AP Biology: Unit One
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Independent Variable (x)
the factor that is manipulated or changed by the researcher
Dependent Variable (y)
the factor that is measured and is expected to change in response to the independent variable
Alternative Hypothesis
Predicts there is a relationship between two variables
Null Hypothesis
Predicts there’s NO relationship between two variables
Inductive Reasoning
Moves from specific observations to broader generalizations
Deductive Reasoning
A general premise or theory and moves to a specific, certain conclusion
Standard Deviation
Measures the dispersion of individual data points within a single sample or population
Standard Error
Measures the accuracy of a sample mean as an estimate of the true population mean
Calculating Standard Deviation
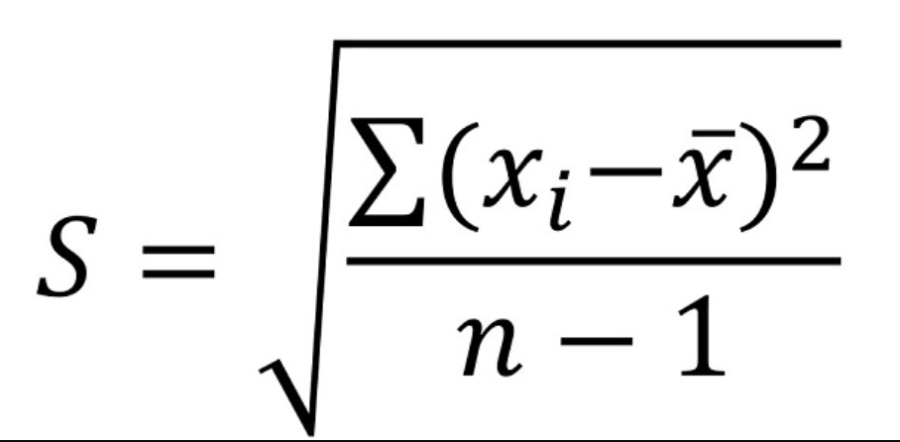
Calculating Standard Error
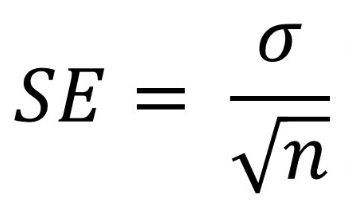
Is a Large or Small Standard Error Desired? Why?
A small standard error is desired because it indicates a more precise and reliable estimate of the true mean
What does overlap in error bars indicate?
There isn't a statistically significant difference between the data sets
Atomic Number (Left, Top)
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table.
Atomic Mass (Bottom)
the mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units. It is approximately equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons in the atom (the mass number) or to the average number allowing for the relative abundances of different isotopes.
How is the number of neutrons calculated?
Atomic Mass - Atomic Number
Ionic Bond
involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, forming positively and negatively charged ions that are attracted to each other
Covalent Bond
involve the sharing of electrons between atoms to achieve stability
Polarity
molecules have an uneven distribution of electron density, creating partial positive and partial negative charges
Nonpolarity
molecules have an even distribution of electrons, with no significant partial charges
If there’s cohesion, is there more or less polarity?
More Polarity
Positive Charge
more protons than electrons
Negative Charge
more electrons than protons
DNA nucleotide consists of what?
Phosphate, Pentose, Nitrogenous Bases
Phosphate
Molecules containing phosphorous and oxygen that gives the nucleotide a negative charge and forms the backbone of DNA
Pentose
A 5-Carbon Sugar (deoxyribose) which provides structural frame for the nucleotide and the DNA molecule
Nitrogenous Bases
Adenine → Thymine
Cytosine → Guanine
Bacteria
Eubacteria
Archaea
Archaebacteria
Eukarya
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
Domain Differences: Bacteria
Prokaryotic (No Nucleus)
Cell Wall: Peptidoglycan
Single Cellular DNA
Asexual
Domain Differences: Archaea
Prokaryotic (No Nucleus)
No Peptidoglycan
Single Cellular DNA
Asexual
Domain Differences: Eukarya
Eukaryotic (Nucleus)
Cell Wall Sometimes
Linear DNA
Asexual/Sexual
Carbohydrate Function
Quick Energy
Carbohydrate Components
Monomer: Monosaccharide
Polymer: Polysaccharide
Elements: C,H,O
Lipid Function
Long-Term Stored Energy, Cell Membranes
Lipid Components
Monomer: Fatty Acids
Polymers: Triglycerides, Phospolipids
Elements: H,C,O
Protein Function
“Work Horses” - Muscle, Antibodies, Enzymes
Protein Components
Monomer: Amino Acids
Polymers: Protein (Polypeptide)
Elements: C,H,N,O, SOMETIMES: S
Nucleic Acid Function
Store and express genetic information
Nucleic Acid Components
Monomer: Nucleotide
Polymers: N.A. —> DNA/RNA
Elements: N,C,H,O,P
Nucleic Acid: Pyrimadines
One nitrogen ring
Nucleic Acid: Purines
Two nitrogen rings
Nucleotide
Bases, Sugar, Phosphate
Nucleoside
Bases & Sugar
DNA
Stable, Double Stranded, Deoxyribose, ONE OXYGEN
RNA
Less Stable, Single Stranded, Ribose, TWO OXYGEN
When is a fatty acid saturated?
No double bonds
When is a fatty acid unsaturated?
Double bonds
Highly electronegative atom on the end of an R-group
Polar Amino Acid
A series of hydrocarbons on the end of an R-group
Nonpolar Amino Acid
Are nonpolar amino acids more likely to be found on the interior or exterior of a globular protein that exists in the cytosol of a cell?
Interior because they are hydrophobic
Are polar amino acids more likely to be found on the interior or exterior of a globular protein that exists in the cytosol of a cell?
Exterior because they’re hydrophilic
Steroids
Multiple rings of carbon atoms connected together
Triglyceride
3 fatty acids
What does too much triglyceride indicate?
Indicator of heart disease
Are phosphate groups polar or nonpolar?
Polar
Are fatty acids chains polar or nonpolar?
Nonpolar
Cell Distinctions: Prokaryotic
No Nucleus
Lack Membrane Bound Organelles
Single Circular Chromosomes
Asexual
Smaller
Cell Distinctions: Eukaryotic
Nucleus
Contain Membrane Bound Organelles
Linear Chromosomes
Asexual/Sexual
Larger
Taxonomy
The scientific discipline of identifying, naming, describing, and classifying living organisms into a hierarchical system based on shared characteristics.
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Natural Selection
The process where organisms with traits that help them survive and reproduce in their environment tend to pass those beneficial traits on to their offspring, leading to changes in a population over generations
Correct Sequence of Life’s Hierarchy
atoms/molecules
organelles
cells
tissues
organs
organisms
communities
populations
ecosystems
biosphere
Cation
positively charged ion formed when an atom loses electrons, making it have more protons than electrons.
Anion
negatively charged ion formed when an atom gains electrons, resulting in more electrons than protons
Why are water molecules attracted to each other? What is this called?
Cohesion: Water molecules are polar, meaning they have a slight positive charge on one end (the hydrogen atoms) and a slight negative charge on the other end (the oxygen atom). The positively charged hydrogen atom of one water molecule is attracted to the negatively charged oxygen atom of a nearby water molecule.
What property of water allows a water strider to walk on its surface?
the high surface tension of water, which results from the cohesive forces between water molecules.
Dehydration
a chemical process where two smaller molecules (monomers) bond together, forming a larger molecule (a polymer) while simultaneously releasing a molecule of water as a byproduct
Properties of Water that Demonstrate Why Water is Essential to Life
Cohesion
Adhesion
Specific Heat
Cohesion
is the force of attraction between molecules of the same substance, leading to properties like surface tension and water droplets forming a sphere.
Adhesion
is the force of attraction between molecules of different substances, enabling actions like glue sticking to paper or water clinging to plant tissues
Specific Heat
the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one Celsius degree
Essential Elements of Life
carbon
hydrogen
nitrogen
oxygen
phosphorus
sulfur
Hydrophobic
referring to substances, usually nonpolar, that repel water and do not readily mix with it, instead forming separate layers or droplets
Hydrophilic
describing substances that readily mix with or are attracted to water, typically due to polar or charged groups that form hydrogen bonds
Hydrolysis
a chemical reaction where a molecule is split into two parts by the addition of water, with the water molecule itself breaking into a hydrogen ion (H+) and a hydroxide ion (OH-)