Veterinary Anatomy: Thoracic Limb Bones
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Clavicle
is not articulated with the skeleton in the dog. It is located at the tendinous intersection of the brachiocephalicus muscle, and its medial end is attached to the sternal fascia by a distinct ligamentous band.
Scapula
is the large, flat bone of the shoulder joint. Its most dorsal part lies just ventral to the level of the free end of the spinous process of the first or second thoracic vertebra.
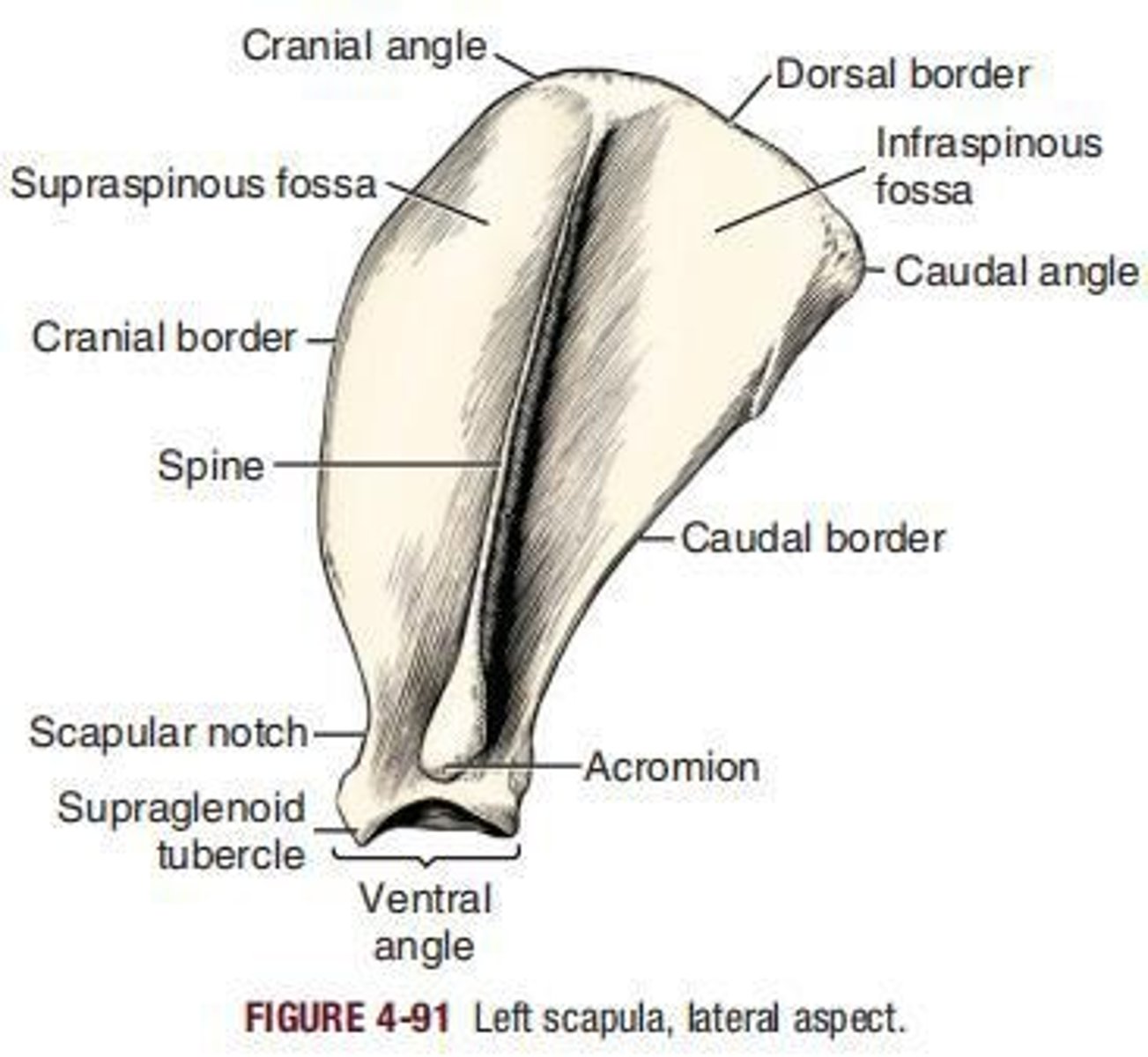
Acromion
The widened truncate distal end of the spine of the scapula is called the ___.
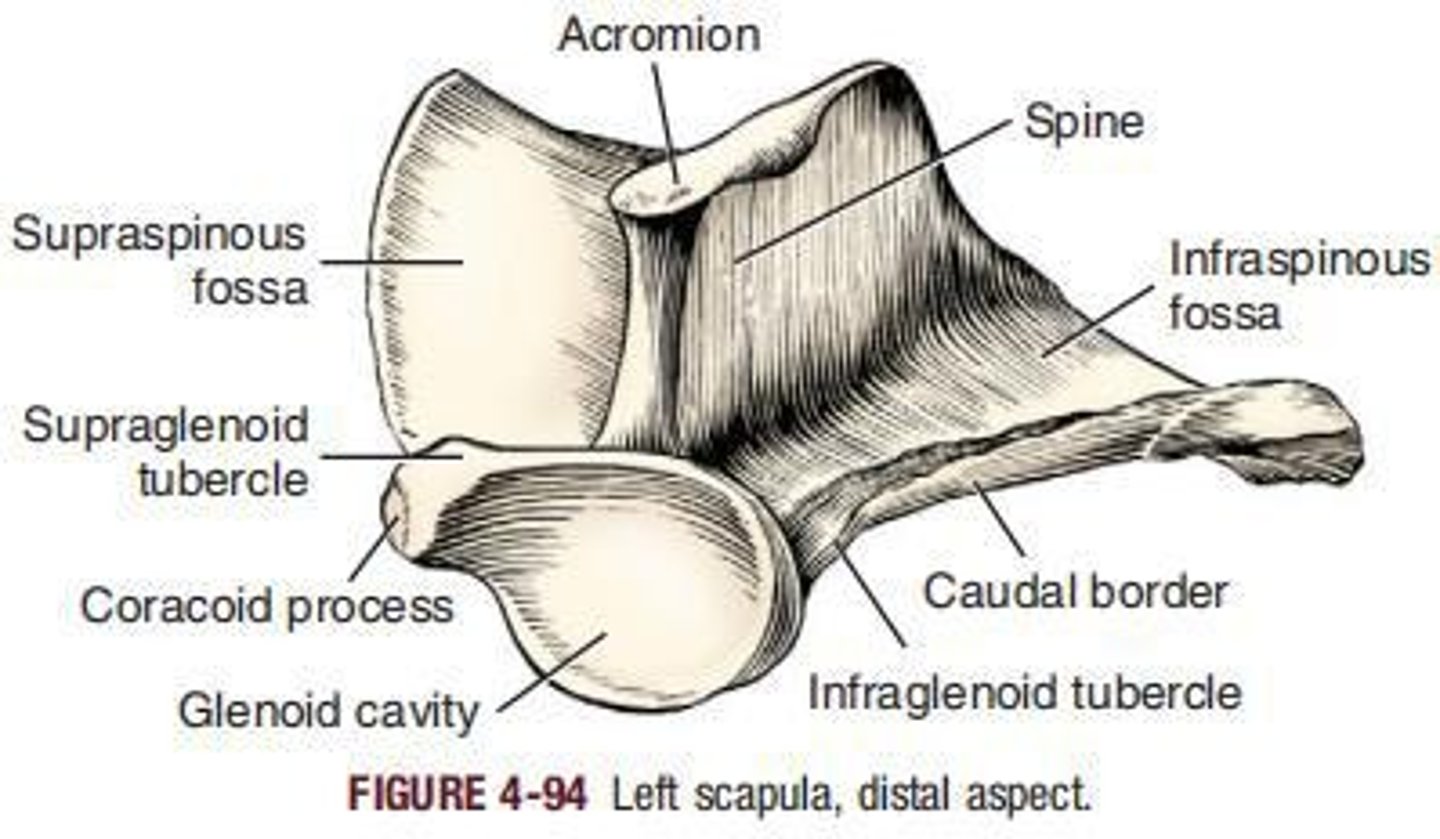
Supraspinous fossa
is bounded by the cranial surface of the scapular spine and the adjacent lateral surface of the scapula.
Infraspinous fossa
is in general triangular.
Dorsal border
sometimes called the vertebral border or base, extends between the cranial and the caudal angles.
Cranial border
is thin except at its extremities.
Scapular notch
Distally, the cranial border forms a concavity, __ , which marks the position of the constricted part of the bone.
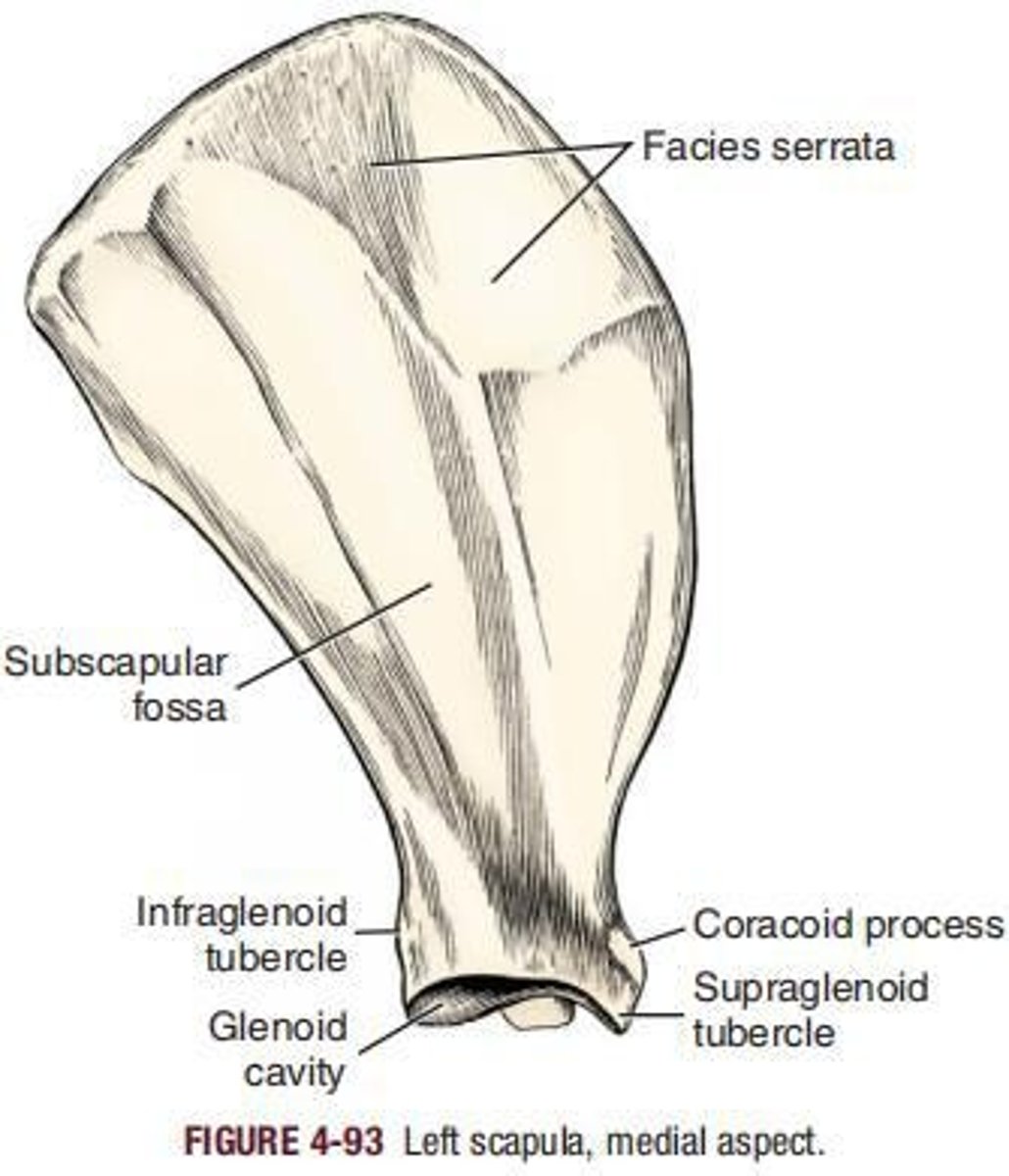
Subscapular fossa
The large remaining part of the costal surface is the ___
Caudal border
is the thickest of the three borders and bears, just dorsal to the ventral angle, the infraglenoid tubercle (tuberculum infraglenoidale).
Glenoid cavity
___ receives the head of the humerus in forming the shoulder joint.
Humerus
is the bone of the arm, or brachium. Proximally it articulates with the scapula in forming the shoulder joint; distally it articulates with the radius and ulna in forming the elbow joint.
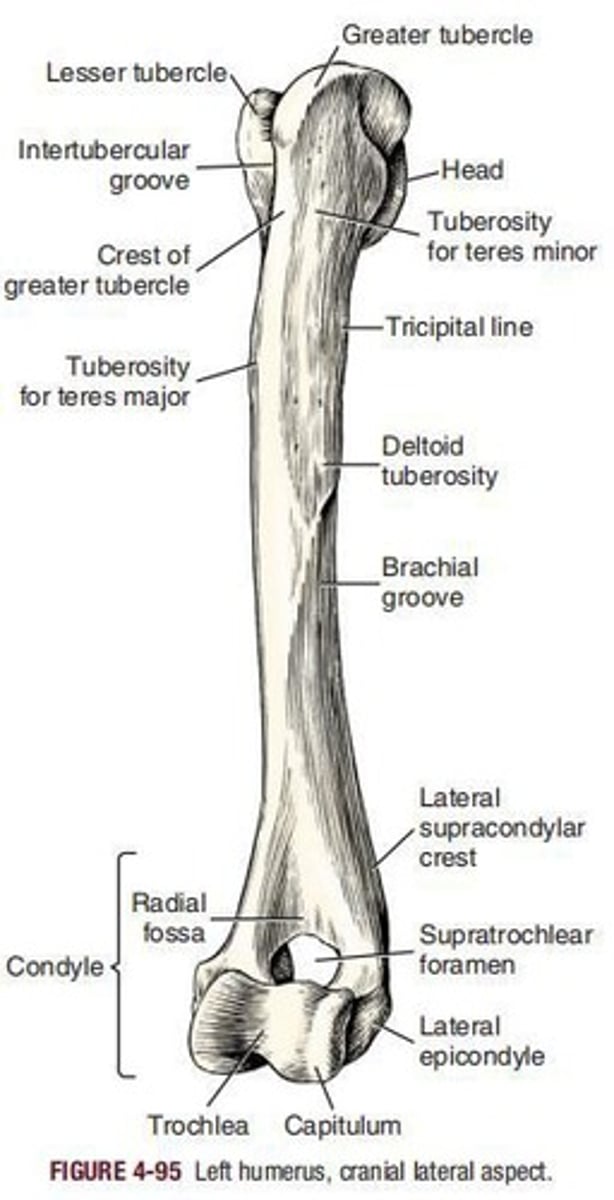
Head of humerus
is oval, being elongated in a sagittal plane.
Intertubercular groove
The articular surface of the head is continued distally by the ____
Neck of humerus
is distinct only caudally and laterally.
Body of humerus
or shaft, is the long, slightly sigmoid-shaped part of the humerus that unites the head and neck with the condyle.
Deltoid tuberosity
is the most prominent feature of the lateral surface of the humerus.
Greater tubercle
is the large craniolateral projection of the proximal extremity of the humerus.
Lesser tubercle
is a medially flattened enlargement of the proximal medial part of the humerus, the convex border of which does not extend as far proximal as the head.
Brachialis groove
the __ or musculospiral groove forms the smooth, flat to convex, lateral surface of most of the humerus.
Tuberosity for teres major
lies in the same transverse plane as the laterally located deltoid tuberosity.
Humeral condyle
is the entire sagittally rounded distal end of the humerus exclusive of the epicondyles.
Capitulum humeri
Small, lateral articular surface for articulation with the head of the radius.
Trochlea humeri
Pulley-shaped part that extends proximally into the adjacent fossae.
Olecranon fossa
Deep excavation of the caudal part of the humeral condyle.
Radial fossa
Fossa on the cranial surface of the condyle opposite the olecranon fossa.
Supratrochlear foramen
Foramen that allows communication between the radial and olecranon fossae.
Lateral epicondyle
Lateral prominence on the humeral condyle, caudoproximal to the lateral articular margin of the capitulum.
Medial epicondyle
Prominence on the medial side of the condyle, proximal to the medial border of the articular surface of the trochlea.
Radius
Main weight-supporting bone of the forearm, shorter than the ulna, primarily for muscle attachment.
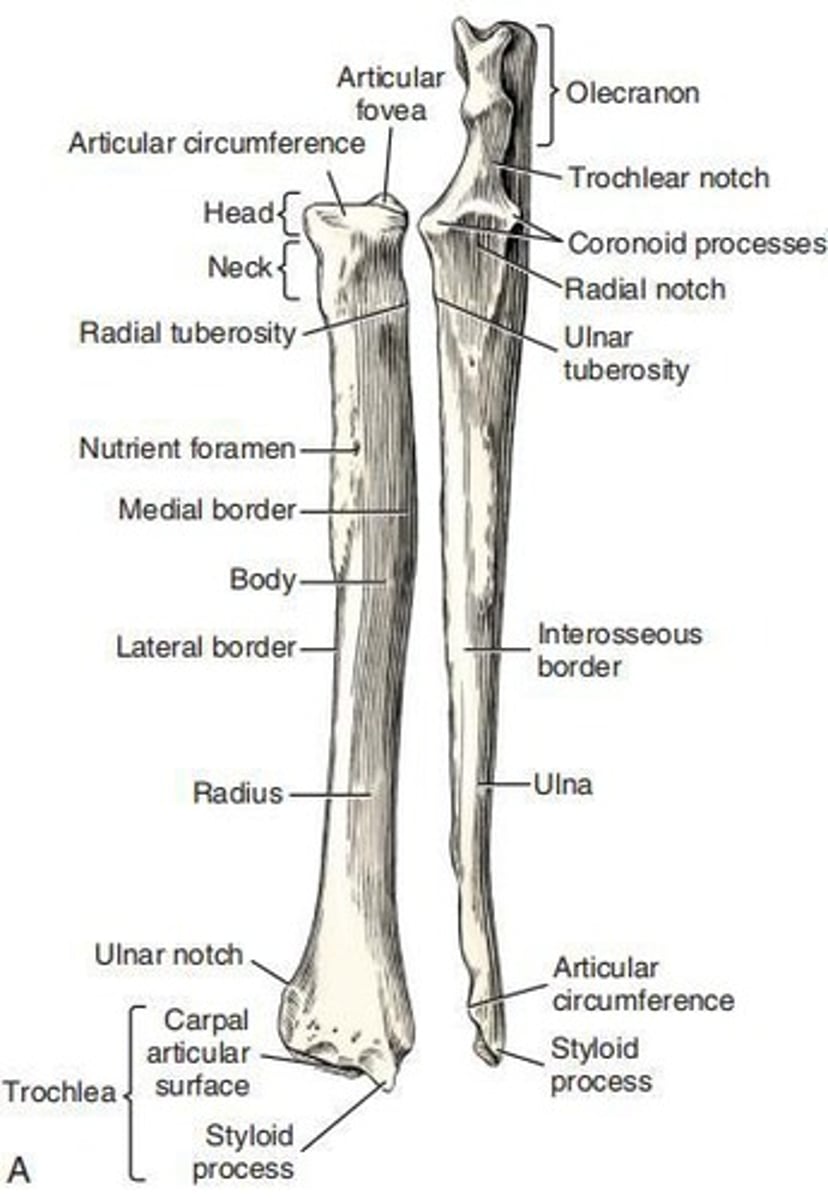
Head of radius
Irregularly oval outline that extends transversely across the proximal end of the radius.
Neck of radius
Constricted segment of the radius that joins the head to the body.
Articular fovea
Concave surface that articulates with the capitulum and lateral part of the trochlea.
Articular circumference
Caudal, smooth, osseous band on the head for articulation with the radial notch of the ulna.
Radial tuberosity
Small projection that lies distally on the neck on the medial border and adjacent caudal surface of the radius.
Body of radius
Compressed shaft presenting two surfaces and two borders.
Trochlea of radius
Distal extremity of the radius and the most massive part of the bone.
Ulnar notch
Slightly concave and lipped surface on the lateral side of the trochlea that articulates with the ulna.
Styloid process
Wedge-shaped projection that extends distal to the main carpal articular surface.
Ulna
Longest bone in the body, divided into a body and two extremities, articulating with the humerus and radius.
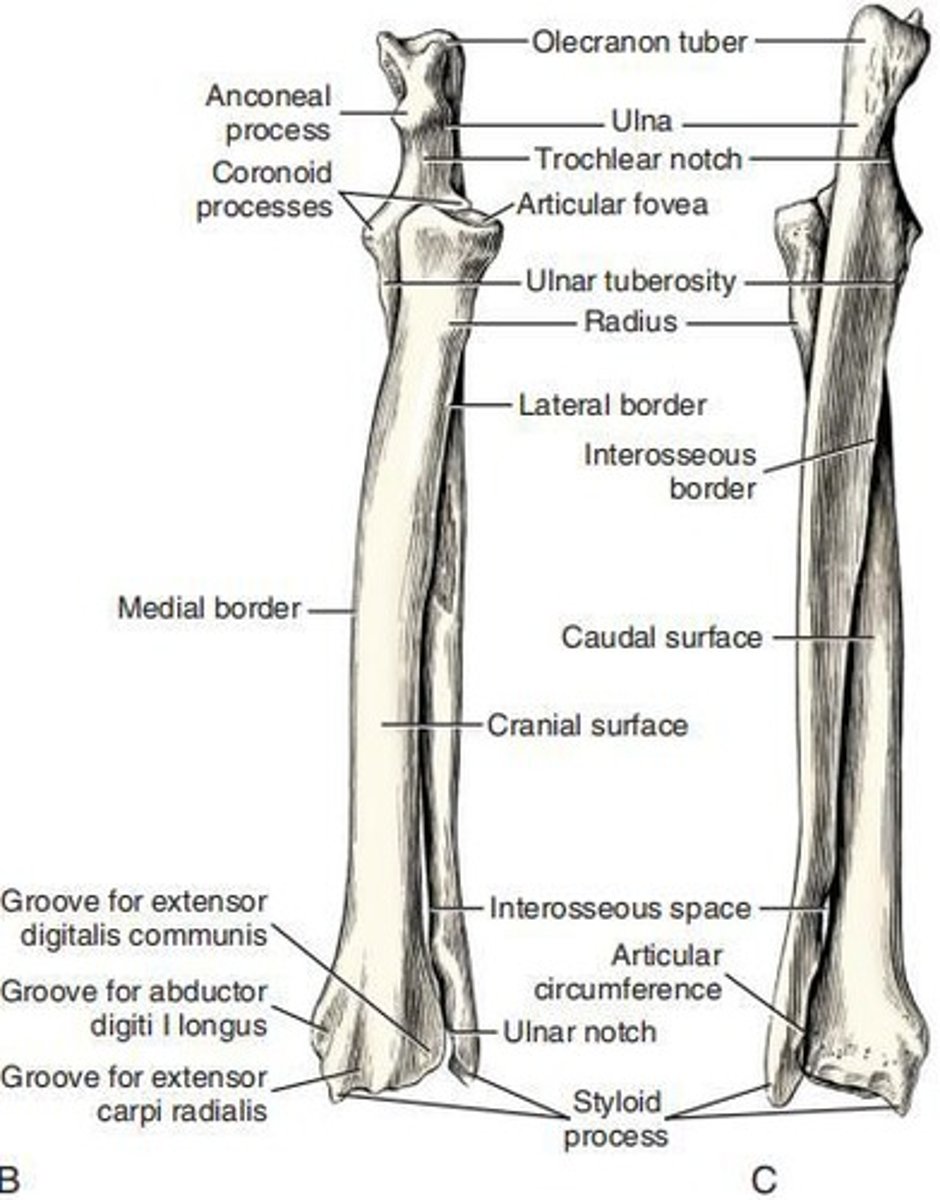
Trochlear notch
Notch on the ulna that articulates with the humerus.
Olecranon
Includes the olecranon tuber, anconeal process, and proximal part of the trochlear notch, serving as a lever arm for extensor muscles.
Cranial surface of ulna
Rough and convex surface, both longitudinally and transversely.
Interosseous border
Border that extends proximally from the notch separating the distal extremity from the body of the ulna.
Caudal border of ulna
Smooth and concave border that tapers toward the head.
Medial border of ulna
Sharper and straighter than the lateral border.
Lateral border
Continues the wide, rounded, caudal border of the olecranon.
Forepaw
The skeleton of the ___ (manus) includes the bones of the carpus, metacarpus, phalanges, and certain sesamoid bones associated with them.
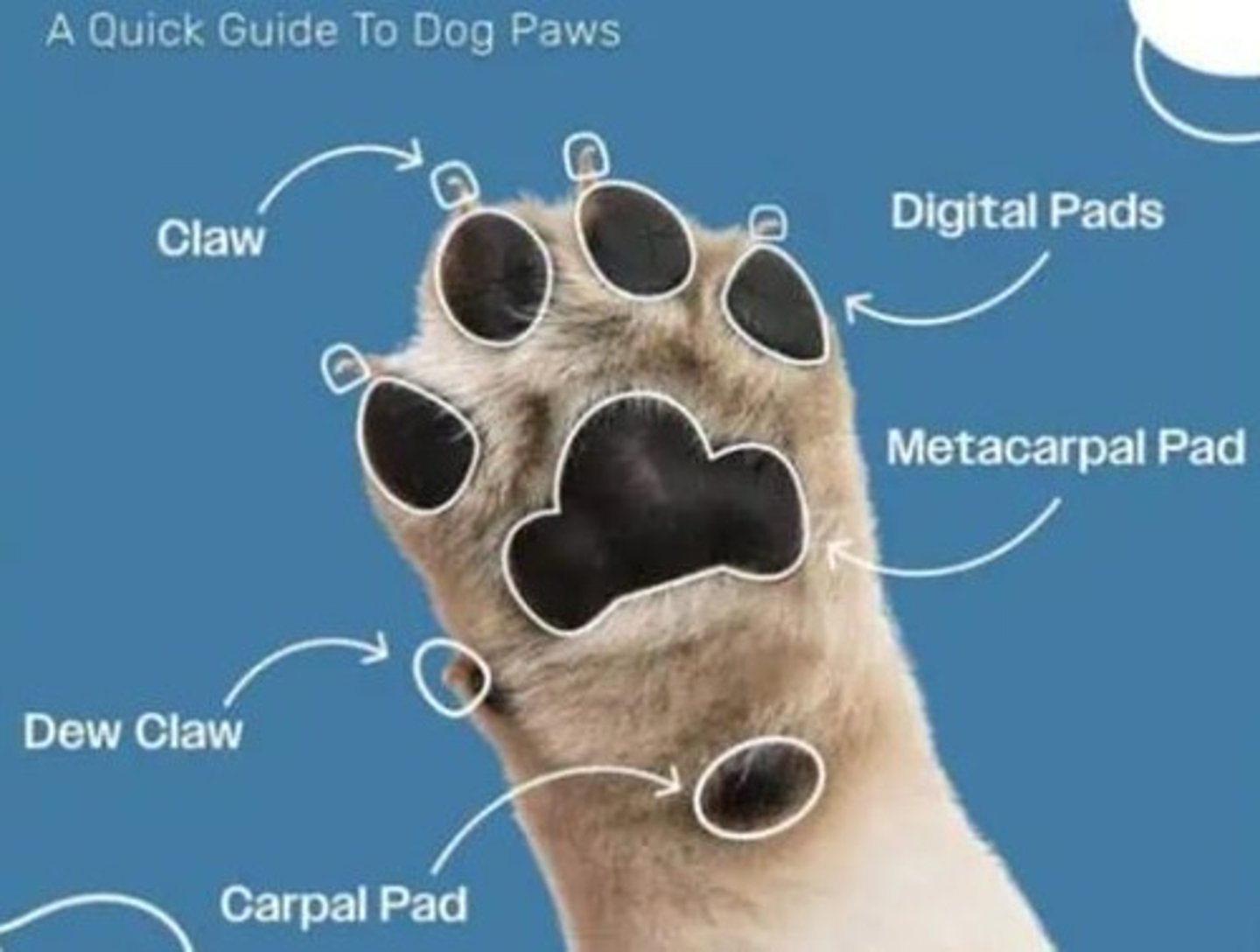
Carpus
Composed of seven bones arranged in two transverse rows, plus a small medial sesamoid bone.

Intermedioradial carpal bone
Located on the medial side of the proximal row, it is the largest of the carpal elements.
Ulnar carpal bone
The lateral bone of the proximal row.
Accessory carpal bone
A truncated rod of bone located on the palmar side of the ulnar carpal.
First carpal bone
The smallest carpal bone.
Second carpal bone
A small, wedge-shaped, proximodistally compressed bone.
Third carpal bone
Larger than the second carpal and has a large palmar projection.
Fourth carpal bone
The largest bone of the distal row.
Smallest bone of the carpus
A spherical sesamoid bone, about the size of a radish seed, located in the tendon of insertion of the m. abductor digiti I longus on the medial side of the proximal end of the first metacarpal.
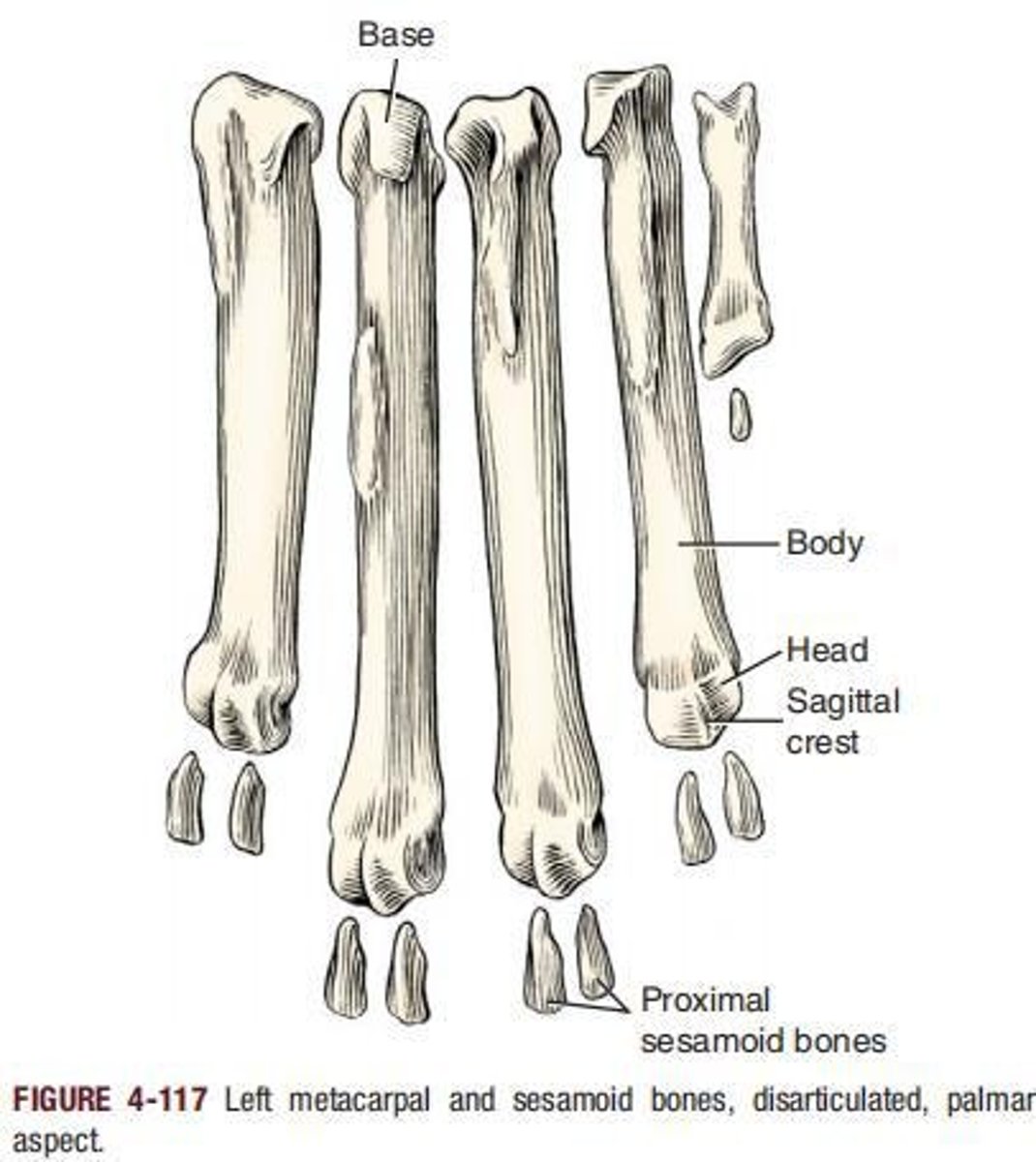
Metacarpus
Refers to the region of the manus, consisting of five metacarpal bones that are each cylindrically shaped and enlarged at each end.
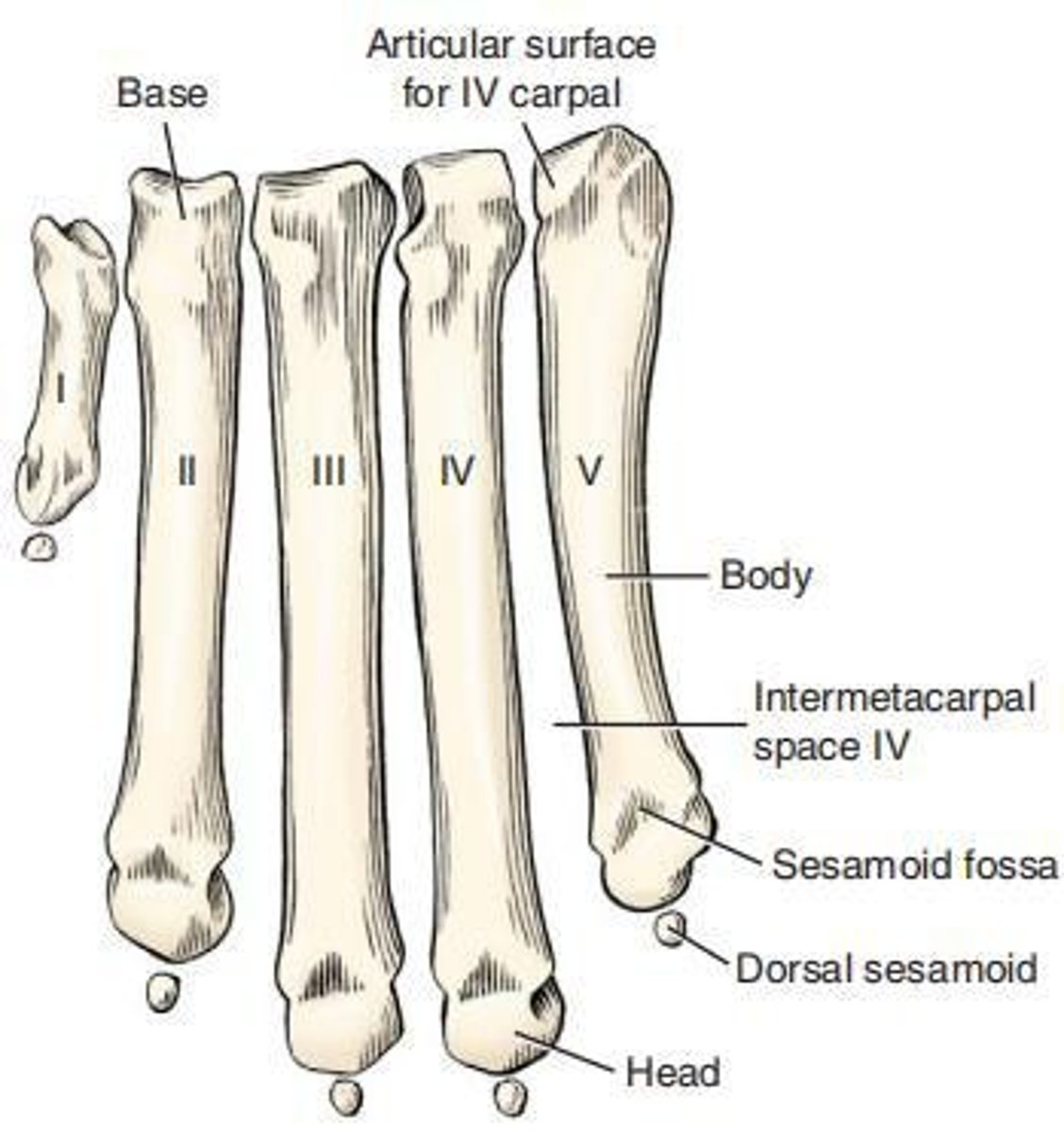
First metacarpal bone
Usually present, it is the shortest and most slender of the metacarpal bones.
Main metacarpal bones
Metacarpal bones II to V, which are irregular rods with a uniform diameter.
Metacarpals II and V
Shorter than III and IV and are four-sided, particularly at their base.
Metacarpals III and IV
More triangular at their base compared to II and V.
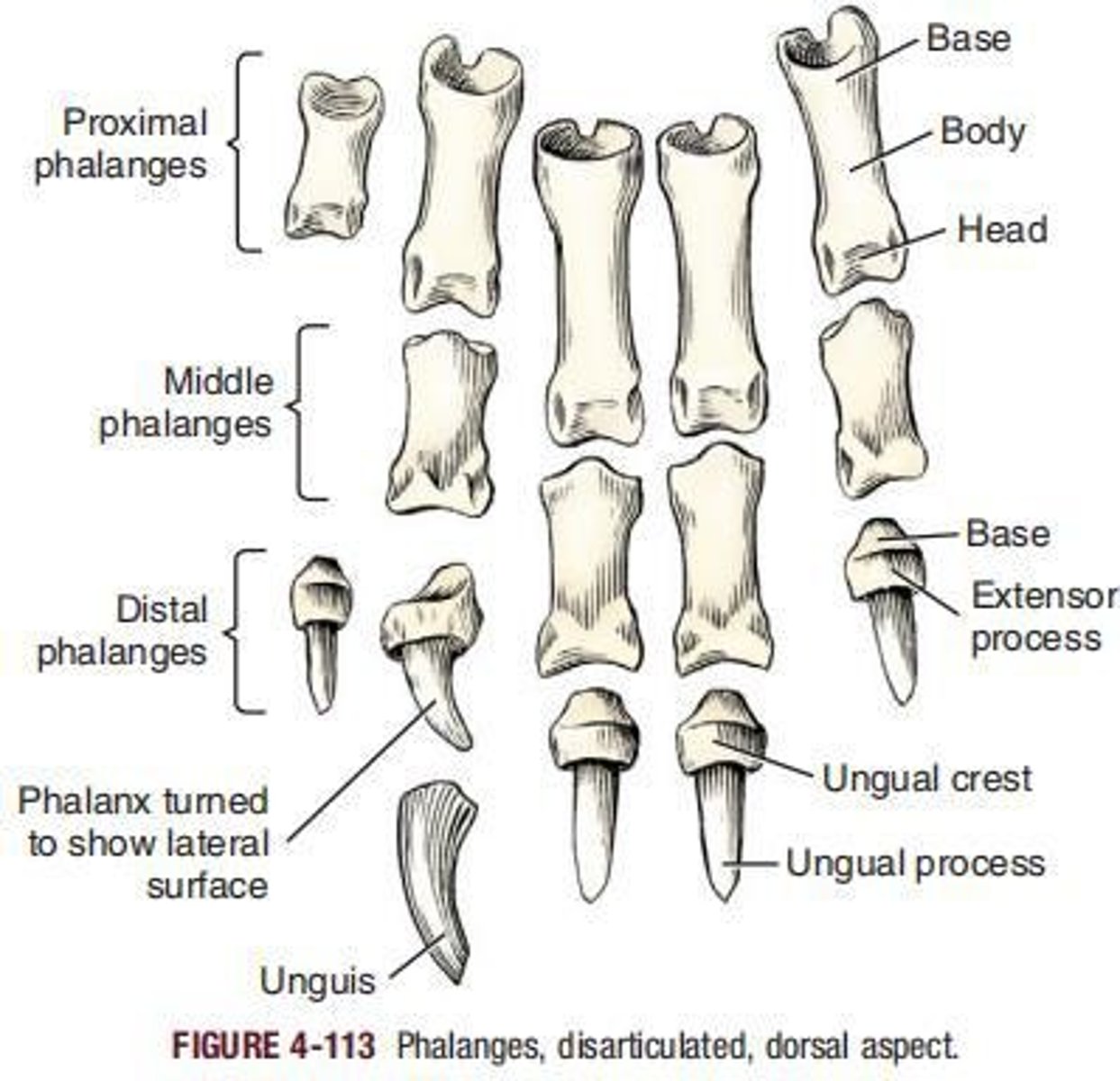
Digital skeleton
___ of the forepaw consists of five units, of which four are fully developed and one is rudimentary.
Dewclaw
The rudimentary first digit, which may be double in some breeds such as the St. Bernard.
Proximal phalanx
the ____ of each of the main digits, II to V, is a medium-length rod with enlarged extremities.
Middle phalanx
Present only in each of the main digits, there being none in digit I.
Distal phalanx
Approximately the same size in all four main digits.
Ungula process
The distal part of the distal phalanx, a laterally compressed cone that is shielded by the horny claw.
Ungual crest
A crescent-shaped shelf of bone under the root of the claw.
Sesamoid bones
On the palmar surface of each metacarpophalangeal joint of the main digits are two elongated, slightly curved sesamoid bones located in the tendons of insertion of the interosseus muscles.