Neuroanatomy
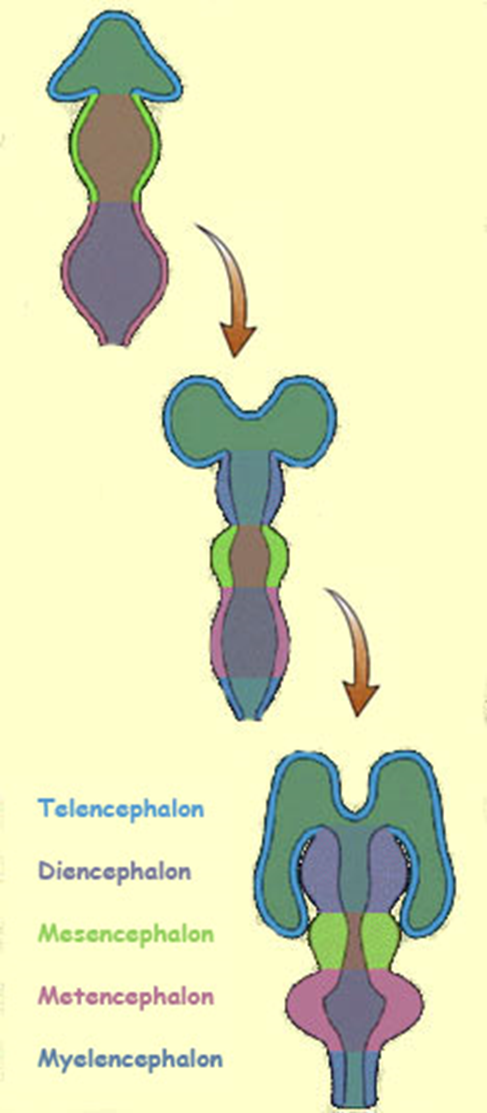
In the 4 week embryo, ___ primary brain vesicles develop from the neural tube. What are these called?
three - the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon
In the five week embryo, ___ secondary vesicles develop
5
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
In the 4 week embryo, ___ primary brain vesicles develop from the neural tube. What are these called?
three - the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon
In the five week embryo, ___ secondary vesicles develop
5
prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon
which becomes hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain?
Prosencephalon: forebrain
Mesencephalon: midbrain
Rhombencephalon: hindbrain
the cerebrum develops from the ____, the diencephalon develops from the ____, the midbrain develops from the ___, the pons and cerebellum develop from the ___, and the medulla develops from the _____.
Telencephalon: cerebrum (telephone—cellphone)
Diencephalon: diencephalon (di-di)
Mesencephalon: midbrain (messy=mid 😕 )
Metencephalon: pons, cerebellum ( T - two)
Myelencephalon: medulla (myyy medulla sharona)
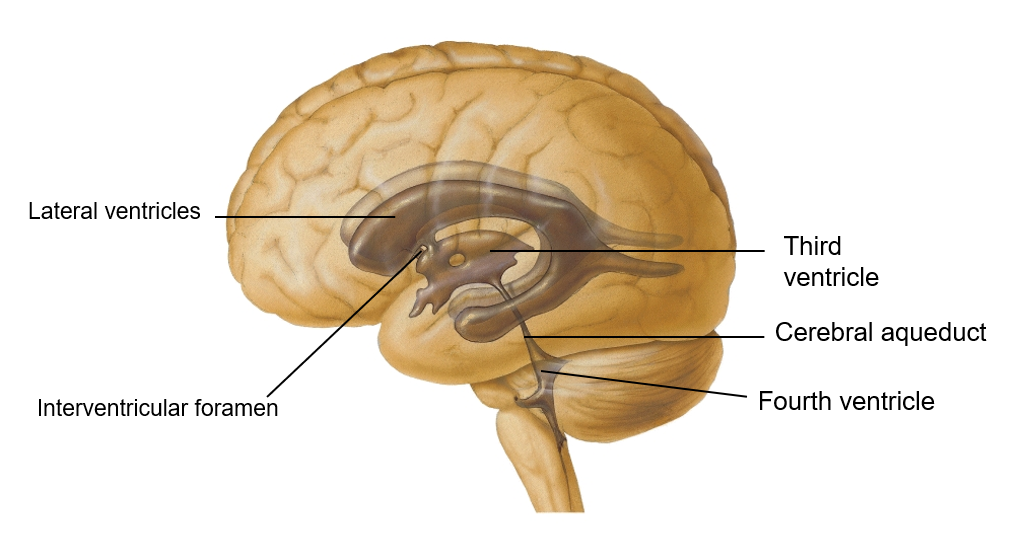
the ventricles of the brain are lined by ____ cells. They contain CSF and are continuous with each other and with central canal of spinal cord.
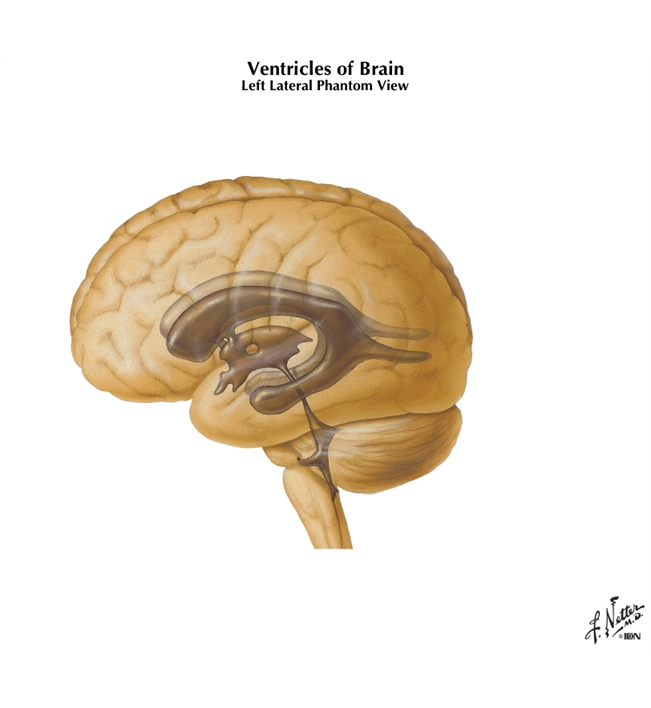
ependymal
what forms the CSF? How is the chemistry/pH of this fluid?
choroid plexus and walls of ventricles
CSF is alkaline with small amounts of amino acids and ions; it doesn’t contain cells
the lateral ventricles are located in each cerebral hemisphere; the third ventricle is in the _______ and the fourth ventricle is located ___________.
Third ventricle- in diencephalon
Fourth ventricle- The fourth ventricle is located dorsal to the pons and upper medulla oblongata
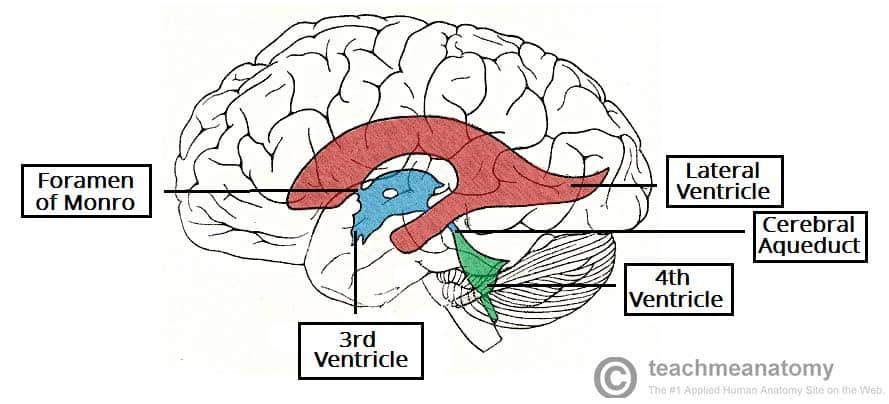
trace CSF from lateral ventricles to subarachnoid space (or central canal of spinal cord)
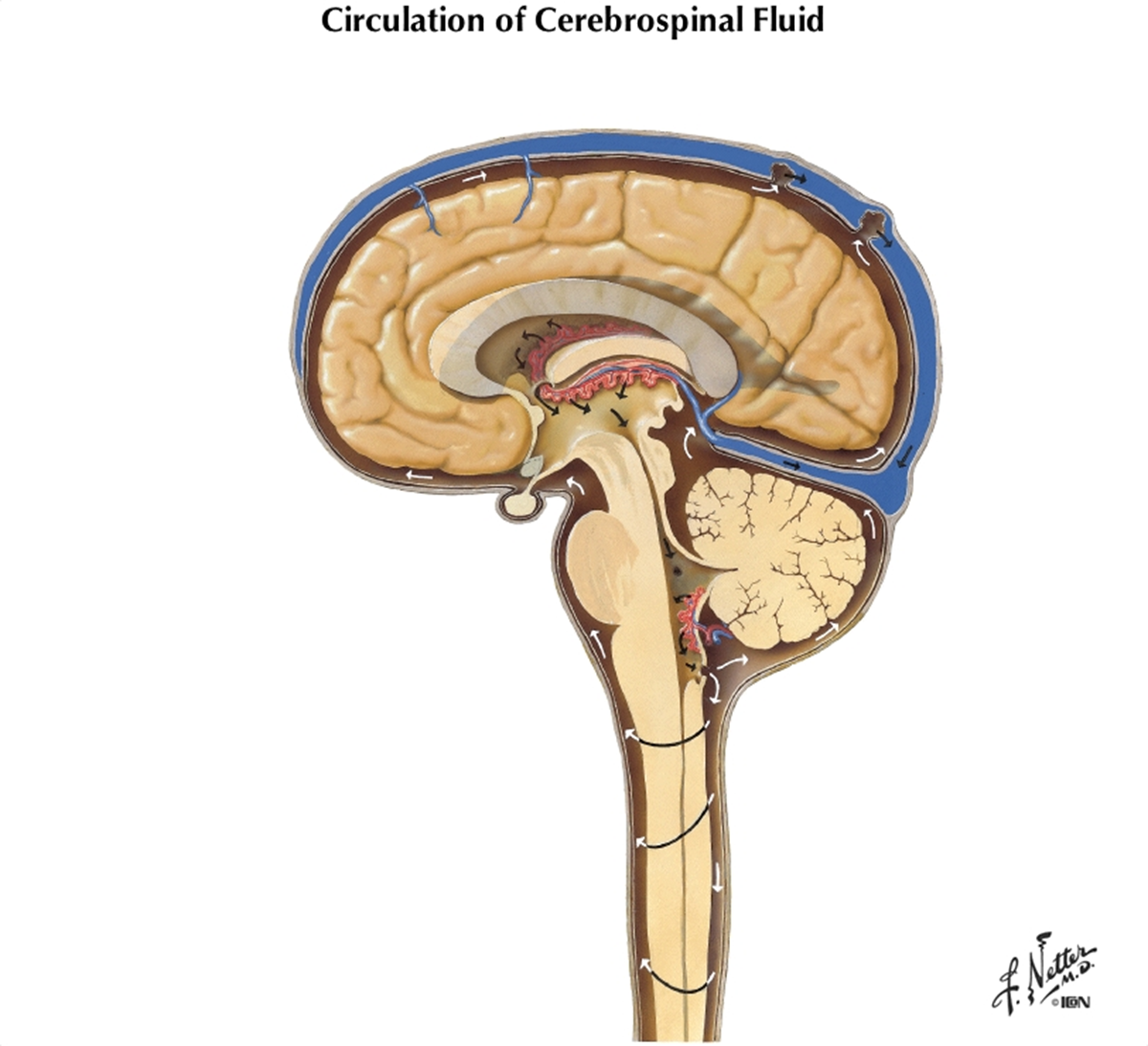
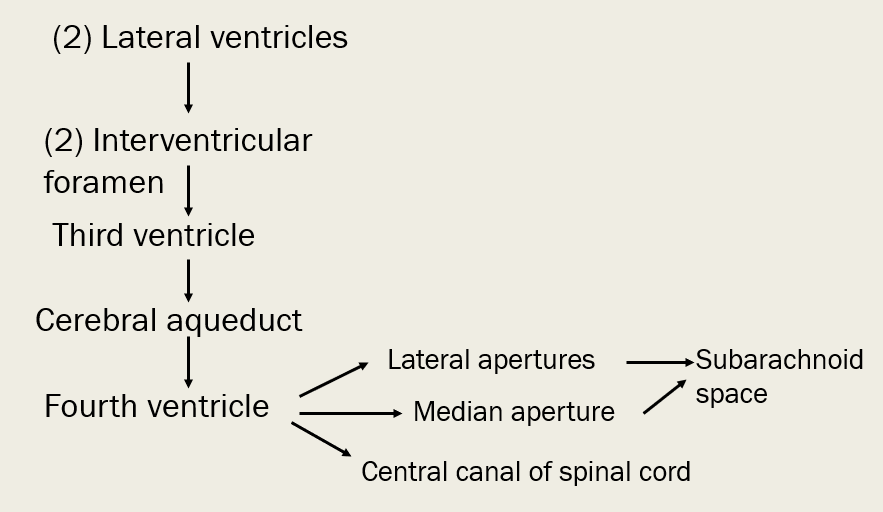
What are some things that can cause hydrocephalus? How can it be treated in infants?
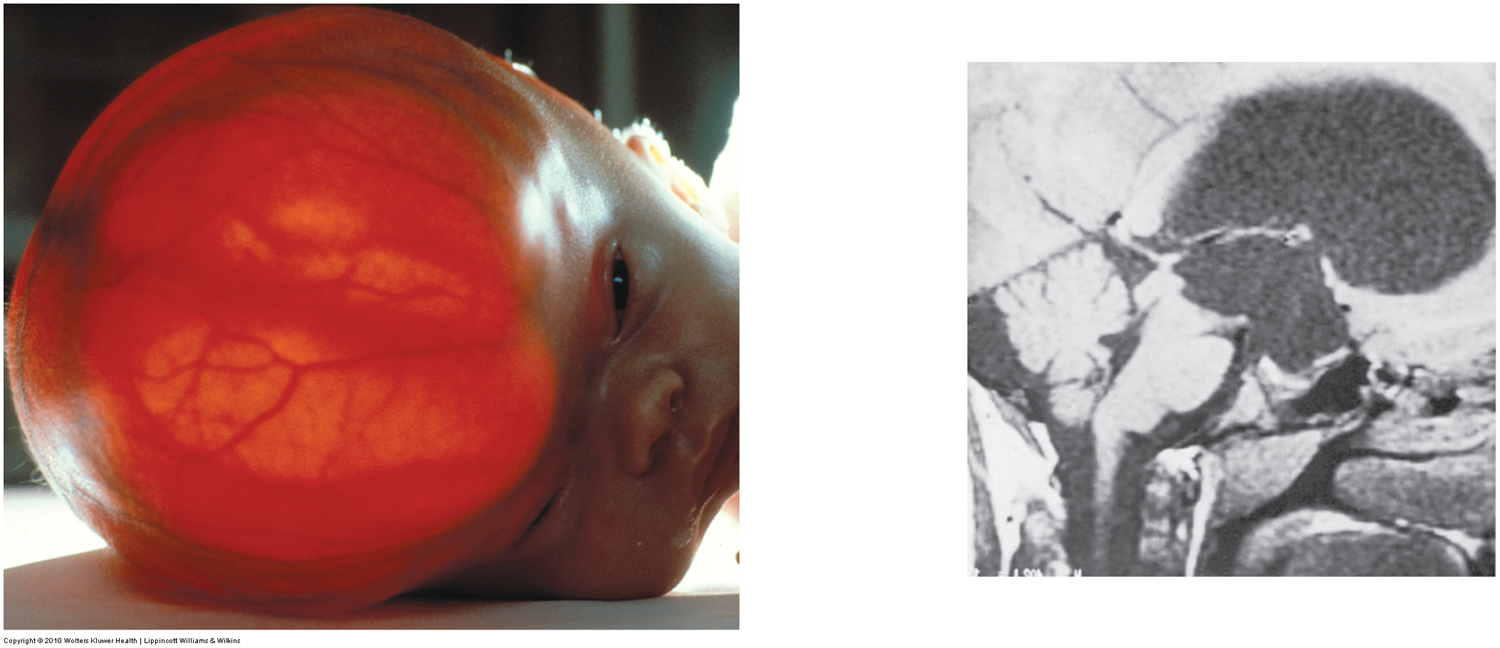
tumor, swelling, meningitis, overdeveloped choroid plexus in newborns
A shunt can be inserted to drain excess fluid to prevent further pressure buildup in ventricles
what is more likely to cause brain damage - hydrocephalus in infants or in adults, and why?
adults- because skull is rigid and pressure pushes inward causing damage to BV and soft neural tissue
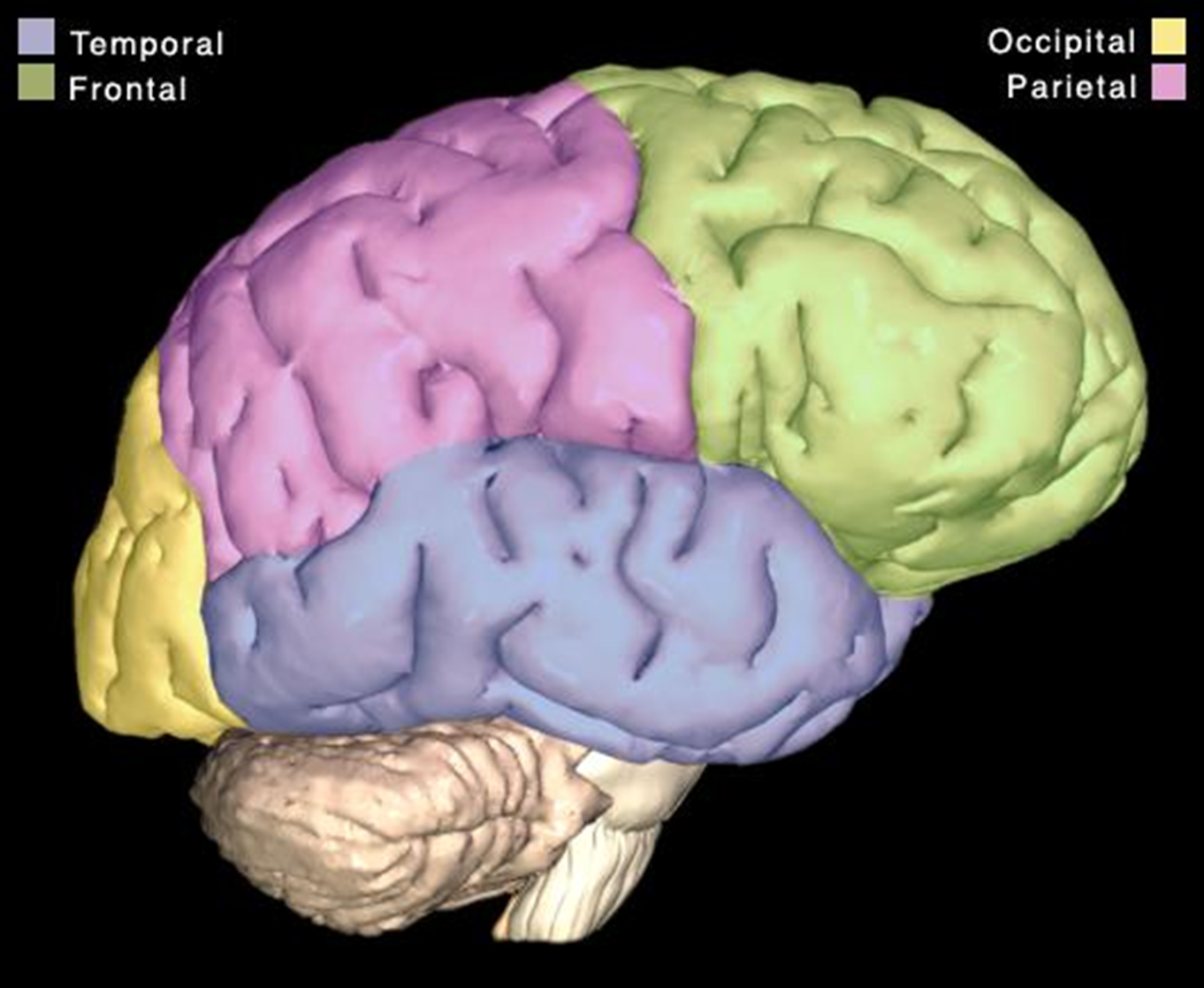
The superior region of the brain is the ____ and divided up into the following lobes…
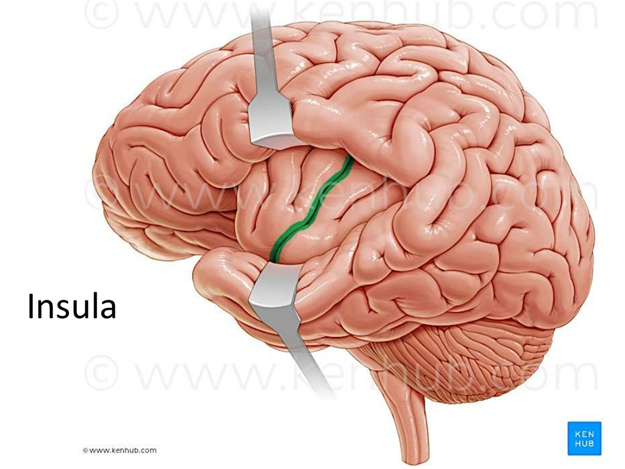
cerebrum
lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, (insula - see image on flip side)
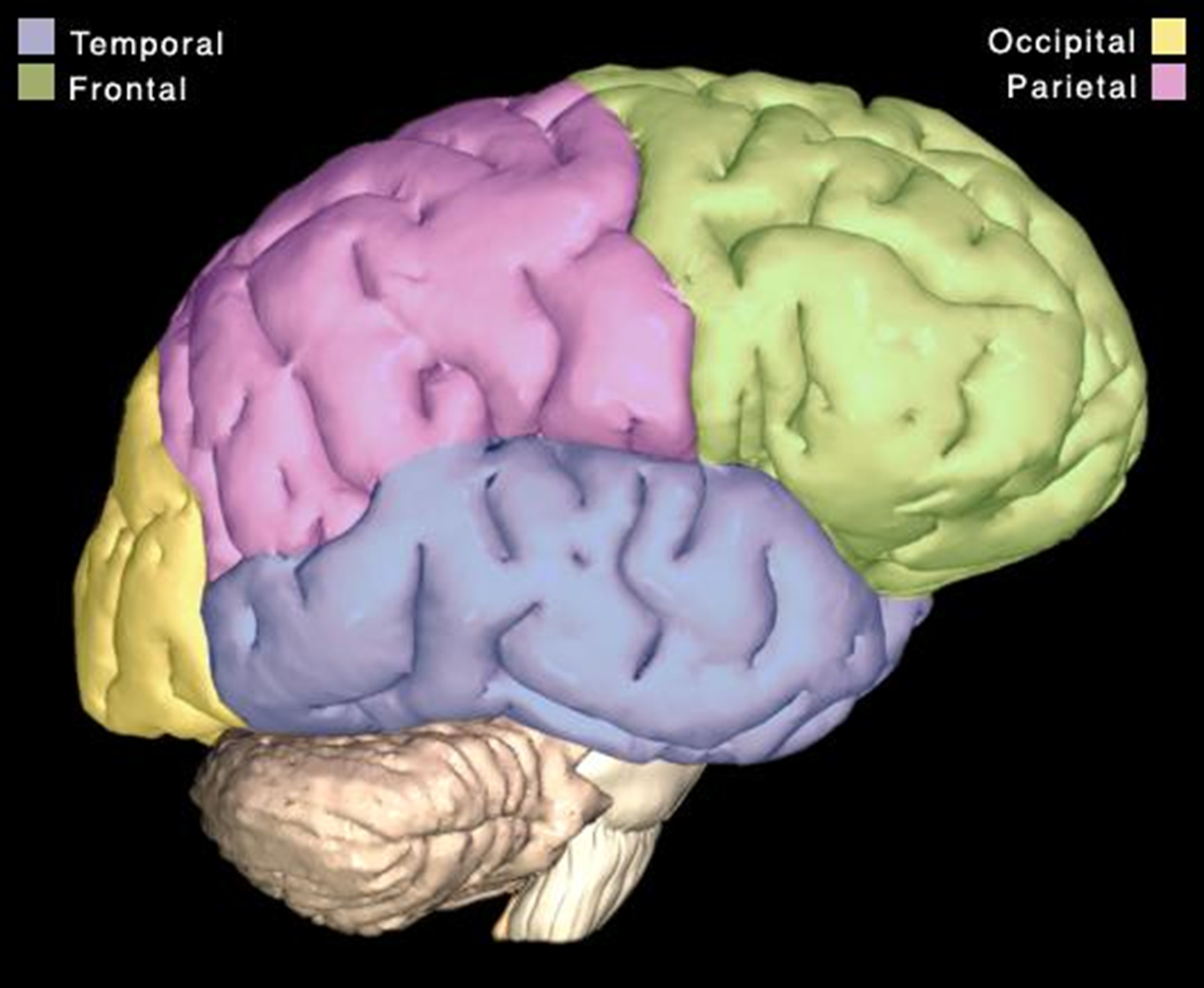
what part of our brain enables us to communicate, remember, and understand?
the cerebrum - processes sensory and motor information for the contralateral body
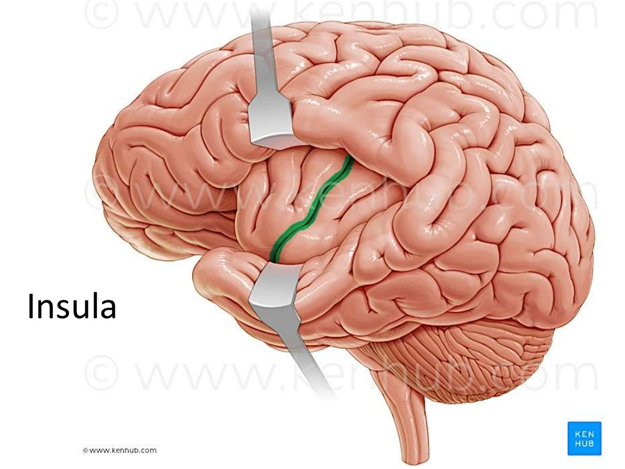
what lobe of our cerebrum processes information perceived as pain, contributes to emotional response to pain, and is included with the limbic system?
insula “feels the insult… inside the brain”
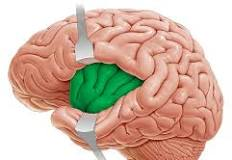
Gray matter, which is located in the cerebral cortex and deep gray matter, is made up of…
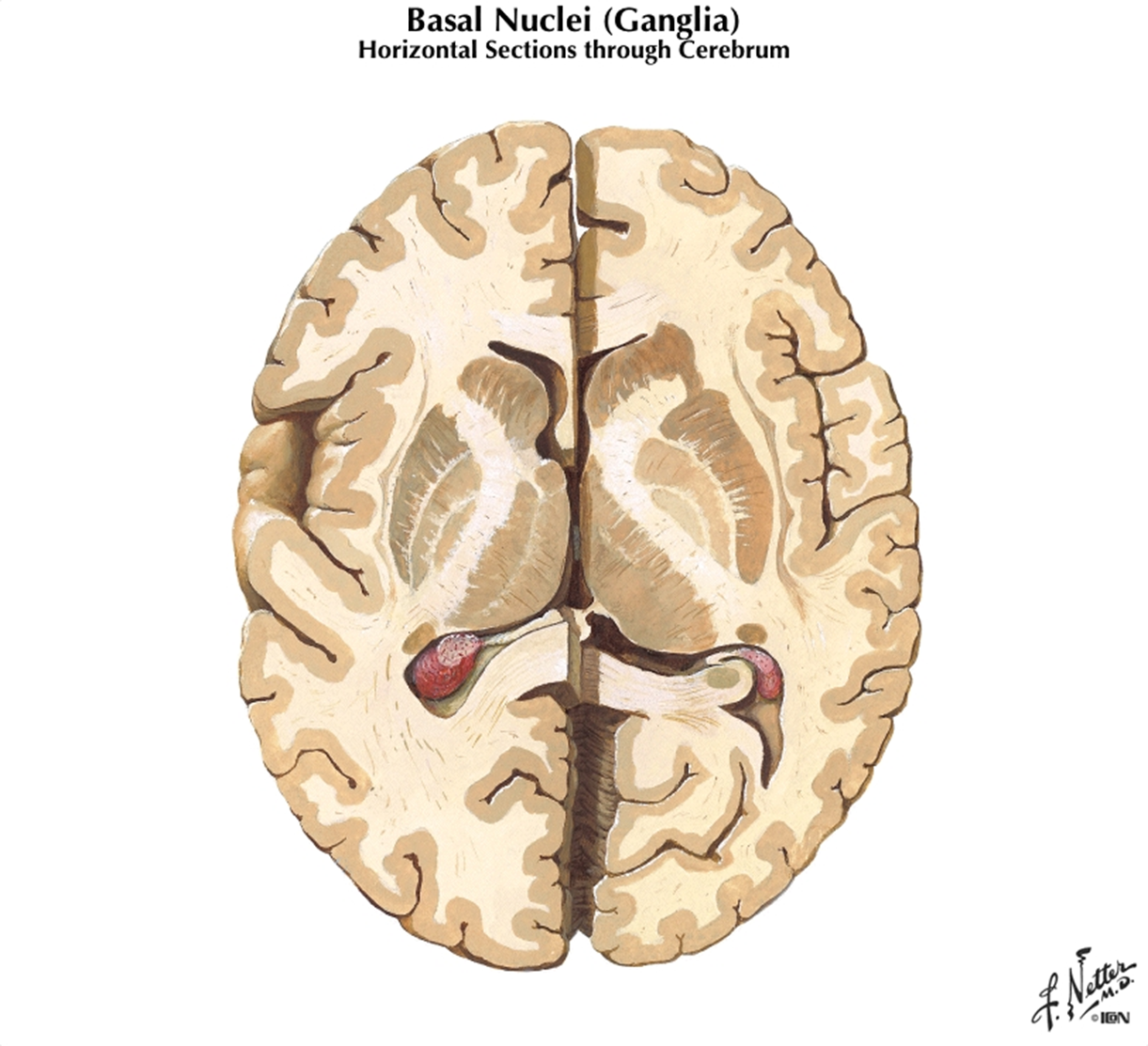
neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons; deep gray matter - basal ganglia/nuclei
the central sulcus separates what lobes?
frontal and parietal lobes
the lateral sulcus separates what lobes?
separates temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes
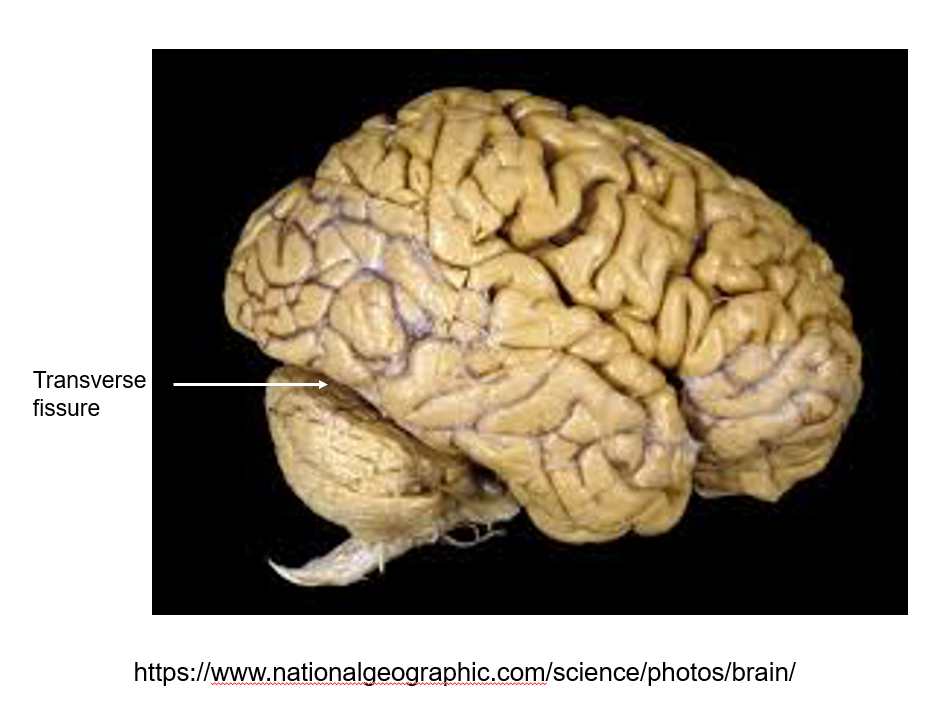
what separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum? what separates the two cerebral hemispheres?
Transverse fissure: separates cerebral hemispheres from cerebellum
Longitudinal fissure: separates cerebral hemispheres
tentorium cerebelli separates cerebral hemispheres from cerebellum; it lies in the transverse fissue
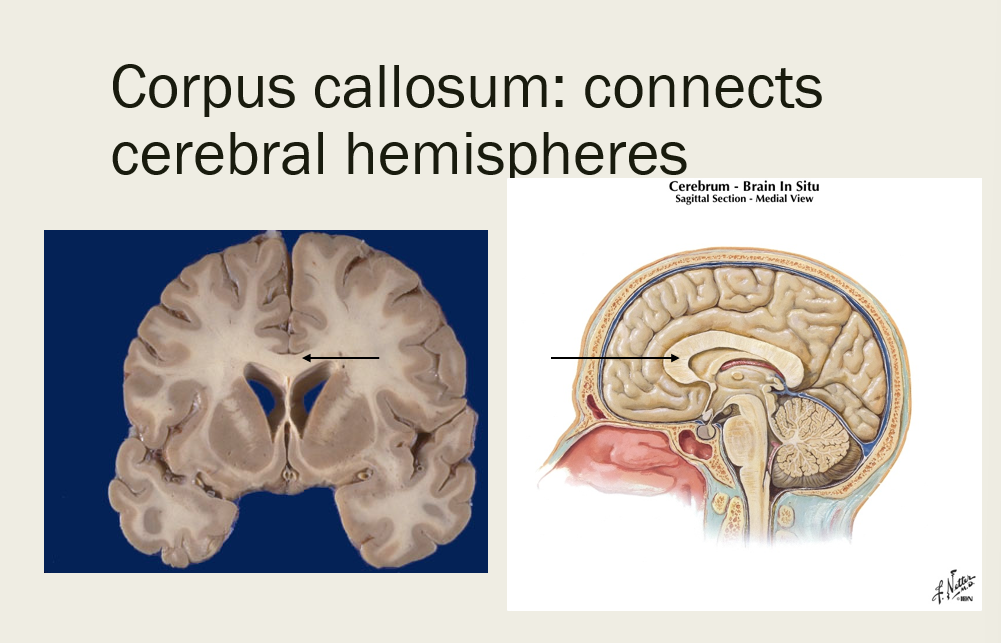
what connects the cerebral hemispheres?
corpus callosum
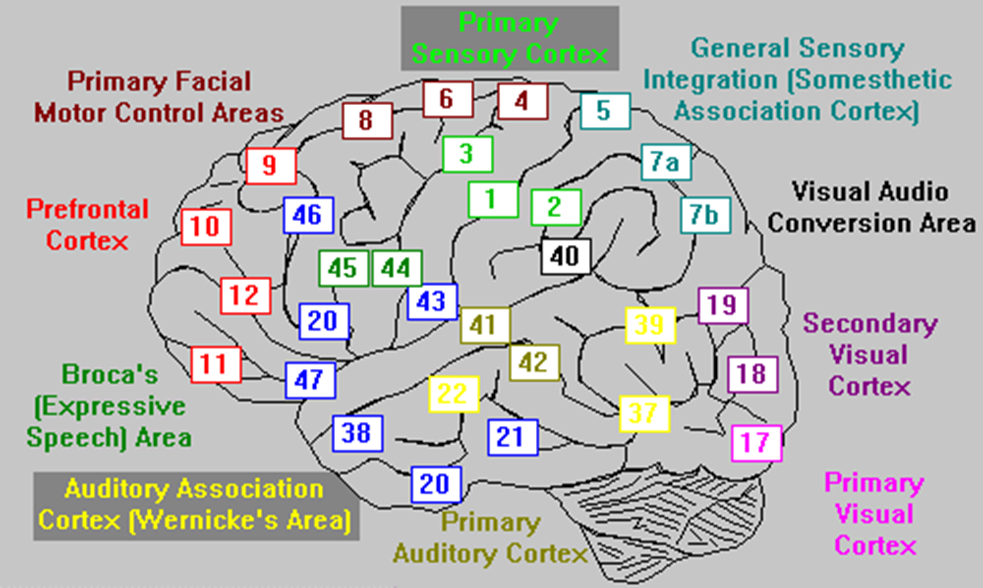
describe broadly what Brodmann’s areas are
regions of the cerebral cortex that control certain functions (i.e. Broca’s (expressive speech) area, primary auditory cortex, primary visual cortex, etc.)
Recall: cerebral cortex are responsible for contralateral sensory and motor control (perceive, communicate, remember, understand, appreciate, initiate voluntary movement)
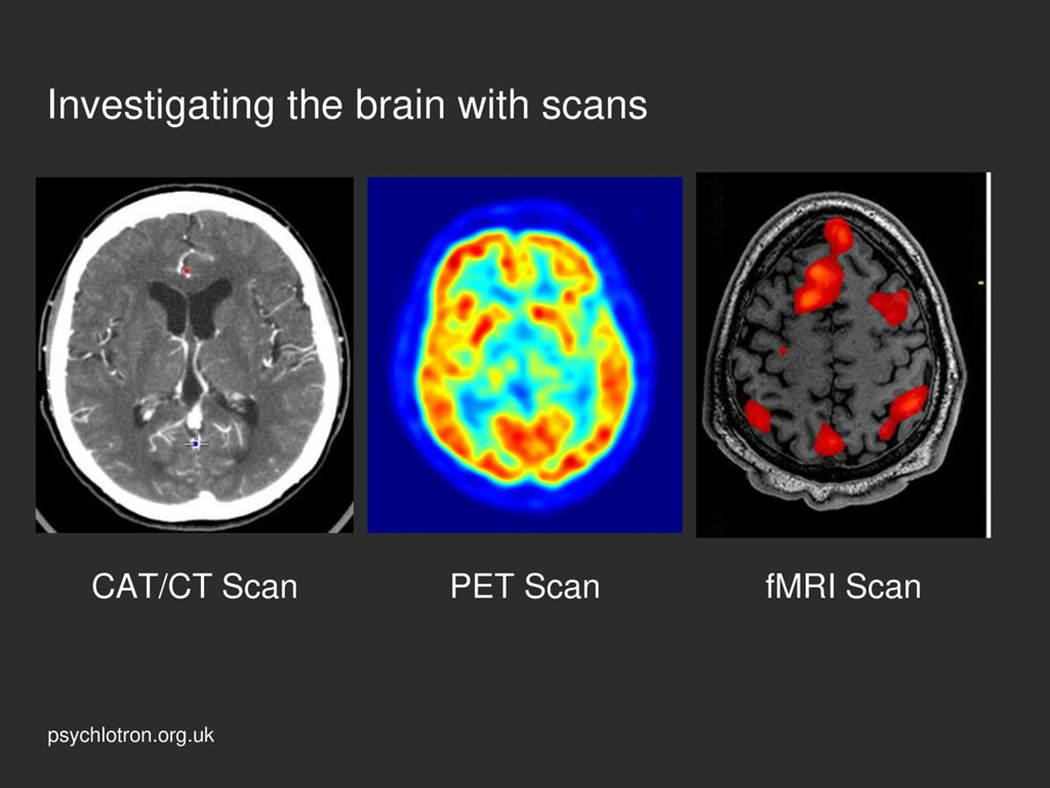
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) measures brain activity based on …
changes in blood flow
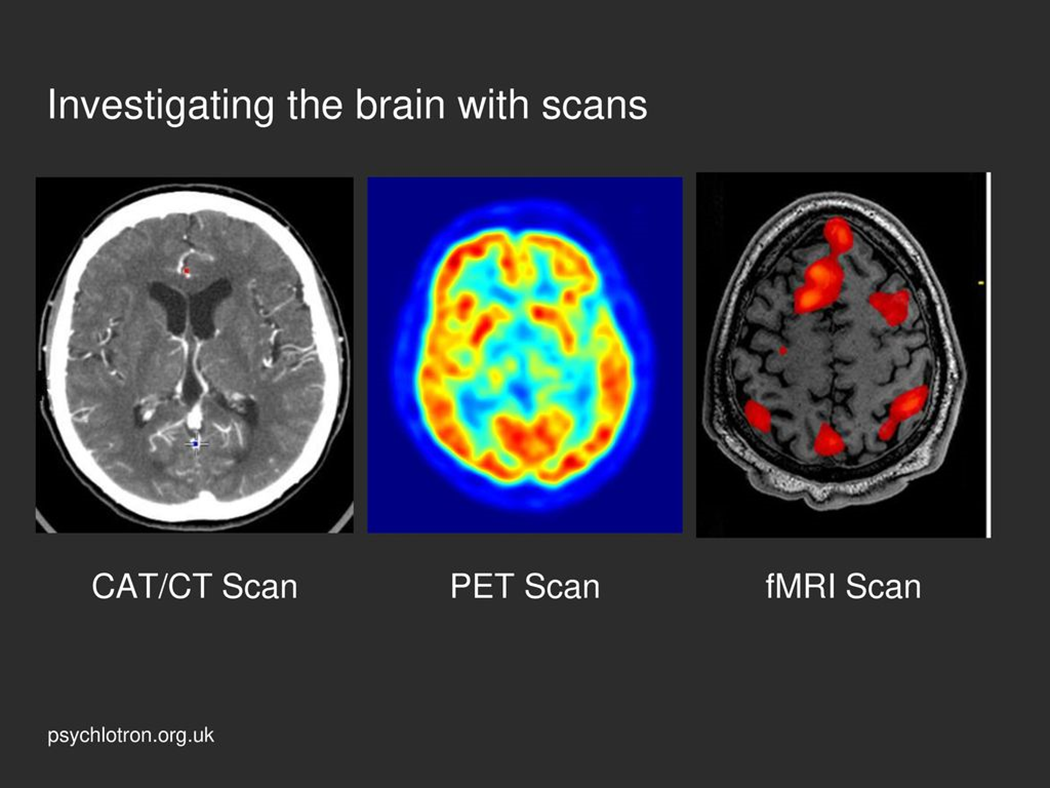
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan uses radioactive tracers to measure …
maximal metabolic activity
true or false - the cerebral cortex controls involuntary movements such as peristalsis and heart beating of the contralateral side
false; it controls voluntary movement to contralateral side (and sensory for that matter)
what is the difference between the primary motor cortex and the premotor cortex?
primary motor - execution
premotor - planning/preparing for movements
The Prefrontal cortex (Anterior Association Area) is responsible for cognitive functions such as…
intellect, judgement, reasoning, abstract ideas, complex problem solving, conscience
Broca’s area is responsible for…
motor speech area; speech production (not understanding)
The primary somatosensory cortex is located near the postcentral gyrus and is responsible for…
identifying body region being stimulated (somatosensory)
stereognosis
tests the individual's ability to perceive and integrate a variety of sensory modalities and to interpret the stimuli to identify small objects placed in the hand
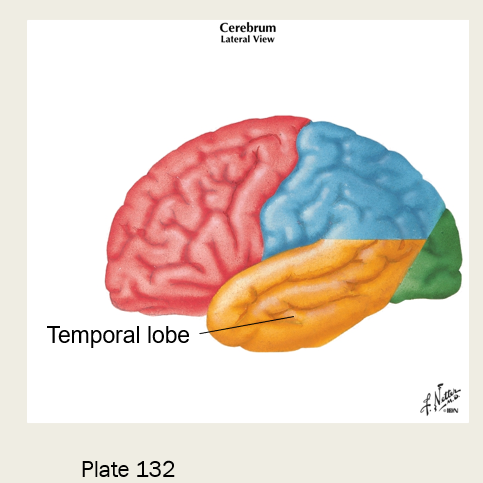
where is the primary auditory cortex located?
temporal lobe
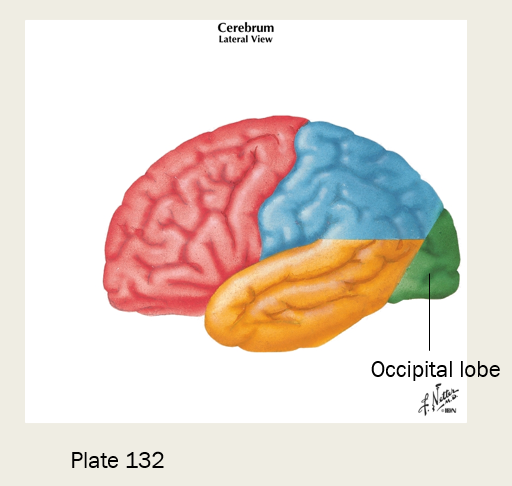
where is primary visual cortex located?
occipital lobe
Where is Wernicke’s area, and what is it responsible for?
left parietotemporal cortex
comprehension of spoken language; interpreting symbols
Which side - R or L is associated with nonverbal communication (gestures, facial expressions, tone of voice, posture)
Right side
the corpus callosum is an example of a _______, which connects two homologous areas of cerebral hemispheres to function as coordinated whole
commissure (connects hemispheres of brain)
unlike association fibers, which are only on one side of the brain
true or false - association fibers connect regions between the two hemispheres
FALSE; association fibers connect different regions (non homologous) of the same hemisphere, but not between the two hemispheres
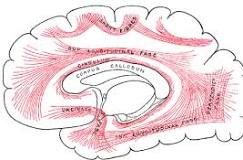
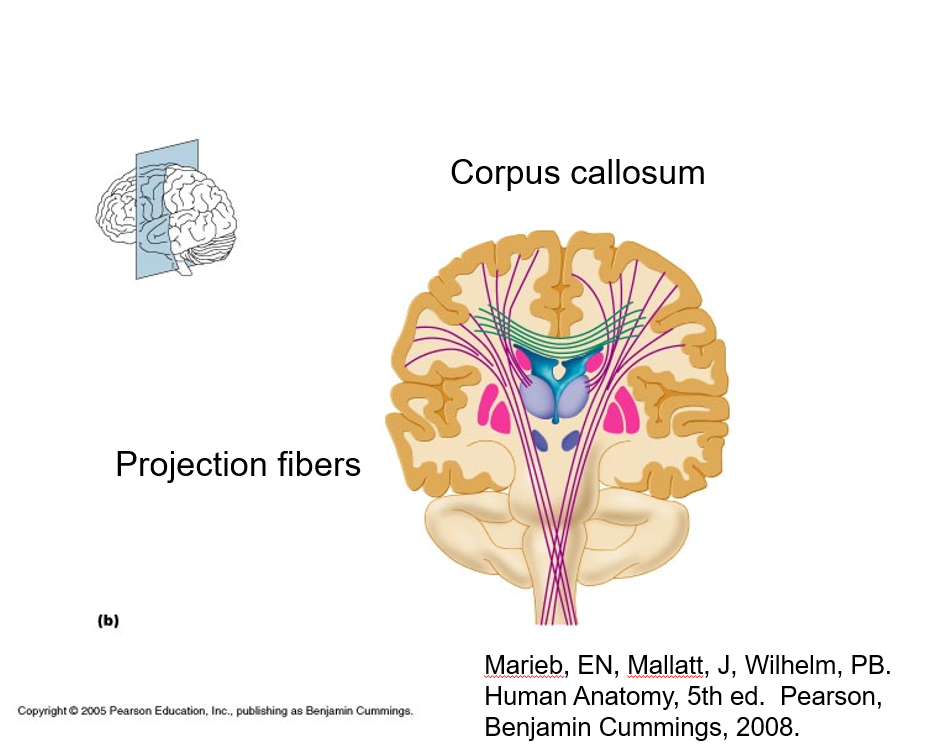
projection fibers connect the ________ with the rest of the nervous system
cortex
Basal Ganglia are involved in controlling __________. Give an example
Basal Ganglia are involved in controlling movement, especially relatively slow and stereotyped movements- arm swing during walking
the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus are all ….
basal nuclei
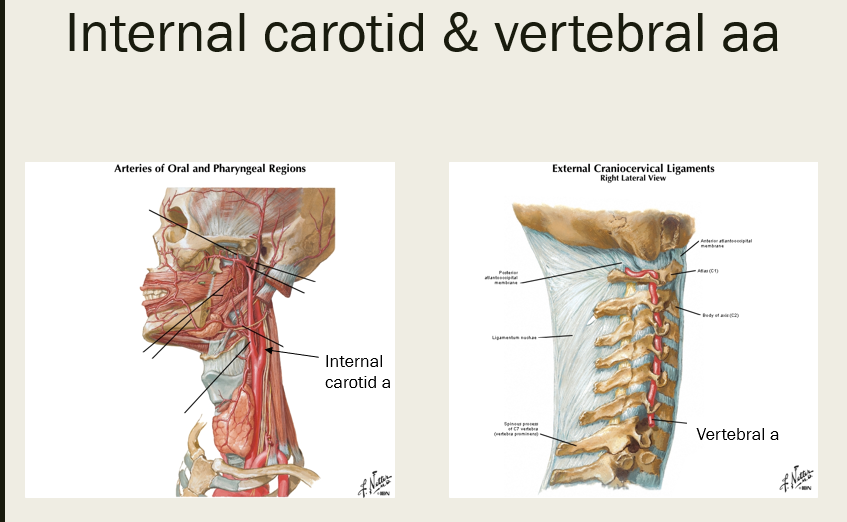
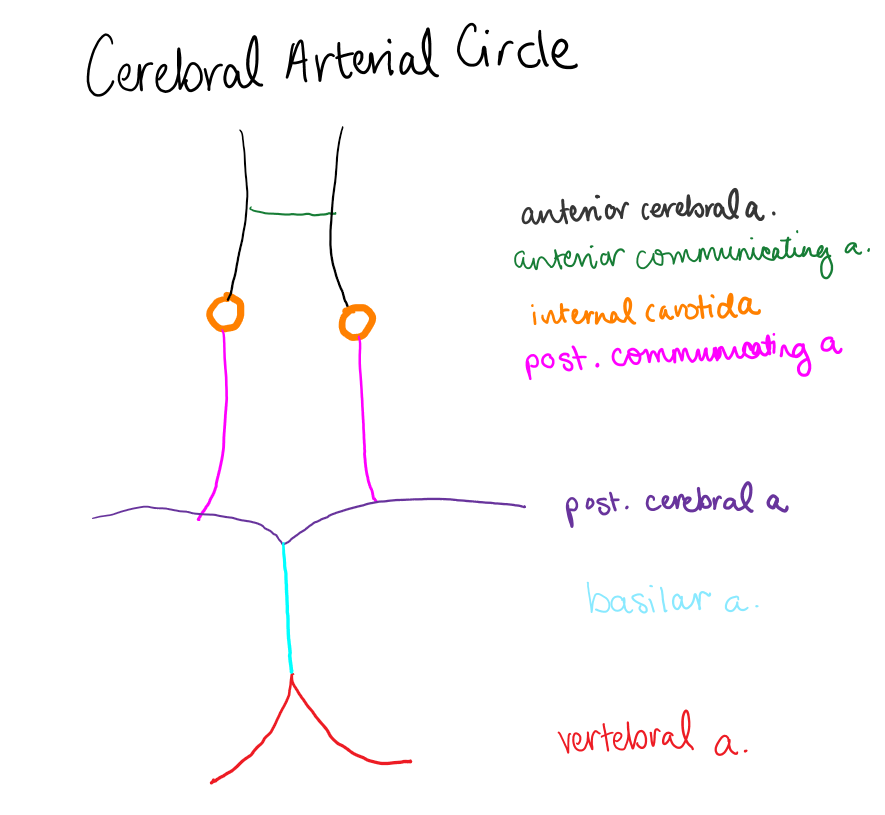
the internal carotid artery and vertebral artery form an anastomosis on the ventral surface of the brain, which is called the…
(see pic of internal carotid and vertebral aa prior to entering skull)
cerebral arterial circle (Circle of Willis is the eponym)
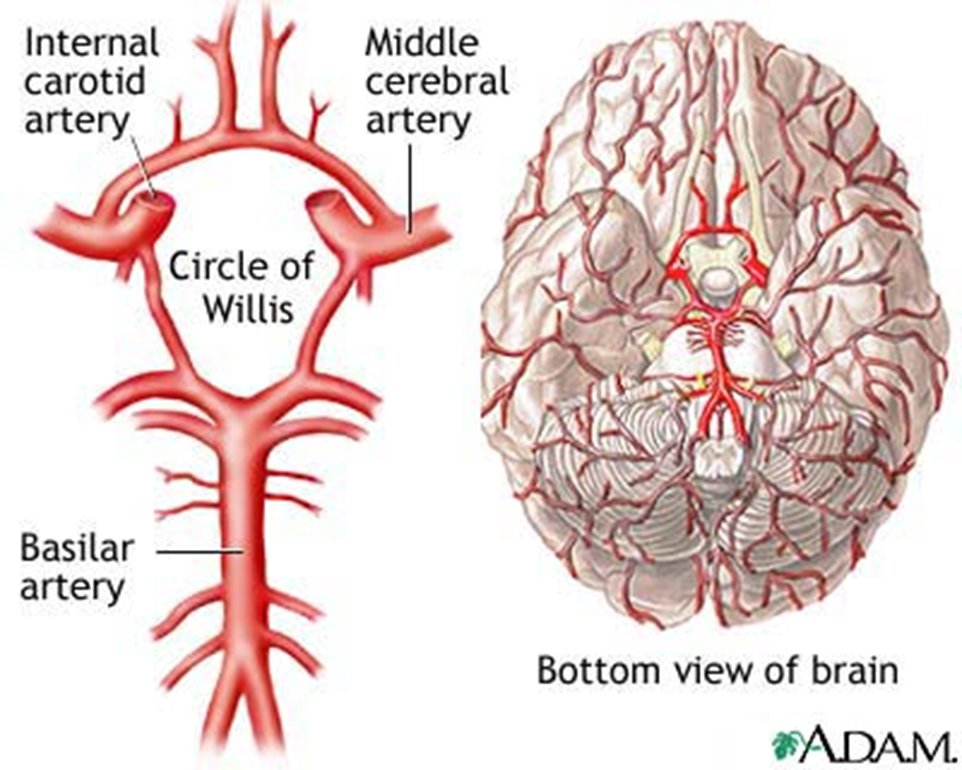
Name the arteries (or draw them out) that form the Cerebral Arterial Circle
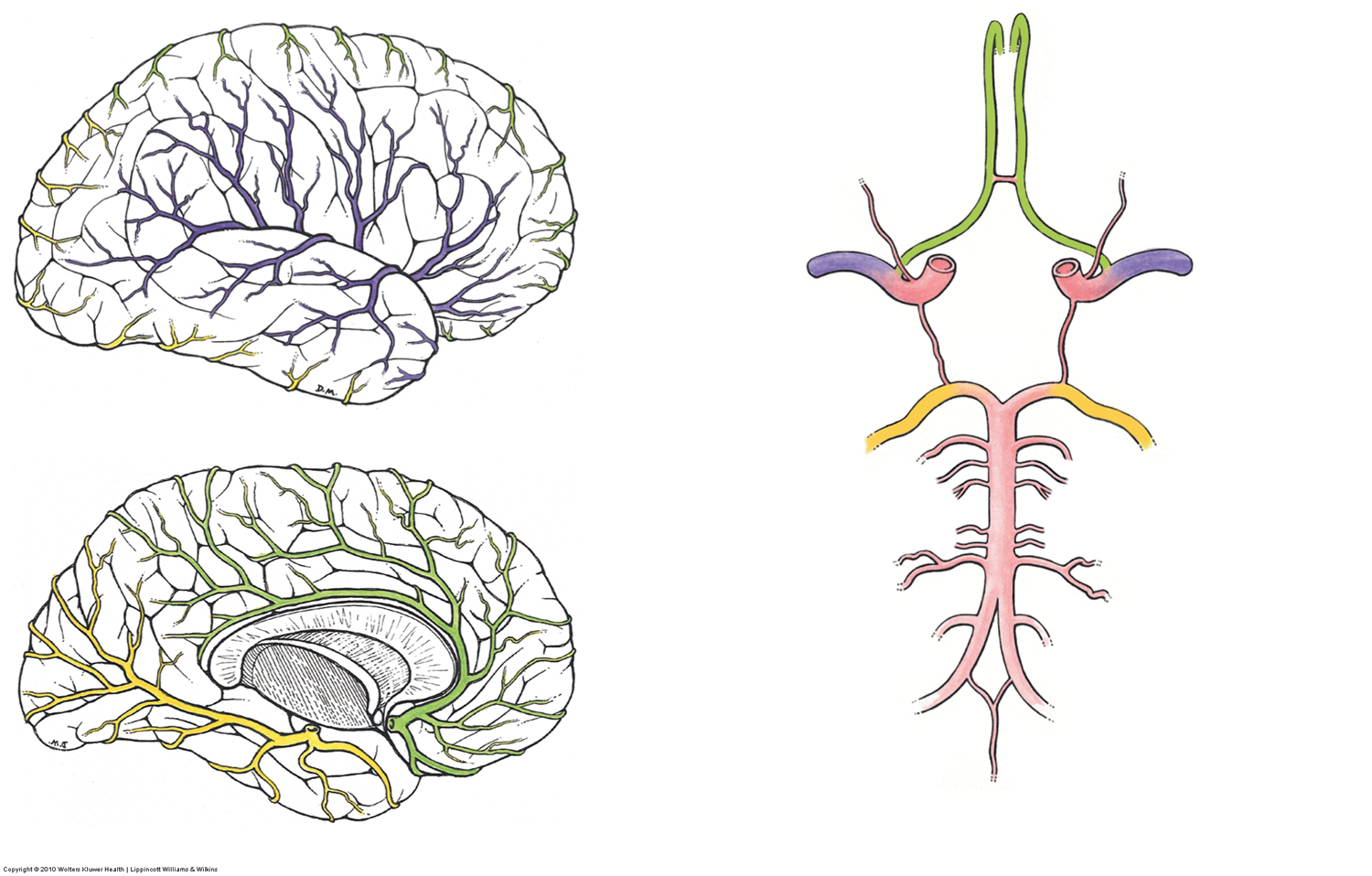
Anterior cerebral aa, anterior communicating a, internal carotid aa, posterior cerebral aa, posterior communicating aa (idk if basilar a counts but i dont think so)
True or False - the Middle Cerebral a and opthalmic are not in the cerebral arterial circle
True - they are not, but they are branches of the internal carotid a which is a part of the cerebral arterial circle
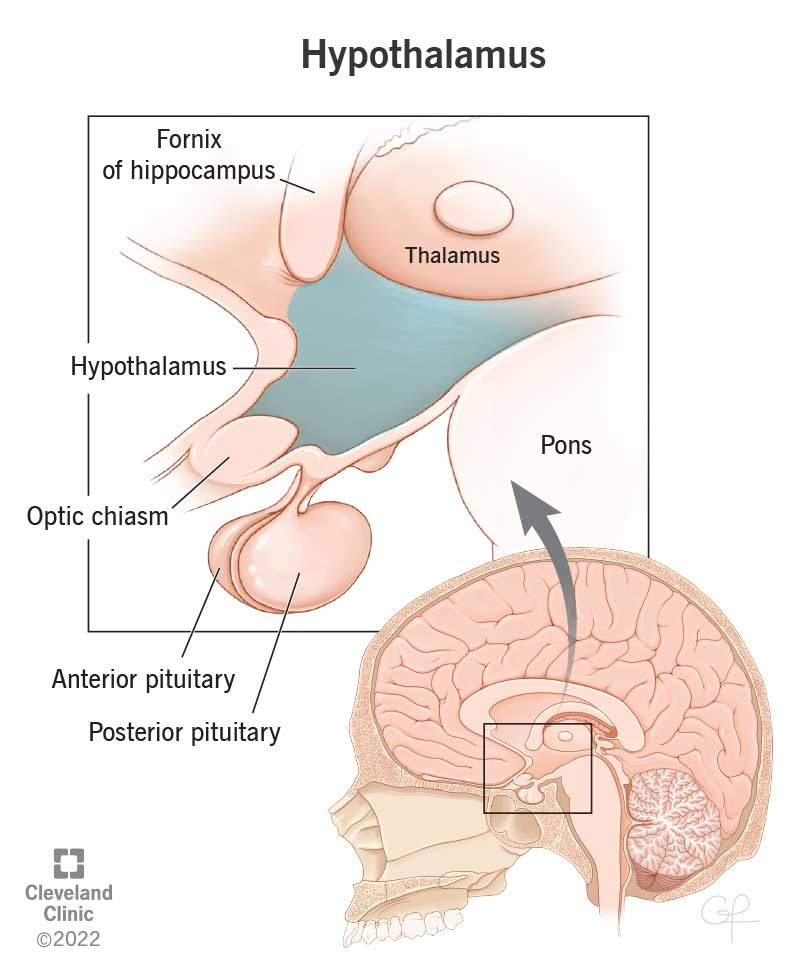
what structure of the brain sits between the thalamus and the pituitary gland?
hypothalamus
which artery is a continuation of the internal carotid a and covers most of the lateral surface of cerebral hemispheres (frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes)?
middle cerebral artery
(see purple)
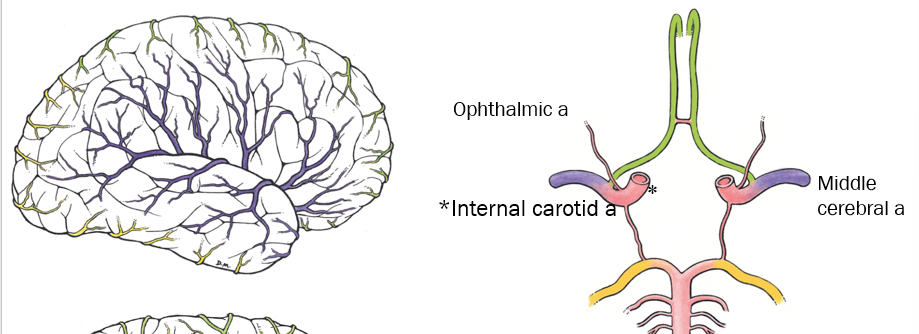
what artery does the vertebral artery branch off of, and what does it travel through before reaching the foramen magnum? (go from inferior to superior)
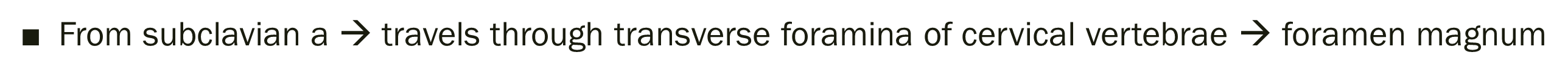
The thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus are all a part of this structure:
diencephalon
What part of the diencephalon is known as the relay center of the brain? What is its role?
Thalamus
mediates sensation, motor activity, cortical arousal, memory
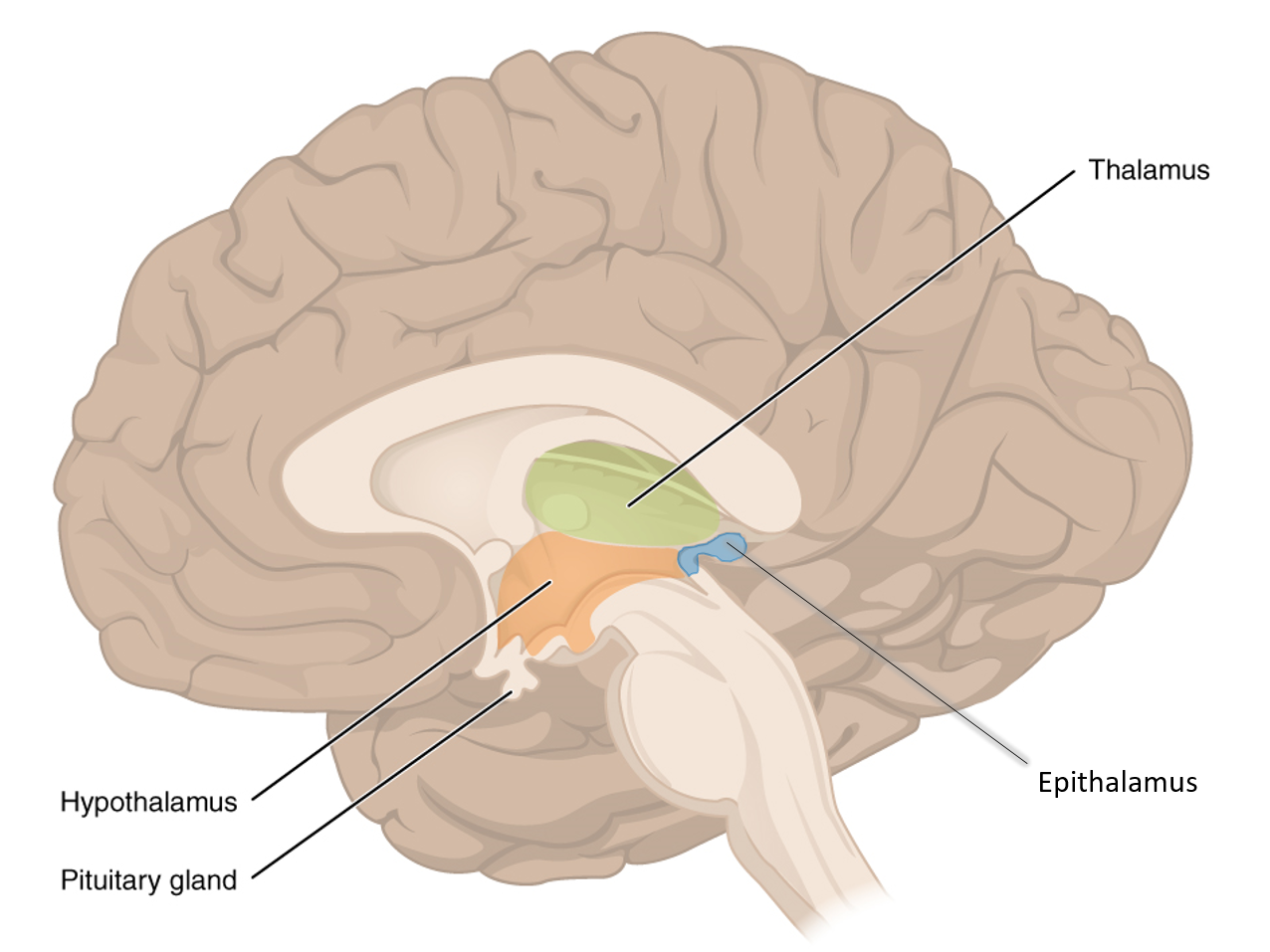
What part of the diencephalon is known as the autonomic control center (helps to control HR, BP, respiration, GI movement/secretion) and is also the center for emotional response and behavior (pleasure, pain, rage, fear, sex drive)?.
hypothalamus
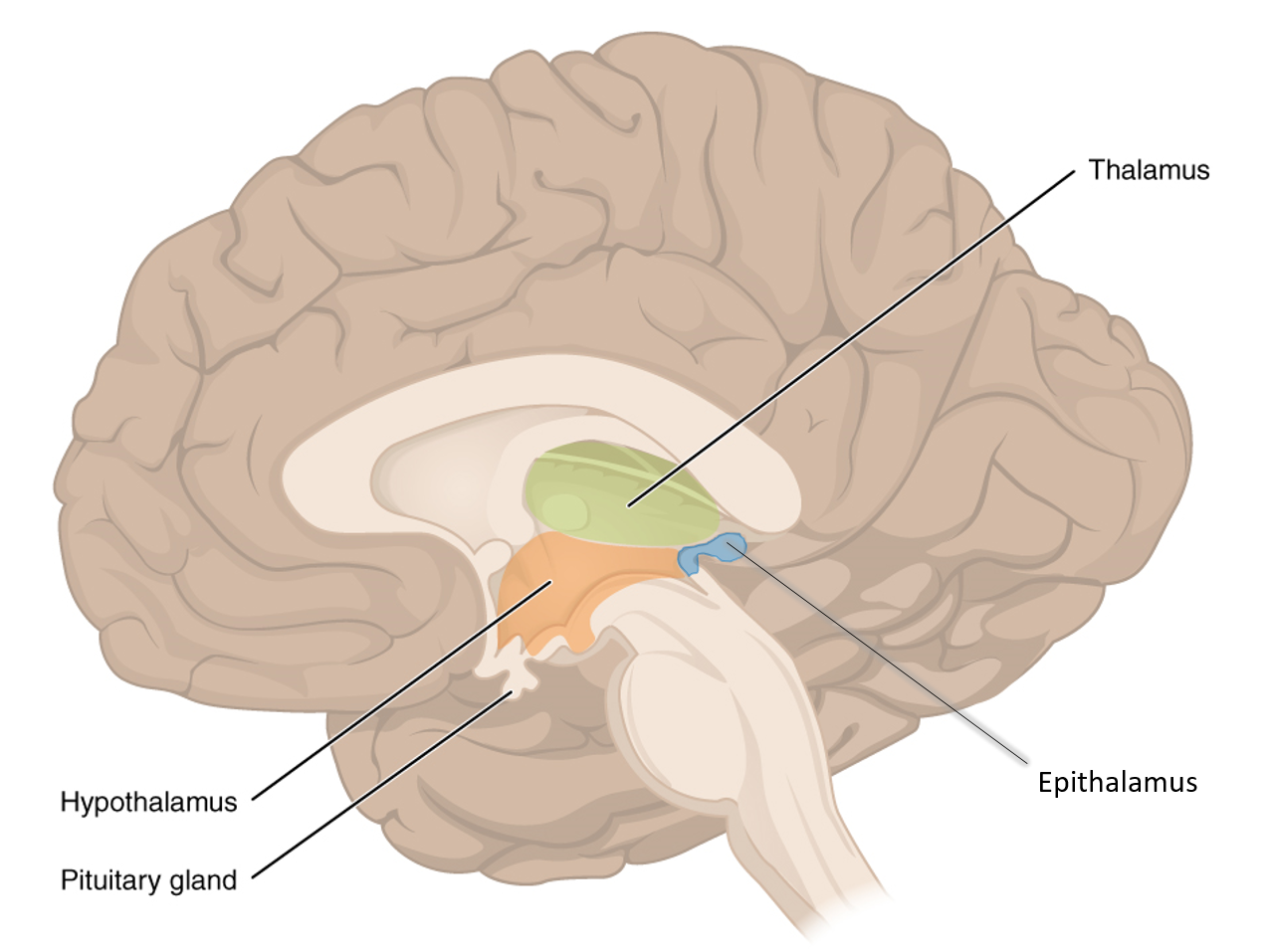
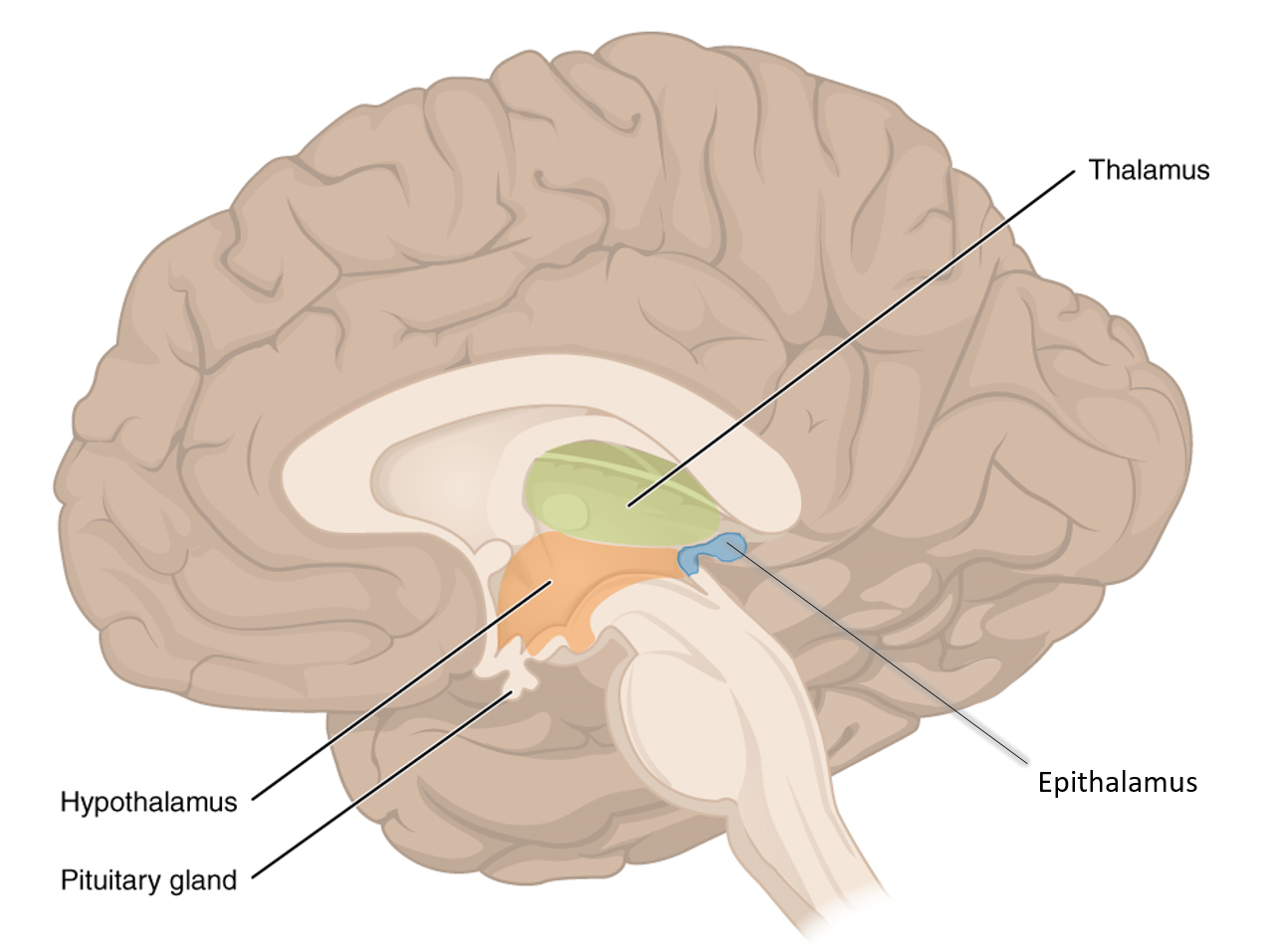
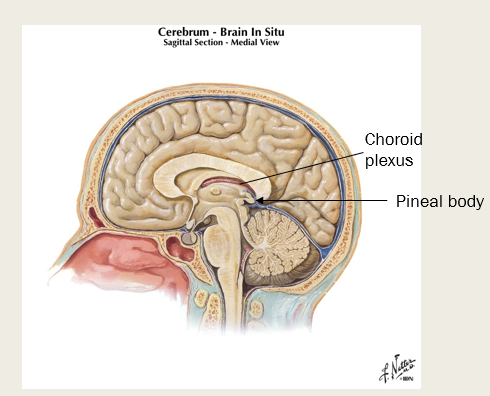
What part of the diencephalon contains the pineal body and choroid plexus (what do each of these structures do?)?
Epithalamus; contains the choroid plexus - which makes CSF, and the pineal body which makes melatonin
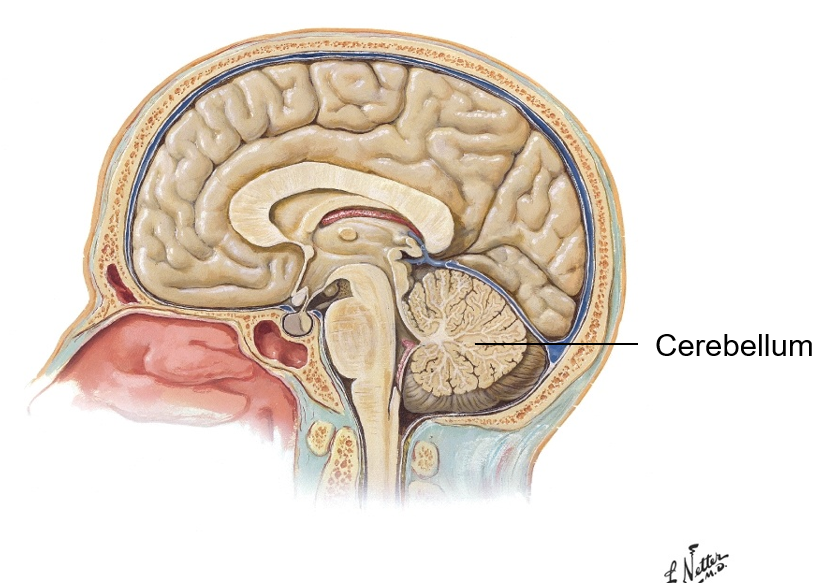
What part of the brain is: under subconscious control, responsible for smooth coordinated movement, and helps maintain posture and equilibrium?
Cerebellum
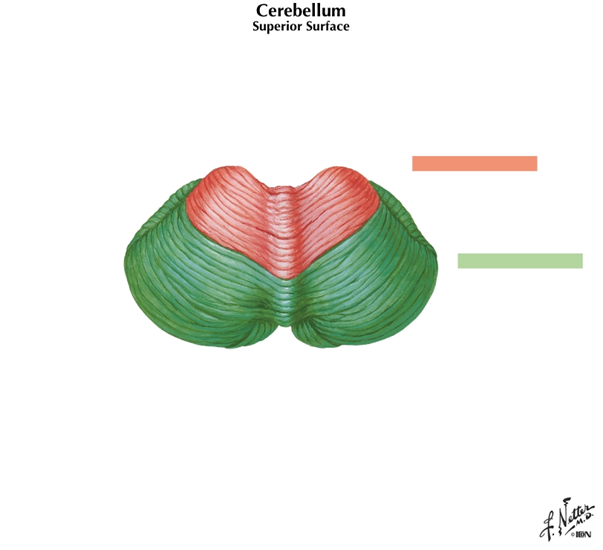
what connects the two cerebellar hemispheres? What are the parallel ridges on the cerebellum called?
Vermis
folia - parallel ridges
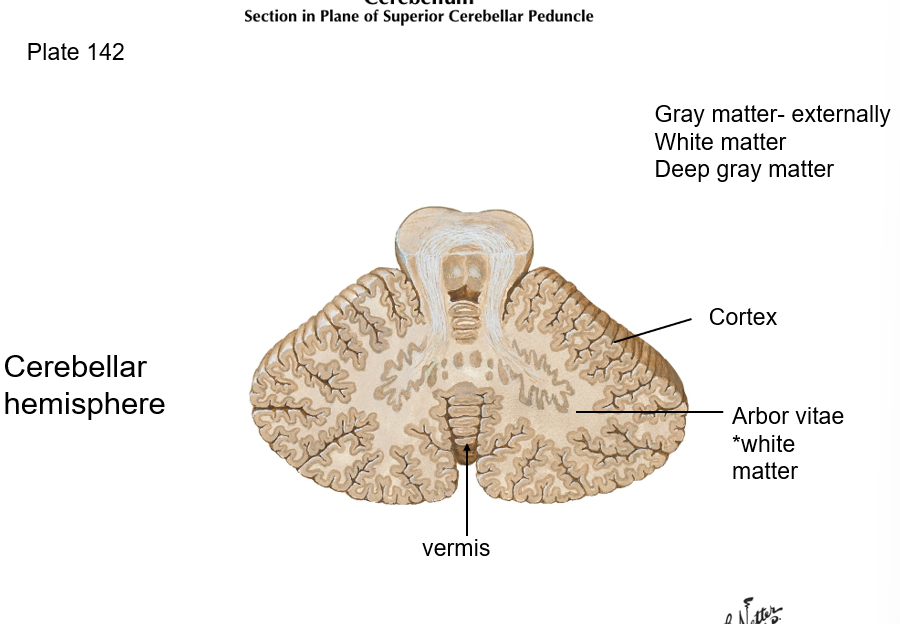
What structure of the brain has white matter known as “arbor vitae”?
cerebellum
What structure of the brain is important for equilibrium and coordination of movement?
cerebellum - it receives information from proprioceptors on current movement of limbs, neck, and trunk; also receives information from cerebral cortex on intended movements
Which pairs of cranial nerves attach to the brainstem?
CN III-XII
(10 of 12 pairs)
which structure of our CNS produces rigidly programmed, automatic behaviors necessary for survival?
brainstem
label the midbrain, pons, and medulla
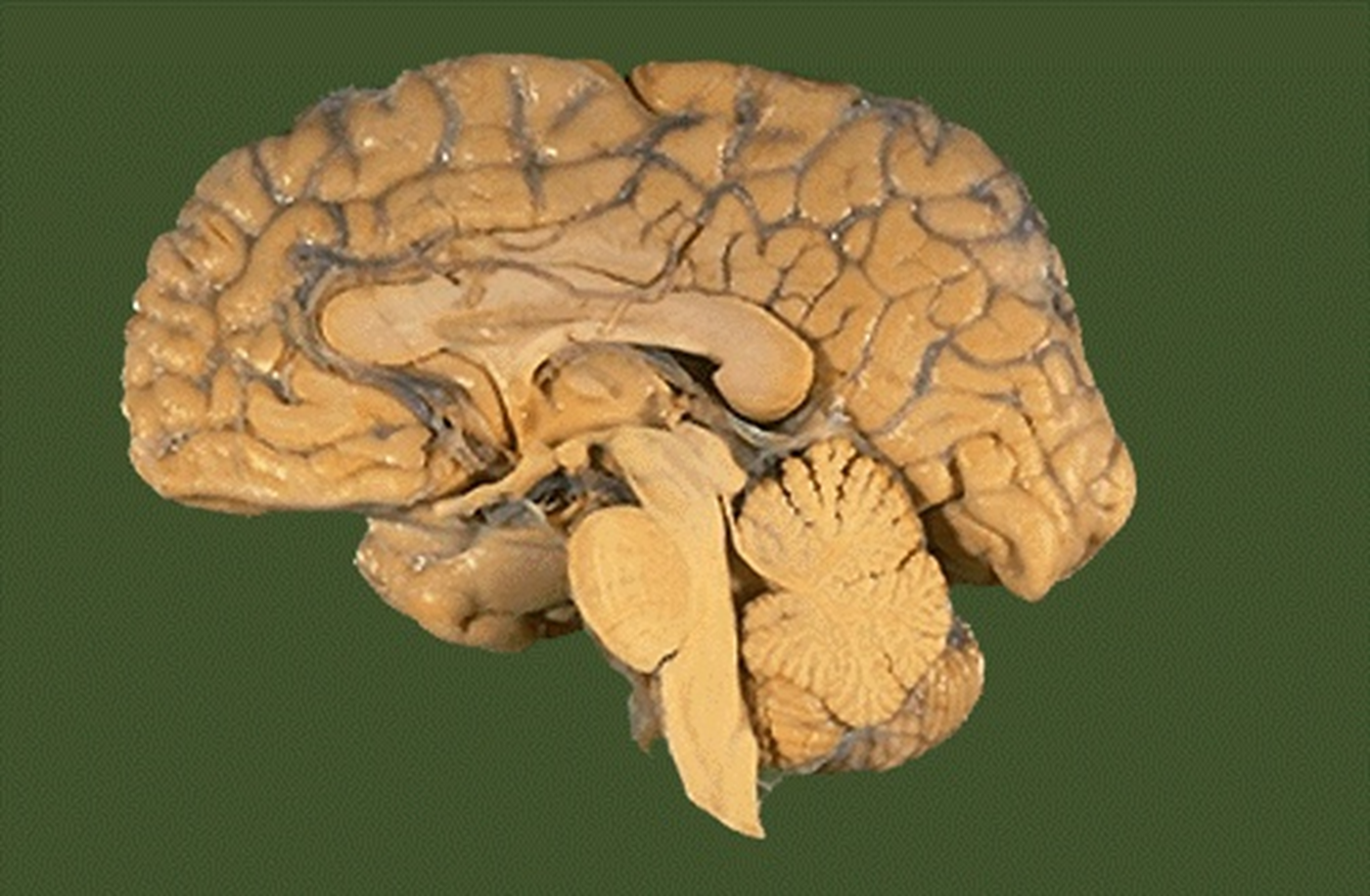
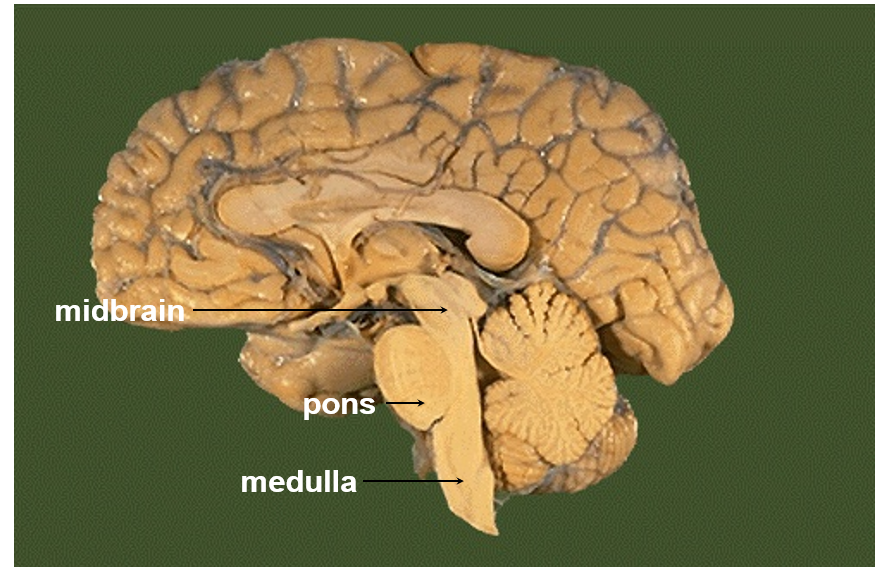
What part of the brainstem contains the visual and auditory reflex center, as well as the substantia nigra?
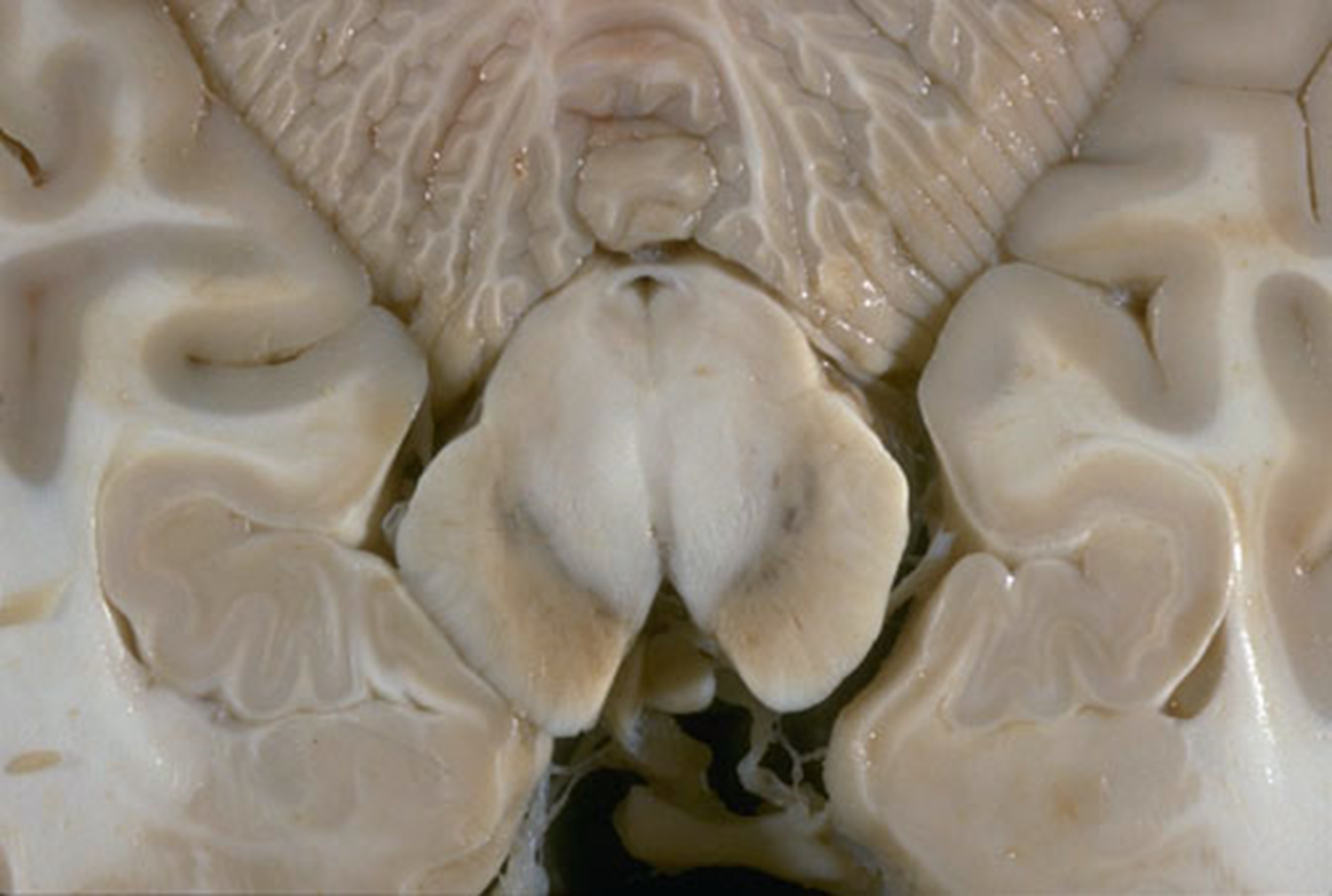
What does the substantia nigra do- and what can happen if it begins to degenerate?
Midbrain
Substantia Nigra influences activity of basal ganglia - degeneration can cause Parkinson’s disease (slow jerky movements, tremors, muscle rigidity)
Which two cranial nerves pass through the midbrain? (Hint: think of centers in midbrain)
Cranial Nerves III & IV (Oculomotor and Trochlear)
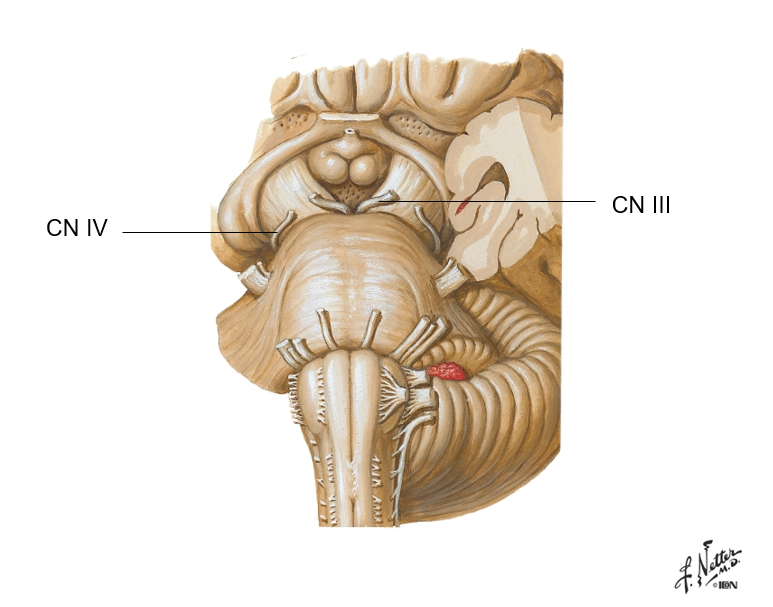
Which part of the brain stem do cranial nerves V, VI, and VII travel through?
Pons
- helps coordinate voluntary movement
Which part of the brainstem contains the CV center, respiratory center and helps maintain body homeostasis?
Medulla (oblongata)
Cranial Nerves … - … run through the medulla
CN VIII-XII
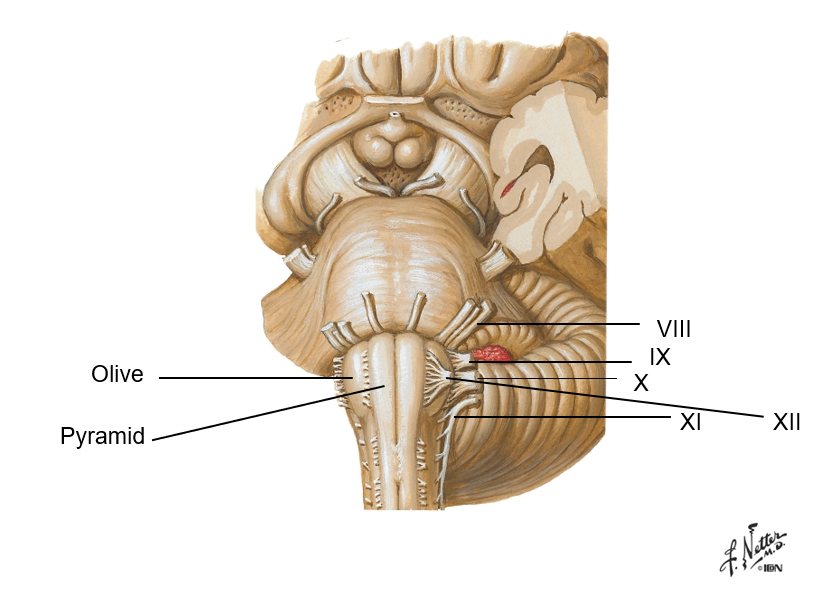
which part of the brainstem is continuous with the spinal cord at the foramen magnum?
medulla oblongata

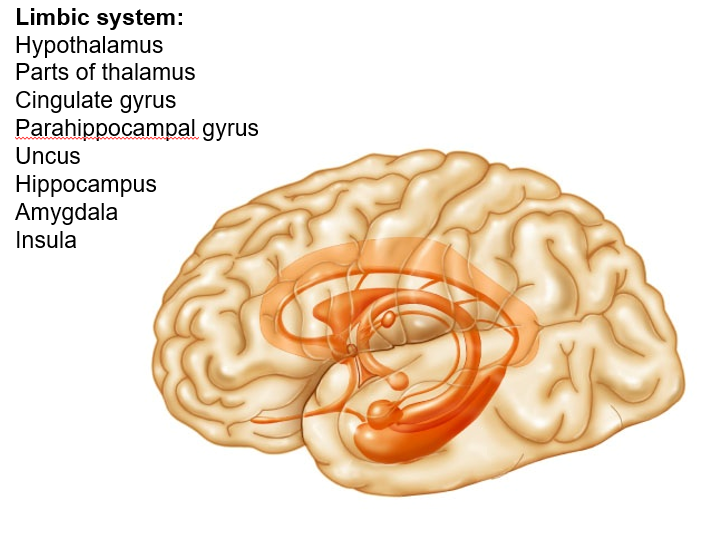
The ____ system, made up of the structures listed below, is known as the emotional brain.
limbic system
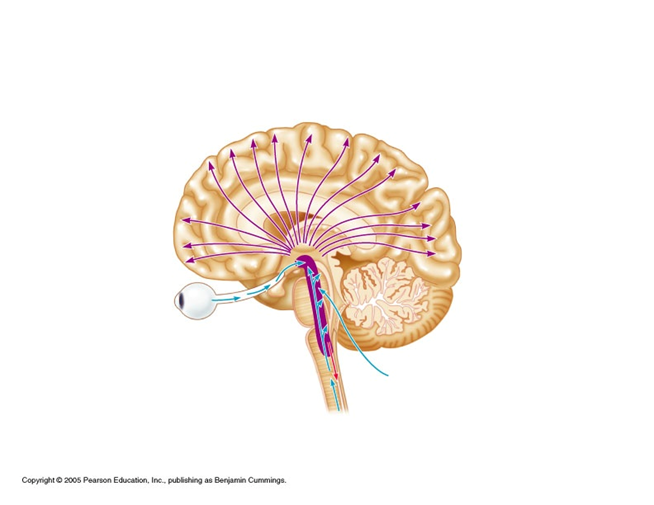
Which system in our brain helps prevent sensory overload?
reticular activating system
What are the CT coverings of CNS that form partitions in the skull?
meninges
What are three different types of meninges? Describe each one.
Dura mater, Arachnoid, Pia mater
Dura Mater - strong outermost layer, surrounds brain, makes dural sinuses
Arachnoid - weblike, transparent (arachnoid granulations)
Pia mater - thin, highly vascularized, adherent to surface of brain and spinal cord
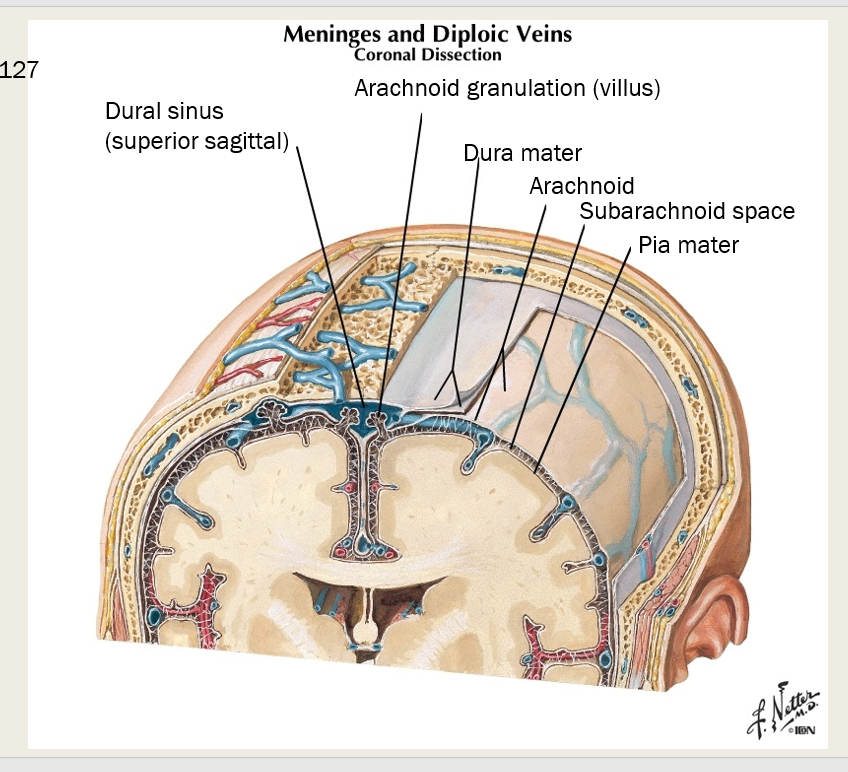
what thin highly vascularized layer of meninge adheres to the surface of brain and spinal cord?
pia mater
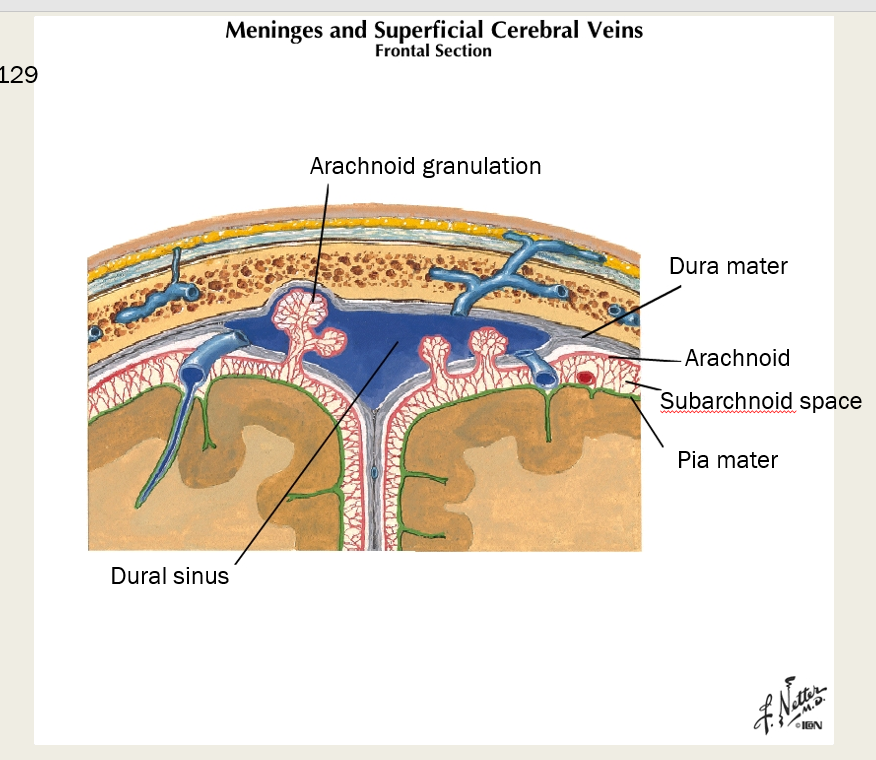
Epidural goes between ___ ____ and the _______
Epidural- between dura mater and periosteum of the bone (potential space/pathological in the SKULL; however, it’s a real space in the spine)
which meningeal space contains the CSF?
subarachnoid
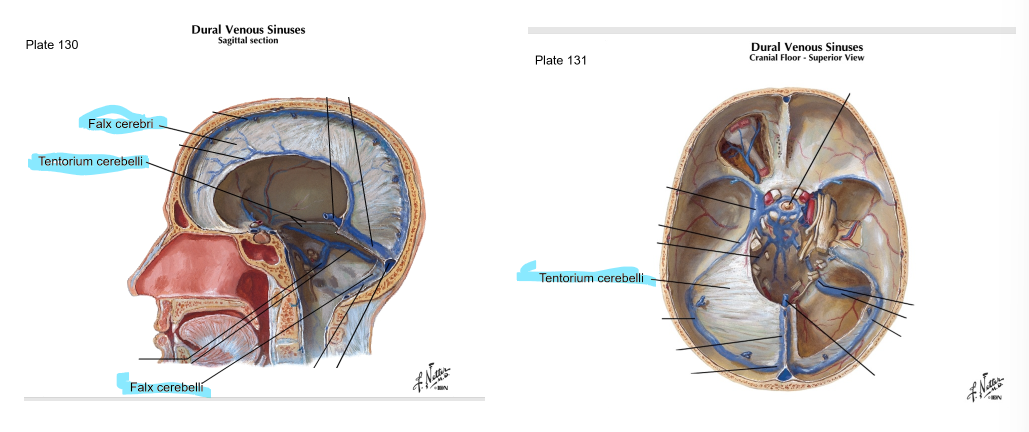
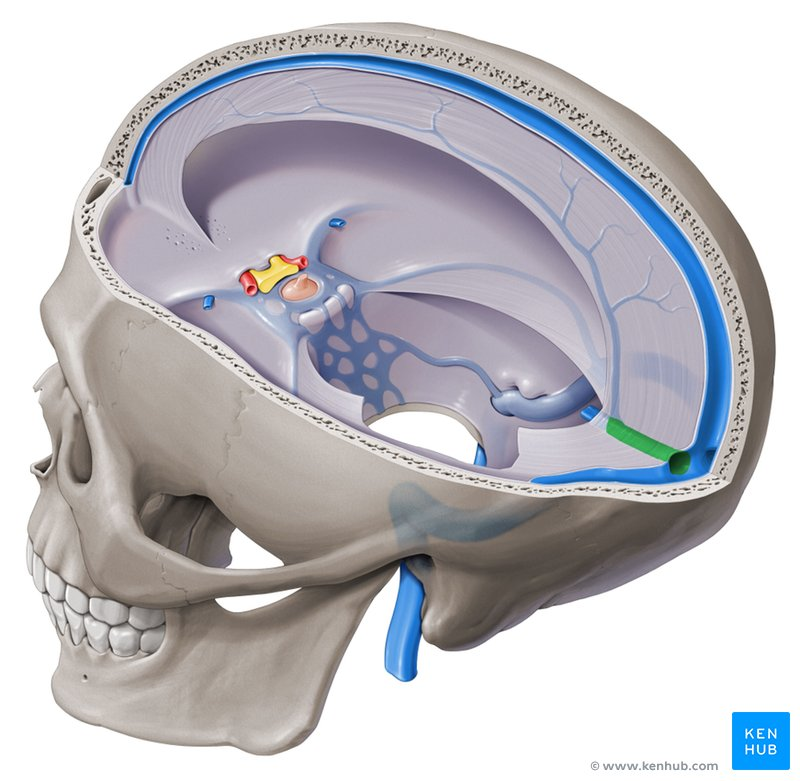
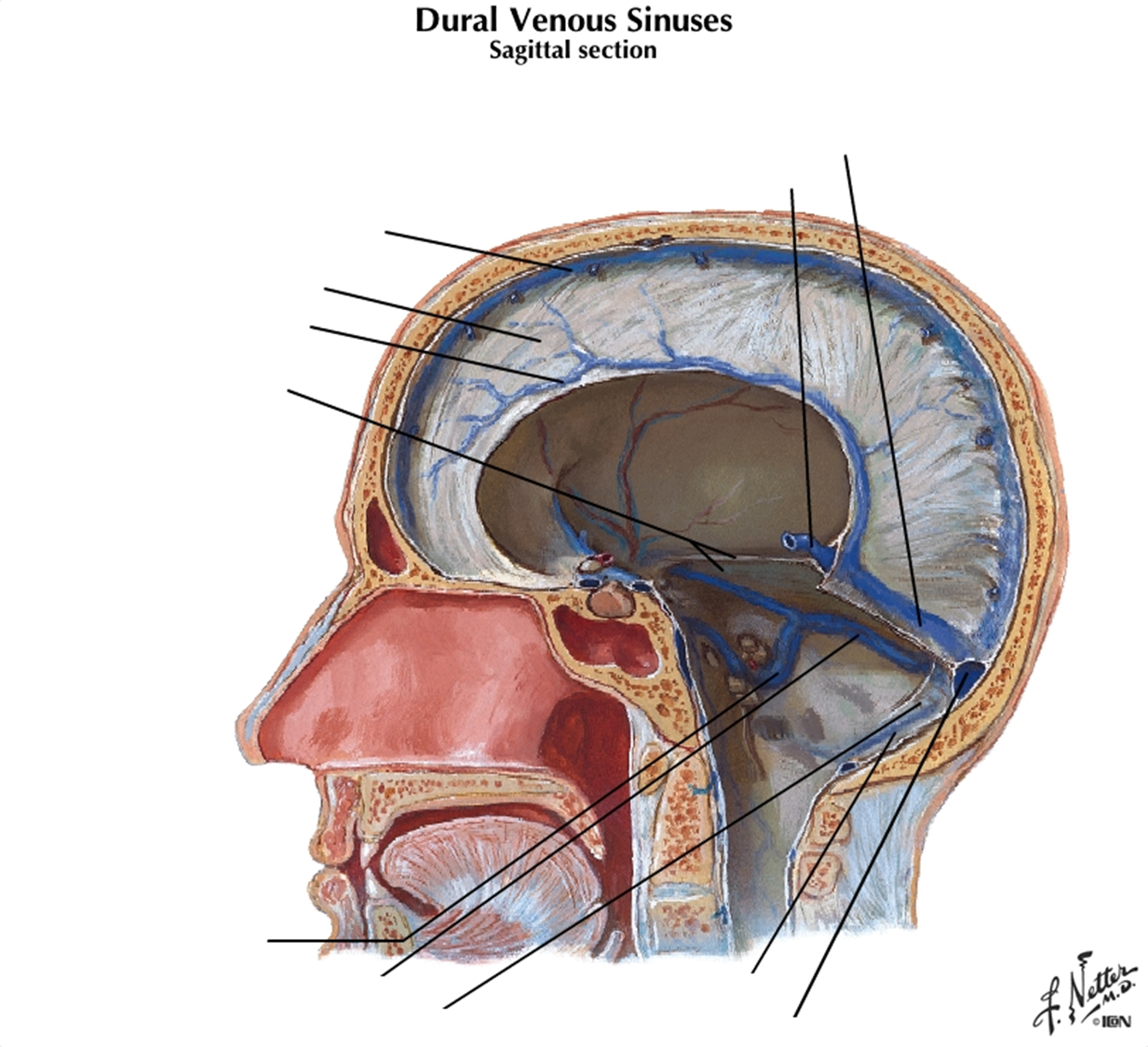
Dura Mater - There are four sections of dura mater: falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, falx cerebelli, and diaphragma sellae. Where are each of these located (here is a picture to point at):
Falx cerebri: sickle-shaped; sep. cerebral hemispheres; reduces side-to-side movement
Tentorium cerebelli: horizontal; sep. occipital lobes from cerebellum; prevents inf. displacement
Falx cerebelli: post part of posterior cranial fossa
Diaphragma sellae: on top of sella turcica; covers pituitary gland
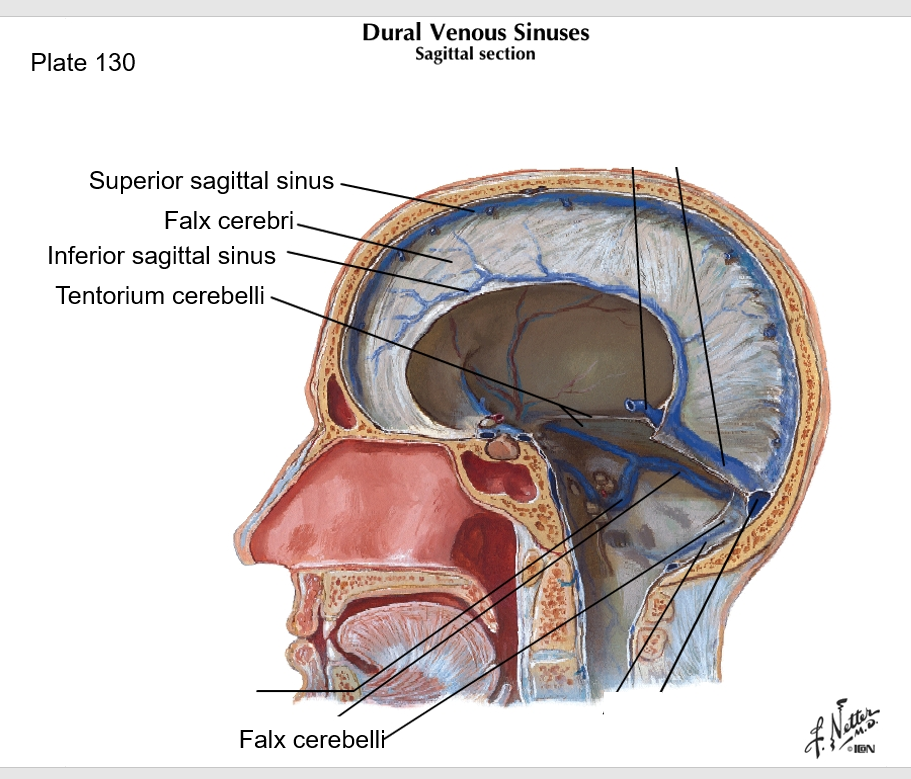
Dural sinuses are formed by layers of dura mater and drain into the ___
IJV
What does falx cerebri separate?
falx cerebri separates cerebral hemispheres and reduces side to side movement
which layer of dura mater is horizontal and separates occipital lobes from the cerebellum, preventing inferior displacement?
tentorium cerebelli
What is the Diaphragma sellae, and where is it?
a thin, horizontal membrane that covers the pituitary gland in the sella turcica (a depression in the sphenoid bone) at the base of the skull
on top of sella turcica; covers pituitary gland
What is the difference between the Falx cerebri and the Falx cerebelli?
the Falx cerebelli is on the posterior part of the posterior cranial fossa, while the falx cerebri separates the cerebral hemispheres.
Falx cerebelli - posterior
Falx cerebri - separates cerebral hemispheres
True or False - The dural sinuses drain into the carotid artery
false; they drain into the internal jugular vein!
true or false - the dural sinuses drain both blood and CSF
true
True or False - The superior border of the falx cerebri is the superior sagittal sinus
true
true or false - the inferior sagittal sinus is the inferior free border of the falx cerebelli
false- The inferior sagittal sinus is the inferior free border of the falx cerebri
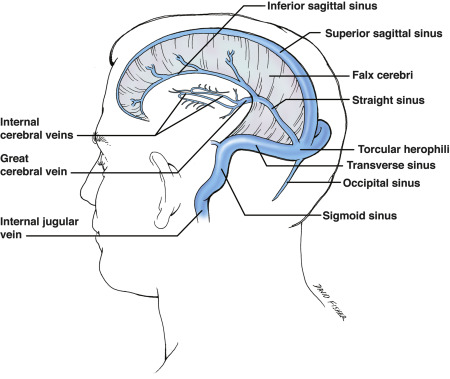
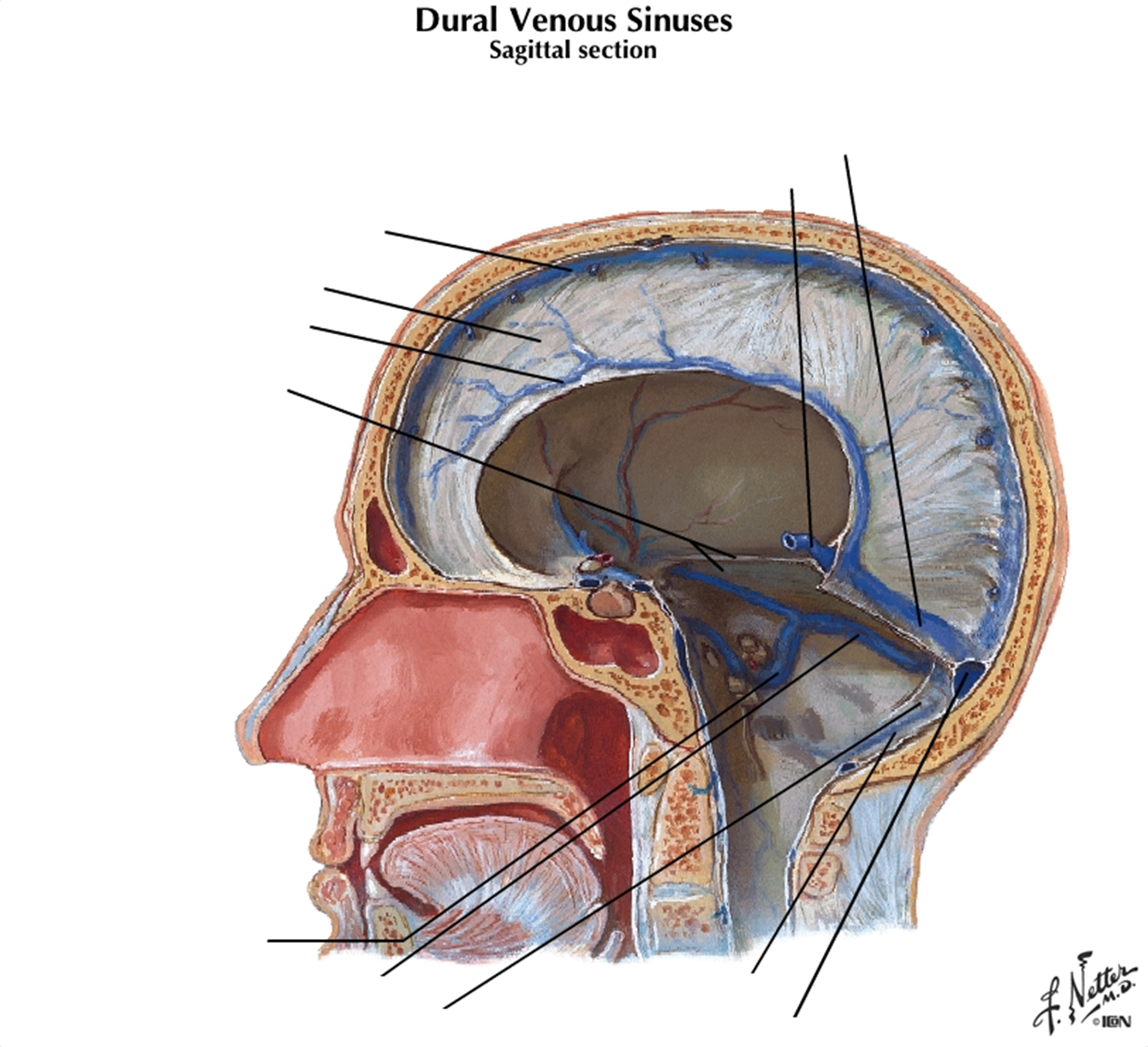
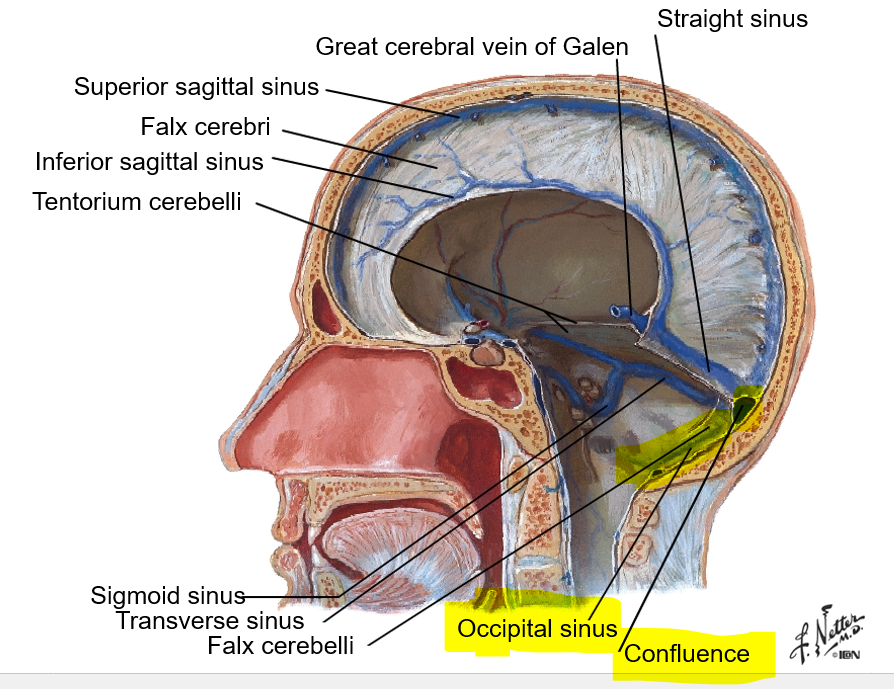
Where do the inferior sagittal sinus and great cerebral vein of Galen join?
at straight sinus (See image)
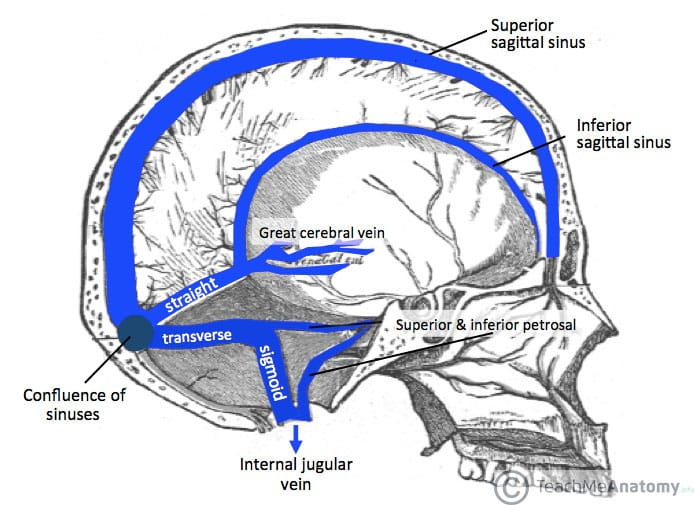
In what dura mater partition is the occipital sinus located?
Where does the occipital sinus drain?
e
in falx cerebelli; it drains posteriorly into the confluence
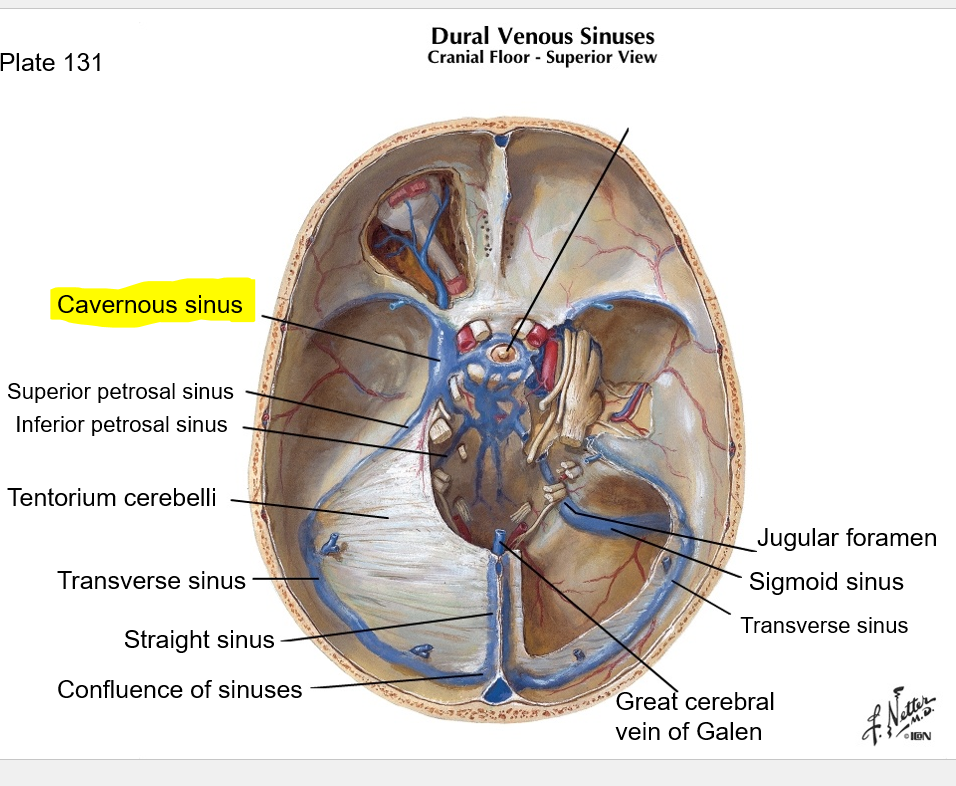
In what meningeal space is the superior petrosal sinus located?
From what sinus does the superior petrosal sinus receive blood, and where does it drain into?
Superior petrosal sinus is in the tentorium cerebelli; it receives blood from the cavernous sinus, and drains into the transverse sinus, then to confluence, then to IJV
The inferior petrosal sinus drains the _______ sinus into the IJV
The inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the IJV
Which large sinus surrounds the pituitary gland, is on either side of the sella turcica, and drains into the superior petrosal sinus?
cavernous sinus
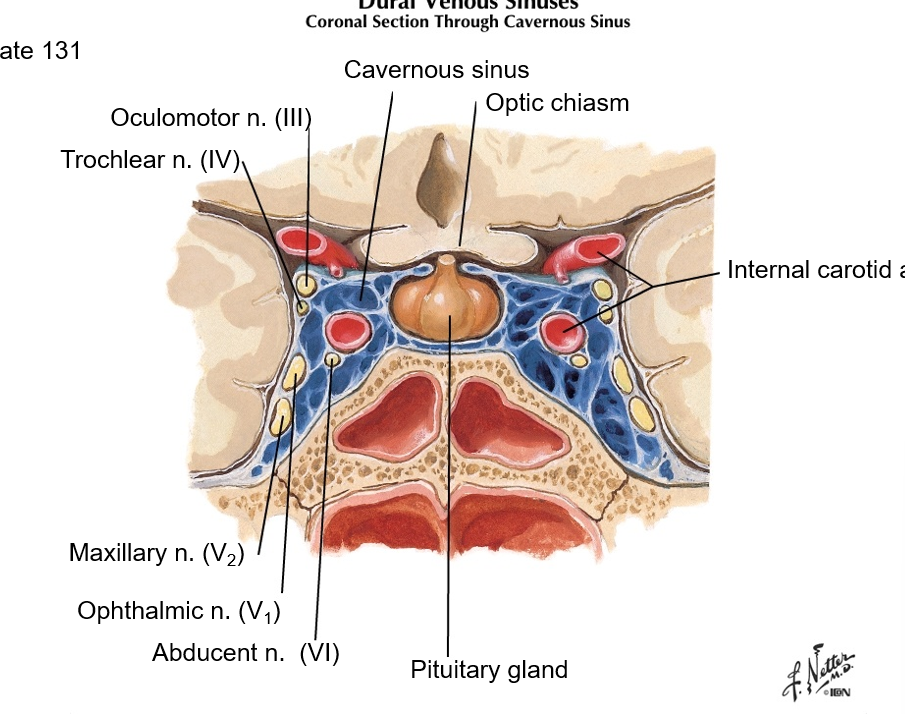
which cranial nerve(s) sit(s) in the cavernous sinus? What artery(ies)?
CN III, IV, V2, V1, VI
Internal carotid artery
optic chiasm is anterior to cavernous sinus
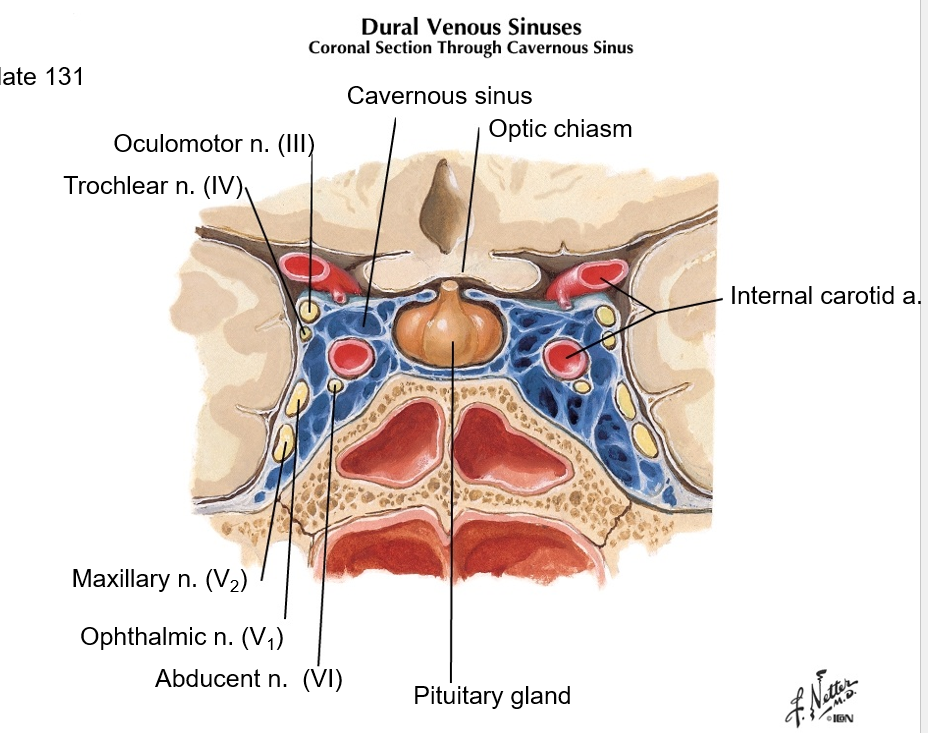
where is the optic chiasm in relation to the cavernous sinus?
the cavernous sinus sits posterior to the optic chiasm, and surrounds the pituitary gland. see image.
which layer of meninges is thin, highly vascularized, and adherent to surface of brain and spinal cord?
pia mater
in which meningeal space is the CSF
subarachnoid
What is the purpose of arachnoid granulations?
Where are they primarily located?
one-way valves, allowing CSF to flow from the subarachnoid space (the area between the brain and arachnoid mater) into the venous system.
They are located primarily along the superior sagittal sinus
outermost layer of meninges
what is it made of?
dura mater
dense, fibrous CT
What is the “dural sac”?
meningeal layer of dura mater, made of dense fibrous CT, that encloses the spinal cord within the vertebral canal.
it’s continuous with dura mater of skull
true or false- the dural sac is continuous with the cranial dura mater
true (@ foramen magnum)
where is the dural sac anchored?
inferiorly to coccyx
Where is the epidural space located? is it a real or potential space?
between dura mater and periosteum of bone (real space in spine, but pathological/potential space in skull)
true or false - the subdural meningeal space is a real space
FALSE; it’s a potential space- if present, it’s pathological (i.e. in subdural hemorrhage)
which is deeper, the subdural or epidural space?
subdural space is deep to epidural space
Where do you do lumbar puncture?
L3-L4 or L4-L5
true or false - when you perform an LP, the needle draws CSF from the epidural space
FALSE; needle goes through: skin, fascia, supraspinous ligament, ligamentum flavum, dura mater, arachnoid
and draws CSF from the subarachnoid space.
true or false - When giving epidural anesthesia, the needle pierces the dura mater
FALSE (remember: subdural space is deep to the epidural space)
collection of nerve cell bodies in the CNS
nucleus
collection of nerve cell bodies in PNS
ganglion
tract
bundles of nerve processes in CNS
bundles of nerve processes in PNS
nerve