Chapter 11 End of Chapter Questions
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Knowledge and Comprehension
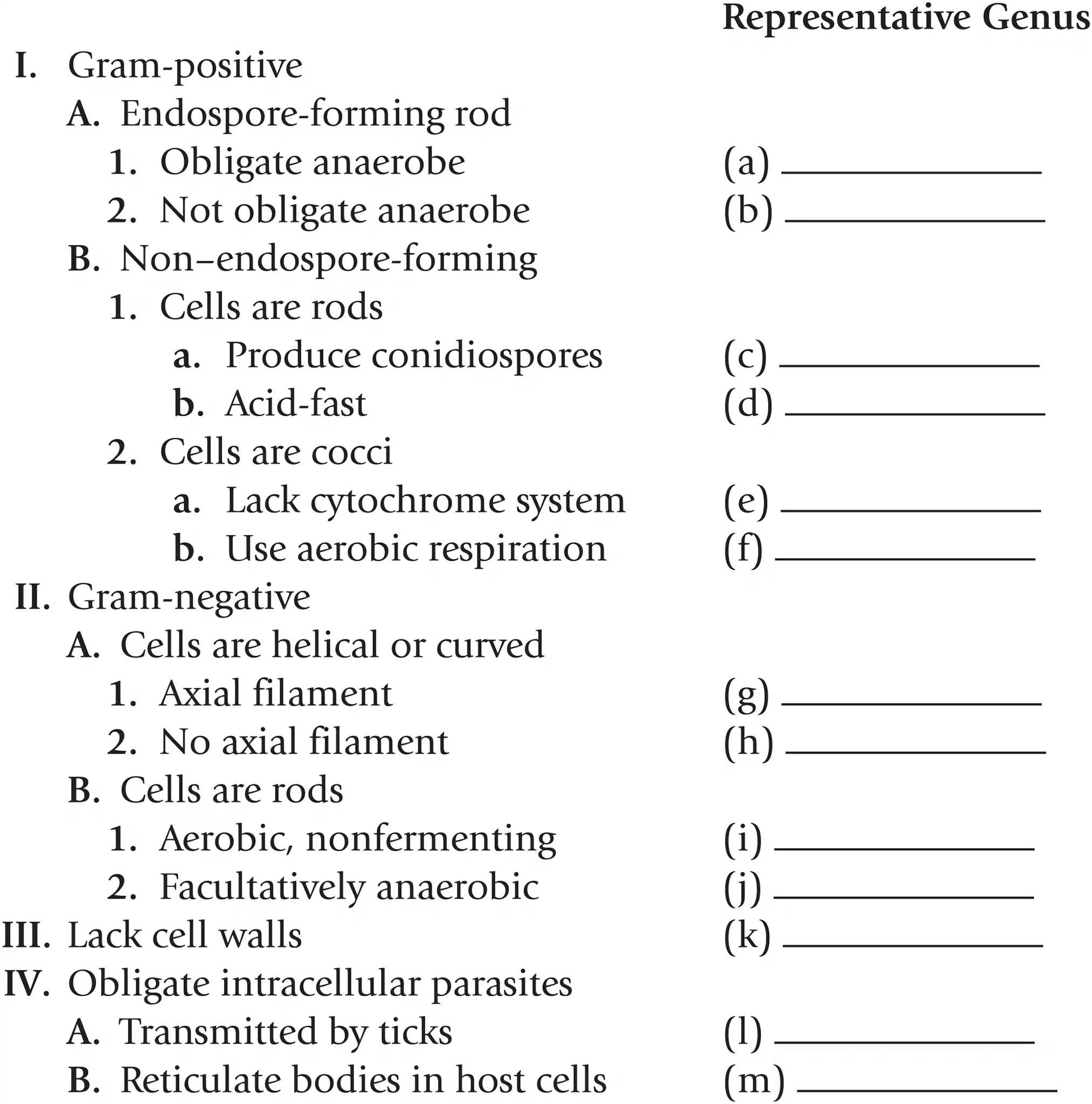
Name a representative genus for gram + endospore forming rods that are obligate anaerobes
Clostridium
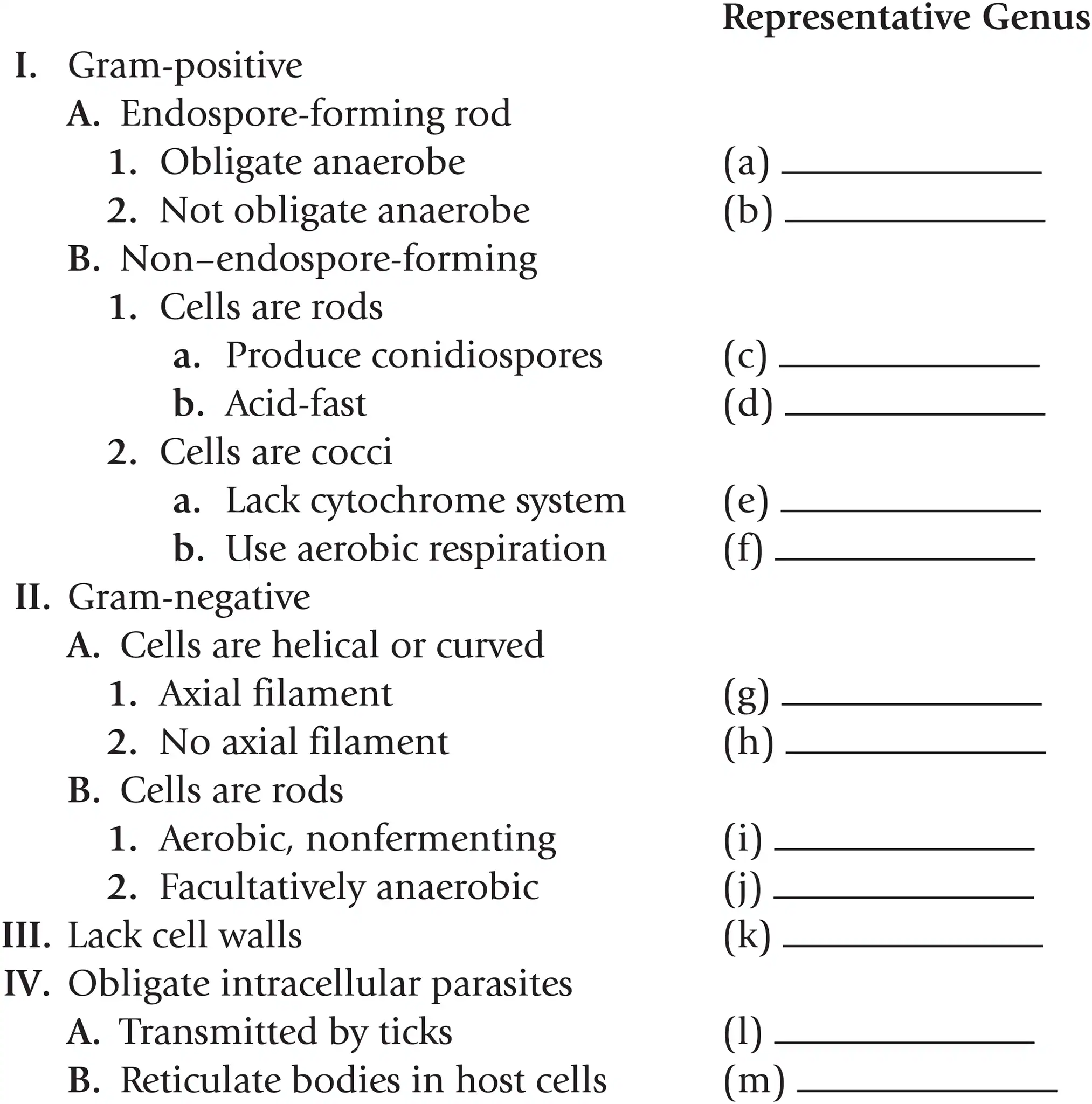
Name a representative genus for gram + endospore forming rods that aren’t obligate anaerobes
Bacillus
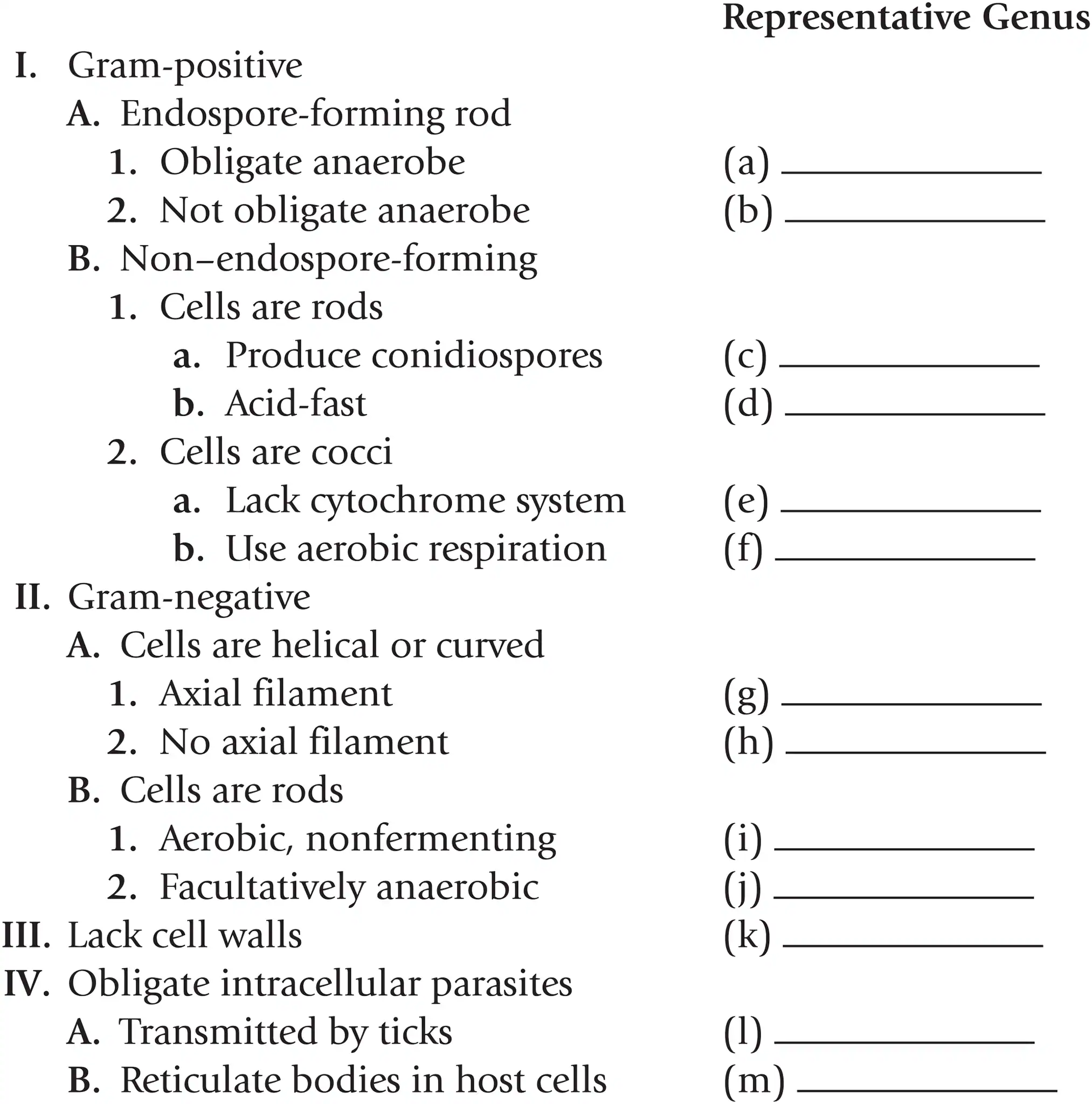
Name a representative genus for gram + non-endospore-forming rods that produce conidiospores
Streptomyces
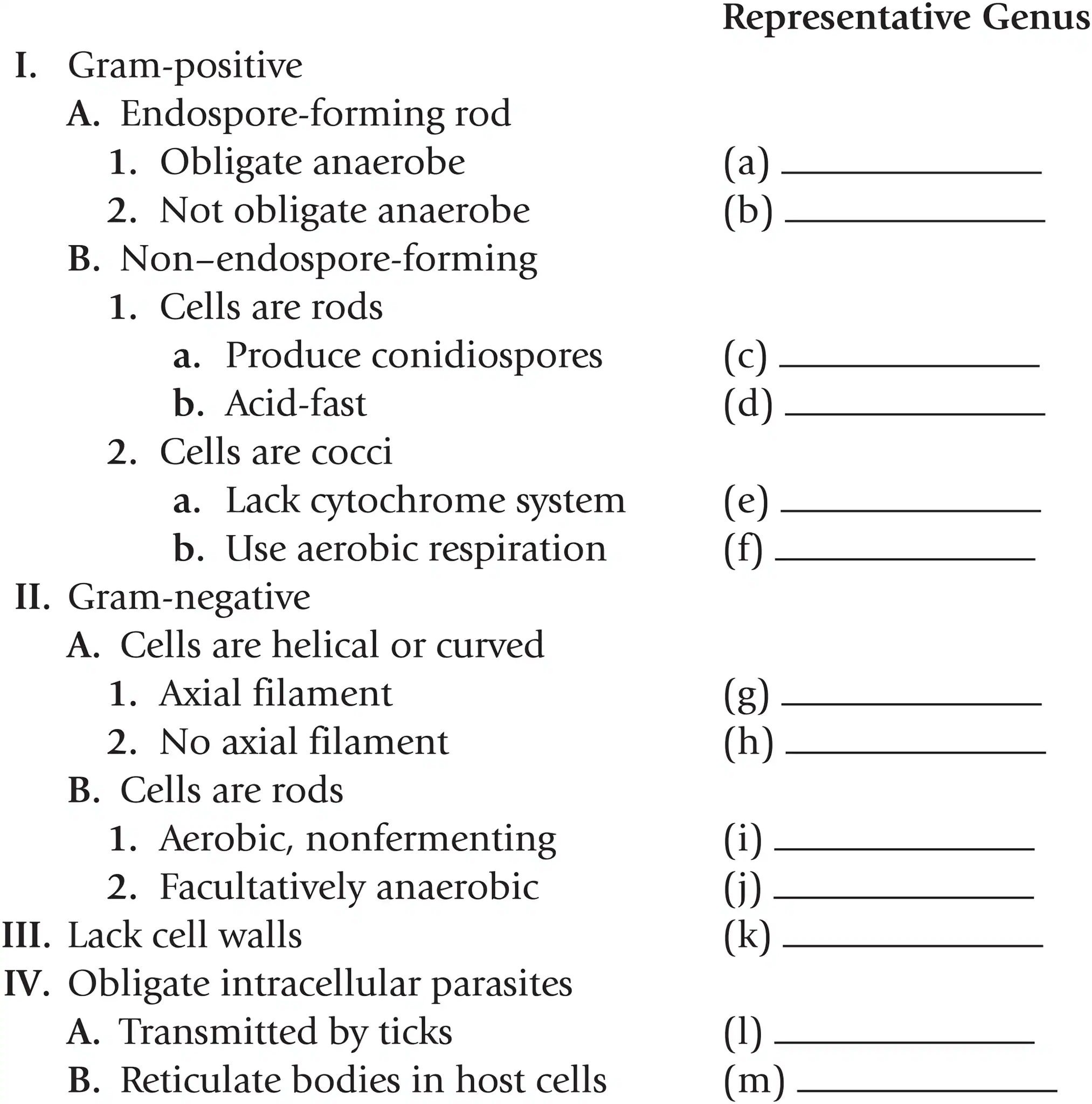
Name a representative genus for gram + non-endospore-forming rods that are acid fast
Mycobacterium
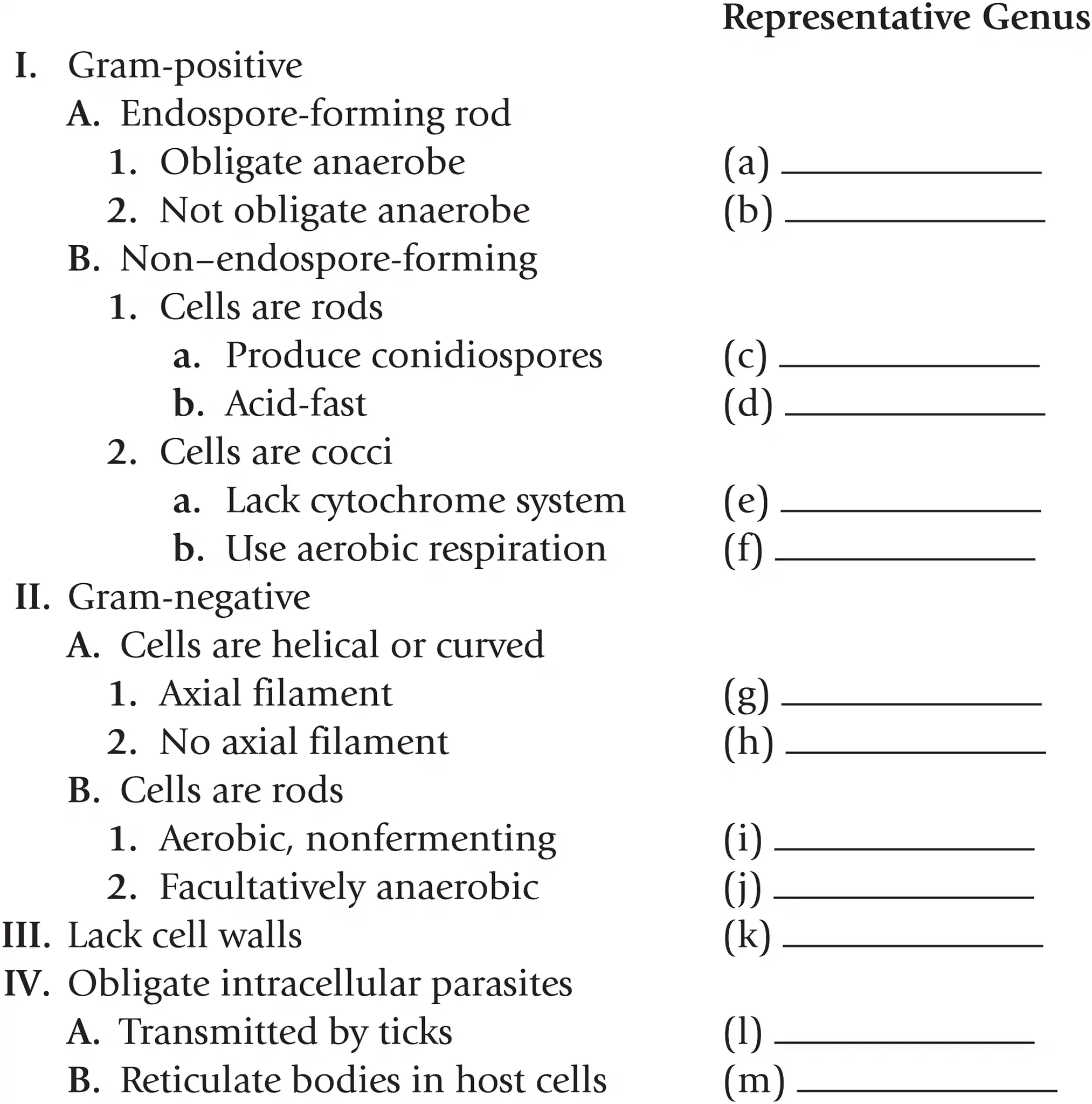
Name a representative genus for gram + non-endospore-forming cocci that lack a cytochrome system
Streptococcus
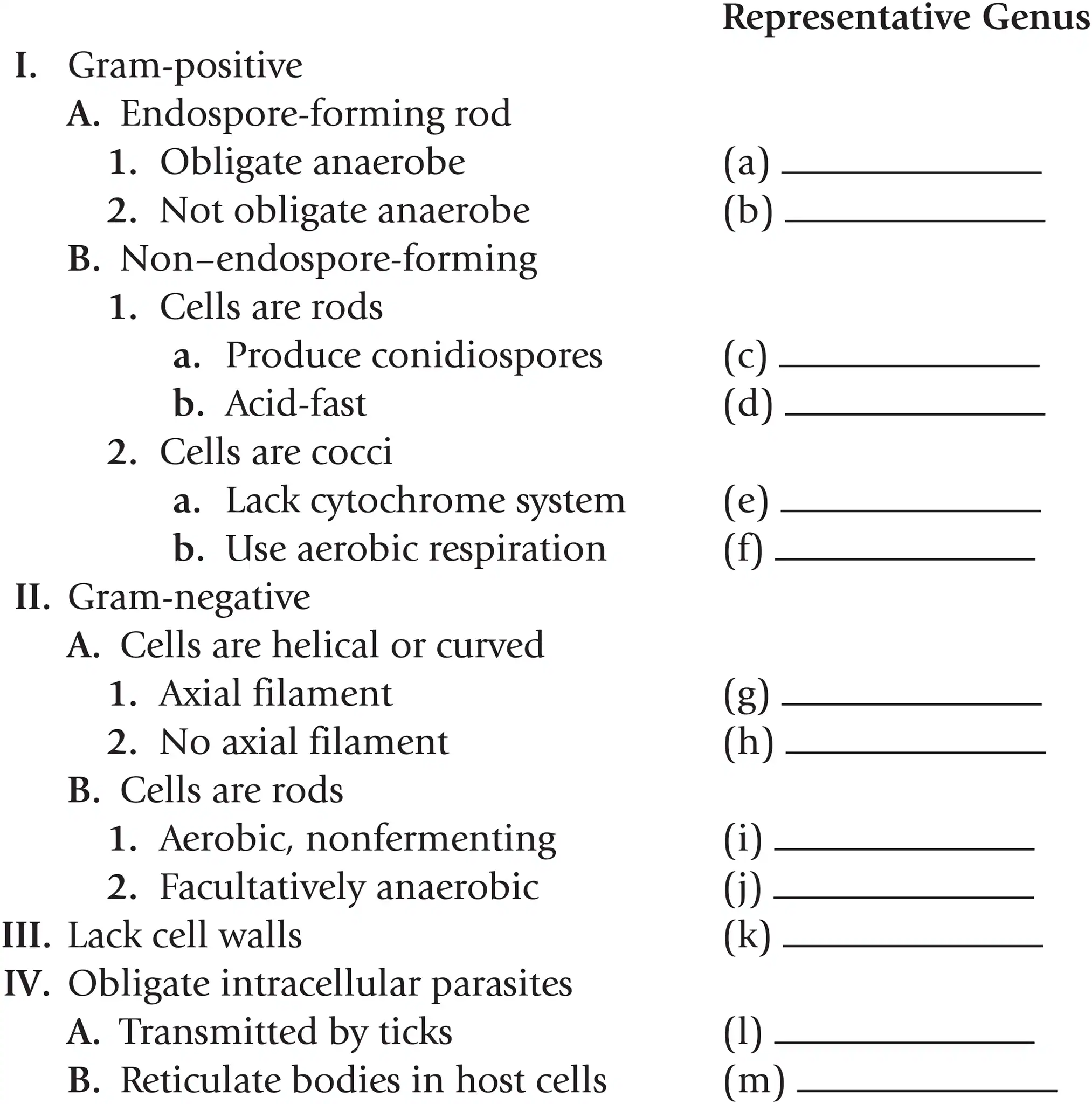
Name a representative genus for gram + non-endospore-forming cocci that use aerobic respiration
Staphylococcus
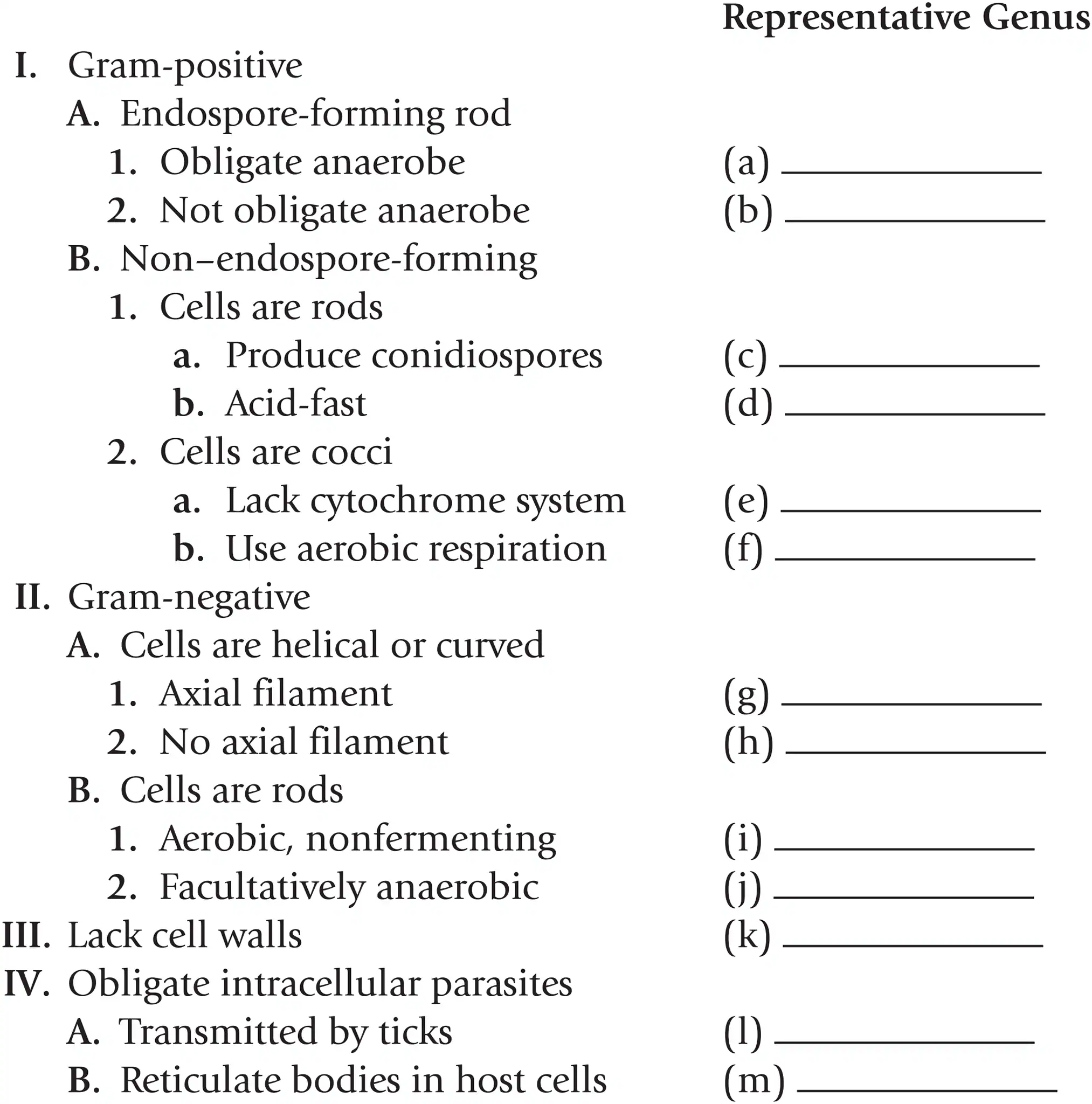
Name a representative genus for gram - helical or curved cells with axial filaments
Treponema
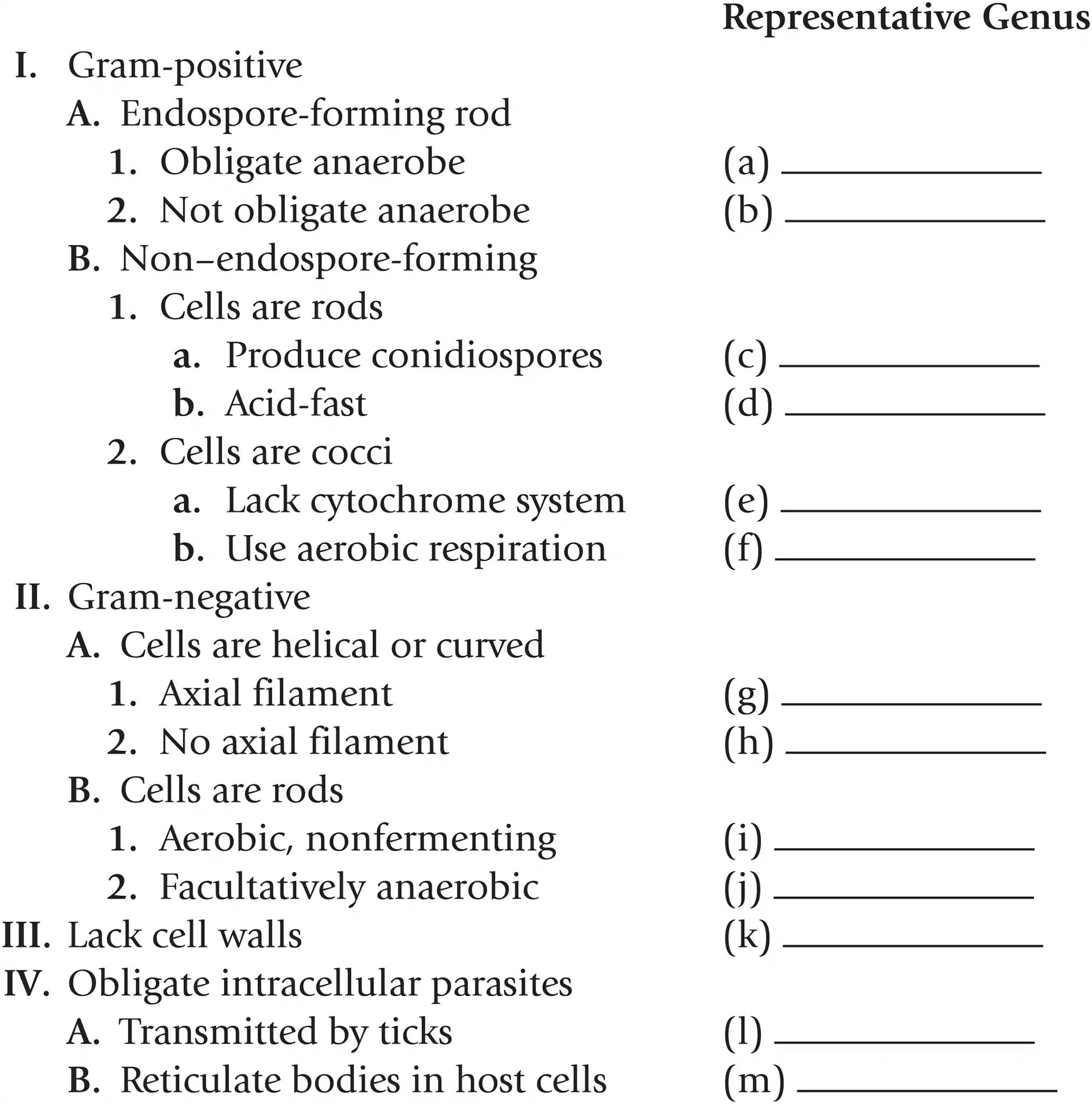
Name a representative genus for gram - helical or curved cells with no axial filaments
Spirillum
Name a representative genus for gram - rods that are aerobic and nonfermenting
Pseudomonas
Name a representative genus for gram - rods that are facultatively anaerobic
Escherichia
Name a representative genus for bacteria that lack cell walls
Mycoplasma
Name a representative genus for obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by ticks
Rickettsia
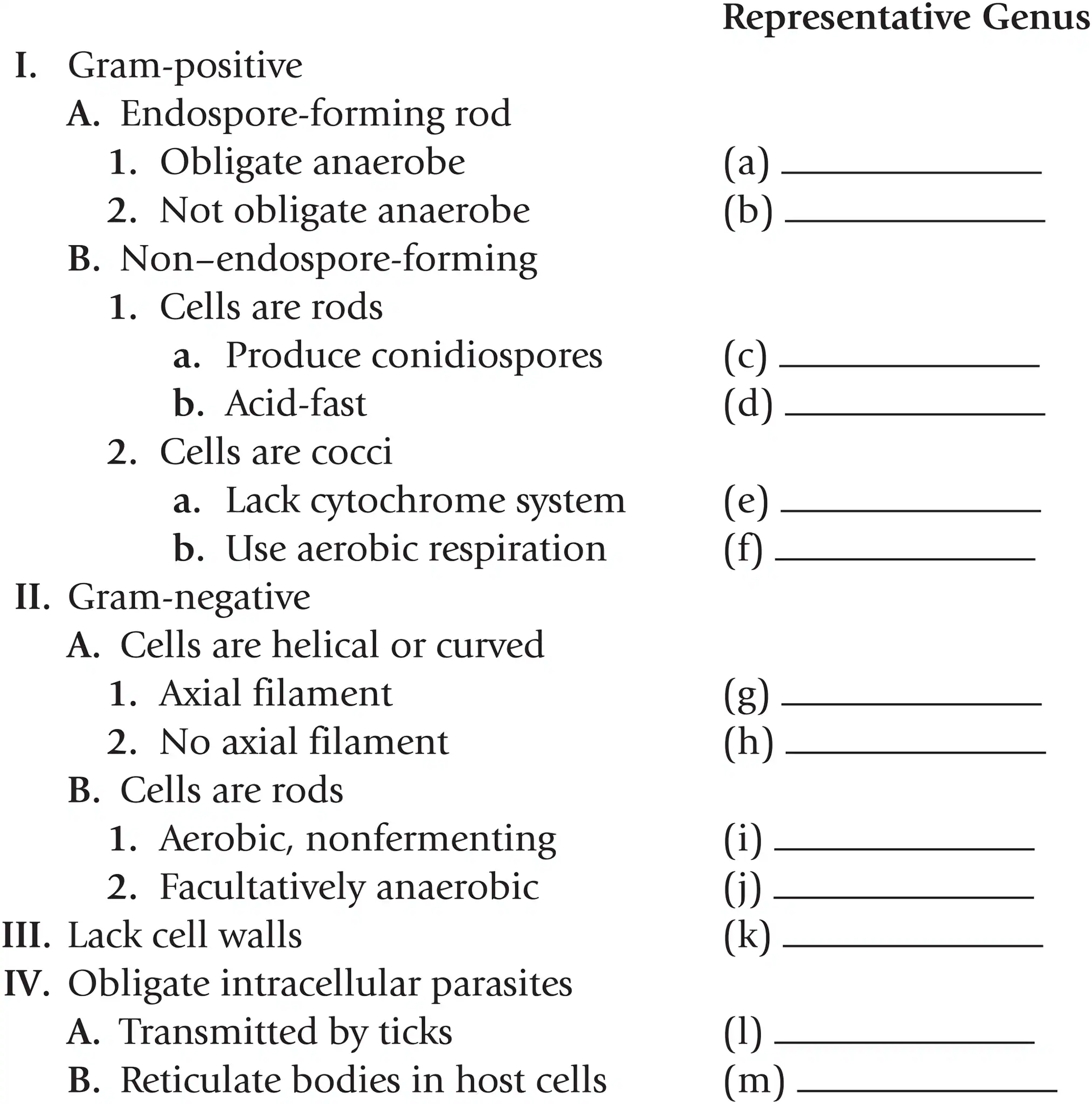
Name a representative genus for obligate intracellular parasites that reticulate bodies in host cells
Chlamydia
Compare and contrast each of the following:
Cyanobacteria and algae
Both are oxygenic photoautotrophs. Cyanobacteria are prokaryotes; algae are eukaryotes.
Compare and contrast each of the following:
Actinomycetes and fungi
Both are chemoheterotrophs capable of forming mycelia; some form conidia. Actinomycetes are prokaryotes; fungi are eukaryotes.
Compare and contrast each of the following:
Bacillus and Lactobacillus
Both are large rod-shaped bacteria. Bacillus forms endospores; Lactobacillus is a fermentative non–endospore-forming rod.
Compare and contrast each of the following:
Pseudomonas and Escherichia
Both are small rod-shaped bacteria. Pseudomonas has an oxidative metabolism; Escherichia is fermentative. Pseudomonas has polar flagella; Escherichia has peritrichous flagella.
Compare and contrast each of the following:
Leptospira and Spirillum
Both are helical bacteria. Leptospira (a spirochete) has an axial filament. Spirillum has flagella.
Compare and contrast each of the following:
Escherichia and Bacteroides
Both are gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria. Escherichia bacteria are facultative anaerobes, and Bacteroides bacteria are anaerobes.
Compare and contrast each of the following:
Rickettsia and Chlamydia
Both are obligatory intracellular parasites. Rickettsia are transmitted by ticks; Chlamydia have a unique developmental cycle.
Compare and contrast each of the following:
Mycobacterium and Mycoplasma
Both are atypical gram-positive bacteria. Mycobacterium is a high G+C, acid-fast genus. Mycoplasma is a low G+C genus that lacks cell walls.
DRAW IT Draw a key to differentiate the following bacteria: cyanobacteria, Cytophaga, Desulfovibrio, Frankia, Hyphomicrobium, methanogens, myxobacteria, Nitrobacter, purple bacteria, Sphaerotilus, and Sulfolobus.
find other examples
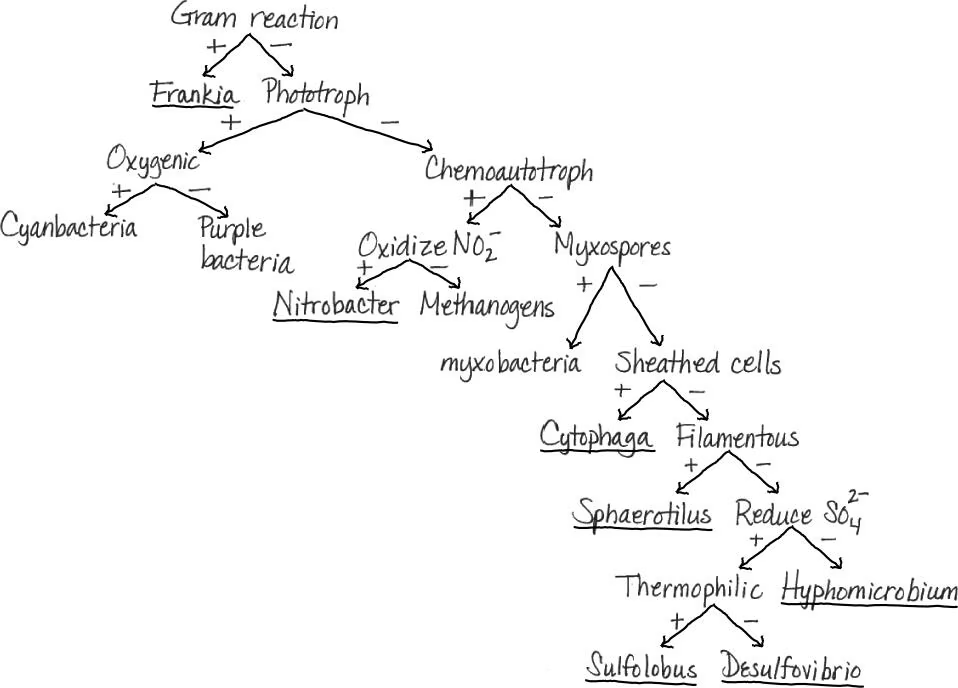
NAME IT These organisms are important in sewage treatment and can produce a fuel used for home heating and for generating electricity.
Methanogens
Multiple Choice
If you Gram-stained the bacteria that live in the human intestine, you would expect to find mostly
gram-positive cocci.
gram-negative rods.
gram-positive, endospore-forming rods.
gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
all of the above.
2
Which of the following does not belong with the others?
Enterobacteriales
Lactobacillales
Legionellales
Pasteurellales
Vibrionales
2
Lactobacillales is a gram + bacteria of phylum Firmicutes while the rest are gram - bacteria from phylum Proteobacteria
Pathogenic bacteria can be
motile.
rods.
cocci.
anaerobic.
all of the above.
5
Which of the following is an intracellular parasite?
Rickettsia
Mycobacterium
Bacillus
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
1
Which of the following terms is the most specific?
bacillus
Bacillus
gram-positive
endospore-forming rods and cocci
anaerobic
2
Which one of the following does not belong with the others?
Enterococcus
Lactobacillus
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
all are grouped together
3
Staphylococcus is of order Bacillales while the others are of order Lactobacillales
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
anaerobic endospore-forming gram-positive rods—Clostridium
facultatively anaerobic gram-negative rods—Escherichia
facultatively anaerobic gram-negative rods—Shigella
pleomorphic gram-positive rods—Corynebacterium
spirochete—Helicobacter
5
Spirillum is not classified as a spirochete because spirochetes
do not cause disease.
possess axial filaments.
possess flagella.
are prokaryotes.
none of the above
2
When Legionella was newly discovered, why was it classified with the pseudomonads?
It is a pathogen.
It is an aerobic gram-negative rod.
It is difficult to culture.
It is found in water.
none of the above
2
Unlike purple and green phototrophic bacteria, cyanobacteria
produce oxygen during photosynthesis.
do not require light.
use H2S as an electron donor.
have a membrane-enclosed nucleus.
all of the above
1
Analysis
Use of culture-independent techniques such as rRNA sequencing and FISH have increased our understanding of microbial diversity without cultivation. Do microbiologists still need to attempt to grow new species? Briefly explain.
Yes, because there are many undiscovered species, mutations occur, exploration of new places leads to the possibility of new microbes
To which of the following is the photosynthetic bacterium Chromatium most closely related? Briefly explain why.
cyanobacteria
Chloroflexus
Escherichia
Escherichia because they’re both gammaproteobacteria in the Phylum class
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that must absorb their nutrients by simple diffusion. The dimensions of Thiomargarita namibiensis are several hundred times larger than those of most bacteria, much too large for simple diffusion to operate. How does the bacterium solve this problem?
The organism acts as a fluid-filled balloon, with an interior central vacuole surrounded by a relatively thin layer of cytoplasm
By having a large central vacuole which reduces the volume of active cytoplasm so diffusion only needs to occur across a thin peripheral layer.
Clinical Applications and Evaluation
After contact with a patient’s spinal fluid, a lab technician developed fever, nausea, and purple lesions on his neck and extremities. A throat culture grew gram-negative diplococci. What is the genus of the bacteria?
Neisseria meningitidis
Between April 1 and May 15 of one year, 22 children in three states developed diarrhea, fever, and vomiting. The children had each received pet ducklings. Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacteria were isolated from both the patients’ and the ducks’ feces; the bacteria were identified as serovar C2. What is the genus of these bacteria?
Salmonella
A pregnant patient complaining of lower abdominal pain with a temperature of 39°C gave birth soon after to a stillborn baby. Blood cultures from the infant revealed gram-positive rods. The patient had eaten unheated hot dogs during pregnancy. Which organism is most likely involved?
Listeria monocytogenes