Chapter 9: Long-Lived Tangible and Intangible Assets
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/62
Last updated 10:12 PM on 8/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
Long lived assets
________ are assets that provide benefits over a length of time (a year or more). They help provide goods or services, but the asset will not be sold.
2
New cards
productive assets
Long lived assets can also be called ________.
3
New cards
tangible assets and intangibles assets
The two categories for long-lived assets are ________.
4
New cards
fixed assets
Tangible assets, also known as ________, are physical assets that are subject to depreciation (land, buildings, equipment).
5
New cards
Intangible assets
________ are non-physical assets that have a limited life. They are created through legal documents and are subject to amortization (patents, logos, trademarks, slogans).
6
New cards
Goodwill and trademarks
________ have an unlimited life and are NOT amortized.
7
New cards

\
Equation for Net Book Value (TANGIBLE)
8
New cards

\
Equation for Net Book Value (INTANGIBLE)
9
New cards
land improvements
Tangible assets can include ________ that can enhance the asset and its functionality (walkways, sprinklers, roadways, fencing, etc).
10
New cards
Land
________ is not depreciable.
11
New cards
Construction in progress
_________ relates to the construction of tangible assets such as buildings and equipment.
12
New cards
cost principle
The ________ has acquisition costs like the initial purchase to prep assets for use (transportation, construction, etc).
13
New cards
capitalizing the cost
When costs are recorded as assets it is called ________, which delays it's recording as an expense.
14
New cards
increase; decrease
Capitalizing costs causes assets to ________ on the balance sheet and expenses to ________ on the income statement.
15
New cards
Purchase cost
Legal fees
Survey fees
Title search fees
Legal fees
Survey fees
Title search fees
The capitalized costs for land:
16
New cards
Purchase cost
Construction cost
Legal fees
Appraisal fees
Construction cost
Legal fees
Appraisal fees
The capitalized costs for buildings:
17
New cards
Purchase cost
Construction cost
Transportation cost
Sales taxes
Installation fees
Construction cost
Transportation cost
Sales taxes
Installation fees
The capitalized costs for Equipment:
18
New cards
basket purchase
A(n) ________ is when assets like land, equipment, and buildings are bought together.
19
New cards
Allocation
________ for each asset is determined by the relative fair market value of each asset.
20
New cards
Ordinary repairs and maintenance.
Extraordinary repairs, replacements, and additions.
Extraordinary repairs, replacements, and additions.
The two types of expenditures:
21
New cards
WANTED
Ordinary repairs and maintenance are ________ changes and small expenditures, which are expensed on the income statement. They don't extend the life of the asset.
22
New cards
NEEDED
Extraordinary repairs, replacements, and additions are ________ changes and are large expenditures. The asset's productivity is increased. They are capitalized.
23
New cards
cost allocation
Depreciation is a ________ process that matches cost of operational assets with periods of its useful life.
24
New cards
balance sheet; income statement
To record depreciation, the acquisition cost of an asset moves from the ________ to the ________ as an expense.
25
New cards
Debit
Income statement
Income statement
What is the normal balance of Depreciation Expense and what financial statement is it on?
26
New cards
Credit
Balance sheet
Balance sheet
What is the normal balance of Accumulated Depreciation and what financial statement is it on?
27
New cards
Depreciation calculations
The acquisition cost (including capitalized cost), estimated useful life, and the estimated residual (aka salvage) value (what the asset is worth if you sell it is all information you need to know to do:
28
New cards
Straight Line Method
The easiest and most widely used method. It indicates that depreciation expense is a constant amount each year, accumulated depreciation increases by an equal amount each year, and book value decreases the same amount each year.
29
New cards
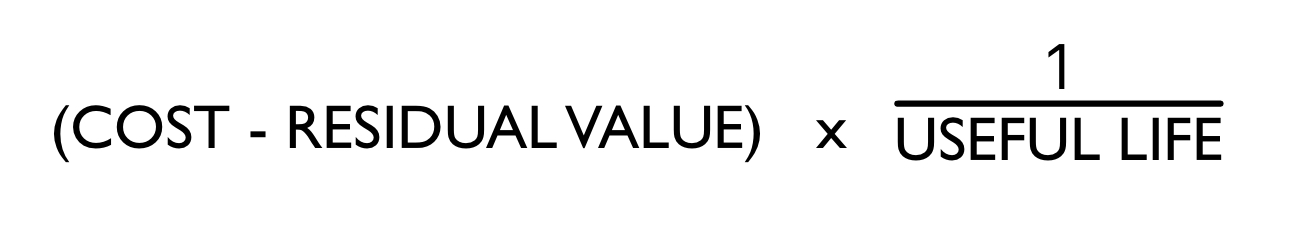
\
Equation for Depreciation Expense (Straight Line Method)
30
New cards
Units of Production
________ is used if the life of an asset is generally measured in terms of units of production.
31
New cards

\
Equation for Depreciation Expense (Units of Production Method)
32
New cards
Declining Balance
A greater depreciation expense is taken from the asset in the earlier years of its life versus its later years.
33
New cards
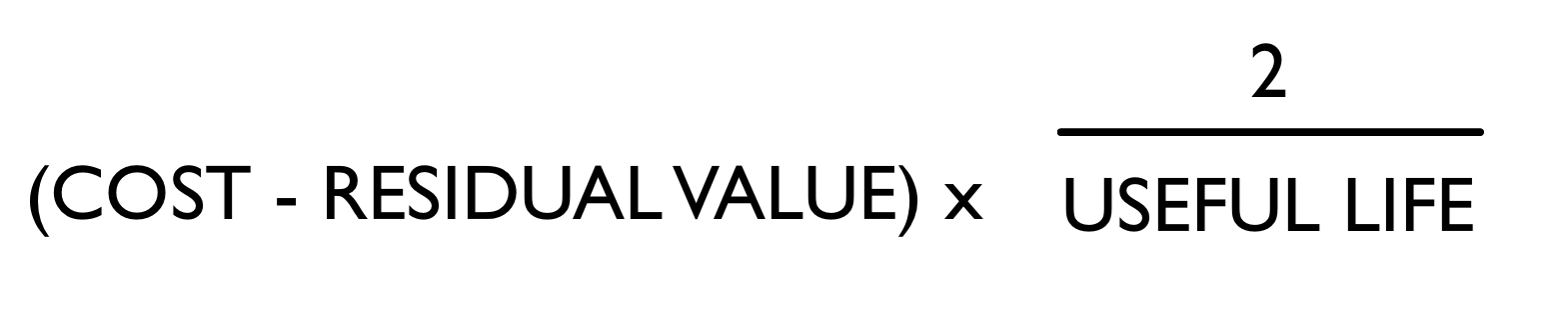
\
Equation for Depreciation Expense (Declining Balance Method)
34
New cards
least and latest
The ________ says taxpayers want to pay the least tax that is legally permitted and want to pay on the latest possible date.
35
New cards
Its value decreases and it can't be recovered.
An asset is impaired when:
36
New cards
Impairments
________ represent a lower asset value than the assets carrying value.
37
New cards
gain
A(n) ________ has a normal credit balance.
38
New cards
loss
A(n) ________ has a normal debit balance.
39
New cards
1. Update depreciation to the date of disposal.
2. Record the disposal.
2. Record the disposal.
Two adjusted journal entries are required for the disposal of an asset to.....
40
New cards
Debit Cash
Debit Accumulated Depreciation
Credit Equipment
Credit Gain on Disposal
Debit Accumulated Depreciation
Credit Equipment
Credit Gain on Disposal
Journal entry if there is a gain on disposal:
41
New cards
Debit Cash
Debit Loss on Disposal
Debit Accumulated Depreciation
Credit Equipment
Debit Loss on Disposal
Debit Accumulated Depreciation
Credit Equipment
Journal entry if there is a gain on disposal:
42
New cards
Debit Loss
There is ________ IF cash received is less than asset's book value.
43
New cards

\
Equation for annual Depreciation:
44
New cards
Amortization
________ is similar to depreciation, but it is specifically used for intangible assets. It writes off the cost of an asset over its useful or legal life.
45
New cards
Trademarks
Slogans, logos, or names associated with a specific business.
46
New cards
Copyrights
An exclusive right granted by the federal government to protect properties.
47
New cards
Patents
An exclusive right granted by the federal government to sell or manufacture an invention.
48
New cards
Licensing Rights
Grant limited permission to use a product or service according to specific terms and conditions.
49
New cards
Technology Assets
Software and web development work.
50
New cards
Franchises
Provides legally protected rights to sell products or provide services purchased by a franchise from the franchisor.
51
New cards
Goodwill
Occurs when one company buys another company. It is not amortized. Purchased ________ is considered an intangible asset.
52
New cards

\
Equation for Goodwill:
53
New cards
purchased
The cost of intangible assets are recorded as assets if they've been ________.
54
New cards
research and development expenses
If the asset is self constructed, the cost is reported as ________.
55
New cards
amortized
Intangible assets with unlimited lives are not ________. Intangible assets with limited lives are capitalized and later ________.
56
New cards
Depreciation
________ is a cost allocation process that matches cost of operational assets with periods of its useful life.
57
New cards
Credit Gain
There is ________ IF the cash received is greater than the assets book value.
58
New cards
greater
Gains for intangible assets are the result of amounts received being ________ than their book values.
59
New cards
less
Losses for intangible assets are the result of amounts received being ________ than their book values.
60
New cards
Fixed asset turnover analysis
_________ is used to see how well long lived assets were used to generate revenue.
61
New cards
\
Equation for calculating the average of fixed assets:
62
New cards

\
Equation for the fixed asset turnover ratio:
63
New cards
great efficiency
A higher fixed asset turnover ratio implies ________.