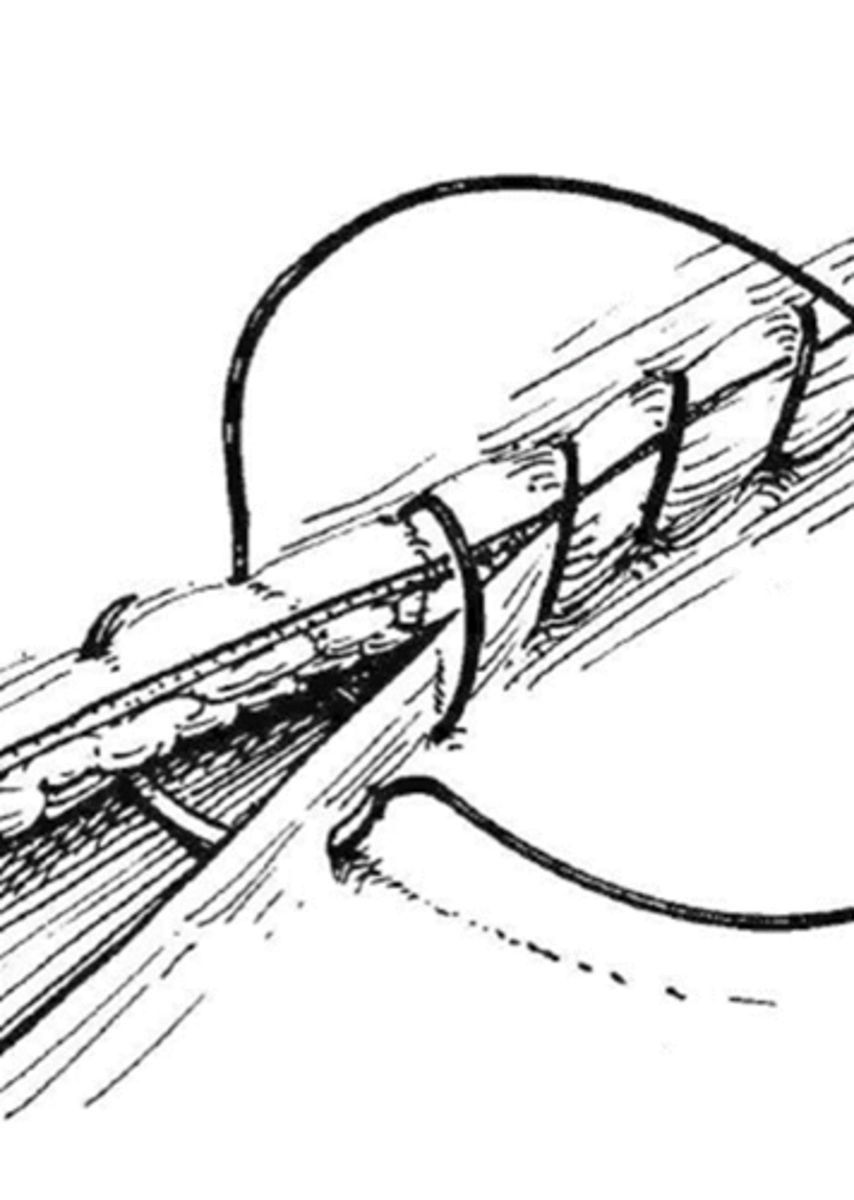
cruciate pattern
appositional, too much tension will cause tissue to invert, faster than simple interrupted, gives a strong closure
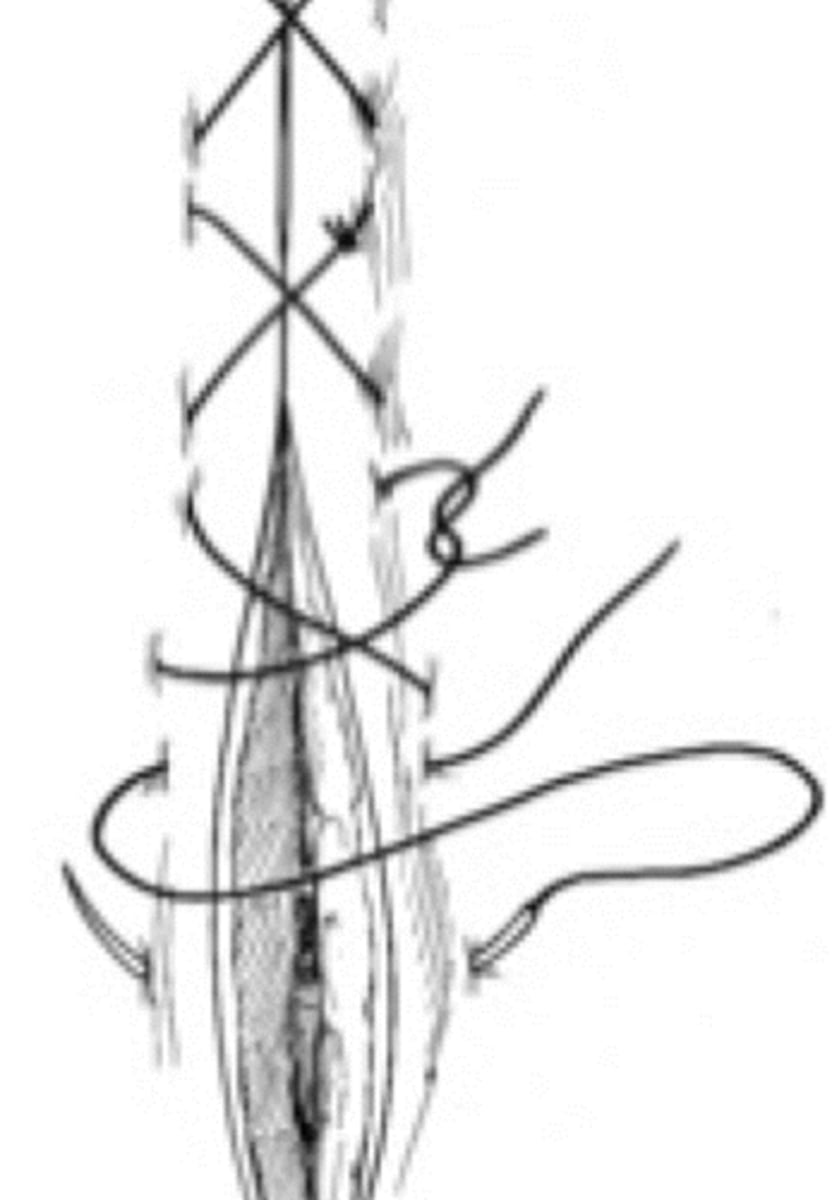
horizontal mattress pattern
tension relieving pattern, distributes forces away from the incision, too much tension will cause tissue to evert and damage blood supply to incision
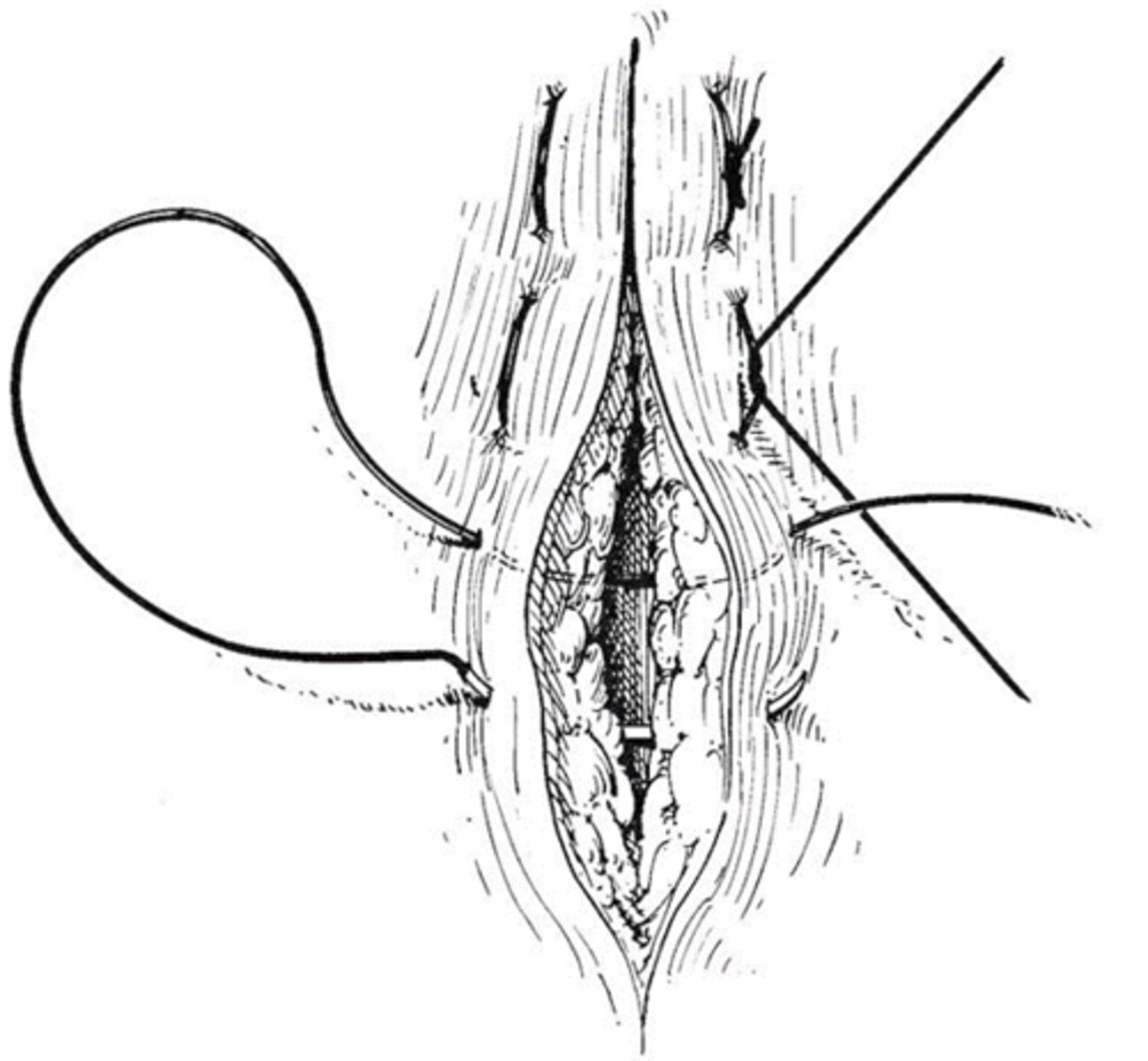
buried patterns
absorbable suture material, appositional, closes dead space, skin sutures support this layer of closure, knot is always at deepest layer
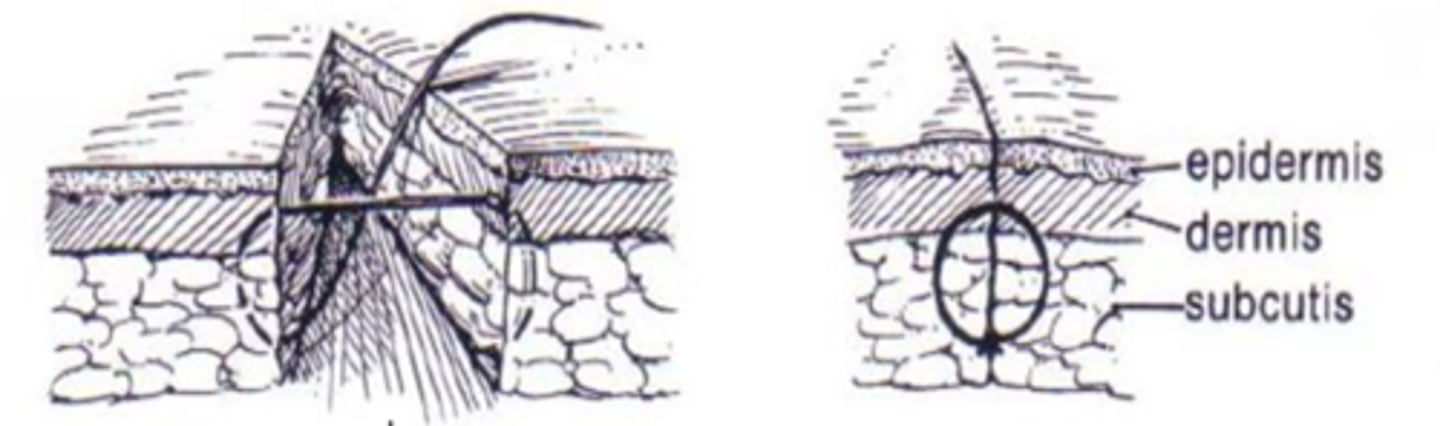
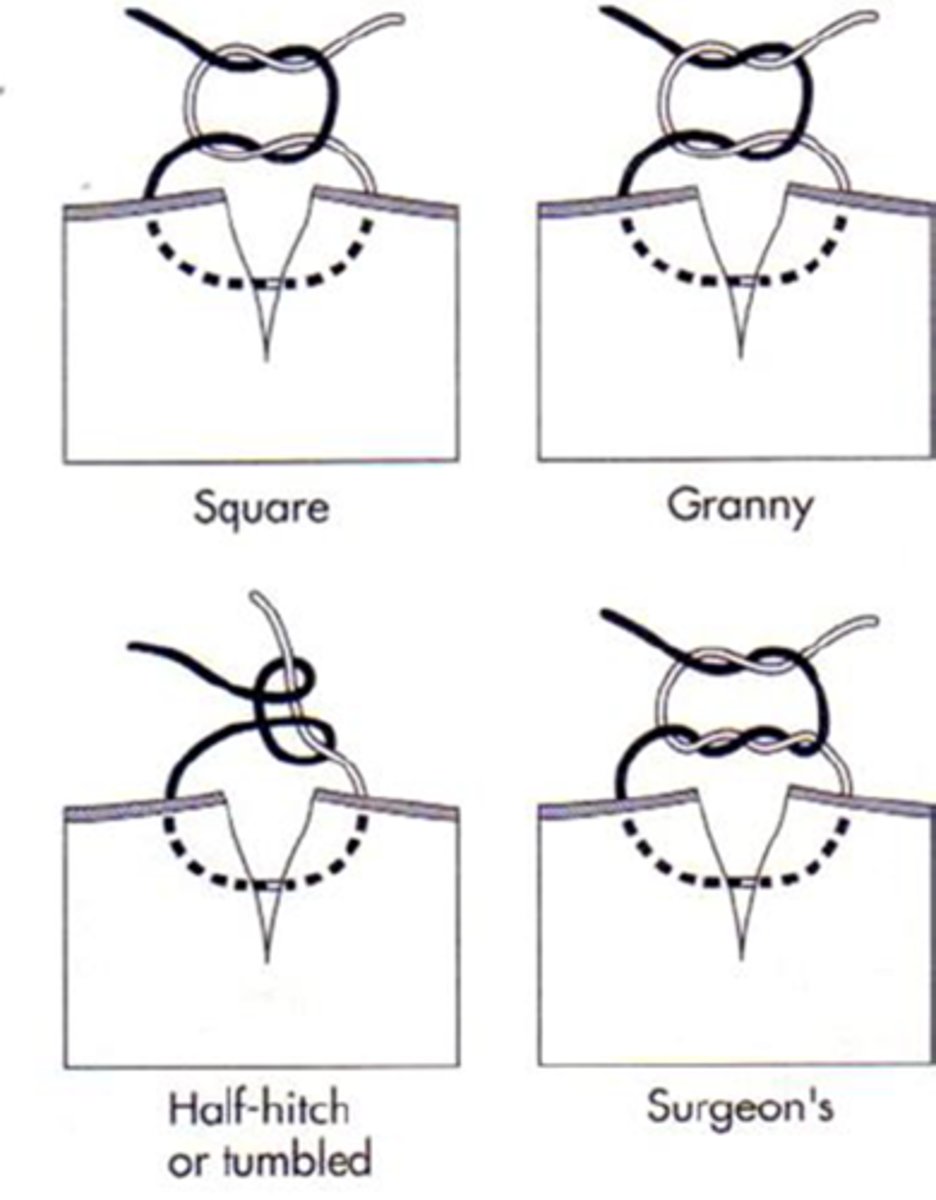
knots
various knot conformations depends on tissue and suture material