Earth Science
1/254
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
255 Terms
Big Bang theory
It explains how the universe began, suggesting it started its expansion about 13.8 billion years ago.
What is the significance of the term 'singularity' in the Big Bang theory?
It refers to the initial state of the universe, predicted to have very high temperature and density.
What phenomenon occurs when matter and antimatter collide in the early universe?
They are destroyed, resulting in the formation of matter.
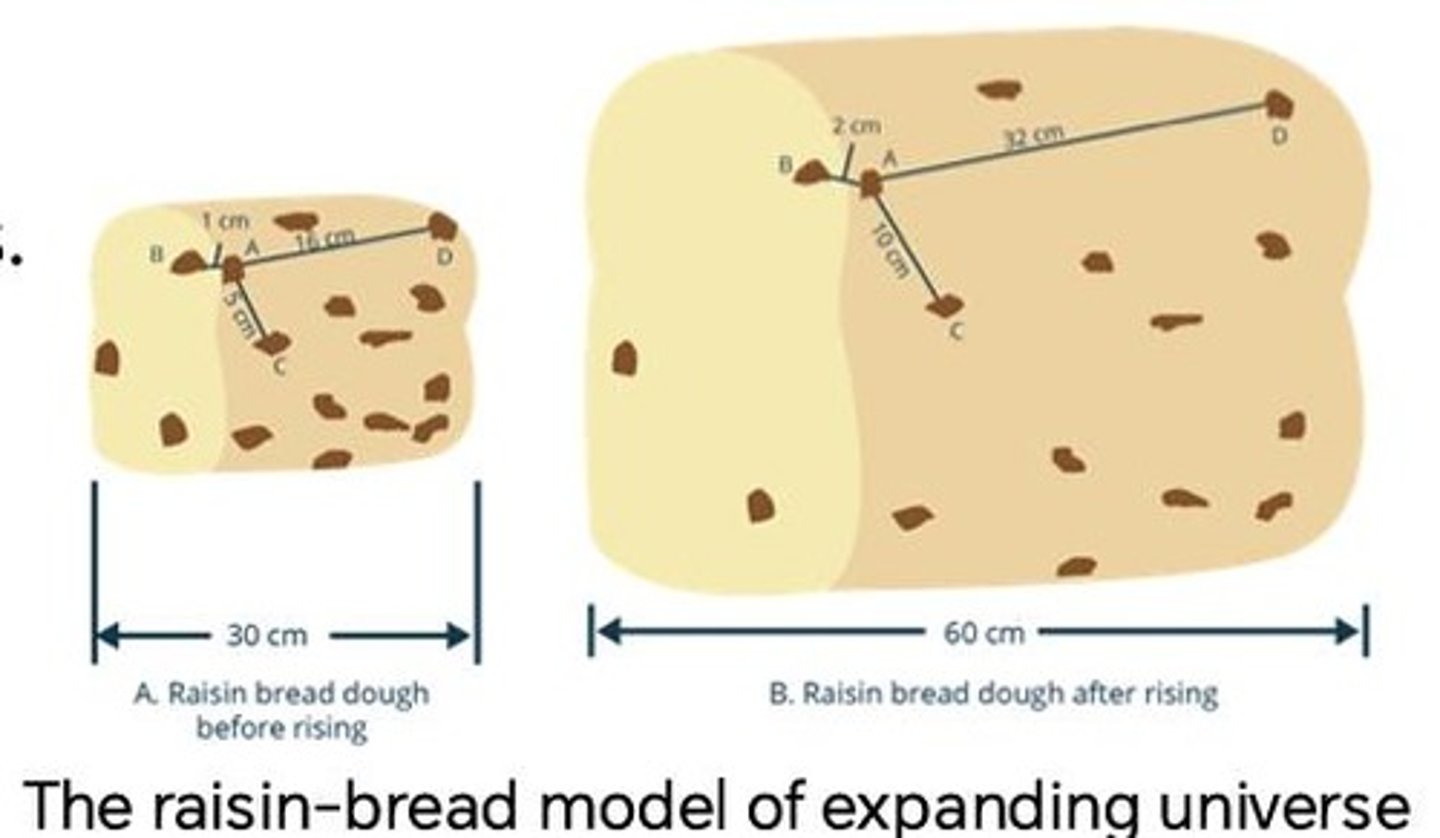
How does the bread and raisin model represent the universe?
The bread represents the universe, while the raisins represent galaxies that are not expanding.
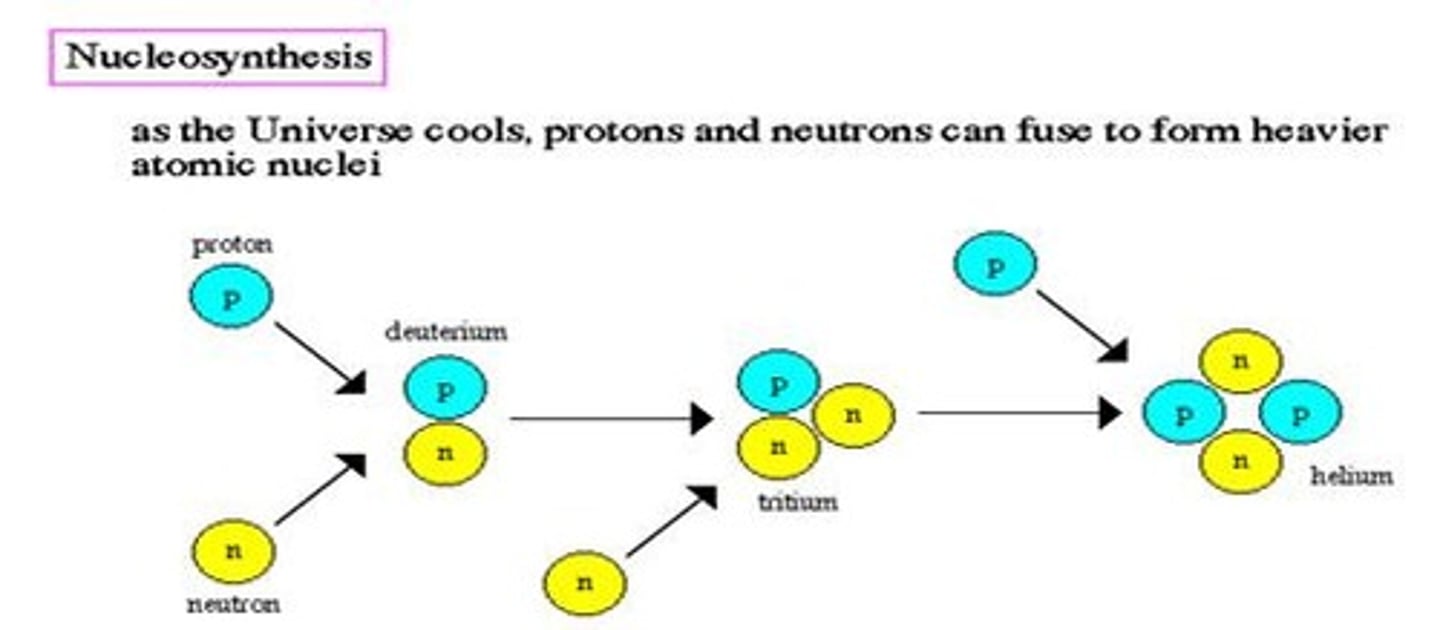
What is nucleosynthesis?
It is the formation of elements, such as hydrogen (H) and helium (He), leading to the formation of stars and galaxies.
What elements were primarily formed during Big Bang nucleosynthesis?
Light elements such as hydrogen, deuterium, helium, and lithium.
What happens to distances between galaxies as the universe expands?
Distances increase due to the expanding universe.
What is the composition of the universe in terms of elements?
92% of the universe is composed of elements, primarily hydrogen (73%), helium (25%), and the remaining 2% consists of heavier elements.
What are the three types of subatomic particles?
1. Protons (positively charged), 2. Neutrons (neutrally charged), 3. Electrons (negatively charged).
What is the difference between isotopes of an element?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons and mass number.
What is the role of nuclear fusion in the early universe?
Nuclear fusion reactions occurred due to high temperatures, resulting in the formation of light elements.
What is the process that began about 100 seconds after the Big Bang?
Nuclear reactions began to form elements through the collision of protons and neutrons.
What are isotopes of hydrogen mentioned in the notes?
Deuterium and tritium are isotopes of hydrogen.
What does the term 'natural synthetic' refer to in the context of elements?
It refers to elements that undergo nucleosynthesis.
What is the evidence supporting the Big Bang theory?
The observation that galaxies are receding from us.
What is the difference between nuclear fusion and nuclear fission?
Nuclear fusion involves the combination of nuclei, while nuclear fission involves the separation of nuclei.
What is the mass contribution of hydrogen and helium in the universe?
Hydrogen contributes 73% and helium contributes 25% of the universe's mass.
What happens to matter as the universe expands according to the Big Bang theory?
Matter dilutes as the universe expands.
How do protons and neutrons interact to form isotopes?
Protons and neutrons can fuse to form isotopes of hydrogen, such as deuterium.
What is the significance of the Big Bang in relation to cosmic bodies?
The presence of stars formed from nucleosynthesis led to the creation of other cosmic bodies like planets, comets, and asteroids.
What is the role of stellar nucleosynthesis in the universe?
It is the process by which elements are formed in stars, contributing to the composition of the universe.
What are the symbols for protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Protons: 1₁p, Neutrons: 1₀n, Electrons: -1₀e.
What does the Big Bang theory suggest about the nature of the universe's expansion?
It suggests that the universe is expanding, leading to increasing distances between galaxies.
What elements were primarily formed through the Big Bang?
Hydrogen, Helium, and a small amount of Lithium.
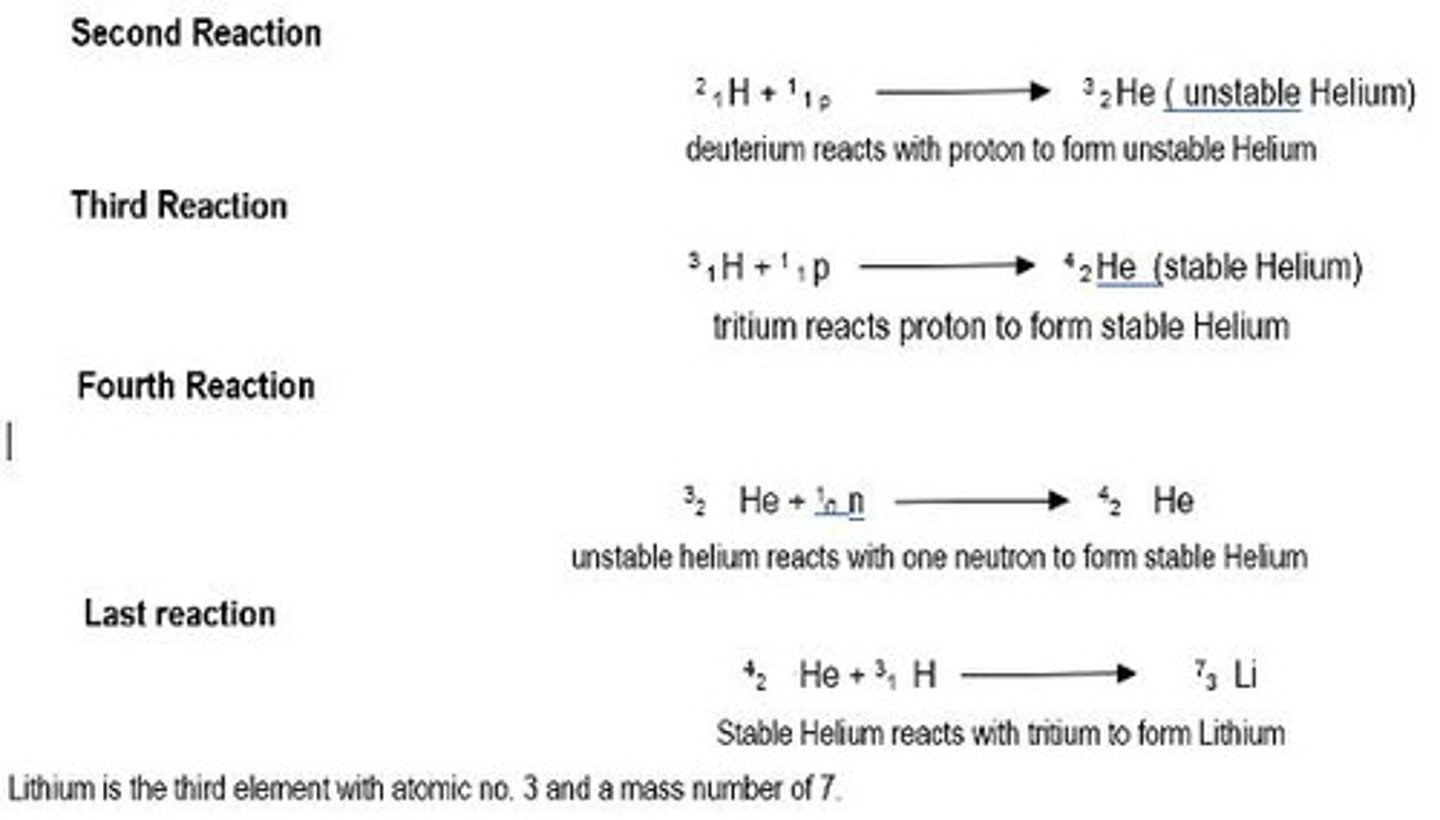
What is the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation?
The residue or heat leftovers from the Big Bang, detectable by radio telescopes.
Who established Hubble's Law and what does it signify?
Edwin Powell Hubble established Hubble's Law, providing evidence that the universe is expanding.
Who was the first proponent of the Big Bang theory?
Georges Henri Joseph Edouard Lemaitre, who suggested the idea of an expanding universe.
What discovery did Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson make related to the Big Bang?
They found a 7 cm wavelength present in space, supporting the existence of the CMB.
What is a significant drawback of the Big Bang Theory?
It fails to explain how the universe was created and does not detail how galaxies formed.
What are the three types of nucleosynthesis?
Big Bang nucleosynthesis, Stellar (star) nucleosynthesis, and Supernova nucleosynthesis.
What elements are formed through Stellar Nucleosynthesis?
Elements from beryllium to iron are formed through nuclear fusion in stars.
What temperature is required for nuclear fusion to occur in stars?
About 15 million degrees Celsius.
What is the state of matter called when fusion occurs?
Plasma, a super-high-energy, electrically charged gas.
What happens to the mass of nuclei during nuclear fusion?
Some of the mass is converted to energy, as described by Einstein's equation E=mc².
What is the primary energy source released during nuclear fusion?
Energy is released in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
What is the significance of the Big Bang Theory in cosmology?
It is the most widely accepted scientific theory about the origin of the universe, supported by multiple lines of evidence.
What occurs during Big Bang nucleosynthesis?
It produced all hydrogen and most helium in the universe within a few minutes after the Big Bang.
What is the role of nuclear fusion in the universe today?
Only stellar and supernova nucleosynthesis are currently occurring, relying on nuclear fusion reactions.
What is the relationship between temperature, pressure, and nuclear fusion?
Nuclear fusion requires extremely high temperatures and pressures, found in stars and during the Big Bang.
What is the primary limitation of the Big Bang Theory?
It does not explain the initial creation of the universe.
What is the significance of the expansion of the universe according to the Big Bang Theory?
The farther a galaxy is, the faster it moves away from us, indicating an expanding universe.
How does nuclear fusion compare to burning material in terms of energy?
Nuclear fusion releases much more energy per gram of material than burning a comparable amount.
What is the primary process by which elements are formed in stars?
Nuclear fusion, where smaller nuclei collide to form larger nuclei.
What was the condition of the universe immediately after the Big Bang?
It was mostly in the form of photons, neutrinos, and anti-neutrinos, which allowed for the formation of heavier elements.
What does the Big Bang Theory explain about the universe?
It explains how the universe evolves but not how it originated.
What initiated the expansion of the universe?
The Big Bang, a phenomenally energetic explosion.
What was present at the moment before the Big Bang?
All matter and energy were compressed at a single point known as a singularity.
How old is the universe estimated to be?
About 13.7 billion years old.
How old is our Solar System compared to the universe?
Our Solar System is approximately 4.65 billion years old.
What are nuclear reactions?
Processes in which a nucleus combines with another nucleus through fusion or splits into smaller nuclei through fission.
What phenomenon involves the emission of energetic particles from an atom?
Radioactivity.
What is an electron and its charge?
An electron is a particle with a negative charge (0 -1 e).
What is a proton and its charge?
A proton is a particle with a positive charge (1 +1 p).
What is a neutron and its charge?
A neutron is a particle with no charge (1 0 n).
What is an alpha particle?
A high-speed particle consisting of 2 protons and 2 neutrons (4 2 α).
What is a beta particle?
A high-speed electron (0 -1 β).
What is a gamma ray?
A high-energy stream of photons (0 0 γ).
What is a positron?
A positively charged electron (0 +1 e).
What defines synthetic elements?
Elements with atomic numbers Z ≥ 93 that are man-made.
How are synthetic elements created?
They are made in particle accelerators by smashing smaller nuclei together or shooting nuclear bullets at larger nuclei.
What is a characteristic of all synthetic elements?
They are all radioactive and decay over time to more stable elements.
What is an example of a synthetic element and its use?
Americium (Am) is used in smoke detectors.
What is alpha decay?
The loss of an alpha particle (4 2 α) from a nucleus.
Provide an example of alpha decay.
Alpha decay of Polonium-210: 210 84Po → 206 82Pb + 4 2α.
What is beta decay?
The loss of a beta particle (0 -1 β) from a nucleus.
Provide an example of beta decay.
Beta decay of Carbon-14: 14 6 C → 14 7 N + 0 -1 β.
What is gamma radiation?
The emission of a gamma ray (0 0 γ) from a nucleus.
Provide an example of gamma radiation.
Gamma radiation in alpha decay of Uranium-238: 238 92 U → 234 90 Th + 4 2 α, followed by 234 90 Th → 234 90 Th + 0 0 γ.
What principle explains the uniform appearance of the universe as it expands?
The perfect cosmological principle, which states the universe is homogeneous and isotropic in space and time.
What is positron emission?
The conversion of a proton in a nucleus into a neutron, along with the release of a positron (0 +1 e), exemplified by the reaction 15 8 O → 15 7 N + 0 +1 e.
What is electron capture?
The process of an electron being absorbed into an atom's nucleus (0 -1 e), illustrated by the reaction 201 80 Hg + 0 -1 e → 201 79 Au.
What does the bombardment of an alpha particle involve?
The addition of an alpha particle to another nucleus, as shown in the reaction 9 4 Be + 4 2 α → 12 6 C + 1 0 n.
What are the main drawbacks of the Steady State Theory?
It does not align with the law of conservation of energy and contradicts the idea that mass/energy cannot be created or destroyed.
What is the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)?
Radiation that supports other theories of the universe's origin, contradicting the Steady State model.
What does the Steady State Theory propose about the universe?
It suggests that the universe has always been expanding at a constant rate and has always existed.
What is accretion in the context of planet formation?
Accretion is a leading theory about the formation of Earth, where planetesimals form protoplanets.
What is a protoplanet?
A planetary embryo that consists of a collection of matter from which a planet is formed.
What is homogeneous accretion?
A theory proposing that the universe expands and will eventually contract, leading to a Big Crunch.
What is the Big Crunch?
The theoretical endpoint where the universe collapses back into a dense state.
What is the Oscillating Universe Theory?
A theory that combines the Big Crunch and Big Bang, suggesting repeated cycles of expansion and contraction.
What is the Big Bounce?
The concept proposed by Richard Tolman, referring to the birth of another universe after a collapse.
What is heterogeneous accretion?
A process where Earth accreted during condensation, forming a differentiated planet.
What evidence supports heterogeneous accretion?
It qualitatively explains the density differences among terrestrial planets.
What are the drawbacks of the Oscillating Universe Theory?
It suggests the universe would collapse on its own after full expansion, conflicting with laws of physics and the existence of dark energy.
What is a key loophole in the homogeneous accretion hypothesis?
It cannot explain the abundance of elements such as osmium, iridium, ruthenium, and rhodium in the mantle.
What is the significance of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation?
It provides evidence against the Steady State Theory and supports the Big Bang model.
Who are the proponents of the Steady State Theory?
Hermann Bondi, Thomas Gold, and Fred Hoyle.
What does the law of conservation of energy state?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
What is the relationship between accretion and volatile elements in Earth's core?
Homogeneous accretion provides a mechanism explaining the presence of volatile elements in the core.
What is the time frame for the accretion process in heterogeneous accretion?
Accretion must occur very quickly, within 10^3 to 10^4 years.
What is a significant challenge for the heterogeneous accretion theory?
The rapid accretion rate does not align with the occurrence of large impact craters.
What is the implication of dark energy in the context of the universe's expansion?
Dark energy drives the universe's accelerating expansion, contradicting some theories of collapse.
What temperature does water reach maximum density?
3.98°C
What is the significance of water's high heat capacity?
It allows water to resist temperature changes, creating stable aquatic habitats.
What are the two main classifications of bodies of water based on salinity?
Saltwater and freshwater.
What is the primary characteristic of saltwater?
It has high salt content.
Name two examples of saltwater bodies.
Seas and oceans.
What is the primary characteristic of freshwater?
It has little to no salt content.
In what forms can freshwater be found?
Rain, snow, and permanently frozen soil (permafrost).